A high pulse with normal blood pressure is not such a rare phenomenon, requiring attention from a general practitioner and cardiologist. If the pulse pressure increases, this fact is rarely noted by the person himself before recording the indicators; usually this condition is manifested by changes in well-being, which is the reason for contacting a specialist. Often, the pulse frequency changes after physical exertion, stress and as a result of fatigue, and this symptom is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure (BP).
But this does not mean that the heart rate cannot increase without an increase in systolic pressure; it can jump even with normal tonometer readings. Today we need to figure out what a high heart rate at the same time as normal blood pressure indicates, what causes the condition, and how to deal with it.
Symptoms with a pulse of 100 beats per minute
If the patient's pulse constantly reaches 100 beats per minute, then the main symptoms are usually a feeling of palpitations, pulsation of the vessels of the neck and shortness of breath. With prolonged tachycardia, they are accompanied by signs of insufficient blood circulation to the heart muscle and brain:
- pain and compression behind the sternum;
- weakness;
- poor tolerance to physical activity (tiredness appears quickly);
- dizziness;
- fainting state;
- darkening of the eyes;
- numbness, tingling in the hands and feet;
- anxiety.
They usually mean that a rapid pulse is a manifestation of heart disease, nervous system or hormonal imbalance.
Why is it dangerous?
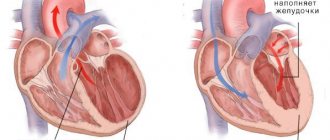
A pulse of 100 beats per minute leads to rapid wear and tear of the heart muscle. Since the myocardium is nourished during a period of relaxation, during tachycardia, due to the short pause between contractions, the heart does not receive enough oxygen and glucose. This leads to weakened muscle contractions, ischemia (lack of blood), which means the risk of heart failure, angina and heart attack increases.
Too frequent a rhythm impairs blood flow to other organs, since the ventricles do not have time to fully fill, cardiac output and blood pressure drop, and renal filtration is impaired. If tachycardia and the disease that provoked it are not treated, then over time it becomes the cause of more serious rhythm disorders, a state of shock (arrhythmogenic shock), and cardiac arrest.
A pulse of 100 is a manifestation of sinus tachycardia, but there is also the same symptom with one of the forms of atrial fibrillation. Its development is dangerous due to the formation of blood clots inside the heart; they can enter the brain vessels with the blood flow and cause a stroke.
Prevention of tachycardia
The best method for preventing tachycardia is to reduce the risk of developing one of the many heart diseases. It is often because of them that irregularities in the heart rhythm appear. To avoid illness, you should constantly monitor your indicators - this will help you notice any deviations in a timely manner and eliminate the problem at an early stage. To reduce the risk of tachycardia, it is recommended to take simple measures of the following nature:
- Regularly engage in physical training to the best of your ability;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy diet with enough fruits, whole grains and vegetables;
- Limit consumption of fatty foods and quit alcohol, drugs and smoking;
- Maintain body weight in the optimal range for your gender, age, weight and professional activity;
- Control blood cholesterol levels;
- Reduce your consumption of coffee and caffeinated drinks to a minimum.
It is also important to use any medications with great caution. From a young age you need to monitor the normalization of blood pressure, and especially in old age. It is necessary to try to avoid psychological stress. Regular visits to the doctor will help you take preventive measures in a timely manner and prevent the development of tachycardia.
You should be aware that caffeine can have an extremely negative effect on your heart rhythm and lead to arrhythmic conditions. It is impossible to say unequivocally what excessive caffeine consumption is, since it is very individual for each person. For some, a cup of coffee a day will not do any harm, but for others, even one cup a week may do a disservice.
Drug treatment
The sinus variety is treated in the system. Medicines that can be used if the pulse is 100 or more:
- Sedatives. Calms the central nervous system and reduces heart rate. Diazepam, Motherwort, Valerian, Phenobarbital in various preparations.
- Calcium channel blockers. They do not allow Ca+ ions to penetrate into the structures of blood vessels and cause their stenosis. Hence the impossibility of rapidly increasing heart rate.
- Magnesium-based products (Magnelis, Magne B6). Helps normalize cardiac activity.
- Beta blockers. Used to relieve irritation of the third reflex zone of the organ. Can be used as emergency aid.
Supraventricular tachycardia:
- Additionally, cardiac glycosides are prescribed.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs.
Ventricular arrhythmia is treated much more seriously, since it is the most dangerous and lethal type. The same groups of media are used, but strictly in combination.
Possible complications
Among the likely consequences of untreated tachycardia:
- Thromboembolism as a result of platelet destruction. The result is delayed death.
- Heart failure. Sudden, uncontrollable and not noticeable during the period before the onset of the condition.
- Heart attack.
- Organ dysfunction due to prolonged overload.
- Cardiogenic shock. The outcome of physical stress against the background of increased heart rate.
- Fainting “out of the blue” with the prospect of injury.
Diagnostic and treatment options if pulse is more than 100
In order to detect the cause of a constant pulse of more than 100 beats per minute, you need to undergo an examination:
- Why calculate your heart rate if you decide to play sports?
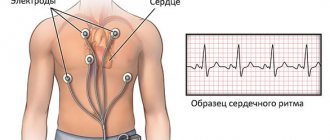
- ECG (standard, with stress, 24-hour Holter monitoring);
- echocardiography, if the results are questionable, an MRI is performed;
- electrophysiological study of the heart for complex rhythm disturbances;
- blood test, if necessary, for hormones and electrolytes;
- electroencephalography.
Based on the results of the examination, a treatment method can be chosen: medications for tachycardia, psychotherapy, sedatives, including folk remedies, the use of hormones, iron supplements and other options.
Medicines
To slow down the rhythm associated with stress and endocrine disorders, drugs from the group of beta-blockers (Anaprilin, Metoprolol) are used. If they are contraindicated, then calcium antagonists (Verapamil, Diacordin) are used.
For neurosis, herbal sedatives can be prescribed: tincture of peony, motherwort, Novo-passit, Persen, dietary supplements - Evening dragee, Motherwort forte. To improve cardiac activity, Riboxin and Panangin are recommended.
Traditional methods
With a pulse of 100-120, you can undergo a course of treatment with herbal remedies, but after serious heart diseases are excluded, that is, specific drug therapy is not required. To prepare an infusion of 300 ml of boiling water, take a tablespoon of one of the herbs:
- lavender flowers,
- lemon balm grass,
- mint leaves,
- hawthorn berries and flowers,
- motherwort grass,
- hop cones.
After infusion for 30 minutes, filter the infusion and take 100 ml half an hour before meals for a month in a warm form. If you are not intolerant, you need to add a teaspoon of honey.
Physiotherapy
With tachycardia and pulse 100 against the background of neurocirculatory dystonia, non-drug methods are more helpful:
- electrosleep;
- magnesium electrophoresis on the collar area;
- general and acupressure massage;
- baths with pine needle extract, valerian, sage or lavender oil.
Is it possible to quickly stop a heart attack?
To quickly deal with palpitations, you can use two simple recommendations:
- Immerse your face in cold water.
The heart begins to beat less frequently as the body cools down. This is an effective method that is accessible to most people. If you don’t have a container on hand to collect liquid, you can simply rinse your face with cool water or wipe it with pieces of ice.
- Perform the Valsalva maneuver.
The person will need to take a deep breath and tense their abdominal muscles. The nose is pinched with two fingers, the mouth and eyes are closed. In this state, you need to try to exhale. At the same time, the abdominal muscles are tensed.
All these methods can be used in cases where increased heart rate was caused by physiological factors. If chest pain appears during an attack and shortness of breath develops, you should seek help from a doctor.
Author of the article:
Molchanov Sergey Nikolaevich |
Cardiologist Education: Diploma in Cardiology received from Perm State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova (2015). Here I completed my postgraduate studies and received a diploma in Cardiology. Our authors
Causes of rapid heartbeat
As already mentioned, there is no physiological tachycardia. It always has a pathological character. The difference is one thing: how significantly and quickly the indicator rises. The duration of changes in the functioning of the organ is also determined.
- Heart rate 50: is this normal or not? Reasons and what to do with low heart rate
Factors for sudden increase
- Intense physical activity. It has a colossal destructive effect on an untrained body. You need to increase your activity gradually, both athletes and people close to them know this. By immediately becoming overtired, patients risk ending up in intensive care: the heart rate is not regulated, the organ does not know how to behave.
After 180 beats per minute the pressure drops. Against the background of tachycardia, this will have catastrophic results: cardiogenic shock is possible. However, the warning signs are immediately noticeable. If you experience a headache, blurred vision, vertigo, weakness, or palpitations, you need to take a break. If tachycardia lasts more than 15 minutes, you should call an ambulance.
- Stressful state, psycho-emotional shock. In this case, there is a vegetative response to a traumatic situation. It develops in parallel with an increase in blood pressure. A heart rate greater than 100 is grounds for calling an ambulance. Although the intensity of the heartbeat does not affect blood pressure, it increases the likelihood of a stroke or myocardial infarction by almost 30%.
- Nightmares. Mental reaction to stressful situations. Accompanied by vegetative manifestations, including an increase in heart rate, usually everything returns to normal within 5-10 minutes. Otherwise, emergency measures must be taken.
In the situations described, there is some trigger factor: physical overload, stress. If the pulse is 100 at rest, we are talking about pathology: only a cardiologist can help.
With increasing changes in cardiac activity, it makes sense to call emergency help.
Regular or constant increase in heart rate
- Hypothalamic syndrome. Associated with damage to the nuclei of the organ or circadian rhythms. This condition is mistakenly called vegetative-vascular dystonia. Such a diagnosis does not exist in any classifier. This is not a nosological unit, but a doctor’s statement of his own incompetence.
A problem can be suspected by systemic disorders in the body, such as: headache, vertigo, weight changes, fainting, regular increase in heart rate depending on environmental factors: weather, humidity.
A complete cure is impossible; the condition is corrected under the supervision of a cardiologist and endocrinologist.
- Hyperthyroidism. It means an excess of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. Develops as a result of poor nutrition or organ tumors. T3, T4, TSH are subject to evaluation as part of a blood test.
The disease is accompanied by constantly rapid heartbeat, neck pain, changes in relief at the throat level (thickening, goiter), bulging eyes, increased body temperature, problems with general condition (fatigue, drowsiness, headache, manifestations of thyroid hormone poisoning).
Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
- Pathologies of the pancreas (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), as well as the adrenal glands with excessive production of cortisol, adrenaline and norepinephrine. As a rule, the second condition manifests itself in the form of Cushing's disease.
The cause is a tumor of the adrenal gland (pheochromocytoma, cancer) or pituitary gland (germinoma, adenoma-corticotropinoma, low-grade glioma, for example, pilocytic astrocytoma, less commonly pituicytoma).
- What is the normal heart rate during sleep?
Symptoms: sudden obesity, moon face, headaches, weakness, discomfort in the limbs, change in voice timbre, constantly elevated blood pressure, high pulse rate of 102-106 beats/min. in a calm state.
- Mitral valve stenosis, cardiosclerosis.
- Inflammation of the pericardium and myocardium as a result of infectious processes. In 90% of cases, the pathology is secondary, caused by the penetration of pathogenic flora into the tissue. The process is accompanied by aching pain behind the sternum, low intensity, constant tachycardia without interruptions.
Increased heart rate of 102-105 beats per minute in the morning, afternoon, evening and even at night, when this should not happen. A sudden stop is possible. If the tachycardia lasts more than 15 minutes, let alone an hour, you need to call an ambulance to receive first aid and, possibly, transport to a hospital.
- Congenital and acquired heart defects. Often not accompanied by any symptoms. They are detected during electrocardiography and ultrasound examination of the organ.
- Anemia. Lack of hemoglobin as a result of iron deficiency, vitamin B12 or persistent bleeding. It makes itself known through brittle hair, dry skin, weakness, drowsiness, perversion of smell and taste preferences (patients can eat pencil leads, chalk, and this is in the most harmless cases).
The problem is detected by performing a simple general blood test. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to undergo examination every six months as part of medical examination of the population.
- Andropause and menopause. Menopause is associated with a lack of specific sex hormones. In men, it manifests itself as persistent erectile dysfunction and decreased sperm quality, drowsiness, weakness, and mood disorders.
In women - dysthymia, dysphoria, constant fluctuations in blood pressure over a wide range, tearfulness and touchiness, and general mental disorders.
The constant use of certain medications also has an effect: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, beta blockers, other types of adrenergic blockers and antihypertensive drugs in general.
Tachycardia as a symptom of the disease
Tachycardia at normal pressure can be caused by:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the stomach, thyroid gland.
The causes of tachycardia in women of physiological type are observed during menopause, with hormonal changes in the body and a decrease in estrogen levels. Estrogen stimulates the autonomic nervous system, affects the intestines, breathing, and heartbeat. For this reason, during menopause, when the concentration of estrogen decreases, the following symptoms of tachycardia occur in women:
- dizzy;
- shortness of breath appears;
- hot flashes occur;
- feeling of pulsation and fluttering in the chest.
The cause of the pathological disease is cardiac, vascular problems, disruptions in the functioning of other systems. The main extracardiac factors include:
- psoriasis;
- dehydration of the body;
- blood loss;
- temperature during a sore throat.
Often, when the disease is tachycardia, the causes may be pain syndromes of various origins and an increase in temperature. Frequent heartbeat can be observed in most heart and vascular diseases.
- Heart attack.
- Myocarditis, pericarditis.
- Heart defects.
In the case of idiopathic increased heart rate, it is impossible to determine the obvious factors of the disturbed rhythm. Therefore, if there is a rapid heartbeat, having eliminated the causes, treatment will be aimed at combating the disease.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of tachycardia, the following measures should be taken:
- Normalize your physical activity regimen. Don't overwork, don't sit still. 2 hours of outdoor walking per day. Exercise therapy is also indicated.
- Avoiding caffeinated drinks.
- Correction of the diet towards vitaminization. You cannot eat at night (less than 2 hours before bedtime).
A heartbeat of 100 beats per minute in a calm state is the result of pathologies of the organ itself, the endocrine, and less often the excretory or nervous systems. Corrected as a matter of priority to prevent fatal complications.
The treatment method is complex: drugs (or surgery), normalization of lifestyle, plus the use of safe herbal remedies. However, self-medication is unacceptable. A cardiologist cares for patients.
Why is it important to monitor your heart rate?
When visiting pediatric cardiology in Saratov, the specialist will pay attention to the fact that sometimes too high a pulse rate does not provoke painful sensations. It is extremely important to monitor the child’s behavior and reaction after physical activity, as well as after emotional outbursts. A small patient may complain of shortness of breath, headache, pain in the sternum radiating to the arm, as well as severe fatigue after:
- active physical exercise;
- long walks at a calm rhythm;
- walking up to low floors.
An increased heart rate in a child can also be observed after emotional stress. A pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will explain that laughter, as well as tears, prolonged viewing of cartoons, and strong emotional reactions can cause an increase in heart rate. It is important to measure the indicators after such a condition, and in addition, parents must make a lot of effort to check the frequency of contractions in the usual way.
What is a normal heart rate in children?
For each age, there are certain indicators that can be checked in pediatric cardiology in Saratov. During the appointment, the doctor listens to the heart, determines or excludes the presence of murmurs, and also counts the number of heartbeats. If necessary, an ECG or ultrasound of the heart may be prescribed. An experienced pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will draw the attention of parents to the fact that the heart rate decreases every year. If at birth 150-160 heart beats are considered normal, then by the age of 12–13 years this number is equal to 75 beats.
The pulse rate directly shows how the heart copes with its function and how efficiently it pumps blood. If there are too many contractions, the heart muscle may become fatigued and heart failure may develop.