MPV (short for mean platelet volume) is the designation of the platelet index, which characterizes the degree of platelet maturity in peripheral blood. The measurement is based on the fact that the size of young cells is larger than that of mature and aged cells. There is a connection between the size of platelets and their functional activity, so the index characterizes the state of the blood coagulation system, which platelets represent.
Determination of MPV in a general blood test is carried out within two hours after collecting the material, since with a later study the result may be distorted.
MPV norm in general blood test
Table: Normal intervals for the MCV platelet index depending on age
| Age, years | Norm MPV, fl |
| Infants up to one year | 7,1 – 8,0 |
| Children from 1 year to 5 years | 8,1 – 8,9 |
| Children, teenagers and adults from 5 to 60 years old | 7,4 – 12,0 |
| Over 60 years old | 9,5 – 12,0 |
Meanwhile, all these norms and the table are very conditional. The reader can verify this for himself by looking for the boundaries of normal values in other sources. The whole point, as always, is in the reference intervals, which vary noticeably in different laboratories, where the norm falls within the range of 6.0 - 13 femtoliters, somewhere narrows its limits (7.4 - 10.4), so before you start worrying Regarding your own analyses, it is useful to ask what values are used by the CDL, which calculated these indicators.
Increase P-LCR
An increased number of large platelets means that there is a pathology in the body. Only in isolated cases is a high P-LCR value an individual characteristic of a person and does not require treatment.
Etiology
The reasons for an increase in P-LCR can be completely different diseases - inflammatory, oncological, hematological, infectious.
Along with this, the P-LCR index increases if the patient has:
- infectious pathology - bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic,
- post-traumatic and postoperative syndrome,
- oncological and hematological diseases - lymphoma, neuroblastoma and hepatoblastoma, anemia,
- spleen diseases,
- cirrhosis or polycystic liver disease,
- damage or inflammation of the spinal cord,
- alcoholism,
- intoxication with chemicals that disrupt bone marrow function,
- atherosclerosis,
- diabetes mellitus
A high P-LCR index leads to the fact that the patient has a tendency to thrombosis. Due to the adhesive properties of platelets, they stick together and form a blood clot, which disrupts blood circulation and prevents the free movement of blood. As the thrombus grows, it narrows the lumen of the vessel, disrupts the blood supply to the organ, and causes hypoxia and ischemia of the tissue. When the coronary arteries are damaged, this leads to myocardial infarction. With thrombosis of cerebral vessels, an ischemic stroke develops. The result of the process is often varicose veins or atherosclerotic changes in the arteries. These pathologies are deadly and often result in the death of patients.
Symptoms
When the P-LCR increases, the patient develops corresponding clinical signs. They may go unnoticed behind the obvious symptoms of the causative disease. Such patients are not treated for thrombocytosis, which further aggravates the situation.
An increase in P-LCR is manifested by the following symptoms:
- hypersensitivity and pain in the fingertips,
- causeless appearance of hematomas,
- irritation and itching of the skin,
- cyanosis,
- asthenia of the body,
- rapid heartbeat,
- shortness of breath at rest,
- visual dysfunction.
These signs are optional. They can appear individually or in various combinations. But despite this, the patient needs to visit a health care facility and undergo certain tests, based on the results of which doctors will determine the cause of the P-LCR deviation and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Treatment and diagnostic procedures
To determine the cause of the disorder and make a correct diagnosis, in serious cases, a bone marrow biopsy is examined and blood is taken again. Additionally, general clinical and molecular tests and ultrasound of internal organs are performed.
To normalize the P-LCR value, the causative disease must be eliminated. If the pathology is not treated, the patient risks dying from thrombosis, or more precisely from its consequences - acute coronary or cerebral failure. These phenomena are very dangerous. They are often fatal. That is why this deviation needs to be corrected. Hematologists carry out diagnostic and treatment measures. Restoration of normal P-LCR levels in a blood test is a sign of adequate and effective therapy.
- Patients are prescribed a diet rich in vegetables and fruits, vegetable oils, freshly squeezed juices and other products that make the blood less viscous. For the same purpose, experts recommend optimizing your drinking regime - drinking up to 2-3 liters of water per day.
- To prevent thrombosis and its consequences, the use of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants is indicated - Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Trental, Cavinton, as well as drugs that improve microcirculation - Dipyridamole, Piracetam, Vinpocetine.
- If the cause of a high level of large platelets is an infectious disease, then after intensive antibiotic therapy, the P-LCR index value returns to normal almost immediately.
- In severe cases, the use of corticosteroids - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone and cytostatics - Anagrelide, Hydroxyurea, Radioactive phosphorus 32P is indicated.
- To stimulate the immune system, Interferon and its derivatives are prescribed.
- There are folk remedies that allow you to correct (but not eliminate) existing violations. These include: mulberry poison, sweet clover infusion, ginger tea, celery juice. These plants have a beneficial effect on the condition and activity of platelets.
MPV during pregnancy
Pregnancy requires a woman’s body to restructure all its functions, and these changes primarily affect the circulatory system. The need to form an additional (placental) circulation requires an increase in the total volume of circulating blood. On average, normal platelet counts in a pregnant woman are considered to be 150–380x109/l. However, deviations from the norm in this condition can lead to serious consequences. That is why a woman should undergo regular laboratory tests throughout her pregnancy.
If pregnancy is accompanied by severe toxicosis, then vomiting and other intestinal disorders can lead to dehydration, which, in turn, will affect the level of platelets - it will increase sharply. During pregnancy, levels should not exceed 400x109/l, otherwise pathological processes may begin, leading to platelet aggregation and the formation of blood clots in the vascular bed. In the early stages, such pathologies can lead to fetal loss, and in the later stages they are fraught with the occurrence of blood clots in the vessels of the legs, accompanied by the development of varicose veins. In order to avoid this, you can use orthopedic knee socks.
No less dangerous is a decrease in platelet levels below 140x109/l. In the early stages, this can cause bleeding and even the risk of fetal loss. Manifestations of thrombocytopenia during pregnancy can include the appearance of bruises on the body even after slight touches, bleeding gums, and nosebleeds. In later stages, thrombocytopenia can cause large blood loss during childbirth and bleeding in the child.
Thus, the average platelet level is an important indicator of the condition of the human body. It allows you to determine the possibility of a particular pathology at an early stage and take measures to prevent it.
Red blood cells, their functions in the body, main indicators
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBC, red blood cells), are red blood cells, biconcave disc-shaped blood cells, lacking a nucleus. The shape of a red blood cell allows the cell to deform as it moves through small blood vessels. The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs, and from them - carbon dioxide to the lungs. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow and destroyed in the spleen; the average lifespan of cells is 120 days. Newborns have larger red blood cells than adults.
The condition in which red blood cells of abnormal sizes are detected in the blood is called anisocytosis.A physiological increase in the number of red blood cells is observed in children in the first days of life, with frequent stress, intense physical activity, malnutrition or fasting, and with prolonged clamping of a limb with a tourniquet during blood collection for a blood test. A physiological decrease in the number of red blood cells occurs immediately after eating, between 17:00 and 07:00 and when blood is drawn from the patient in the supine position.
In the blood, in addition to normal red blood cells, there may be cells that differ in size - larger (macrocytes) or small (microcytes) red blood cells. The condition in which there are more than 50% macrocytes in the blood is called macrocytosis. If 30–50% of microcytes are present, microcytosis is diagnosed. The appearance of red blood cells of different volumes in the blood is called anisocytosis, the degree of which allows one to determine the RDW index.
Erythrocyte indices are determined during a general (clinical) blood test. The count is carried out using an automatic hematological analyzer, according to the appropriate formulas and/or in a stained blood smear under a microscope when calculating the leukocyte formula. In addition to RDW, erythrocyte indices in a general blood test include MCV (mean erythrocyte volume), MCH (mean hemoglobin content in erythrocytes), MCHC (mean hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes).
Additional examinations
A blood test gives an approximate idea of the state of the body. It only allows us to state a fact: there is a problem. Why it arose is a different question, and the answer to it is sought using auxiliary techniques.
The examination is carried out by a hematologist. Third party specialists are brought in as needed.
- Oral interview with the patient. Complaints are informative in some cases. Symptoms indicate damage to one or another organ.
- Anamnesis collection. Lifestyle, past and current diseases, family history, genetics and other points. The doctor collects them for interpretation and determines the possible source of the problem. Its origins.
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract. First of all, specialists are interested in the liver.
- To study the functional state of the largest gland in the body, scintigraphy is prescribed. Radioisotope technique.
- A blood test for hormones helps identify thyroid diseases.
- Specific, extreme measures are possible. Bone marrow puncture, histological evaluation of the obtained material.
- If necessary, diabetes is diagnosed with special tests: sugar curve and others.
The question of examination is within the competence of the doctor. The list can be expanded or narrowed. Of necessity.
Treatment
If the test shows that your platelet level is below normal, you should undergo testing to find out the reason and decide how to increase your level. Treatment depends on the cause of this condition and is aimed primarily at eliminating it.
If the low platelet count is due to medications, they are discontinued. If severe bleeding occurs, platelet and plasma transfusions are performed. With significant blood loss and the development of severe anemia, transfusions of red blood cells and plasma may be required. To increase platelet production and suppress autoimmune reactions, immunoglobulin and corticosteroids are prescribed.
If there is no desired result with conservative treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura, heavy repeated bleeding, hemorrhages in important organs, splenectomy may be indicated - an operation to remove the spleen, the effectiveness of which is high (about 80%).
For thrombocytopenia, in order to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and increase blood clotting, a course of medications based on natural ingredients can be prescribed. These include products such as Derinat, Sodecor, and Etamzilat.
If your platelet count is low, doctors recommend eating right. It is necessary to avoid alcoholic drinks, hot and spicy foods. The menu should include more foods rich in vitamins A, C and promote better blood clotting. These are liver, fish oil, chokeberry, bell pepper, celery, green apples, parsley, rose hips, carrots, peanuts, pine nuts, almonds, grape and lingonberry leaves, birch sap.
In addition to proper nutrition, doctors recommend adhering to a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a daily routine, getting enough sleep, and not overexerting yourself physically and psychologically.
Video about the functions of platelets and the reasons for the decrease in their number in the blood:
Average platelet volume is increased
An increased average platelet volume can be a diagnostic sign of various (usually hematological) pathologies or act as a laboratory symptom accompanying certain diseases. For example, MPV is increased when:
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (an autoimmune process that leads to massive death of blood platelets and intense bone marrow hematopoiesis) and other autoimmune diseases (SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus);
- Myeloproliferative processes;
- Hemorrhagic thrombocytodystrophy or Bernard-Soulier syndrome (rare hereditary disease, autosomal recessive transmission);
- Hereditary large-platelet thrombopathy (a disease characterized by large platelets, but their function is not impaired);
- May-Hegglin anomalies (familial thrombocytopenia, autosomal dominant inheritance);
- Anemic syndrome caused by acute blood loss;
- Thalassemia;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Hypersplenism and enlargement of the spleen, which can be either isolated (rarely) or accompany various hematological pathologies, for example, myeloproliferative processes (massive death of blood platelets occurs in the spleen, and the bone marrow at this time works in emergency mode, releasing young cells into the bloodstream large sizes);
- Removal of the spleen (however, the MPV indicator in this case changes its values for a short time; soon after the operation it returns to normal);
- The first signs of the formation of a neoplastic process;
- Development of inflammatory reactions;
- Development and progression of the atherosclerotic process (especially in smokers);
- Thyrotoxicosis (high functional activity of the thyroid gland and an increase in the level of its hormones as a result).
An increased MPV is not always associated with the development of some pathology, for example, in people who actively puff on a cigarette, as well as on holidays and weekdays who drink strong drinks, the average volume of blood platelets is always increased.
Folk remedies for the treatment of low platelet count
If you want to get rid of thrombopenia, you can use folk remedies (if the decrease is not associated with illness). For therapy, various natural ingredients are used, products that stimulate the production of platelet plates.
Sesame oil
Sesame oil makes good progress in the treatment of thrombopenia. You need to choose virgin oil, consume 1 tablespoon 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks. It is advisable to consume the product 30 minutes before meals.
Sesame oil is recommended because of its rich composition. Contains microelements:
- omega-3;
- vitamin E;
- lignans.
Sesame oil
When consumed orally, in addition to increasing platelets, it is possible to improve digestion, increase immunity, strengthen the cardiovascular system, and reduce the level of bad cholesterol. The product has virtually no contraindications for use. Long-term use is possible.
Nettle for thrombocytopenia
If a person suffers from low platelet concentration, it is possible to correct the condition using nettle. Decoctions and infusions are prepared from it. You can use the following recipe:
- You will need to prepare 2 tablespoons of dry nettle.
- Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the nettles.
- Let the prepared infusion brew for several hours.
You need to drink liquid 30 minutes before meals every day. The duration of treatment is 3-4 weeks. It is permissible to consume nettle over a long period of time.
Among the beneficial properties are stimulation of the immune system and improvement of metabolism. In addition, nettle infusions and decoctions actually increase platelets. After a certain period of time, their amount in the blood becomes normal. Coagulability improves.
It is important to know! To achieve noticeable results, therapy should continue for at least 2 weeks. After treatment, preventive measures must be taken to prevent the recurrence of thrombocytopenia.
Chokeberry
Rowan has a fairly large number of useful properties. With the help of chokeberry, it is possible to treat uncomplicated thrombocytopenia. The fruit contains many vitamins, nicotinic acid, and flavonoids. To prepare a medicine based on rowan, you can use one of the following recipes.
- Decoction - add 20 grams of fruit to boiling water. After this, you need to cook the liquid for 5-10 minutes. The decoction is consumed daily in small portions of 50 ml. The number of doses per day is 3-4 times.
- Infusion - 1 teaspoon of fruit needs to be poured into 250 ml of boiling water. Then let the liquid brew in a thermos for 5 hours. You need to drink a glass of the infusion every day.
- Jam - you need to take 500 g of fruit, 400 grams of sugar, 20 g of citric acid. The fruits are passed through a meat grinder and covered with sugar. Everything is thoroughly mixed. Add citric acid and other ingredients to taste. Jam is consumed with tea or any other drink.
Appearance of this type of rowan
You can also consume up to 150 g of fresh fruit almost every day for a long time. Using mountain ash you can experiment in different ways. In their fresh natural form, the fruits bring the greatest help. In winter, decoctions are made from frozen fruits.
MPV in blood test is increased
When, when assessing the results of a detailed analysis, it is revealed that the average platelet volume is increased, doctors talk about thrombocytosis. This condition is characterized by a significant increase in the number of platelets in the circulating blood. There are 2 types of thrombocytosis: relative - the average volume of platelet mass is increased by 1-2 units, critical - the indicator is almost twice the norm. To accurately determine the cause of changes, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out.
Mean platelet volume MPV is increased - reasons
Doctors carefully study the results of the study. After a blood test is performed, MPV is increased, what this means, what is the reason – no specialist can immediately answer. There are many reasons for changes in the values of this indicator. In most cases, they directly concern the blood coagulation system and blood circulation, however, general pathologies can provoke an increase in MPV. Among the common factors causing the disorder:
- posthemorrhagic anemia;
- hyperthyroidism;
- diabetes;
- preeclampsia;
- platelet purpura;
- May-Hegglin anomalies;
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome.
An increase in MPV index values is also possible after removal of the spleen. The risk of developing pathology is increased in individuals with atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels due to smoking. Age-related changes can also provoke an increase in the values of this indicator, since the balance between new cells and dead old ones is disrupted.
MPV increased - what to do?
If a patient has an increased average platelet volume, doctors try to initially determine the cause of the deviation. When the phenomenon is temporary and physiological in nature, medical intervention is not required.
In case of a pathological increase in MPV values, therapy is carried out in the following two directions:
- The use of anticoagulants to restore normal blood concentrations.
- Elimination of the main cause of the violation.
Therapy is carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of doctors. With a high MPV in a blood test, what this phenomenon is and what it is associated with helps to determine:
- blood biochemistry;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- blood test for hormones.
What does a decrease in MPV mean?
A decrease in MPV may mean an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly), the presence of liver cirrhosis, hypoproteinemia, kidney disease, and thyroid pathologies. The platelet index decreases in aplastic anemia, septic thrombocytopenia, congenital megakaryocytic hypoplasia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, X-linked thrombocytopenia with platelet microcytosis, thrombocytopenia caused by immunological destruction of cells, as well as during chemotherapy and during pregnancy. A significant decrease in MPV in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates a threat of miscarriage.
Preparing for the test
There is no need to take special preparatory measures for the procedure of donating blood for the MCHC index. Usually this indicator is included in a general blood test. You just need to follow some medical recommendations:
- You need to donate blood strictly on an empty stomach, i.e. 8-12 hours after your last meal. It is for this reason that routine blood tests are taken in the first half of the day;
- On the eve of the procedure (in the evening, during dinner), it is advisable to exclude heavy fatty and fried foods from the diet. It is also not recommended to overeat;
- 2 days before donating blood, drinking alcohol is prohibited;
- 1 hour before blood sampling, you should not smoke or use nicotine replacement drugs (tablets, patch, chewing gum, spray). The presence of nicotine in the blood may affect test results;
- It is also not recommended to donate blood after physical treatment or X-ray diagnostics;
- a few days before the procedure, you should try not to be nervous, avoid stress and heavy physical activity;
- Consult your doctor first about taking/discontinuing medications intended for permanent/long-term use. It is possible that their action may negatively affect the results of the analysis.
Compliance with all the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the procedure ensures that you receive reliable diagnostic information and also allows you to avoid repeated examinations. If clarification of the data from the primary study is still required, then it is advisable to take blood for analysis at the same time as the first time (this is due to individual time fluctuations in the human body).
1. Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC). – Medscape, Feb, 2014.
Important! All materials are for reference only and are in no way an alternative to face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
What does the analysis show and why is it prescribed?
The study is carried out to assess the functional and structural integrity of internal organs and systems of the human body. There are quite a lot of indications:
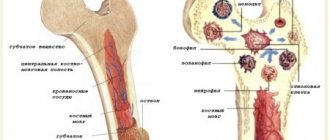
- Determination of bone marrow condition. It is the basis of hematopoiesis and is responsible for the synthesis and maturation of all formed cells. Including platelets. They develop from the same type of immature structures. Differentiation occurs here. Therefore, bone marrow examination is an informative method for diagnosing all disorders of the hematopoietic system.
Suspicious symptoms may prompt a doctor to think about a possible pathology. Whether it is low coagulability, excessive blood viscosity or spontaneous appearance of bruises, hematomas on the body. For no clear reason.
- Diagnosis and confirmation (verification) of more serious bone marrow pathologies. For example, malignant myeloproliferative processes. A special case, but fundamentally different from what is described above. These hematological disorders are deadly and without timely detection and treatment, quickly lead to critical complications. Suspicion is sufficient to order a study of average platelet volume.
- Anemia. Especially when the diagnosis is confirmed. The task is to assess the degree of dysfunction of formed cells. The pathological process does not always provoke such deviations. But over a long period of time this is possible and even probable. It makes sense to undergo a laboratory examination for preventive purposes.
- History of diabetes mellitus. Complex endocrine disease. Provokes coagulation disorders. Not to the same extent as coagulopathies, but dangerous complications are still possible. Especially if the pathology is decompensated, the patient does not receive treatment. This is a double risk.
Based on the results of a blood test, the doctor makes a conclusion about the properties of liquid connective tissue, the preservation of platelet shape and other factors. Endocrinologist patients with such a complex diagnosis need to be checked regularly. Donate blood at least once every six months. Possibly more often.
- Underwent surgery to remove the spleen. This organ plays an important role in storing (depositing) formed blood cells. It works as an auxiliary “base” for the accumulation of platelets; if necessary, they go into the mainstream and perform their functions.
Removing the spleen deprives the body of such a valuable component. Therefore, compensation will take time. During the rehabilitation period, the average platelet volume may change up or down. This is normal, the body adapts to changing new conditions.
At the end of the adaptation period, everything will be restored without medical help.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland. The same as with diabetes. The disease provokes hormonal imbalances. The formed elements of the blood are indirectly affected.
If the disease is not treated, it will inevitably cause critical illness. Normal hematopoiesis will stop, abnormal hematopoiesis will take its place, and immature cells will begin to circulate along the bloodstream. They are unable to perform the functions of platelets. This is fraught with ischemic processes throughout the body.
- The average volume is checked for smokers and alcohol drinkers. Both harmful habits early provoke hematopoietic disorders. Moreover, the more a person consumes alcohol and the more actively he “tars,” the faster destructive phenomena grow. A study of the indicator is necessary after the lifestyle has been changed. To evaluate the speed and quality of recovery.
- Inflammatory processes. We are talking not so much about the role of formed cells in such disorders, but about the influence of the change itself on cytological structures. For example, infectious diseases provoke a reduction in the number of healthy platelets, and so on. Such facts cannot be left without attention; special supportive treatment is needed.
What does the analysis show? Much. Doctors pay attention to points that are important for specific diagnostic purposes. In general, based on the results of the measures, we can talk about the size of platelets and their usefulness in terms of structure. Also about functionality. All deviations are interpreted as a probable pathology. Although there are exceptions.
It is not possible to say what caused the problem, however. Just state the fact. Further auxiliary diagnostics will be required. Without it, it will not be possible to determine what was the root cause of the violation.
Reasons for deviations
The mean platelet volume in the blood can be elevated for physiological and pathological reasons. In the second case, this condition requires treatment. In the initial stages, it is often enough to change habits and lifestyle, to maintain health using traditional medicine. And as the disease progresses, drug therapy will be needed.
Platelets promote blood clotting
When is an increase in mean platelet volume normal?
Platelets play an important role: they promote blood clotting, prevent significant blood loss, and thanks to them, tissue healing occurs faster. Therefore, in some cases, an increase in the average volume is justified and is positive, indicating the proper functioning of the hematopoietic organs.
In what cases is an increase normal?
- In newborns due to the immaturity of the hematopoietic organs.
- After injuries or surgical interventions accompanied by large loss of blood.
- During menstruation in women, especially with heavy discharge accompanied by anemia.
- After treatment that stimulates hematopoiesis.
- After bleeding.
The increase in the volume of blood cells in these cases is due to the desire to restore blood loss and is compensatory in nature.
When is an increase in platelet volume a reason to think about it?
Often, platelet levels increase due to various diseases that require treatment. This happens in the following cases:
- Thromocytopenia.
- Enlarged spleen, hypersplenism.
- Blood diseases in which there is an increase in myeloproliferative processes.
- Diabetes.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Macrocytic degeneration of Bernard-Soulier platelets. With this pathology, mature platelets have irregular sizes and shapes.
- May-Hegglin anomaly, in which the platelet count is reduced and the cells are defective.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Alcohol abuse.
Frequent alcohol consumption may increase blood platelet levels
Important! A slight increase in platelets is possible in acute respiratory diseases. This is normal, after recovery everything will go back to normal
But only a doctor can judge the presence of pathology after additional research and examination. Most often, a repeat analysis is prescribed. This comprehensive approach allows us to establish the cause of the increase in blood cell volume and make the correct diagnosis.
In this video: Lisitskaya Ksenia Valerievna - Head. laboratory of pathomorphological diagnostics of the veterinary clinic “Biocontrol”, histologist, cytologist, hematologist, will talk about platelets and their quantitative changes.
Program of this video course:
- 1. Platelets and their quantitative changes in the blood.
- 2. Types and principles of operation of modern hematological analyzers.
- 3. What is included in a typical clinical blood test form? Indicators and their value.
- 4. Red blood cells - functions, morphological changes and their significance.
- 5. Reticulocytes and regenerative anemias.
- 6. Non-regenerative anemia and why a patient’s bone marrow analysis is needed.
- 7. Leukocytes in the blood - types, function and morphology.
- 8. Morphological changes in leukocytes in the blood and their significance.
- 9. Main types of leukograms.
- 10. To summarize: how I personally analyze hemograms.
What to do if the MVP level is increased?
A thrombus, circulating with blood throughout the body, can enter a vessel of the heart or brain.
An increase in MVP production indicates that more cells are being produced than required.
Due to this, the consistency of the blood increases and the concentration becomes thicker. This disease is called thrombocytosis.
Thrombocytosis is dangerous because in excess blood clots begin to be created, which, reaching impressive sizes, can block the vessel and limit the blood supply.
Fatal outcomes are quite possible. Subsequently, it leads to heart attack and stroke, after which a third of sick people die.
Thrombocytosis is of two types:
- Relative – the norm is not significantly exceeded (from 20 to 30%)
- Critical - the norm is exceeded by 3-5 times.
In a critical case, urgent medical intervention is required!
An increase in MVP indicators is possible in two options:
- Certain physiological states of the body,
- Development of pathologies.
Physiological condition includes:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Certain medications
- Features of the child's body,
- Various types of bleeding.
The development of such pathologies affects the increase in MVP:
- Injuries (mostly in large numbers),
- Surgical interventions
- Various types of bleeding.
The main reasons for increasing MVP are some diseases:
- Alcoholism,
- Atherosclerosis,
- Diabetes
- Deterioration of the thyroid gland,
- Blood cancer,
- and others.
A peculiarity in pregnant women is a frequent increase in platelets, which in the vast majority of cases is as it should be. Since the body of the expectant mother changes and adapts to more comfortable conditions for gestation. This can be explained by the fact that the fetus needs its own circulatory system. It is for this purpose that a woman’s circulatory system produces more platelets.
Platelets are very sensitive
Blood platelets are very sensitive to changes in external conditions (atmospheric pressure, weather) and the state of the body, so their average volume can be increased or decreased not due to disease, but due to certain circumstances. This should not be forgotten when going to the laboratory. Therefore, you should not just drop in and donate blood, but prepare properly:
- Do not drink, eat or smoke in the morning;
- Avoid heavy physical work and mental stress the day before;
- Avoid taking various medications (you can take them after the test);
- If an R-graphy is prescribed on the day of testing, then it is better to reschedule it and do it later, and the same should be done with physiotherapeutic treatment.
For example:
- In children of the younger age group, MPV sometimes leaves the normal range due to the fact that the hematopoietic system has not yet completed its development;
- Deviations from the norm may be the result of surgical operations, injuries or acute blood loss;
- The average platelet volume may leave the normal range in women before and/or after menstruation.
All this can be explained simply: the body turns on compensatory mechanisms, active production of new blood platelets begins in the bone marrow, and young, large platelets appear in the bloodstream.
Where is there such an indicator as MPV. If in a general blood test this indicator is indicated with an error, taking into account only the total number of platelet cells, then in a detailed analysis MPV is determined by a separate item. What this indicator says and what its normal values are for different categories of the population, we will analyze further.
MPV in a blood test involves an indicator such as the average platelet volume. It differs from the total number of platelets in the blood in that it has not only quantitative, but also qualitative characteristics. The fact is that platelets are lamellar, anucleate cells that are synthesized by bone marrow cells, after which their life expectancy does not exceed 7 days. During this time, they go through the full development cycle of any living organism: from origin to extinction. During this time, the functionality of the cells is not the same. Young cells have a spherical and round shape, as well as large sizes. If necessary, activation of their receptors located on the cell membrane occurs in a split second. More mature cells are less active, but also carry a biological load
In this regard, MPV analysis allows you to determine the average platelet count, which is important when studying many diseases
The importance of this analysis lies in the biological functions of platelets. If their synthesis is slowed down or accelerated, in which a deviation from the norm is noted, this indicates problems with hematopoietic function, as well as pathologies of organs, which should be treated immediately
Platelets perform three essential functions for the body:
- They prevent the development of extensive blood loss when the integrity of the vessels is violated - their ability to stick together and attach to the surface of the vascular walls protects the body from premature death.
- Capable of enhancing the synthesis of collagen cells, which are involved in the process of regeneration of damage to the integrity of the vessel.
- Strengthen cell membranes, preventing viruses, fungi and bacteria from penetrating them.
As you can see, the functions of platelets are quite important for maintaining the normal functioning of the body, so this analysis is recommended to be performed at least once a year for adults and at least twice a year for children.
What to do if platelets have dropped?
With low MVP, thrombocytopenia actively develops.
If the indicators keep the bar below normal, then the histogram shows a low number of working cells, while there are many old and newly appeared ones.
Aging cells cannot perform their functions at full capacity and do not carry a biological load, but those created are not yet ready for this.
The disease is especially in that with a sufficient number of platelets, their quality can contribute to the development of pathologies.
There are three types of thrombocytopenia:
- The bone marrow reduces the synthesis of newly appeared cells. This may be a consequence of chronic alcoholism and problems with the liver or spleen.
- Increased platelet death indicates diseases of the spleen and liver, and also as a result of autoimmune diseases.
- Imbalance of platelet mass during distribution - many platelets are stored in the spleen, when they are not in demand.
It is difficult to detect thrombocytopenia in the early stages, due to the fact that external symptoms do not appear. But when tested for MVP, this disease can be detected.
At later stages, the manifestations of external symptoms of the disease begin:
- Nose and gums bleed
- Callos and urine contain blood,
- Vomiting blood
- Longer and more unpleasant menstruation in women,
- Hemorrhages under the skin, with a significant area.
Low platelet levels also occur for the following reasons:
- Blood diseases (congenital),
- Oncology,
- Viruses and microbes in the body.
Reduced MVP may indicate the following diseases:
- Enlarged spleen
- Heart attack
- Some medications
- Inflammatory diseases
- Oncology,
- and others.
If the platelet count decreases in pregnant women, there is a possibility of miscarriage.
During pregnancy, the number of these cells in the blood should be monitored more frequently and more carefully.
How to keep your MVP metrics healthy?
To maintain the average volume and MVP within normal limits, it is necessary to do prevention, which consists of the following actions:
- Take a clinical blood test with MVP indicators at least once every three months,
- Carefully select medications during treatment. Some drugs have a negative effect on platelet function,
- Bring your diet back to normal. Reduce the amount of fatty foods, and instead of fatty meat, it is recommended to use fish, turkey or rabbit meat,
- Drink enough water.
Following all these recommendations, you should consult a doctor if:
- Sudden weight loss
- Constant fatigue, drowsiness,
- Changes in skin tones
- Nosebleeds,
- A sharp decline in health
- Tachycardia.
Treatment in the early stages is much easier and cheaper!