Antiarrhythmic drugs are a large and diverse group of drugs that eliminate heart rhythm disturbances and are used for arrhythmias.
An important feature of antiarrhythmic drugs is their highly targeted action - they specifically affect the conduction system of the heart.
The heart consists of two types of cells - cardiomyocytes: typical and atypical (atypical).
Typical cardiomyocytes in structure and function are ordinary muscle cells that are capable of contracting, thereby ensuring the pumping function of the heart and the movement of blood through the vessels. The heart contracts under the influence of bioelectric impulses.
Atypical cardiomyocytes, in structure and function, are more reminiscent of nerve cells capable of reproducing and transmitting electrical impulses. Atypical cardiomyocytes constitute the conduction system of the heart, ensuring uniform impulse conduction throughout the heart, as well as the ability to autonomously reproduce and maintain this impulse when necessary. It is these processes that determine the normal (measured) rhythm of heart contractions.
The bioelectric impulse is generated and conducted through the heart due to the currents of sodium, potassium and calcium ions, as well as the work of β-adrenergic receptors.
The conduction system permeates the entire heart and consists of the following main parts: the sinus (sinoatrial) node, the atrioventricular node, internodal conduction bundles, the His bundle and Purkinje fibers.
Each section of the conduction system is responsible for the sequential contraction of certain parts of the heart - the atria, interventricular septum and ventricles. Violation of the conduction of excitation in any part of the conduction system of the heart leads to the development of arrhythmias.
Clinical features and treatment tactics for arrhythmias depend to the greatest extent on the area of the conduction system where the conduction of the bioelectric impulse is regularly disrupted.
Depending on the mechanism of action, as well as the characteristics of the effect on certain rhythm disorders, all antiarrhythmic drugs are divided into 4 main classes: sodium channel blockers (class I), β-adrenergic receptor blockers (class II), potassium channel blockers (class III), blockers calcium channels (class IV).
Let us consider in detail class I antiarrhythmic drugs - sodium channel blockers or membrane stabilizers.
Basics of treatment with class I antiarrhythmic drugs
Considering certain features and difficulties in selecting an individual dose and a specific drug, as well as a wide range of side effects and interactions with other drugs, any antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed only by an experienced cardiologist.
Class I antiarrhythmic drugs are used for a long time, most often for life.
Cancellation, dose adjustment or replacement of a class I antiarrhythmic drug should be carried out only by a physician and under the supervision of a physician, since there is a risk of developing serious cardiac arrhythmias.
Classification of drugs
There are several classifications of antiarrhythmic drugs. The most famous is the Vaughan-Williams classification (1971), according to which there are 4 classes of antiarrhythmics.
I class.
Substances that block fast sodium channels. Drugs in this group help reduce the rate of depolarization and slow down conduction along Purkinje fibers and the His bundle. Among the many modern antiarrhythmic drugs in this group, propafenone deserves special attention. Propafenone causes a dose-dependent decrease in the rate of depolarization, inhibits phase 0 of the action potential and its amplitude in Purkinje fibers, which leads to an extension of the effective refractory period in the atria, atrioventricular node, accessory bundles, and, to a lesser extent, in the ventricles
II class.
Beta-blockers - reduce the impact of sympathetic (adrenergic) impulses on the heart muscle, which can play a role in the development of arrhythmia. Most of the drugs in this group help to slow the heart rate and reduce sinoatrial and atrioventricular conduction.
III class.
Drugs that slow down repolarization. These include sotalol and amiodarone. Antiarrhythmics of this group help to increase the duration of the action potential (AP) of cardiomyocytes and slow down the conduction of impulses in all areas of the conduction system of the heart.
IV class.
Group IV includes calcium ion antagonists, which block “slow” calcium channels. They help inhibit the slow flow of calcium ions into myocardial cells, which reduces the automaticity of ectopic foci of excitation in the heart.
Features of treatment with class I antiarrhythmic drugs
Class IA antiarrhythmic drugs have a pronounced antiarrhythmic effect and are effective both for ventricular arrhythmias and for supraventricular cardiac arrhythmias.
Class IB antiarrhythmic drugs are effective and are used only for ventricular arrhythmias.
Class IC antiarrhythmic drugs are used for ventricular arrhythmias that are resistant to the action of other antiarrhythmic drugs.
A 10% lidocaine solution for intravenous injection is used as an antiarrhythmic agent. For local anesthesia, a lower concentration of lidocaine solution is used - 2%.
Medicines that reduce the flow of sodium ions into heart cells.
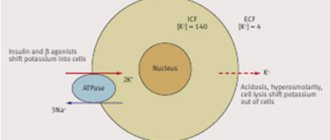
As is known, the occurrence and propagation of an electrical impulse in cells in general and in heart cells in particular is associated with the activity of ion channels, among which a special role belongs to the sodium channel. Substances that block these channels stabilize cell membranes (they are also called membrane-stabilizing) and prevent the abnormal occurrence and propagation of electrical impulses. A malfunctioning cell becomes electrically “silent”, while the activity of normal cells does not change. However, with increasing doses, these substances suppress impulse conduction in normal tissues, provoking arrhythmia. Moreover, even a therapeutic concentration of the drug can become “arrhythmogenic” with rapid heartbeat, acidosis or hyperkalemia.
The ancestor of drugs in this group is quinidine, which is a derivative of quinine, an alkaloid from the bark of the cinchona tree. It also includes procainamide, disopyramide, lidocaine, mexiletine, moricizine, propafenone and others. They all have the same mechanism of action, similar to the action of local anesthetics that block sodium channels inside the cell.
Indications for use
Class III antiarrhythmic drugs are equally indicated for ventricular arrhythmias and supraventricular arrhythmias - disturbances of heart rhythm at the level of the ventricles and atria, respectively. In addition, class III antiarrhythmic drugs are also used for special arrhythmias - extrasystoles, which are characterized by extraordinary premature contractions of the heart.
Additionally, class III antiarrhythmic drugs are used for coronary heart disease (angina).
Medicines that block beta-adrenergic receptors.
This group of drugs has already been discussed in Chapter 3.2 and a little in this chapter. Beta-blockers, along with other pharmacological properties, can reduce the excitability of the heart. You already know that the involuntary activity of the cardiovascular system is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, in particular its sympathetic division, with the participation of chemical intermediaries - mediators that transmit impulses from one nerve cell to another. Stress, anxiety, and intense physical work stimulate the production of such mediators, and they, in turn, excite the receptors of the heart, causing a response to the body’s increasing need for oxygen. By blocking beta receptors in heart cells, beta blockers change their response to a number of mediators, collectively called catecholamines (norepinephrine is also a catecholamine). As a result, the influence of these mediators on the heart is eliminated, excitability and heart rate are reduced, and the rhythm is normalized.
Review of the most effective drugs for arrhythmia with name and price
The names of medications are arranged by class in accordance with the table.
Class I. Membrane stabilizing drugs
Class 1 substances regulate the phases of the action potential. Currently, a number of drugs in this class are not produced or used due to low efficiency and serious side effects.
Novocainamide
Price: 120 rub.
The active substance is represented by procainamide, a modified novocaine molecule.
Produced by a Russian manufacturer in the form of tablets and injection solution.
Treatment of arrhythmia is due to its cardiodepressive effect.
Suppresses the conduction of electrical impulses, inhibits the muscular apparatus of the myocardium.
Does not have a serious effect on blood pressure.
Indicated for therapy:
- Paroxysmal tachycardia;
- Atrial flutter;
- Atrial fibrillation.
Injections are used to relieve acute conditions.
Note! The injection solution is administered intravenously only in a hospital setting.
The medicine is contraindicated for certain heart rhythm disorders:
- Atrioventricular block;
- Cardiogenic shock.
Severe renal and heart failure, hypertension are also restrictions on taking the medicine.
When taking pills you need to adhere to certain rules:
- Take the tablets strictly on an empty stomach, 1 hour before meals;
- Drink with milk.
Requires frequent use - up to 4 times a day.
During therapy, it is necessary to monitor heart function and regularly measure blood pressure.
Despite the absence of a direct hypotensive effect, it can cause an excessive decrease in blood pressure in elderly people.
Irritates the gastric mucosa and negatively affects the blood system.
When taking the medication, symptoms of dyspepsia may appear - bitterness in the mouth, nausea and vomiting, epigastric pain.
May cause drowsiness, lethargy, dizziness, headaches, aggravated by decreased blood pressure.
Lidocaine
Price: from 30 rub.
Antiarrhythmic activity is due to blocking sodium channels localized in cell membranes.
Reduces myocardial automatism, suppresses foci of excitation.
Does not have a pronounced cardiodepressive effect.
It practically does not affect blood pressure levels, although in some cases it may slightly reduce it.
It has a rapid onset of effect and a short-term effect. It is widely used as emergency care in hospital settings for acute cardiac conditions, for example, myocardial infarction or severe ventricular arrhythmias.
The solution is well tolerated. In rare cases, convulsions are observed.
The most common side effects:
- Bradycardia, arrhythmias;
- Excessive decrease in pressure;
- Lethargy;
- Headache;
- Drowsiness.
Ethacizin
Price: 1420 rub.
Polish tablets with arrhythmogenic action.
The therapeutic effect of taking the drug is due to the blocking effect on cell membranes and their permeability.
Reduces myocardial conductivity and contractility.
Improvement occurs 1-2 days after the start of treatment.
The list of indications for prescribing the drug is similar to other membrane stabilizers.
The use of the drug is limited in severe heart pathologies of an organic nature.
Not compatible with other class I drugs.
Tablets are taken 2-3 times a day.
It has a negative effect on intraventricular conduction and myocardial contractility, and has an arrhythmogenic effect (provokes the appearance of arrhythmia), especially after a myocardial infarction.
Dizziness, staggering when walking, lethargy and headaches are the most common side effects. As a rule, after adaptation (3-4 days after starting treatment), these symptoms disappear.
Propanorm
Price: 360 rub.
The active substance is propafenonone, a class C1 substance.
Antiarrhythmic effectiveness is due to the membrane-stabilizing and local anesthetic effect on cardiomyocytes (heart cells).
Against the background of heart failure, it reduces myocardial contractility.
Suppresses electrophysiological processes in contractile fibers, Purkinje fibers. Due to this, the repolarization rate decreases and the ERP lengthens.
The severity of the effect is higher in areas with ischemia.
The therapeutic effect lasts for about 12 hours.
The use of the drug is advisable for the treatment of:
- Flutters, atrial fibrillation, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome;
- Atrioventricular tachycardia;
- Extrasystoles (ventricular and supraventricular).
This remedy is a reserve and is used in cases where other medications are ineffective.
The following side effects are possible when taking tablets:
- Heart rhythm disturbances;
- Bronchospasm;
- Deterioration of the digestive tract with accompanying discomfort;
- Increased fatigue, lethargy.
The drug is contraindicated in severe forms of heart disease, including chronic heart failure and/or myocardial infarction.
Particular care is required when treating:
- Patients with bronchial asthma and other pathologies characterized by narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi;
- Patients with a pacemaker;
- Elderly persons.
If your heart rate is slow and your blood pressure is low, you cannot use an antiarrhythmic drug.
Rhythmonorm
Price: 500 rub.
American original drug with propafenone in tablets.
It is of high quality.
Propaphenone
Price: 240 rub.
An affordable substitute for Ritmonorma and Propanorma from a Macedonian manufacturer.
The main advantage is the affordable cost.
Class II: beta blockers
When adrenaline and catecholamines are produced in the body, beta-adrenergic receptors in the myocardium are irritated. Arrhythmia and instability of electrophysiological processes occur.
The antiarrhythmic effect of adrenergic blockers is due to the blocking effect on specific areas - beta-adrenergic receptors located in the cells of the heart and coronary vessels.
Such receptors are found not only in the cardiovascular system, but also in other organs - in the uterus and bronchi.
Some drugs act on all adrenergic receptors and are non-selective, others selectively, only on those located in the heart and blood vessels (selective drugs).
When choosing a medicine, the doctor takes this point into account to eliminate unwanted side effects.
Both classes of beta blockers are currently used.
Anaprilin
Price: from 30 rub.
The drug contains propranolol.
When taking tablets, the following pharmacological effects are observed:
- Membranes are stabilized;
- The excitability and contractility of the myocardium and its need for oxygen decrease;
- Heart rate decreases;
- Ectopic foci of excitation are reduced;
- The automatism of the sinus node is inhibited;
- Blood pressure decreases.
A stable effect is observed after 2 weeks of course treatment.
The medicine is not selective, therefore it affects other systems and organs:
- Increases the tone of the uterus and enhances its contractions;
- Suppresses the central nervous system (in large dosages);
- Reduces the synthesis of aqueous humor in the chamber of the eye, thereby reducing intraocular pressure;
- Stimulates bronchial tone.
Found application in the treatment of:
- Angina pectoris;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Tachycardia;
- Extrasystoles;
- Diffuse toxic goiter;
- Atrial fibrillation;
- Essential tremor;
- For the prevention of migraine attacks.
Tablets cannot be used for vasomotor rhinitis.
A number of heart and vascular diseases limit their use, including:
- Reduced heart rate;
- Acute and severe cardiological pathologies;
- Low pressure;
- Sinoatrial block;
- Obliterating arterial diseases;
- Weakness of the sinus node;
- Metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus.
The dosage regimen depends on the diagnosis.
Frequency of use: 2-3 times a day.
Betalok Zok
Price: from 270 rub.
The original English product with metoprolol selectively acts on beta-adrenergic receptors.
The medicine reduces the effect of catecholamines produced during stress.
Prevents increased heart rate, cardiac contractility and increased blood pressure.
The difference between this antiarrhythmic drug is its prolonged effect due to its slow release. The concentration of the drug in the blood plasma is constant and guarantees a lasting clinical effect throughout the day.
Due to its slow absorption, it has a mild effect and does not cause side effects due to the simultaneous administration of a high dose. When taking modified-release tablets, there is no weakness, sharp decrease in blood pressure and bradycardia, characteristic of short-acting beta-blockers.
The therapeutic effect lasts about a day, so it is enough to take 1 tablet per day.
Has a cardiotropic effect. Prevents the development of a common complication - left ventricular hypertrophy, which occurs in pathologies of the cardiovascular system, accompanied by increased pressure in the bloodstream.
Reduces the likelihood of recurrent myocardial infarctions.
Note! The tablets can be taken after the acute phase of the heart attack has healed.
Indicated for treatment:
- Ventricular extrasystoles;
- Tachycardia;
- Migraine attacks;
- Atrial fibrillation.
Restrictions on use are similar to other beta-blockers.
Egilok
Price: from 150 rub.
Hungarian analogue of Betalok Zok.
However, unlike the original product, it does not have a delayed release. Therefore, when taking a medicine, peak concentrations of the substance in the blood are observed, which may cause additional side effects.
The medicine must be taken 2 times a day.
Metocard
Price: from 70 rub.
Polish drug with characteristics similar to Egilok.
It has an affordable price.
Metoprolol
Price: 40 rub.
Russian cheap analogue of Betalok. It also does not have a prolonged effect.
Concor
Price: 190 rub.
The Norwegian medicine contains a selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker - bisoprolol.
After taking the tablet, a therapeutic effect develops within 1-2 hours, lasting about a day.
Has a complex effect on blood vessels and the heart:
- Reduces cardiac output;
- Affects the physiological process responsible for increasing blood pressure (inhibits the production of renin in the kidneys);
- Dilates blood vessels;
- Reduces high blood pressure;
- Promote a better supply of oxygen to the myocardium;
- Reduces heart rate.
The use of tablets is advisable for:
- Chronic heart failure;
- IHD;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Angina pectoris.
Generally well tolerated.
Bisoprolol
Price: from 100 rub.
Cheap substitute for Concor from a domestic manufacturer.
Coronal
Price: from 190 rub.
Czech antiarrhythmic drug with bisoprolol.
Biprol
Price: from 190 rub.
Selective beta-blocker based on bisoprolol, produced in Russia.
Niperten
Price: 150 rub.
High-quality generic Concor produced in Slovenia.
Sold in advantageous packaging - 30 and 100 tablets.
Aritel
Price: from 120 rub.
The Russian drug with bisoprolol is similar in properties to Concor and its substitutes.
Bisogamma
Price: from 130 rub.
German antiarrhythmic drug with bisoprolol.
Cordinorm
Price: from 150 rub.
Icelandic medicine with bisoprolol.
Additionally, it is produced in advantageous packages of 90 tablets.
Atenolol
Price: from 50 rub.
Refers to selective beta-blockers. Its cost, regardless of the manufacturer, does not exceed 100 rubles.
The pharmacological properties are similar to bisoprolol preparations.
It also has a long-lasting effect and is taken once a day.
In some cases, it can greatly slow down heart contractions and cause atrioventricular block.
Indicated for the treatment of tachyarrhythmias.
Class III: potassium channel blockers
Medicines in this group have an antiarrhythmic effect due to prolongation of repolarization and lengthening of the refractory period, and, as a consequence, an increase in the action potential of cardiomyocytes.
Such antiarrhythmic medications interfere with the transport of potassium ions across the cell membrane, block calcium and sodium channels, thereby reducing the sensitivity of adrenergic receptors to stress mediators.
Dilate blood vessels.
Cordaron
Price: from 300 rub.
Positively affects energy metabolism in the myocardium.
Reduces blood pressure and slows heart rate.
The therapeutic effect develops gradually.
The effect of taking it lasts for 2-3 months.
The drug contains iodine. With prolonged use, it can turn the skin purple and negatively affects the condition of the thyroid gland and hormonal regulation in general.
The use of tablets is advisable for the prevention and treatment of:
- Tachycardia;
- Extrasystoles;
- Atrial flutter.
It has proven itself well as a prophylactic agent for reducing angina attacks.
Like other antiarrhythmic drugs, it should not be used for bradycardia, low blood pressure, or pregnancy.
During treatment with the drug, the sensitivity of the skin to solar radiation increases, so it is necessary to use sunscreen and avoid visiting a solarium.
Changes taste sensations.
Negatively affects liver health.
The medicine is not recommended for drivers due to decreased concentration and inhibition of the nervous system.
Amiodarone
Price: from 150 rub.
Russian budget substitute for cordarone.
Sotahexal
Price: from 90 rub.
Swiss antiarrhythmic drug with double action.
It has the following effects:
- Non-selectively blocks beta-adrenergic receptors;
- Suppresses calcium channels.
This is manifested by the following pharmacological effects:
- Extends the absolute refractory period, action potential;
- Slows heart rate and AV conduction
- Suppresses myocardial contractility.
Indicated for the treatment of atrial fibrillation and tachycardia.
It affects the respiratory system, so patients with COPD and bronchial asthma are not recommended to drink sotalol.
Class IV: calcium channel blockers
The positive results from the use of such antiarrhythmic drugs are due to the blocking of slow calcium channels.
Impaired transport of calcium ions inhibits myocardial conductivity. This lengthens the refractory period in the atrioventricular node.
Medicines in this group protect the heart from the negative effects of excessively high frequency stimuli. Reduces the automaticity of the sinoatrial node.
The antiarrhythmic effect is combined with a hypotensive and vasodilating effect.
Injection solutions and tablets are used:
- To relieve a hypertensive crisis (in injection form);
- In the treatment of arterial hypertension;
- For the prevention and treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias.
Drugs of this class have characteristic side effects:
- Swelling of the ankles;
- Flushing of blood and redness of the face;
- Excessive decrease in pressure;
- The occurrence of bradycardia (slow heartbeat).
Diltiazem
Price: from 100 rub.
Taken three times a day.
The doctor chooses the required dosage, taking into account the patient’s condition. If the effectiveness is insufficient, the dosage can be increased.
Verapamil
Price: from 60 rub.
The dosage regimen is individual, on average 3 doses per day are required.
Isoptin SR
Price: from 450 rub.
American original drug containing a prolonged form of verapamil.
This form of release ensures a constant concentration of the drug in the blood plasma, so there are no side effects in the form of sudden surges in pressure and pulse rate.
Taken once a day.
Other antiarrhythmic drugs
This includes a number of drugs used for arrhythmia as an independent or auxiliary remedy.
Digoxin
Price: from 50 rub.
Produced in tablets and ampoules with injection solution.
Coming with a cardiac glycoside, it excites nerve endings localized in the heart, reflexively slowing down the frequency of its contractions.
Affects the transport of ions across the membrane:
- Reduces the penetration of K+ ions;
- Increases Na+ concentration.
Increases the force of myocardial contractions, stroke volume of blood increases.
There is a vasodilating effect.
A number of factors influence a positive result:
- Eating food and other medications;
- Dosage form;
- Digestive health.
This is a fairly serious drug that should not be taken without a doctor’s recommendation due to a possible overdose. The following symptoms develop:
- Pain of various localizations;
- Arrhythmia;
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain;
- Visual impairment (dots before the eyes, yellow-green spots).
Coraxan
Price: from 1150 rub.
A French antiarrhythmic drug based on the latest generation substance - ivabradine, developed in Europe.
By influencing the If channels of the sinus node, it prevents the occurrence of spontaneous diastolic depolarization. Normalizes heart rate without affecting the speed of electrophysiological processes and myocardial contractility.
Increases tolerance to physical activity.
Prevents the development of hypoxia in myocardial cells and complications such as coronary heart disease.
The medicine has undergone many clinical trials, confirming the safety and positive results from its use.
Does not have a negative effect on endocrine processes. Fat and glucose levels do not change.
Approved for use in diabetes mellitus.
With long-term treatment (more than 1 year), there is a steady decrease in tachycardia.
A possible side effect is changes in color perception, sensitivity to bright light.
Indicated for patients with angina accompanied by normal sinus rhythm.
Restrictions on use are similar to beta-blockers.
Bravadin
Price: 500 rub.
An analogue of Coraxan from a company specializing in the production of high-quality generics.
It is distinguished by the presence in the assortment of advantageous packages of 56 tablets.
Ryan
Price: from 600 rub.
Hungarian antiarrhythmic drug with ivabradine.
Panangin
Price: from 150 rub.
A vitamin product containing potassium and magnesium salts is used as an adjuvant. The antiarrhythmic effect is due to the normalization of metabolic processes.
The drug has a positive effect when rhythm changes are caused by electrolyte imbalance.
An overdose may cause respiratory depression.
The medicine is available without a doctor's prescription and can be used for preventive purposes.
Vitamins enhance the effectiveness of other cardiovascular medications and have a positive effect on nervous regulation.
Asparkam
Price: from 60 rub.
Domestic budget substitute for Panangin.
Useful: Cough syrup for children