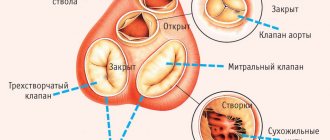
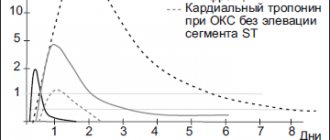
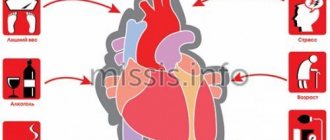
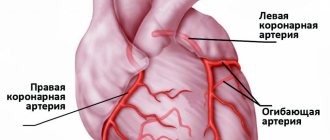
General information
As statistical studies show, myocardial infarction most often develops in men aged 40 to 60 years. In women, this disease occurs approximately one and a half to two times less often.
Myocardial infarction occurs in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD), atherosclerosis, and arterial hypertension. Risk factors for the development of myocardial infarction include smoking (as it causes a narrowing of the coronary vessels of the heart and reduces the blood supply to the heart muscle), obesity, and lack of physical activity.
At the same time, myocardial infarction may be the first manifestation of IHD.
Unfortunately, myocardial infarction is now one of the main causes of disability in adulthood, and the mortality rate among all patients is 10-12%.
Causes of myocardial infarction
Oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the cells of the heart muscle by a special branched network of vessels called coronary vessels. During myocardial infarction, one of these vessels is blocked by a thrombus (in 95% of cases, a coronary artery thrombus forms in the area of an atherosclerotic plaque). The supply of oxygen to the heart muscle cells fed by the blocked artery will last for 10 seconds. The heart muscle remains viable for about 30 minutes. Then the process of irreversible changes in the cells begins and by the third to sixth hour from the onset of occlusion, the heart muscle in this area dies. Depending on the size of the dead area, large and small focal infarctions are distinguished. If necrosis involves the entire thickness of the myocardium, it is called transmural.
The clinical picture of myocardial infarction is varied, which makes it difficult to make the correct diagnosis as quickly as possible. The diagnosis is made based on three criteria:
- typical pain syndrome
- changes on the electrocardiogram
- changes in biochemical blood test indicators, indicating damage to heart muscle cells.
In doubtful cases, doctors use additional studies, for example, radioisotope methods to identify the focus of myocardial necrosis.
3.Bypass surgery
If for some reason angioplasty cannot be done, emergency coronary artery bypass grafting
. Sometimes bypass surgery is preferred because of the specific location of the artery blockage or multiple blockages.
After a heart attack
the patient needs to stay in the hospital for at least a few more days. All this time, doctors will closely monitor your health. Checking your pulse, heart rhythms, blood pressure, and your body's response to medications will help ensure that your heart attack is not serious.
Your doctor will likely recommend that you take medications that reduce the risk of another heart attack or complications. Ultimately, they will help maintain health and prolong life after a heart attack. These medications may include angiotensin-converting enzymes, aspirin, antiplatelet medications, beta blockers, and statins.
These medications will need to be taken over time. And perhaps throughout life. You should not violate the dosage regimen recommended by your doctor or decide to stop treatment on your own, even if you feel well. All this increases the likelihood of recurrent myocardial infarction.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Symptoms
Typically, myocardial infarction shows the following signs:
- prolonged intense squeezing-pressing pain behind the sternum in the heart area, which can radiate to the arm, neck, back or shoulder blade area;
- pain does not go away after taking nitroglycerin;
- pale skin, cold sweat;
- fainting state.
The disease does not always manifest itself in such a classic picture. A person may only feel discomfort in the chest or interruptions in the functioning of the heart. In some cases there is no pain at all. In addition, there are atypical cases of myocardial infarction, when the disease manifests itself as difficulty breathing with shortness of breath or abdominal pain. Such cases are especially difficult to diagnose.
Diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition in Medical
When should you see a doctor?
A person needs to consult a cardiologist if symptoms of a cardiovascular system pathology appear (chest pain, dizziness, cough, shortness of breath, bluish skin, etc.). You should not self-medicate. Numerous methods of traditional medicine are permissible for use only after the doctor’s permission and after treatment of the acute period of the disease.
Drug treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition
Patients in a pre-infarction state are prescribed drugs that improve blood supply to the heart muscle, anti-atherosclerotic agents, and vitamin-mineral complexes.
In the acute period of a heart attack, analgesics, anticoagulants (prevent blood clotting) and thrombolytics (dissolve an already formed blood clot) are indicated.
Surgery
It is possible to more effectively restore blood supply to the myocardium through surgical intervention, which must be carried out in the first hours of a heart attack, then the chances of successful healing are greatest.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
The method of operation is to create a bypass route for blood supply to the affected area of the myocardium. The aorta and coronary vessel beyond the blockage are connected using a section of vein taken from the patient's lower leg.
Coronary artery angioplasty
Narrowing of the artery can be relieved by inserting an instrument that widens the artery through the femoral vein. Next, a stent is installed, which fixes the shape of the vessel, preventing its narrowing and restoring blood flow.
What can a doctor do in case of myocardial infarction?
To avoid mistakes, at the slightest suspicion of a heart attack, the patient is taken to the hospital as soon as possible. Treatment of myocardial infarction must be carried out in the intensive care unit of the hospital.
Therapy includes painkillers, drugs that help dissolve the formed blood clot, drugs that lower blood pressure, reduce the volume of circulating blood, and reduce the heart rate. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the time elapsed from the onset of the disease to hospital admission.
After hospitalization, an unusually important period of rehabilitation begins, which lasts up to 6 months. The doctor will prescribe the necessary therapy for you. Some medications you will have to take for the rest of your life. However, if you follow the instructions, stop smoking and follow a diet, people after myocardial infarction live full healthy lives for many years.
Life after a heart attack
Currently, coronary insufficiency and myocardial infarction are one of the main causes of death and disability among the population of most industrialized countries. According to WHO experts, mortality from cardiovascular diseases will steadily increase in the coming decades. In Belarus, the situation with cardiovascular diseases in general and myocardial infarction in particular is also alarming.
More than 4,000 cases of this disease are registered annually in Minsk alone, of which up to 25% are people of working age. According to the City Cardiology Center, 90% of patients of working age, as a rule, return to work, of which 35% are fully employed and in their previous profession.
This means that a heart attack in itself is not a death sentence, and life continues after it, but it makes adjustments to the patient’s thinking, his lifestyle, his attitude towards himself and others.
WHAT IS A MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION?
WHAT PSYCHOLOGICAL PROBLEMS DO THE PATIENT ARISE?
AND HOW TO OVERCOME THEM
Myocardial infarction is the acute and most severe form of coronary heart disease, in which a section of the heart muscle dies as a result of blockage of the coronary artery that supplies it with blood.
Myocardial infarction itself is a severe stress for the patient. He is instilled with constant fear of a possible recurrence of a heart attack.
The patient is constantly harassed by:
Internal tension— concern for the outcome of the disease, for the well-being of the family, for work, for the future prognosis. In this case, you need to contact a psychotherapist or a psychologist , who will help you calm down and calm your worried relatives.
Fear of developing a recurrent myocardial infarction and sudden death “from a heart attack.” Anxiety increases with physical stress, leaving the house, or moving away from a place where medical care can be provided. Such patients should walk gradually, increasing their mileage daily, go out with an escort in the first days, and have nitroglycerin with them.
Unjustified concern for your health . Patients often and without reason count their pulse, measure their blood pressure, and visit various specialists. In such a situation, you need to talk with your doctor, psychologist, psychotherapist, and switch your attention to other events in life in order to divert attention from unreasonable fears.
Psychasthenia syndrome - a person is overcome by general weakness, a feeling of constant fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbance, decreased performance . There may be a depressed mood, apathy, a feeling of hopelessness, tearfulness - depression syndrome . In these cases, it is necessary to consult a psychotherapist. The patient must be explained that a heart attack is not a death sentence.
Not often, but there are also cases of “disease denial,” when the patient refuses to believe that he has a serious illness and ignores the doctor’s recommendations. It should be remembered that for a patient who has suffered a myocardial infarction, both overestimation of the severity of his condition and its underestimation are equally dangerous.
METHODS OF REHABILITATION OF THE PATIENT
Currently available methods of rehabilitation (restorative treatment) of patients after myocardial infarction can be combined into two groups: non-pharmacological and medicinal.
Non-drug treatment methods involve, first of all, changes in lifestyle and lifestyle. This includes:
To give up smoking. Quitting smoking for two years reduces the risk of coronary death by 36%.
Normalization of body weight. To assess the correspondence between weight and height, the body mass index is used. In order to calculate your body mass index (BMI), you need to divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters, squared, according to the formula:
BMI= weight (kg)/height (m²)
Normal index values are 20-25 kg/m². An increase in the index to 25-30 kg/m² indicates the presence of excess body weight, more than 30 kg/m² - obesity.
Changing the nature of nutrition. The main goal of the diet is to reduce cholesterol and other atherogenic blood lipids while maintaining the physiological completeness of the diet.
It is necessary to give preference to a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, with sufficient amounts of vegetables, fruits, and grain products that will provide the body with essential vitamins, minerals, fiber (fiber) and complex carbohydrates. This includes :
Regular consumption of a variety of vegetables and fruits - at least 400 g.
Moderate consumption of dairy products - (0.5-1% fat content) milk, low (20%) fat cheeses, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurts, buttermilk.
Give preference to fish , including fatty fish (cod, haddock, flounder, herring, sardine, tuna, salmon). Fish should be present in the diet at least 2-3 times a week.
From meat products, choose meat without streaks of fat: turkey, chicken, veal, game, rabbit, young lamb.
Consume no more than 2-3 eggs per week . Limit your consumption of yolks.
Recommended drinks : tea, black coffee, water, sugar-free soft drinks.
Consume sugar only in moderation, table salt - less than 5 grams per day.
Limit (it is better to completely refuse) the consumption of alcoholic beverages - less than 30 grams of pure alcohol for men and 20 grams for women per day.
A balanced diet should be combined with systematic physical training . Under the influence of moderate-intensity physical training, there was a reduction in overall mortality by 23% and sudden death by 37% in patients who had previously suffered a myocardial infarction.
Physical activity also includes household activities : housekeeping, seasonal work in the garden or vegetable garden, walking up the stairs instead of using the elevator, walking to work and home, etc.
Before starting physical activity, you should talk to your doctor! We must always remember that along with the positive effect, inadequate physical activity can lead to the development of severe complications during the course of the disease .
It is impossible to give a single recommendation for all patients regarding the timing of the resumption of sexual activity . In the vast majority of cases, this is one to one and a half months from the date of the heart attack. But it is better to consult your doctor on this issue.
Know and control blood pressure. In a person who has had a myocardial infarction, it should be 120/80 mm. rt. Art.
Drug treatment of coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction includes:
The first and basic rule is to constantly take medications. “And the best medicine will not help the patient if he refuses to take it.” Cervantes (1547 - 1616).
The second rule is the rule of combination therapy.
Patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction are simultaneously prescribed several drugs with different mechanisms of action. At a minimum, they must take five medications, four of which (except the second - for life):
Acetylsalicylic acid helps reduce the formation of blood clots in the heart and blood vessels and is the basis for the prevention of arterial thrombosis. Regular use of acetylsalicylic acid reduces the risk of recurrent myocardial infarction by an average of 23%.
Clopidogrel - has an antiplatelet effect, like aspirin, and requires mandatory use for at least 12 months after myocardial infarction.
Statins are drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels, are safe for long-term use, are well tolerated by most patients, and reduce the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular complications.
Beta blockers interrupt the signals that the body sends to the heart during exercise and emotional stress, reduce the risk of sudden death, recurrent myocardial infarction, and increase the life expectancy of patients who have had a myocardial infarction
ACE inhibitors are drugs that prevent the development of heart failure, increase the duration and improve the quality of life of patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PATIENTS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
Changing your lifestyle means changing your previously established rules and habits.
Start your morning so that you have time to have a quiet breakfast and take your medications. Some medications (such as nitrates) should be taken 20-30 minutes before leaving home.
Leave the house early so that you can stand at the entrance for a few minutes, especially in the cold season.
Get rid of the habit of starting walking at a fast pace. Give your heart time to get used to, adapt to the given rhythm.
Give up the habit of rushing, running after departing transport as if it were the last bus (trolleybus) in your life.
Wherever you are (at home, at work, visiting, in the forest, at the dacha, etc.), you must have nitroglycerin (tablets, capsules, spray) with you.
If you leave home for any period, even for a short period of time, you need to have the necessary supply of the medications you take with you in order to feel safe and not create unnecessary problems for others.
It is advisable that in your purse (purse, car glove compartment, etc.) there is the latest electrocardiogram that you had at your doctor’s appointment. No one knows where you may need medical help, and then the old “film” will do a good service to your heart.
Remember! The most important rule for successful treatment and recovery after a heart attack is cooperation between the doctor and the patient.
Know! By following the recommendations outlined, you can live a long and quality life after a heart attack!
Author: Evtukh O.V. – head of outpatient
outpatient department of the GCC
Editor: Arsky Yu.M.
Computer layout and design: Zgirskaya I.A.
Responsible for the release: Tarashkevich I.I.
Health Committee of the Minsk City Executive Committee
Healthcare Institution “2nd City Clinical Hospital”
City Health Center
Minsk-2012
Preventive measures
Prevention of myocardial infarction is annual medical examination and timely adequate treatment of chronic diseases such as coronary heart disease, hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.
The diagnosis of coronary heart disease is the basis for assessing the condition of the coronary arteries using coronary angiography (coronary angiography). Specially taken X-rays allow you to determine the exact location of atherosclerotic plaques and the degree of narrowing of the coronary arteries. If indicated, the found narrowings can be expanded from inside the vessel - this procedure is called coronary angioplasty. In addition, a stent can be implanted into the coronary artery - a metal frame that will maintain the open state of the vessel. In some cases, a complex coronary artery bypass surgery is performed, when additional vessels are inserted between the aorta and the coronary arteries, going around the narrowing of the coronary vessel and creating the opportunity for blood to flow to the heart muscle.
Recovery period
The rehabilitation period is aimed at restoring lost functions and improving the quality of life of patients who have suffered a stroke. The doctor develops a rehabilitation program individually for each patient, taking into account the scale of the vascular accident, age, comorbid pathology, etc.
In case of strokes, doctors assign a special role to the prevention of recurrent strokes, which includes proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, eliminating excess weight, and regular monitoring by a doctor.
Is full recovery possible after a stroke?
The patient’s relatives play a significant role in the rehabilitation of a patient after a stroke. It depends on their attention, care, patience and correct actions whether the patient’s lost functions can return.
The recovery process after a stroke is a difficult period, both for the patient himself and for his loved ones. The rehabilitation time depends, first of all, on the degree of damage to brain tissue. Patients may have impaired coordination of movements, mobility of limbs, speech, memory, hearing, and vision.
The patient’s persistence and positive attitude can speed up the recovery time of lost functions.
An experienced team of doctors will speed up the rehabilitation process thanks to a well-designed individual treatment program.
Levels of recovery after stroke
After hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, there are three levels of recovery:
- the first is the highest. We are talking about the complete restoration of lost functions to their original state. This option is possible in the absence of complete death of nerve cells in a region of the brain;
- the second level is compensation. The early stage of recovery, usually in the first six months after a stroke. Lost functions are compensated by the involvement of new structures and functional restructuring.
- The third level involves readaptation, that is, adaptation to the emerging defect. The patient’s relatives and friends play a significant role in this process. They are the ones who help the patient learn to live with the emerging defect.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, if necessary, work with the patient’s relatives, teaching them the specifics of care, as well as providing them with psychological support.