General information about heart defects in children
Heart disease
- a violation of the anatomical structure of the walls or valves of the heart, as well as the blood vessels that enter or exit it. Cardiac function and hemodynamics in the entire circulatory system are impaired.
Depending on the reasons for development, there are congenital
and
acquired vices
.
It is believed that congenital ones appear during the first weeks of pregnancy during the “initial formation” of future life. The reasons for the development of defects have not been studied reliably, but they predispose to them:
- genetic diseases (50% of children with Down syndrome suffer from this disorder);
- diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman;
- bad habits of the expectant mother (half of children with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) have heart defects);
- infections (a mother who has had rubella in the first trimester will almost always have a child with severe pathology);
- taking medications prohibited for pregnant women;
- phenylketonuria in an expectant mother.
However, heart disease does not always develop from birth. It can manifest itself as a complication of diseases suffered in childhood (rheumatism, influenza, tonsillitis) in severe forms. This disorder is called an acquired defect.
hearts.
Degrees of heart defects in a child
Depending on the severity of the symptoms of heart disease, there are four degrees of impairment:
- first degree
- heart function deviates slightly from the norm; - second degree
- symptoms of the disease appear, parents can notice them; - third degree
- in addition to specific symptoms, disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system appear, as a result of a lack of oxygen to the brain; - fourth degree
- respiratory and cardiac activity is inhibited, such changes can lead to the death of the child.
Types of heart defects
| Type | Name |
| Congenital | |
| Without the development of cyanosis (pale type) | Defects of the interventricular and interatrial septa |
| Patent ductus arteriosus | |
| Pulmonary stenosis | |
| Coarctation of the aorta | |
| With the development of cyanosis (blue) | Transposition of the great vessels |
| Common ventricle | |
| Tetralogy of Fallot | |
| Purchased | |
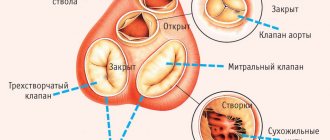
| Mitral valve (between the left atrium and ventricle) | Mitral stenosis |
| Mitral regurgitation | |
| Tricuspid valve (between the right atrium and ventricle) | Tricuspid valve stenosis |
| Tricuspid valve insufficiency | |
| Aortic valve (between the left ventricle and the aorta) | Aortic stenosis |
| Aortic insufficiency | |
| Pulmonary valve | Pulmonary valve stenosis |
| Pulmonary valve insufficiency | |
Stenosis
- narrowing of the valve opening, which causes difficulty in blood flow.
Failure
- inability of the valves to close tightly. In people with valve stenosis, valve insufficiency develops over time - this is called combined PS.
Septal disorders:
A condition in which the septum between the chambers of the heart is damaged:
- atrial septum -
“extra” blood enters the right atrium and causes it to enlarge; - interventricular
- blood flows from the right to the left ventricle, expanding its boundaries.
Changes are found in 2 out of 1000 newborns. Perhaps the most favorable form, since small defects can heal on their own.
Coarctation of the aorta:
Narrowing of the lumen of the main vessel in the area of the isthmus - the transition of the arch to the descending part. The defect causes disruption of the blood supply to organs. This form of pathology accounts for 10% of all defects. Often combined with disruption of interchamber septa. A serious condition requiring medical attention immediately after birth.
Pulmonary valve stenosis:
At the site of the valves from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, a narrowing occurs. The heart requires more effort to pump blood. 10% of the total number of defects.
Transposition of the great vessels:
Rare pathology (about 5%). In this case, the main vessels “change places.” Arterial blood flows through the veins, and venous blood through the arteries.
Tetralogy of Fallot:
The most severe form. Consists of four violations simultaneously:
- the opening between the left and right ventricles;
- pulmonary stenosis – narrowing of the pulmonary trunk;
- enlargement of the right ventricle;
- Aortic displacement is the exit of the aorta from the heart in an atypical location.
How to register a disability: about passing a medical and social examination
The decision to recognize a person as disabled is made by federal state institutions of medical and social examination based on the results of the examination. However, the Moscow Department of Labor and Social Protection receives many questions about how to register disability. We describe the algorithm of actions.
A referral for a medical and social examination (MSE) can be obtained from medical organizations, as well as from bodies providing pensions, from social protection bodies if the citizen has medical documents confirming impairment of body functions due to diseases, consequences of injuries or defects. Only the attending physician, knowing the diagnosis, results of treatment, rehabilitation and habilitation of the patient, determines whether there are signs of disability, so it is best to contact him for a referral for medical examination.
To pass the ITU, the corresponding application and necessary documents are submitted to the ITU office at the place of residence. Information on the addresses of divisions of the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise in cities and regions can be found on the website.
List of documents for examination at the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise:
- Consent of the citizen (his legal or authorized representative);
- An identification document (passport or other identification document), for foreign citizens and stateless persons permanently residing in the territory of the Russian Federation - additionally a “residence permit”; the refugee certificate is presented in person, for non-resident citizens - a certificate of registration at the place of residence;
- A referral for a medical and social examination issued by a medical organization or a social protection authority, or a pension authority;
- Report on an industrial accident in form N-1 (certified copy);
- Act on occupational disease (certified copy);
- For those discharged from military service - a certificate of illness drawn up by the Military Military Commission (certified copy, the original must be presented in person);
- Conclusion of the interdepartmental expert council on the causal relationship of the disease, disability with exposure to radioactive factors (certified copy, original presented in person);
- Certificate of participant in the liquidation of the consequences of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant or living in the exclusion or resettlement zone (copy, original presented in person);
- A copy of the work record;
- Medical or military medical documents indicating the citizen’s state of health (outpatient card, hospital extracts, consultant reports, examination results, Red Army or military record book, certificate of injury, etc.);
- Professional and production characteristics from the last place of work.
During the examination, bureau specialists will study the submitted documents, as well as social, everyday, professional and other aspects of the candidate’s life.
A person recognized as disabled receives a certificate of disability indicating the assigned group, as well as an individual rehabilitation or habilitation program (IPRA).
If, based on the results of the examination, a person is not recognized as disabled, then, at the request of the applicant, he is issued a certificate of the results of the medical examination. You can appeal the decision of the ITU within a month from the date of the examination by contacting the bureau that conducted the ITU, in writing on paper or electronically on the State Services website. The bureau also operates a hotline for medical and social examination issues.
We remind you:
Re-examination of people with disabilities of group I is carried out once every 2 years, groups II and III - once a year, and children with disabilities - once during the period for which the child is classified as a “disabled child”.
Important:
During the period from October 2, 2021 to March 1, 2021 inclusive, the “Temporary Procedure for Recognizing a Person as Disabled” (Temporary Procedure) is in effect. Medical and social examination is carried out in absentia .
Recognition of a citizen as a disabled person whose re-examination period begins during the period of validity of the Temporary Order, in the absence of a referral to medical examination, is carried out by extending the previously established disability group (category “disabled child”), the cause of disability, as well as the development of a new individual rehabilitation or habilitation program for a disabled person (child). -disabled person), including previously recommended rehabilitation or habilitation measures.
Disability is extended for a period of 6 months and is established from the date until which the disability was established during the previous examination.
Extension of disability for a citizen who, during a previous examination, was assigned the category of “disabled child” before reaching the age of 18 years and whose re-examination period begins during the period of validity of the Temporary Order, is carried out by establishing disability group I, II or III for a period of 6 months in accordance with the conclusion federal state institution of medical and social examination on the severity of persistent disorders of body functions resulting from diseases, consequences of injuries or defects, information about which is available in the protocol of the citizen’s MSA at the federal state institution of medical and social examination at the last examination.
Extension of disability is carried out without requiring the citizen (his legal or authorized representative) to submit an application for medical examination. In this case, the written consent of the citizen is not required.
Press service of the Department of Labor and Social Protection of the Population of Moscow
Symptoms of heart defects in newborns and children
Usually the pathology is detected by a neonatologist in the first days of a baby’s life:
- cyanosis (blue discoloration) or grayness of the skin;
- tachypnea - rapid shallow breathing;
- widening of the nostrils when inhaling;
- grunting while inhaling;
- swelling of the legs, abdomen, face;
- breathing problems when feeding.
In a less severe form, it manifests itself at a growing age:
- fatigue during exertion;
- shortness of breath, pain in the heart area when playing sports;
- swelling of the hands, ankles, feet.
The earlier the clinical manifestations appear, the more difficult the process.
Important! Note to parents
Regardless of whether a child has a heart pathology or not, it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations.
It is especially important to make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist before starting sports. There are disorders in which the cardiovascular system can cope with them through compensatory force. Diseases go undetected for years.
When playing sports, the load on the cardiovascular system increases many times over. Compensatory mechanisms in this mode are often insufficient, which is manifested by dizziness, loss of consciousness, and can cause a life-threatening condition for the child.
This does not mean that playing sports is strictly contraindicated. The type of sport and load must be determined by a doctor.
If a child is diagnosed with a heart defect, medical supervision when playing sports is mandatory. A medical examination by a pediatric cardiologist, pediatrician, or cardiac surgeon is required.
Approaches to determining disability in children with congenital heart defects
Back to the program
Zubov L.A.
GBOU HPE Northern State Medical University;
Target.
In the structure of congenital developmental anomalies leading to disability in children of the Arkhangelsk region, in recent years the leading place (52–58%) has been occupied by congenital heart disease. Children with congenital heart disease make up about 20% of all children initially examined by the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise (MSE).
A wide variety of congenital heart diseases with different hemodynamics sometimes causes difficulties in expert assessment of the degree and prognosis of functional disorders of the cardiovascular system in children. Every year, 150-170 children in the Arkhangelsk region are operated on in cardiac surgery centers for congenital heart disease. Timely diagnosis, modern advances in cardiac surgery and adequate rehabilitation have made it possible to ensure a decent quality of life for the majority of children with congenital heart disease, including those with complex combined defects. Assessing the degree of recovery and adaptation of hemodynamics after surgery and carrying out rehabilitation measures in such children requires an integrated approach. To a large extent, this relates to the correct interpretation of clinical and instrumental indicators in children.
Methods.
The criteria for determining disability in 583 children with congenital heart disease examined at the Main Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise in the Arkhangelsk Region were analyzed.
Results.
Thanks to the established practice of jointly resolving expert issues with pediatric cardiologists, unified practical approaches to establishing disability in children with congenital heart disease have been developed. Functional stress tests help to objectify the assessment. Medical criteria for medical and social examination for congenital heart disease with increased pulmonary blood flow are the degree of heart failure, the presence of pulmonary hypertension, the need to prescribe basic drug therapy (cardiac glycosides, diuretics, ACE inhibitors), the presence of complications (infective endocarditis, pulmonary, cardiac arrhythmias) and the effectiveness of surgical correction.
In case of blue-type CHD with reduced pulmonary blood flow, the severity of the course (frequency and severity of dyspnea-cyanotic attacks), the need for basic medications (beta-blockers), the presence of chronic hypoxemia (dysfunction of the central nervous system, dystrophy of internal organs) or complications (infective endocarditis, thromboembolism), radicality and effectiveness of surgical correction (long period of adaptation to new hemodynamic conditions in combined congenital heart disease).
In case of coarctation of the aorta, aortic stenosis, the indications for recognizing a child as disabled are the severity of NC, the degree of chronic insufficiency of cerebral and coronary circulation, complications (stroke, infective endocarditis, the formation of a prestenotic aortic aneurysm), the effectiveness and complications of surgical intervention.
Conclusions.
Clinical and functional criteria for establishing disability in congenital heart disease with different hemodynamics facilitates medical and social expert assessment of the degree and prognosis of functional disorders of the cardiovascular system in children.
Diagnosis of heart defects in children
During the initial examination, a pediatrician, neonatologist or pediatric cardiologist conducts an examination and auscultation of possible heart murmurs. The presence of swelling, shortness of breath, heart rhythm disturbances, and problems with physical or intellectual development are checked. Based on the results of the inspection, the question of the necessary examination is decided.
Cardiac echocardiography (EchoCG) – combines cardiac ultrasound and cardiogram. The method determines the rhythmogram and structural changes in the heart. EchoCG is an informative method.
Radiology shows the actual size of the heart, its chambers and the relationship of the organ to the size of the chest.
Coronary angiography – a catheter is inserted through the veins or arteries in the arm, groin, or neck (vein only) and reaches the heart. Then a contrast agent is passed through it. This method determines the contractile function of the heart.
Medical equipment uses expert-class equipment from world-famous manufacturers.
The task of the Children's Medical Department is to provide a full range of medical care from prevention to treatment, when symptoms of a defect appear from birth to 18 years.
In our children's department, appointments are conducted by doctors who have undergone special training to identify health problems in children and infants, taking into account all age-related characteristics.
Pediatric doctors at the Paracelsus Clinic work according to the principles of evidence-based medicine (international protocols drawn up on the basis of clinical trials). This minimizes the likelihood of a false diagnosis.
Parents play a big role in the early diagnosis of heart defects in children. The direction in which the preliminary examination will be carried out depends on how closely the parents monitor the health of their child and how correctly they can describe his condition to the doctor.
How to apply for disability
How to apply for disability
- Obtain a referral to an ITU or a certificate of refusal to be referred to an ITU (from a medical organization, from a pension agency, or from a social security agency);
- Prepare identification documents: a passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation, a temporary identity card of a citizen of the Russian Federation, issued before issuing a passport, or their certified copies.
- Prepare a written application for an ITU.
- Contact the ITU office at your place of residence or place of stay with a package of documents: an identity document, an application for an ITU, a referral to an ITU or a certificate of refusal to refer, medical documents confirming a health impairment.
- Wait for an invitation to ITU.
- Go through a medical examination and get a decision.
- Obtain a certificate confirming the fact of disability.
What to do if referral to ITU is denied?
If you are denied a referral to the ITU, you must be issued a certificate of refusal to refer to the ITU, which gives you the right to submit documents to the ITU yourself without a referral (clause 19 of the Rules for recognizing a person as a disabled person, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 20, 2006 No. 95)
.
What to do if the patient is unable to come for examination to the ITU facility?
If the recipient of a public service cannot come to the bureau and it is necessary to conduct an MSE at home, an appropriate conclusion from a medical organization providing medical and preventive care is additionally submitted (clause 90 of the Regulations for the provision of public services for conducting a medical and social examination)
.
How is disability determined?
When establishing disability, a quantitative assessment of the severity of persistent dysfunctions of the human body due to neoplasms is taken into account. It is based primarily on the assessment of local prognostic factors: localization and size of the tumor, anatomical form of growth, growth rate, degree of invasion of the organ wall (degree of invasion), histological structure and degree of differentiation, degree of malignancy, nature of damage to regional lymph nodes, presence or absence of distant metastases , stage of the tumor process (according to the TNMG system). The possibility of adaptation and compensation, and the presence of complications are also taken into account.
(Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 17, 2015 N 1024n (as amended on July 5, 2016) “On classifications and criteria used in the implementation of medical and social examination of citizens by federal state institutions of medical and social examination" (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on January 20, 2016 N 40650 ) Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on January 20, 2021 N 40650)
What is IPRA for a disabled person?
IPRA for a disabled person is a set of optimal rehabilitation measures for a disabled person, which includes certain types, forms, volumes, terms and procedures for the implementation of medical, professional and other rehabilitation measures aimed at restoration, compensation for impaired body functions, formation, restoration, compensation of the disabled person’s abilities to perform certain types of activities.
How to make changes to the IPRA of a disabled person?
If it is necessary to make additions or changes to the disabled person’s IPRA, a new referral for medical and social examination is issued and a new disabled person’s IPRA is drawn up.
Is an employee obliged, after his disability group has been determined, to inform the employer about this?
The employer is not legally required to provide documents confirming his disability. An employee can submit such documents at his own request, both when applying for a job and during his work activity.
Can an employee refuse the rehabilitation measures specified in the IPRA?
The employee has the right to refuse one or another type, form and volume of rehabilitation measures specified in the IPRA (IPR), as well as the implementation of the program as a whole. In this case, the employer is released from liability for its implementation. (Part 5 of Article 11 of Law No. 181-FZ, Part 7 of Article 11 of Law No. 181-FZ.)
What rights does a disabled person have at work?
- Duration of working hours of disabled people and payment for their work - no more than 35 hours per week with full pay (for disabled people of groups I and II);
- Involvement of disabled people in overtime work, work on weekends, holidays, and also at night is allowed only with their written consent and provided that this is not prohibited for them for health reasons in accordance with a medical report;
- The duration of annual paid leave for disabled people has been increased and must be at least 30 calendar days (Part 5, Article 23 of Law No. 181-FZ)
; - The employer is obliged to provide a disabled employee, upon his written application, leave without pay for up to 60 calendar days per year (paragraph 5, part 2, article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, letter of Rostrud dated 04/16/2014 N PG/3387-6-1)
; - The employer is obliged to create and equip (equip) special workplaces for the employment of disabled people. (Part 1 of Article 22 of Law No. 181-FZ.)
; - Establishment of easy labor for disabled people.
If a disabled person, in accordance with the IPRA, can no longer work at his previous job?
An employee who needs to be transferred to another job in accordance with a medical report with his written consent, the employer is obliged to transfer to another available job that is not contraindicated for the employee for health reasons (Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
, the employee retains the same average earnings for one month from the date of transfer.
Also, according to clause 9 of the Rules for recognizing a person as a disabled person, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 20, 2006 No. 95
, disability of group I is established for two years, and disability of groups II and III - for one year. Thus, if a disabled employee who needs easier work has provided the employer with documents confirming the establishment of disability for a specified period, a temporary transfer is issued.
If an employee refuses to be transferred to another job in accordance with his medical report?
If, in accordance with a medical report, an employee needs a temporary transfer to another job for a period of more than four months or a permanent transfer, then if he refuses the transfer or the employer does not have a suitable job, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with clause 8 of Part 1 of Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the dismissed employee is paid severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings (Part 3 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What is VMP and how much does it cost?
VMP – high-tech medical care.
VMP is provided in accordance with the List of types of VMF included in the basic compulsory medical insurance program and the List of types of VMF not included in the basic compulsory medical insurance program. Regardless of the type of medical care, it is free, since it is included in the Program of State Guarantees for the provision of free medical care to citizens and is financed by the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
How to get high-tech medical care?
Step 1. Contact your doctor.
Step 2. Wait for the VMP coupon to be issued.
Step 3. Wait for the decision of the commission of the medical organization providing medical care and hospitalization in the receiving medical organization.
Step 4. Upon completion of VMP, receive recommendations.
How to find out the status of a VMP coupon?
The status of the coupon can be viewed on the official website of the Russian Ministry of Health:
What to do if a doctor refuses to refer a patient for advanced medical care?
- Submitting an application or complaint to another authorized person of the referring medical organization;
- Filing an application or complaint to Roszdravnadzor or the government body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in the field of healthcare;
- Contacting a medical insurance organization or territorial compulsory medical insurance fund;
- Applying to the court to declare illegal the inaction of medical workers or refusal to refer for the provision of medical treatment.
What is the validity period of the quota and where can I get it?
The quota is issued by the health department at the place of residence in a specific medical institution and is valid from the moment of its issuance until December 31 of the current year.
Will the quota be valid for re-hospitalization?
If you are hospitalized again, you must take a new quota for treatment, even if hospitalization is planned for the current year.
What to do if there is a prescription, but the pharmacy does not have the medicine?
You need to fill out a prescription for deferred care at the pharmacy. There they are required to register it in the register of unsatisfied demand. Such a magazine should be in every pharmacy that dispenses drugs on preferential prescriptions. After registering a prescription, the pharmacy must submit a request for the drug to the pharmaceutical company authorized to supply preferential drugs to the region and provide the drug to the patient within 10-15 days. Deferred care is not a pharmacy's choice—it is the pharmacy's legal responsibility to arrange deferred care.
Prescriptions are issued with a validity of 30 days. Can a prescription be issued for a longer period of validity?
Prescriptions for medications written out on prescription forms Form N 148-1/u-04 (l) and Form N 148-1/u-06 (l), citizens who have reached retirement age, disabled people of the first group, disabled children, and also for citizens suffering from chronic diseases requiring long-term course of treatment, valid for 90 days from the date of issue.
For the treatment of chronic diseases, the specified categories of citizens can be issued prescriptions for medications for a course of treatment of up to 90 days. (Appendix No. 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated December 20, 2012 No. 1175n)
IMPORTANT MEDICATION INFORMATION!
1. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 30, 1994 N 890 (as amended on February 14, 2002) “On state support for the development of the medical industry and improving the supply of medicines and medical products to the population and healthcare institutions”
2. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated December 20, 2012 N 1175n (as amended on April 21, 2016) “On approval of the procedure for prescribing and prescribing medications, as well as forms of prescription forms for medications, the procedure for processing these forms, their recording and storage”
3. Federal Law of July 17, 1999 N 178-FZ (as amended on December 19, 2016) “On State Social Assistance”
4. Federal Law of November 21, 2011 N 323-FZ (as amended on July 3, 2016) “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation”
5. LIST OF VITAL AND IMPORTANT DRUGS FOR MEDICAL USE FOR 2021 (Approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 28, 2016 N 2885-r)