28.06.2017
Last modified: July 1, 2021 at 11:26 pm
High blood pressure after eating is an important symptom that needs to be taken seriously. Indicators above normal may be the first prerequisite for an imminent hypertensive crisis. An incorrectly selected diet only makes the situation worse.
Why does blood pressure rise after eating? What products are allowed and prohibited? Only current information for reference.
General facts about blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the force of blood flow pressure on the walls of the circulatory system. The indicator determines the volume of blood that passes through the vessels, the speed of its movement, viscosity and accompanying conditions of the body.
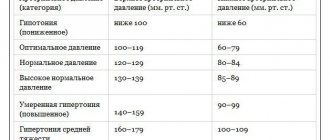
For reference! The average blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. Art. An increased number indicates the beginning of the development of hypertension.
Blood pressure may fluctuate throughout the day.
Reasons for this:
- being in a state of sleep and wakefulness;
- physical exercise;
- overvoltage;
- sexual arousal;
- acts of defecation.
One of the other factors that increases blood pressure is eating fatty or heavy foods.
Content:
- Clinical signs of low glucose levels
- Causes of low blood sugar
- Hypoglycemia in newborns
- Hypoglycemia in a healthy person
Hypoglycemia - low blood sugar. Symptoms develop gradually, over 20-60 minutes. It occurs mainly in people suffering from type I diabetes mellitus (insulin dependent) when the rules of replacement therapy are violated. Sometimes occurs in pregnant women or newborn children. The minimum acceptable blood glucose level is 3.3 mmol/l. With decompensated diabetes, symptoms of a drop in blood sugar in a person occur already at 4.5 mmol/l. In the most severe cases, hypoglycemia can occur at 6-7 mmol/l.
Food and Performance: Explanation of Impact
The intake of certain foods leads to imbalances in systolic (upper) and diastolic (lower) pressure. These indicators characterize the movement of blood through the vessels. When you abuse prohibited foods, the load on the blood system and heart function increases (the balance of indicators is disturbed) and the person suffers from the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the back of the head;
- sensation of tinnitus;
- pulse quickens;
- profuse sweating;
- shortness of breath and nausea.
After food enters the body, the digestion process begins. In this case, significant energy reserves are spent on the production of acids and enzymes (enzymes). For the process to proceed normally, oxygen is needed, which enriches the blood and accelerates its movement through the veins. A signal is sent from the brain to the heart to begin more intensive work. The speed of blood flow is affected by the fluid in the blood (the thicker it is, the slower the movement).
Note! Eating foods that contain a high percentage of sugar, fat, and sodium leads to slower blood flow and increased workload.
Are there other reasons?
An increase in blood pressure after eating also occurs due to the high content of waste and toxins. These wastes remain from the processing of difficult-to-digest and unhealthy food (they are not promptly removed from the body during the act of defecation).
Important information: Hypertensive patients and pregnant women should not drink: the main harm of mineral water has been identified
A slight increase in blood pressure after eating certain foods is a natural process. If the indicator does not normalize (or remains high even on a diet), this is a reason for urgent consultation with a specialist.
Treatment of tachycardia
In the case when tachycardia occurs once and quickly stops on its own, this should not be a cause for concern. But if this symptom appears constantly, then you need to consult a cardiologist. It should be remembered that tachycardia can be a symptom of both a functional disorder of the nervous system and a serious heart disease.
Depending on the indications, cardiologists at the CELT clinic conduct examinations to identify the cause of the patient’s tachycardia:
- ECG;
- Holter ECG monitoring;
- Stress test;
- Transesophageal ECG and atrial stimulation;
- EchoCG;
- Study of sugar metabolism disorders;
- Tests for the activity of thyroid hormones.
Having determined the cause of the increased heart rate, the doctor will be able to choose the optimal treatment regimen for the underlying disease.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What products are prohibited
Does your blood pressure rise after eating? The reason for this is forbidden, harmful and unhealthy foods.
- Spicy foods. Doctors categorically do not recommend eating dishes with pepper, contrary to popular belief about their usefulness and vasodilating effect.
- An abundance of salt - slows down water circulation, increases the amount of blood and increases the intensity of heart contractions.
- Caffeine (hot chocolate, tea, coffee). Even green tea contains small amounts of caffeine. Replace the listed drinks with purified water.
- Raw beets. Eat in limited quantities.
- Abuse of sugar and yeast products. These include ice cream, baked goods, cheesecakes, and cakes with butter cream. Eating sweets affects blood thickness.
- Alcoholic drinks. Under the influence of alcohol, blood vessels expand and quickly narrow, the blood becomes more viscous.
For reference! Blood pressure may also rise due to eating salted fish, smoked lard, pickled mushrooms and cucumbers, sauerkraut, black olives.
Revealing the mechanism of manifestations
If your blood pressure rises after eating, this is one of the signs of gastrocardial syndrome. Associated symptoms for diagnosis:
- heartbeat may increase;
- the appearance of pain in the area of the heart muscle;
- dizziness.
Symptoms disappear after belching or vomiting. The syndrome is dangerous due to the similarity of symptoms with heart diseases. Against the background of pathology, other ailments are hidden (difficult to identify without differential diagnosis).
For reference! If your blood pressure rises and chest discomfort persists for several hours after eating, there is a high risk of developing angina.
Other increasing factors include improper functioning of the renal system. The kidneys cannot cope with the load, the volume of fluid increases, and the pressure on the walls of blood vessels increases. The cardiovascular system begins to work more intensely, and the pressure becomes higher.
Important information: Who is most at risk for preeclampsia?
Who to turn to for help
If over the past few days the pressure has risen to a critical level (above 180 mm Hg), and at the same time a person suffers from dizziness, nausea, blurred vision, chest pain - these are the first signs of a hypertensive crisis. This condition is very dangerous and requires urgent help.
The patient needs to see a physician to measure blood pressure and collect anamnesis. This specialist also prescribes a number of tests (blood and urine tests). In addition, you need to visit a cardiologist and neurologist. These are highly specialized professionals who conduct detailed diagnostics (interpretation of ECG data, assessment of blood vessels).
To summarize: all safety measures
A regular increase in heart rate and increase in blood pressure after eating puts a person at risk. People in this category should monitor their daily diet and completely eliminate dry snacks, late-night dinners, and overeating.
Actions to prevent blood pressure from rising due to food.
- Diet variety with fiber - carrots, cabbage, bran, fresh peas. These products retain liquid in the fibers and speed up digestion.
- Rational consumption and gradual reduction in the amount of coffee, tea, alcohol, tobacco.
- Saturating the body with foods to normalize blood pressure - spinach, potatoes, nuts, pumpkin.
- Maintaining fluid balance. Drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day.
Why blood pressure rises depends on food intake and the condition of the internal organs. Don’t turn a blind eye to the problem and don’t attribute constant increases in blood pressure to overwork. A mandatory action in such a situation is to attend a consultation with a therapist or cardiac surgeon and obtain treatment prescriptions.
32nd city clinical clinic
Rehabilitation reminder after COVID-19
Memo on self-rehabilitation for patients who have suffered from covid-19
- How to eat after a coronavirus infection.
Meals should be regular, without long “hungry” intervals. It is advisable to divide meals into 4–5 times. The energy value for practically healthy individuals is 1500-1800 kcal per day. With four meals a day, the number of calories per day is distributed as follows: 25% - first breakfast; 15% – second breakfast or afternoon snack; 35% – lunch; 25% – dinner. Limit salt to 5 g/day
The diet should contain: Potassium, magnesium, zinc: cereals, jacket potatoes, green peas and beans, carrots, pumpkin, beets, peppers, cabbage, cucumber, avocado, fresh milk and meat, buckwheat, millet, beans, carrots, spinach , potato. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids : Marine fish such as halibut, salmon, herring, tuna, mackerel and sardines, as well as flaxseed oil, are high in Omega-3 acids, which have a beneficial effect on the immune system. 1-7 grams of Omega-3 fatty acids are needed per day for the normal functioning of the body. Phospholipids : The daily requirement for phospholipids is approximately 5 g. Chicken eggs contain 3.4%, unrefined vegetable oils - 1-2%, butter - 0.3-0.4%.
The loss of the ability to distinguish tastes and smells makes all dishes tasteless, and the process of eating becomes boring and uninteresting. Because of this, a person does not want to eat. To help improve nutrition, you can experiment with the texture of food, spices and aromatic herbs, the appearance and method of serving the dish, and also try to eat slowly and carefully, “with taste.” Options for changing food texture:
- dishes made from products of different consistencies (for example, omelette with vegetables); Steam vegetables to keep them crispy;
- use chopped nuts and dried fruits as filling;
- dried bread and toast.
- Breathing exercises and exercises
II period . For 3-4 weeks after the disappearance of acute symptoms (the first period) and then daily, subject to the restoration of respiratory function and well-being, perform exercises ONLY in a sitting position with your back tightly pressed to the back of the chair and a tense abdominal wall (stomach retracted):
| II period. I.p. - sitting on a chair | ||
| Sitting on a chair (as if on a horse), clasping your arms and pressing your chest to the back of the chair The abdomen is tense, the diaphragm is pulled inward and upward CONSTANTLY! Monitor your heart rate – it should not increase by more than 10-12 beats/min. | Exhale in 4 counts , while pressing your chest against the back of the chair and helping yourself with your hands, grasping the back of the chair, relax slowly, shallowly inhaling “to half-inhale” | 6-8 times, rest interval between repetitions 30′ |
| Sitting with your back resting on the back of a chair, The stomach is pulled in, hands are on hips, legs are relaxed. Breathing is free, not forced. INHALE is not full | Perform 4 counts of simultaneously bringing your shoulders forward (slouch) – inhale, straightening your back for 4 counts, relax, bend slightly - exhale. THE STOMACH is tense and retracted | 4-6 times, rest interval between repetitions 30′, or as you feel |
| Sitting with your back resting on the back of a chair, The stomach is pulled in, the arms hang freely, the legs are relaxed. Breathing is free, not forced. INHALE is not full | Inhale in 4 counts , while clasping yourself with your arms crossed over your chest; relax your grip - breathe out calmly | 4-6 times, rest interval between repetitions 30′, or as you feel |
| Sitting with your back resting on the back of a chair, The stomach is pulled in, the arms are clasped around the chest in the diaphragm area, the legs are relaxed. Breathing is free, not forced. INHALE is not full | On a count of 1-2, move your right arm to the side and back, grab yourself by the chest with your left - inhale. Return to I.p. - exhale freely. Repeat also with your left hand to the left. | 4-6 times, rest interval between repetitions 30", or as you feel |
| Sitting with your back resting on the back of a chair, The stomach is pulled in, the arms are bent and pressed to the chest, the forearms are parallel, the hands are in a fist under the chin, the legs are relaxed. Breathing is free, not forced. INHALE is not full | Perform for 1 count - jerky exhalation through the mouth, pulling the diaphragm inward and upward, straining the stomach and pressing the arms to the chest. Relax, breathe freely and shallowly. | 6-8 times, rest interval between repetitions 30", or as you feel |
| Sitting on a chair. Hold the seat with your hands. Legs free. | Perform bending for 2 counts, bringing the shoulder blades together - shallowly , bend your torso forward, slightly rounding your back, exhale. | 4-6 times, rest interval between repetitions 30", or as you feel |
III period . For 4 or more weeks (if there is no deterioration in well-being after exercise, the pulse rate and breathing are uniform), it is possible to use the initial position lying on your back, standing with support, standing and walking.
- Regardless of the period. The pace of the exercises is slow, medium.
- In all exercises, a superficial (shallow) inhalation is performed through the nose, and exhalation through the mouth.
| 3. III period. Starting position (hereinafter referred to as i.p.). - lying on your back; kneeling with emphasis on hands; standing with support; standing; while walking | ||
| Lying on your back, arms along your body, legs free | Take a light, normal breath in 2 counts, close your lips and slowly exhale as if you were blowing out a candle. The stomach should retract as much as possible. | 4-6 times, do not force breathing - do not make you dizzy |
| Lying on your back, arms to the sides, legs free | On the count of 1.2, spread your arms to the sides - inhale, “hug yourself by the shoulders” - exhale on 5,6,7,8. | 6-8 times, rest interval between repetitions 10-15", or as you feel |
| Lying on your back, arms along your body, legs apart | Perform simultaneous clenching of the hand into a fist and flexion-extension of the ankle joints. Breathing freely | 10-12 reps |
| Lying on your back, arms along the body, hands “locked”, legs apart | At 1.2 - simultaneously raise your arms up - inhale, at 3.4 return to I.p. -exhalation | 6-8 times |
| Lying on your back, arms along your body, legs bent, feet flat on the floor | Perform: on 1, 2, simultaneous extension of the arms to the sides, bending the legs at the hip joints, pressing the thighs to the chest - exhale. On 3, 4 - return to I.p. – relax while exhaling. | 4-6 times, rest interval between repetitions 30", or as you feel |
| Kneeling with emphasis on hands | Breathe with your stomach, protruding it as you inhale and relaxing it (pulling in your stomach) as you exhale. Breathing is calm, without tension, | 3-6 reps. |
| Walking in place | Perform steps combined with breathing. For steps 1-4, smooth continuous inhalation, for steps 5-8 - smooth, slow exhalation. | Within 1 – 1.5 minutes |
| Walking in place | Take a shallow breath in steps 1 and 2; Steps 3 and 4 – holding your breath while inhaling; Steps 5 and 6 – exhale; Steps 7 and 8 – hold your breath as you exhale. | Within 1 – 1.5 minutes |
Measured walking: start at a slow pace with 30-40 steps per minute, at a gradually increasing pace - 60-80-100 steps per minute. Be sure to monitor your heart rate (count your pulse) at least 3 times: at the beginning, middle and at the end of the lesson. The pulse after exercise should return to its original values.
- Balance training exercises prevent falls, which often lead to disability. Balance training involves shifting the center of gravity when performing exercises in an unstable position. A simple exercise to improve your balance is to stand on one leg. To do this, you need to stand up with your legs closed together - you can hold on to a chair or wall. You can then raise one knee, stand there for 30 seconds, and then change legs. If you stand firmly on your feet and easily perform all the exercises, proceed to perform them with your eyes closed. An effective exercise for training coordination is to imitate walking on a tightrope (to do this, just place the “rope” on the floor and slowly walk forward across the room, placing one foot directly in front of the other. Squats and lunges forward alternately on each leg also work well.
It is worth remembering the safety rules: if you are just starting to practice, use the back of a chair or table for support, and also ask someone to stand next to you for protection.
- How to control the load of physical activity yourself?
Speaking test:
Very high: only one or a few words can be spoken during exercise.
Optimal: You can say 2 sentences of 5 words without shortness of breath.
Low: more than 2 sentences of more than 5 words can be spoken.
- Psychotherapy
If alarming symptoms occur (prolonged depressed mood; things that used to lift your spirits are no longer satisfying; feelings of indecision persist for a long time; sleep disturbance; decreased concentration, etc.), you should consult your doctor for help. In order for the doctor It was easier to understand your emotional state and well-being on your own at home, you can take a test that will help you assume that you have this disease. (HADS scale is attached; telephone numbers where you can contact for help are included).
- How to evaluate the effectiveness of the body's recovery?
To independently assess the effectiveness of recovery, it is advisable to use mobile applications or a fitness tracker, which allow you to measure the distance traveled, heart rate, blood pressure, sleep quality, and keep a diary, where saturation and sleep quality, and a decrease in shortness of breath are taken into account as parameters for daily monitoring.
Self-monitoring diary for a patient who has had COVID -19
| 1st week after discharge | 2nd week after discharge | 3rd week after discharge | 4th week after discharge | 5th week after discharge | 6th week after discharge | ||||||
| Arterial pressure (Normal 110-139 systolic, 60-89) | |||||||||||
| Heart rate (Norm 60-90) | |||||||||||
| Load per day (steps or meters) | |||||||||||
| Cognitive functions (has memory, attention improved) | |||||||||||
| Sleep (duration, quality, were there any awakenings) | |||||||||||
| Nutrition (amount of protein consumed) | |||||||||||
| Shortness of breath at rest, with minimal movements, with exertion) | |||||||||||
*evaluation of indicators 2 times a week
Psychotherapy rooms at clinics in Minsk
| Urban Borderline Center | 351-61-74 | st. Mendeleeva, 4 Mon.-Fri. from 8.00 to 15.00 (1st shift) from 13.00 to 20.00 (2nd shift) |
| 3rd central district clinical clinic | 395-73-48 | st. Voronyanskogo 13/2 |
| 4th city clinic | 369-64-45 | Mikula A. (registration for the clinic’s service area) Mon., Wed. 8.00 -15.00 Tue., Thu. 13.00 - 20.00 Fri. 10.00 – 17.00 Pobediteley Ave., 93 |
| 5th city clinical clinic | 376-19-65 | st. Yesenina, 21 |
| 8th city clinic | 268-13-19 (helpline) | around the clock st. Nikiforova, 3 |
| 10th city clinic | 374-37-08 | st. Sukharevskaya, 19 |
| 11th city clinic | 328-34-13 | st. Velikomorskaya, 36 |
| 12th city clinic | 396-79-47 | st. Olshevsky, 61 |
| 17th city clinical clinic | 297-49-39 | st. Gerasimenko, 49. Psychologist's work schedule Mon., Wed., Fri.: 8.00-16.30, break 12.00-12.30 |
| 19th central district clinic | 268-86-90 | Independence Avenue, 119 |
| 21st central district clinic | 295-02-38 | st. Filatova, 13 |
| 26th city clinic | 380-32-40 | st. Kuntsevshchina, 8 |
| 28th city clinic | 286-44-12 | st. Gintovta, 28 |
| 30th city clinical clinic | 380-09-55 | st. Koltsova, 53/2 |
| 32nd city clinical clinic | 277-04-90 | Golubeva st., 25 |
| 33rd city student clinic | 331 29-19 | st. Surganova, 45/4 |
| 34th central district clinical clinic | 237-31-39 | st. Kulman, 22 |
| 35th city clinical clinic | 324-96-33 | st. Serova, 15 |
| 36th city clinic | 344-38-09 | st. Bachilo, 9 |
| 37th city clinic | 298-79-90 | st. Ya. Luchiny, 28 |
| 39th city clinical clinic | 374-39-84 | st. Karolinska, 3 |
| 40th city clinical clinic | 317-98-70 | st. Lyutsinskaya, 3 |