Proper nutrition after a stroke
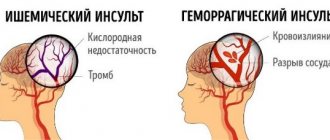
ACVA (acute cerebrovascular accident - stroke) is a pathological condition, in the treatment of which it is very important to undergo a competent rehabilitation process. Meanwhile, rehabilitation specialists are increasingly noting that the recovery of patients with this condition is complicated by an incorrectly selected diet or insufficient adherence to it. If there is a violation of the diet, the supply of nutrients in insufficient quantities greatly reduces the quality of rehabilitation and does not allow some body functions to return to normal. At the same time, the length of hospitalization, as well as the risks of mortality or complications, increase significantly.
In order for the restoration of functions lost due to a stroke to proceed faster, it is important to provide the patient with adequate care, especially in the first days, when the condition is most severe. During rehabilitation, a properly formulated diet plays a significant role so that the patient can receive all the necessary nutrients, vitamin and mineral components.
There is no special diet for people who have suffered a stroke; it is developed individually, based on the patient’s condition, age, general condition and ability to eat, chew and swallow. Some require the use of nutritional mixtures (in the acute period) with a gradual transition to regular food (as their condition improves and functions are restored), including at home under the supervision of caring relatives or nurses.
The first signs of a microstroke
The very first sign of a microstroke is numbness of the extremities for a short time (many patients attribute it to “numbness” of the leg or arm). Also, the first, that is, appearing earlier than others, signs of a microstroke include:
- Short painless blindness in one eye (as if a shadow had crept into the field of vision for 20-30 seconds);
- Temporary and sudden numbness of the face (the person will not be able to smile);
- Loss of the ability to speak coherently (sounds and words are confused, sometimes it is impossible to utter a word at all);
- A sharp headache (like a flash) - does not go away even if you take any medications;
- Short-term disturbances in coordination of movements are possible (objects fall from hands, the patient simply cannot lift them for some time);
- The skin becomes pale;
- Weakness appears throughout the body (a person suddenly wants to sit down or lie down);
- Sweating increases sharply for no apparent reason.
Nutrition problems after cerebral stroke
Experts highlight certain problems and features of caring for people who have had a stroke:
- Possible difficulties with chewing and swallowing food;
- if the mobility of the hand is affected, it may be difficult to use a fork or spoon;
- Appetite may worsen, moodiness and selectivity in eating may occur;
- memory impairment is possible - the patient forgets what and when he ate.
- Many patients are prescribed strict bed rest due to the threat of recurrent stroke, general serious condition, and partial impairment of motor functions.
Patients after a stroke need a diet that will help quickly restore lost body functions, while also providing the necessary substances for life (including in cases of impaired swallowing reflex and chewing process).
Treatment of microstroke
Treatment is aimed at normalizing blood supply and metabolism, preventing relapses and preventing stroke. In case of hemodynamically significant occlusion of large arteries, surgical treatment by angiosurgeons is possible. Patients with a ministroke are usually prescribed:
- Drugs aimed at restoring blood microcirculation in blood vessels;
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow;
- Agents that prevent platelet accumulation;
- Drugs that improve brain activity;
- Vitamins.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient visits:
- Exercise therapy (to restore motor activity);
- Massage sessions (to stimulate motor activity in the limbs);
He also follows a diet (without fatty, spicy and salty foods) and does special breathing exercises (to ensure that sufficient volume enters the body).
But if the patient delays diagnosis and treatment, complications may arise. In this case, with a microstroke, the doctor prescribes the following groups of drugs responsible for restoring the body:
- improving blood microcirculation;
- improving metabolic processes in blood vessels;
- dilating vessels;
- preventing the formation of blood clots;
- stimulating brain activity;
- vitamins (to strengthen the immune system and improve brain activity).
Nutrition guidelines for stroke: food, calories, fluid
When developing nutrition for bedridden patients after a stroke, the menu should be as balanced as possible in terms of calories, taking into account age and inactivity, and limited in the amount of table salt (so as not to provoke an increase in pressure). In addition, the food should be light so that there is no overload of digestion, but at the same time the body is provided with all the necessary nutrients. It is also important to ensure that the patient receives a sufficient amount of fluid, proteins with physiological consumption of fats and carbohydrates, which will help prevent thrombosis and the progression of atherosclerosis.
It is also important to know what foods are allowed and prohibited for an elderly person after a stroke. Helpful after a stroke:
- fish (low-fat) and various seafood;
- lean meat, poultry;
- egg white;
- vegetable oils;
- low-fat dairy products;
- dried fruits and nuts;
- dishes made from whole grains (porridge, side dishes);
- fresh fruits, ripe berries;
- fresh, boiled, stewed vegetables;
- a lot of greenery;
- drinking water, green tea, compotes, natural fruit drinks and juices diluted with water.
Not recommended after a stroke:
- fatty foods (lard, fatty meat, lard, bacon);
- black tea or coffee;
- marinades, pickles, spicy dishes;
- roast;
- sweets, candies, chocolate;
- alcohol.
In addition, it is important for patients to have a complete supply of B vitamins, colecalciferol (vitamin D), magnesium, potassium and iron.
And it seems that all these problems can be solved simply by a balanced diet. But the problem is complicated by the condition of people who have suffered a stroke. They often experience serious damage - paresis, problems swallowing food, impaired coordination and other similar consequences. As a result, regular food is not always available to such patients. Moreover, due to the transferred condition, a depressive background often develops, appetite and the desire to make efforts to process the necessary food disappear. As a result, doctors have to use tube feeding (the nutritional mixture is administered through a special tube) or siping.
The second nutrition option - siping - is relevant if the patient is able to swallow on his own, so regular nutrition in combination with specially developed products that cover all the needs associated with useful substances is suitable for him. That is, the patient eats regular food and at the same time drinks drinks rich in beneficial elements. Or he drinks exclusively nutritious mixtures.
Causes of microstroke
- Atherosclerosis (in this case, the cause of the disease is a plaque in the vessels, which either comes off or sticks to the wall of the vessel: both lead to obstruction of blood through the vessel);
- Thrombosis - separation of a blood clot, disruption of the nutrition of neurons in the lower extremities;
- Vascular spasm, as a result of which blood does not flow to the brain;
- Anemia - a drop in hemoglobin levels, a decrease in oxygen levels in the brain;
- Increased blood viscosity (usually due to chronic diseases, polycythemia, insufficient fluid intake);
- High blood pressure;
- Obesity (there is an increased load on the heart when the body has extra pounds);
- Hereditary brain pathologies;
- Heart attack and other heart diseases that weaken it;
- Previous heart surgery;
- Stress (provokes increased blood pressure);
- Age (despite the fact that this disease is getting younger, more often older people still suffer from it, since their blood vessels are worn out);
- Abrupt climate change (more than 10 degrees).
Features and benefits of special mixtures for patients after a stroke
Special mixtures are nutritious and balanced food products in a drinking format. They are completely ready for use and balanced in all necessary components (contain the required amount of protein, slow carbohydrates and all mineral and vitamin components).
Moreover, everything you need is in small 200 ml bottles. The essence of sipping nutrition is that such mixtures can be consumed either through a straw, or in the usual way, but in small sips (within half an hour), which is quite convenient for a patient undergoing rehabilitation. Such mixtures replace a large number of products and are a quality addition to the menu of a sick person.
The Nutricia company, one of the leaders in the field of specialized nutrition, has just developed products for feeding people undergoing rehabilitation. As a supplement to your regular diet, you should drink from one to three bottles of the Nutridrink mixture per day. If the patient cannot eat regular food, it can be completely replaced with Nutridrink - but in the amount of 5-7 bottles per day. To ensure that special nutrition evokes only pleasant sensations, patients are offered several flavors: vanilla, chocolate, banana and strawberry.
Doses of special nutrition must be further discussed with a nutritionist and attending physician - they are prescribed individually, taking into account the personal calculation of nutrients for a particular person. With the correct calculations, Nutridrink will provide the body with everything it needs and will contribute to better and faster rehabilitation after a stroke.
Who does the disease affect?
This disease is getting younger and, if previously it was believed that it only affected older people, now this is not the case. Much depends on the person’s health status, lifestyle and chronic diseases.
Still, patients with the following problems are at risk:
- Atherosclerosis (chronic artery disease);
- Hypertension (pressure surges can trigger a minor stroke);
- Vascular lesions;
- Diabetes mellitus (high sugar content affects the walls of blood vessels);
- Alcohol abuse (the functionality of brain vessels decreases, toxins destroy tissue);
- Congenital and acquired heart diseases.
Busy people suffer a micro-stroke on their feet, that is, they do not pay attention to its symptoms and first signs, trying to maintain their usual activity. This should not be done under any circumstances, since within 24-48 hours there is a high risk of a stroke; the consequences in this case can be disability and even death. Therefore, a minor stroke is an indication for emergency hospitalization of the patient.
Fully or partially limited products
Entirely puff pastry products, meat/fish/mushroom broths. You cannot make soups from legumes. It is not allowed to consume fatty pork, poultry, cooking fats, kidneys and liver, which contain large amounts of cholesterol, sausages, canned food and various smoked meats.
Fatty fish, canned fish and fish roe (high cholesterol content), as well as salted and smoked fish are undesirable due to their high salt content. Fat cheese and cream, fat cottage cheese and sour cream are prohibited.
Radishes, radishes and mushrooms are difficult to digest vegetables and cause bloating; they should be excluded from the diet. Sorrel and spinach are undesirable due to their high oxalic acid content. You cannot eat chocolate, sweets, ice cream, or products with cream. Strong tea, coffee and cocoa are prohibited. Highly extractive sauces, as well as mustard and horseradish, are excluded.
Dishes made from beans, peas, and beans are limited, as they cause bloating, and egg yolks due to their high cholesterol content. If you are obese, you should very rarely eat grapes, honey, raisins, and limit pasta and cereals.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 11% | 16,0 | 11,0 | 1,0 | 170 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Prevention of micro-stroke
Prevention is always simpler and more effective than treatment, and preventive measures are usually the same, so by following simple rules, you can eliminate many diseases from your life. What should be done?
- Maintain normal blood pressure. Any stroke is a surge in pressure, so just measure your blood pressure at least once a day using a home blood pressure monitor;
- Give up bad habits: for example, coffee and alcohol increase blood pressure, smoking thins the walls of blood vessels. All this provokes strokes of varying severity;
- Follow the diet recommended by your doctor: it is aimed at reducing cholesterol levels and, accordingly, preventing the appearance of plaques;
- Exercise regularly: physical activity keeps all body systems in good shape;
- Monitor your sleep status, sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- Monitor hormonal levels;
- Seek help for head injuries;
- Visit doctors periodically and promptly treat vascular diseases.
An example of a one-day home menu for a patient
In the morning, breakfast after hygiene procedures:
- liquid low-fat cottage cheese diluted with milk;
- toast brushed with honey;
- green tea with mint.
After 1.5–2 hours - banana.
For lunch:
- vegetable broth soup seasoned with buckwheat;
- steam cutlet with grated carrot and cabbage salad;
- freshly squeezed fruit juice or grated apple.
For afternoon snack: chicory drink with dry cookies.
For dinner:
- steamed fish with mashed potatoes;
- prune compote.
Shortly before bed: a glass of yogurt or kefir.
Since many people get confused when it comes to preparing boiled dishes, we provide dietary recipes.
Porridge with pumpkin
You can cook it from rice or millet cereals to taste, or mix them in half.
Peel the pumpkin, cut into cubes, add water (2-3 cups) and cook for 10 minutes.
Add washed millet or rice (to remove gluten, it is better to first soak them in water for 2 hours) and cook for another 15 minutes, stirring.
Once ready, wrap the pan tightly with a warm cloth and leave the porridge to simmer.
Add a teaspoon of butter to a plate. You can replace it with honey.
Vitamins and microelements necessary for successful rehabilitation
The main goal of the diet proposed by doctors is to replenish and subsequently maintain the deficiency of vitamins and microelements, which are extremely important for the full functioning of the body. Therefore, the diet should consist of foods that help reduce blood viscosity and reduce the risk of blood clots. They should saturate the brain with vital compounds.
| Vitamins, microelements and other vital compounds | Impact on the body | What products contain | Note |
| Vitamins B, C and D | Reduce the quantitative level of homocysteine, which can provoke a recurrence of stroke | Various nuts (cashews, hazelnuts), sunflower seeds, asparagus | Contains fiber useful for intestinal motility |
| Polyunsaturated acids omega-3 and omega-6 | Normalize the activity of the vascular system, improve biochemical reactions in the brain | Varieties of sea fish and seafood, olive and vegetable oils | It is not recommended to include river and lake fish in the diet |
| Folic acid | Reduces the likelihood of a recurrence of an attack in the future, normalizes blood pressure | All legumes (lentils, chickpeas, peas, beans) | Especially recommended in case of ischemic stroke |
| Calcium, phosphorus, potassium, iron, etc. | Accelerate metabolism, have a positive effect on the condition of all organ systems | All citrus fruits, tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, bananas | After the attack has stopped, it is recommended to consume a clove of garlic once a week. |
| Protein | Helps restore the entire body | Any dietary meat (rabbit, turkey) | Fatty meats (pork, lamb) are strictly prohibited |
| Anthocyanides | Reduce capillary permeability, stabilize the functioning of the heart muscle | Various blue vegetables and fruits (eggplants, grapes, onions) | If you have problems with stool, it is better to choose seedless fruits |
| Beta carotene | Effectively reduces blood pressure levels | Pumpkin, red pepper, carrots, apricots | The body receives more benefits from raw foods. |
| Antioxidants | Remove free radicals from the body, normalize metabolic processes in the body | Blueberries, cranberries, all varieties of cabbage | To eliminate the pronounced bitterness in cranberries, they can be eaten with honey. |
| Complex carbohydrates | Effectively reduce blood cholesterol levels and activate metabolic processes in the brain | Honey, various cereals (oatmeal, barley), brown rice, apples | Products in this category are highly nutritious, which must be taken into account when preparing a diet and calculating its calorie content. |
The products presented in the table differ in availability. When it comes to vegetables and fruits, it is better to choose seasonal options. In this case, the benefits for a weakened body will be much greater.
Diet according to Pevzner
In 1923, the Institute of Nutrition was created in the USSR. One of its leaders was M.I. Pevzner. His developments in nutrition even today have a high therapeutic potential. Moreover, the nutritional system he developed, also known as “Table No. 10,” is used to treat post-stroke patients. It pursues several goals at once:
- normalization of blood pressure indicators;
- restoration of the vascular system;
- preventing the formation of blood clots;
- decrease in blood viscosity.
The daily calorie intake is 1900-2500 kcal. In this case, all products must be boiled or baked in the oven. It is possible to cook them on the grill. Ready-made meals can be eaten hot or cold. Among the main features of the Pevzner diet, it is necessary to highlight the complete absence of animal fats and salt-free recipes. In addition, meals should be fractional and in small portions.
You are allowed to consume no more than 450 g of complex carbohydrates per day. Proteins should account for up to 60% of the total diet, and the amount of healthy fats should not exceed 70 g. Salting dishes is allowed only in the post-acute period.
Selected tips
We offer small culinary tricks to prevent negative emotions in the patient.
- To make food with limited salt tasty, you can add crushed garlic, parsley, dill, and seaweed.
- If the patient cannot swallow solid food, it is necessary to prepare everything in the form of purees or purchase high-quality baby food in jars at the store.
- A blender will help grind the vegetables into a mass. But you should make sure that the resulting dish is warm.
- For constipation, the menu should include a decoction of figs, dried apricots, and prunes, and drink it on an empty stomach. Be sure to give kefir in the evening.
- Legumes are very healthy; they contain folic acid, which activates the B group of vitamins. If the patient has difficulties with daily bowel movements, they should not be cooked.
Nutritionists do not advise deciding on your own the issue of adding immunostimulants (ginseng, aloe) to a patient’s drinks. They are contraindicated for hypertension. You should consult your doctor.
Prepared on the basis of flaxseed oil with cumin extract, it has valuable qualities