Detailed description of the study
The liver is an organ in which complex metabolic processes occur. The functional activity of the liver is provided by hepatocyte cells, they are responsible for:
- Bilirubin exchange and bile formation;
- Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism;
- Regulation of fat metabolism;
- Formation of many proteins, including enzymes;
- Neutralization of toxic substances (medicines, alcohol, etc.).
Bilirubin is an orange-yellow pigment formed during the breakdown of heme (a component of hemoglobin). Every day, the human body synthesizes about 350 mg of indirect (free) bilirubin. Most of it is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells, a smaller part (about 20%) is formed from other heme proteins in the liver and bone marrow.
Free bilirubin is insoluble in water; it is transported in human blood plasma in combination with a protein - albumin. Next, the liver captures free bilirubin, and after a series of transformations it is converted into direct (associated with glucoronic acid) bilirubin, which is soluble in water.
Bound bilirubin in bile is sent to the gallbladder and released into the small intestine during food digestion. In the small intestine it is metabolized by bacteria to urobilinogen. Most of the urobilinogen is transformed into stercobilin, which turns the stool brown. A small amount of urobilinogen is reabsorbed by the liver and returns to the bile. A small part is excreted in the urine.
Normally, the level of indirect bilirubin in the blood is very low. If the concentration of bilirubin and its fractions increases, a person may develop yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes. This condition is called jaundice.
Depending on the cause of bilirubin metabolism disorders, there are three types of jaundice:
- Hemolytic;
- Parenchymatous;
- Mechanical.
1) Hemolytic, or suprahepatic, jaundice is associated with increased release of bilirubin into the blood due to increased breakdown of red blood cells. The pigment formed during destruction is not captured by hepatocytes, but remains in the blood (having a toxic effect). A similar pathology can be observed in newborns when their Rh factor is incompatible with that of the mother (Rh conflict).
In rare cases, a congenital disorder of bilirubin metabolism known as Gilbert's syndrome occurs. This disorder is associated with reduced activity of the enzyme glucuronyl transferase, which converts indirect bilirubin into direct bilirubin. As a rule, it is determined by chance and has a favorable clinical course.
Hereditary diseases associated with defects in the functioning of enzymes responsible for bilirubin metabolism also include Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome.
Increased release of indirect bilirubin into the blood accompanies hemolytic anemia. This condition is also associated with the premature breakdown of red blood cells and the inability to fully metabolize this pigment in liver cells due to its excess.
May be caused by internal defects in the red blood cells themselves (hereditary pathology) or:
- Taking certain medications (methyldopa, penicillin, quinine, etc.);
- Immunological disorders;
- Infections;
- Mechanical damage to blood vessels;
- Toxic effects (copper, lead).
2) Hepatic, or parenchymal, jaundice occurs due to lesions of the liver tissue. Such conditions are diagnosed with viral hepatitis, poisoning, sepsis, etc.
3) Mechanical, or subhepatic, (obstructive) jaundice occurs due to the presence of mechanical obstacles (stones, tumors) in the bile ducts, which impairs the outflow (excretion) of bile.
A bilirubin test may be used as part of an annual physical to evaluate liver health. It is also used to determine the causes of jaundice and helps the specialist determine the tactics of further therapy.
The study is also carried out in newborns with jaundice to determine its causes.
Indications for the study
A blood test for direct bilirubin is carried out during the diagnosis of liver pathologies. Its results are required to confirm diseases of the bile ducts, hepatitis, and hereditary liver diseases. The test is mandatory if there are characteristic symptoms of liver problems (jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium, etc.). Its results are interpreted in conjunction with data from other studies. In most cases, a comprehensive examination is required for accurate diagnosis and selection of an effective treatment method.
References
- Clinical guidelines “Drug-induced liver damage”, 2019. - 35 p.
- Pakhomova, R.A., Kochetova, L.V. Clinical manifestations of obstructive jaundice and liver failure, depending on the severity of obstructive jaundice of benign origin.” — Modern problems of science and education, 2021. — No. 6. — P.47.
- Sullivan, J., Rockey., D. Diagnosis and evaluation of hyperbilirubinemia. — Current opinion in gastroenterology, 2021. — Vol. 33(3). — P. 164-170.
Determination of bilirubin level
The amount of bilirubin is determined using a biochemical blood test. Material for research is collected from a vein. If the patient is a newborn, blood may be taken from the heel. The test must be taken on an empty stomach. However, it is recommended to have dinner the night before. A long hunger strike can affect the possible results. It is better to make the menu before taking the test from dairy products, fruits and vegetables. But it’s better to avoid alcoholic beverages. Taking them before taking a biochemical blood test is strictly prohibited. You should not eat fatty and spicy foods. You should also give up coffee. The last meal should take place 8 hours before the procedure.
You should not take antibiotics, drugs that irritate the blood, choleretic agents and enzymes. Stop using them one day before donating blood. If refusal to take medications is impossible for health reasons, it is recommended to notify the laboratory technician about this fact.
Blood is drawn using a syringe and needle or catheter. The procedure is not very painful. Relatively recently they began to use TBI. The procedure does not involve causing mechanical damage to the patient for blood collection. During its implementation, a device is used that measures pigment in the skin in the area of the bridge of the nose and on the chest. The head of the measuring device is placed against the area being tested and then fixed for a few seconds. When the measurement is completed, the resulting data is displayed on a digital display. The device allows you to very accurately monitor the course of the disease and the progress of treatment. However, the method of measuring bilirubin is not yet used in all medical institutions.
The results are influenced by a large number of factors. If the amount of bilirubin in the blood is significantly deviated from the norm, but no pathologies are observed, it is recommended to take the test again.
Treatment
The choice of treatment regimen is made by the doctor taking into account the identified pathologies. When making a diagnosis, the nature of the enzyme deviation from the norm (increased or decreased value) is taken into account.
There are no special pharmacological agents that lower bilirubin. In cases where the provoking factor is medications or toxic substances, it is necessary to stop taking them. If we are talking about vital medications, the doctor selects safe substitutes.
When the enzyme level is too high, the following methods are used:
- the use of drugs that activate the outflow of bile (Allahol, Hofitol);
- cleansing droppers with glucose (stimulating the elimination of indirect toxins);
- phototherapy (irradiation with special lamps, under the influence of light the molecules of indirect bilirubin and other substances bind together);
- taking pharmacological agents that accelerate metabolic functions (Mezim, Festal, Pancreatin);
- dietary diet.
Preventive measures
To prevent the amount of bilirubin in the blood from deviating from normal, experts recommend taking preventive measures. To do this, you need to try to get rid of bad habits. Do not overuse fried, salty or other foods that can harm the body. It is better to use purified water. It is necessary to increase the amount of natural vegetables and fruits in the daily menu. It is better not to eat regular sugar. Experts recommend replacing it with reed. It is necessary to select a vitamin complex that can provide the human body with all the necessary substances.
Symptoms of abnormal bilirubin levels and when to see a doctor
Some factors may indicate an increase in the concentration of pigment in the blood even before the test results are obtained.
What to pay attention to:
- pain in the left hypochondrium after physical activity or sports training;
- feces become light-colored and urine darkens;
- the appearance of vomiting and nausea;
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes, skin and mucous membranes;
- dizziness and weakness;
- nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite;
- chronic fatigue and anxiety.
Preparing for the test
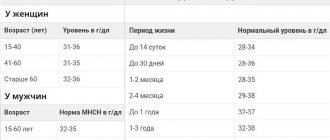
Bilirubin - the norm for women by age (table below) - indicates the proper functioning of organs such as the spleen, liver and bile ducts. But sometimes research results can be distorted. This occurs due to violation of certain conditions before taking the test.
Reasons that may affect the results of the study:
- abuse of coffee, alcohol, fatty foods before analysis;
- long exposure to the sun;
- taking hormonal medications and contraceptives;
- taking diuretics;
- taking medications containing codeine, caffeine, alcohol;
- taking sedatives containing barbiturates;
- heavy physical activity or a strict diet before taking the test;
- taking the test after completing a course of chemotherapy or after the last dose of antibiotics (at least 14 days must pass).
Blood is donated from a vein in the morning before breakfast . If it is not possible to refuse food for any reason, it is given 4–5 hours after the morning meal.
The rules for passing urine for bilirubin are no different from the usual ones applied to passing a general analysis. Before the examination, you must take a bath or shower. The initial portion of urine is passed, and the next one is collected in a sterile container.
Reasons for changes in the level of bilirubin in the blood in women
The reasons for changes in the level of bilirubin in the blood can be physiological and pathological. So, the indicator may increase slightly during menstruation or pregnancy. Usually during this period of time there is an exacerbation of existing diseases. A deviation from the norm in itself is not a diagnosis. This is only a symptom of the underlying disease.
Incorrect blood sampling and alcohol abuse on the eve of a laboratory test can lead to a distortion of the result. Therefore, minor deviations from the norm are often ignored.
Increasing the indicator
An increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood can be suspected without testing. It is expressed in the effect of yellowness. It usually affects the sclera of the eyes, the oral mucosa and the skin of the face, palms and soles. First of all, doctors pay attention to the sclera of the eyes. This is the main sign used in diagnosis. Then the appearance of the skin in other areas is taken into account. As the disease progresses, its shade may change on all parts of the body. A change in skin color is a signal of the need to take a biochemical blood test and determine the amount of bilirubin in the blood.
Popularly, this symptom is often attributed to the effects of the hepatitis A virus. However, jaundice can occur in the presence of a whole list of pathologies. An increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood in women after 50 years of age may indicate:
- the presence of congenital hemolytic anemia;
- the presence of hepatitis A, B or the course of chronic hepatitis C;
- poisoning caused by food or medication;
- hereditary characteristics;
- course of autosomal diseases;
- liver tumor;
- hepatitis developed due to brucellosis or leptospirosis.
An increase in the amount of bilirubin occurs as a result of the accelerated breakdown of red blood cells, a malfunction in the functioning of metabolism, and difficulty in the outflow of bile.
Decrease in indicator
The level of bilirubin in the blood of women after 50 years of age can not only increase, but also decrease. This phenomenon occurs much less frequently. Previously, no attention was paid to the decrease in the indicator, not considering that this indicated any pathology. However, studies have proven that a decrease in the level of bilirubin in the blood of women is also an alarming symptom that requires taking a number of measures. The following factors can provoke the occurrence of pathology:
- the woman is depressed;
- the patient follows a grueling diet;
- a woman often abuses coffee;
- intoxication is observed;
- there is a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood;
- The woman developed coronary heart disease.
What test should be taken for bilirubin?
Most often, a biochemical blood test is performed to determine the concentration of bilirubin. Analysis will help determine the overall meaning of the dye and its associated species. And the indirect view is simply calculated from these two values.
Bilirubin is measured in micromoles per liter with very high accuracy, making it possible to detect problems in the body even before painful symptoms appear. Most often, the result of the study is ready the next day, but it is possible to conduct an urgent analysis, in which all indicators will be known within a few hours.