Author
Victor Gennadievich Sturov , hemostasiologist, hematologist, doctor of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences
According to statistics, vascular thrombosis affects 70% of people around the world. Every year, one in 250 people living on Earth dies from this disease - despite the huge number of drugs created to combat this terrible disease.
What is thrombosis
Many biological systems are responsible for the vital functions of our body. One of them is hemostasis. The task of hemostasis is to keep blood in a liquid state, stop bleeding if the walls of blood vessels have been damaged, and dissolve blood clots - blood clots that, like a patch, cover the damaged area of the vessel.
On the one hand, thrombosis protects us from blood loss. On the other hand, it can provoke serious diseases associated with impaired blood flow: stroke, myocardial infarction, ischemia of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space, gangrene of the extremities.
Until the mid-19th century, thrombosis remained a mystery to doctors. Rudolf Virchow, a German pathologist, managed to uncover it. He studied the mechanisms of thrombosis and identified three main causes:
- Deterioration of the condition of the walls of blood vessels (this may be the consequences of injuries and surgical interventions)
- Slow blood flow (blood clots accumulate where the speed of blood flow changes)
- Change in blood viscosity (“thick blood”)
What is thrombosis?
Thrombosis can be venous or arterial. Venous is considered an acute disease; it appears due to disruption of the structure of the venous wall during injury, surgery, radiation or chemotherapy, due to increased blood clotting, due to a slowdown in the speed of blood flow.
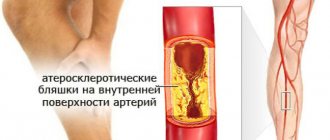
Arterial thrombosis is a pathological condition. Patients have atherosclerotic plaques - cholesterol deposits that narrow the lumen of the artery and provoke circulatory deficiency. Over time, the plaques become clotted.
There is also pulmonary embolism (PE), a fatal disease when the lumen of the pulmonary artery is completely or partially blocked by a blood clot. According to statistics, almost 50% of patients with massive pulmonary embolism die within 30 minutes after its occurrence.
Blood clot prevention: an alternative to aspirin
Atherothrombosis is the main cause of myocardial infarction and one of the main factors in the development of stroke. The risk of atherothrombosis can be reduced with antiplatelet therapy. We talked about prevention with acetylsalicylic acid in the previous article “Blood clots and acetylsalicylic acid.” However, in addition to it, other antiplatelet agents are also used.
Handyman
Let's begin the description of the representatives of the group of antiplatelet agents with dipyridamole (Curantil), which has been used for many decades. The drug blocks the enzyme phosphodiesterase, which breaks down a compound called cyclic AMP (cAMP), thereby causing increased levels of this substance in the blood. At high concentrations, cAMP prevents platelets from sticking together and prevents blood clot formation.
The ability of the drug to reduce the risk of vascular accidents in patients who have suffered vascular ischemia is confirmed by Cochrane data1. Indications for the use of dipyridamole include the prevention of arterial and venous thrombosis, including after installation of stents and coronary artery bypass grafts.
However, today dipyridamole is not prescribed for the prevention of strokes as part of monotherapy, since it is significantly inferior in activity to modern antiplatelet agents. But it has found quite widespread use as a drug that normalizes blood flow in cases of cerebrovascular accidents, as well as placental insufficiency in pregnant women. In addition, it increases the body's resistance to viral infections - influenza and ARVI - and is used for the prevention and treatment of these diseases.
Modern and famous
Drugs of a potentially new class - P2Y12 receptor inhibitors - have become hope and support for many people who suffer from heart and vascular diseases or have already suffered a heart attack or stroke. These receptors located on the surface of platelets play a central role in platelet activation, their subsequent “clumping” and blood clot formation. Blocking the P2Y12 site can effectively resist thrombosis and thus reduce the risks of cardiovascular accidents.
One of the first drugs in this series of antiplatelet drugs was clopidogrel, which appeared on the market in the late 1990s under the trade name Plavix. Its antiplatelet effect appears just a few hours after taking the first 75-milligram dose (working dosage of the drug), and the drug has its maximum effect after 3-7 days of regular use. If you need to get immediate results, “loading” doses of 300–600 mg are prescribed. In such situations, clopidogrel has a powerful antithrombotic effect just a few hours after administration.
The original clopidogrel, Plavix, is registered in more than 100 countries around the world and is one of the drugs whose sales reach several billion dollars per year2. Until the patent expired, Plavix was the world's second-leading seller. Today, dozens of generic clopidogrel are available in pharmacies, which, of course, has greatly increased its availability.
In addition, other drugs from the group of P2Y12 inhibitors have already been registered in the Russian Federation. Prasugrel (trade name Effient), ticagrelor (Brilinta), ticlopidine (Ticlid) are widely used in clinical practice for the prevention of stroke, myocardial infarction and death from vascular disease in patients who have had a stroke or suffer from coronary heart disease or chronic diseases of the lower extremities ( intermittent claudication). The effectiveness of all drugs in this group, without exception, has been confirmed by many clinical studies and cannot be doubted.
It should be noted that the original prasugrel, ticagrelor and ticlopidine, like the original clopidogrel, are quite expensive. However, the vital indications for which they are prescribed and the results they provide make the investment worthwhile.
One drug is good, but two are better
Antiplatelet drugs definitely help reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, but sometimes resistance to the drugs develops and the likelihood of vascular events increases dramatically. Combination therapy, in which several drugs are prescribed at once, helps to overcome resistance.
Most often we are talking about two drugs, this is called double therapy. Increased effectiveness of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) compared to the use of a single drug is achieved due to the influence of drugs with different mechanisms of action on different stages of thrombus formation.
One of the essential components of DAT is always acetylsalicylic acid. Almost all people with coronary heart disease must take it constantly throughout their lives. The second component of the regimen is usually a P2Y12 inhibitor - clopidogrel, prasugrel or ticagrelor. The doctor decides which of the three drugs will be prescribed, based on the individual risk of blood clots and bleeding, the likelihood of which, alas, increases when taking antiplatelet agents.
The duration of dual antiplatelet therapy is also determined in each case. Patients who have had a myocardial infarction may be prescribed a combination of drugs for at least one year. If the risk of bleeding is low, DAPT may be extended. For patients after coronary artery stenting or those with a high risk of bleeding, DAPT is prescribed for at least a month.
Combination drugs that reduce the risk of thrombosis also include combinations of aspirin with dipyridamole (Agrenox) and aspirin with magnesium hydroxide (Cardiomagnyl). They have nothing in common with standard DAPT, which is based on a combination of acetylsalicylic acid + a P2Y12 inhibitor.
The first is approved for secondary prevention of stroke, but it is significantly inferior in activity to combinations with P2Y12 inhibitors. And the drug Cardiomagnyl is aimed at reducing the negative effect of acetylsalicylic acid on the gastric mucosa due to the absorption of hydrochloric acid by magnesium hydroxide. This improves aspirin tolerability, which is important during long-term treatment.
Marina Pozdeeva
Photo istockphoto.com
1 De Schryver EL, Algra A, van Gijn J (2007). Algra A, ed. Dipyridamole for preventing stroke and other vascular events in patients with vascular disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD001820.
2Top Ten Global Products – 2007″ (PDF). IMS Health. 2008-02-26.
Products by topic: (dipyridamole), (clopidogrel), (prasugrel), (ticagrelor), (Agrenox), [product strict="Cardiomagnyl"](Cardiomagnyl), (Thrombomag), (Trombital), (Fazostabil)
Symptoms of thrombosis
There are two main forms of venous thrombosis: deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and superficial vein thrombosis (thrombophlebitis). The first form is the most dangerous and may be asymptomatic at the onset of the disease.
Symptoms of thrombosis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities
- heaviness in the legs
- pain along the thrombosed veins, limitation of movements
- swelling of a nearby limb
- redness of the skin along the hardened vein
- increased skin sensitivity
- deterioration in general health: weakness, malaise, chills, increased body temperature
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
- feeling of fullness and heaviness in the limb
- pain on the inside of the foot, leg, thigh
- swelling of the entire limb or part of it
- the skin of the affected leg becomes pale and bluish in places
- the temperature of the affected limb is 1.5-2ºС higher than that of the healthy one
- bursting pain in a limb
If you experience any symptoms of thrombosis, consult your doctor immediately. Prevention of thrombosis Prevention of thrombosis is a whole series of measures that are aimed at improving the rheological properties of blood (blood and plasma viscosity), preventing heart and vascular diseases, strengthening blood vessels, normalizing blood flow, etc.
To avoid blood clots, you need:
- Adhere to a special diet that prevents the formation of blood clots.
- Give up bad habits and spend more time in the fresh air: fight physical inactivity, give yourself adequate physical activity.
- Strengthen the immune system, thereby preventing the development of infectious processes.
- Wear compression socks and special stockings made of jersey.
- Properly organize your daily routine, carefully plan long trips by plane or car, when you have to spend many hours in a sitting position.
- Do not wear outerwear, underwear and accessories that cause discomfort and put pressure on certain parts of the body (for example, tight jeans, belts, corsets, uncomfortable shoes).
- Avoid general hypothermia. Do not walk in too hot weather, try not to take hot baths.
- Contact your doctor to prescribe medications to prevent thrombosis. Attention: medications cannot be taken without agreeing on the dosage with a specialist.
How to protect yourself from thrombosis?
14.10.2019
Thrombosis , along with the most dangerous diseases, claims a huge number of lives every year. In Europe alone, almost five hundred thousand people die every year. In poor countries this number can be several times higher. So why is this disease so dangerous and how to deal with it, we will tell you in this article.
To begin with, what is thrombosis ? Thrombosis is the occurrence of a blood in blood vessels , whether veins or arteries . Even if small in size, such a clot can be very dangerous. Because of it, blood stops flowing to important organs or muscles. When a blood clot adheres to the wall of a vessel , it begins to grow and eventually completely blocks the blood flow, which can lead to dire consequences. The blood clot also break loose, which can be even more dangerous. In any case, it is better to treat thrombosis before it occurs.
There are two types of thrombosis:
- arterial;
- venous.
Venous thrombosis is dangerous because a blood clot can form in the veins of the legs or pelvis, which can lead to it entering the main vessel of the pulmonary artery , and if this happens, it will be very difficult to save the person.
most often affected by venous thrombosis . The main causes are varicose veins , as well as pregnancy and childbirth . In these cases , the blood stagnates in one place, and blood clots form there, which later grow and become more dangerous.
Arterial thrombosis . It mainly occurs in people with heart and is often accompanied by atherosclerotic plaques. It can also occur with atrial fibrillation. Because of this, blood flow in the arteries . Arterial thrombosis is the main cause of arterial embolism, and this can lead to a heart attack .
Prevention of thrombosis
The main cause of thrombosis is a high level of low-density cholesterol in the blood . With heavy consumption of fatty, salty or fried foods, the amount of low-density cholesterol increases and atherosclerotic plaques begin to form. This leads to clogging of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots.
In order to avoid this, you need to monitor your diet, exclude fatty and salty foods from your diet, and also actively engage in sports. It is also necessary to regularly check the presence of cholesterol in the blood , thereby protecting yourself.
Excessive physical activity can also cause thrombosis . With high stress on the legs and back , blood clots can form the vessels Therefore, if you engage in strenuous sports or have hard physical work, then try to better monitor your diet and visit your doctor .
Women have an increased risk of thrombosis if they wear high heels. When a woman wears heels higher than three centimeters, the calf muscles stop pumping blood in the legs . If you often wear heels, blood will stagnate the veins , which will lead to the formation of blood clots. Therefore, it is better to refrain from wearing high-heeled shoes, and if you wear them, then you need to actively engage in sports and periodically go for a massage . This will reduce the risk of thrombosis .
In addition to all of the above, do not forget that a sedentary lifestyle also leads to the formation of blood clots. If you have an office job or often sit, then do not forget about exercise and massage . This will help you avoid consequences from your work.
By following all the points mentioned in the article, you will not only protect yourself from thrombosis , but also become much stronger and healthier. If you don't forget about physical activity and proper nutrition, many problems, including thrombosis , will bypass you.
Published in Phlebology Premium Clinic
Antithrombotic nutrition
To prevent thrombosis, the diet should be designed in such a way as to normalize the balance of lipids and carbohydrates, adjust the amount of salt and introduce bioflavonoids into the daily diet, which improve metabolism, strengthen and restore the walls of blood vessels.
Recommended products: lean meat, fatty sea fish, vegetable oil, fresh low-fat milk, low-fat fermented milk products, cereals (except wheat and pearl barley), durum pasta, whole grain bran bread, vegetables (except potatoes and sugar beets), legumes, fruits (except bananas and grapes), nuts, freshly squeezed juices, dark chocolate.
Products that need to be reduced to a minimum: fatty meat and offal, hard and soft fatty cheeses, full-fat dairy products, butter and combined fats, smoked meats, sausages, dried and salted fish, chips, fast food, alcohol, lemonade, candy , milk chocolate, baked goods, potatoes, fatty sauces.
The daily amount of salt should be no more than 6 grams. 1/3 animal protein should account for at least 2/3 vegetable protein and fiber. To prevent thrombosis, you need to add vitamins: C, E, A (retinol), B3 (rutin), bioflavonoids (quercetin, hesperidin).
Be sure to follow the drinking regime: the daily norm for an adult is from 1.5 to 2.5 liters of water per day (soups, tea and coffee are not included here). These simple tips are relevant not only for patients with thrombosis, but also for people with risk factors for this disease. Always be hematologically healthy, and if you identify symptoms of thrombosis, do not self-medicate - contact an experienced specialist, a hematologist-hemostasiologist!