Detailed description of the study
Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum. Transmission of infection occurs primarily through sexual contact without the use of barrier contraception. However, it is possible to become infected with treponema pallidum through contact and household contact if personal hygiene rules are not observed, as well as transmission of the pathogen from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. Syphilis can affect any organs and systems. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease becomes chronic. Initially, a hard chancre is formed at the site of contact with the source of infection - a painless ulcer with a small amount of transparent content on the surface. Often the body reacts to the introduction of the pathogen by inflammation of the lymph nodes located near the site of the lesion. Within a few weeks, a scar forms in place of the chancre. However, the disease does not recede, and after some time the infected person notices the appearance of a specific rash on the body - the appearance of small bright pink spots (rosacea rash). This stage is called secondary syphilis. The disease is prone to periodic exacerbations with changes in the nature of the rash. Tertiary syphilis is the result of untimely diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Along with the formation of nodes and tubercles on the skin, which are called gummas, prone to ulceration and scarring, damage to internal organs is observed. Diagnosis and treatment of syphilis is carried out by a dermatologist. To confirm the diagnosis, a modern test for determining rapid plasma reagins, or RPR test (Rapid Plasma Reagins), is used. These proteins are antibodies to the lipid components of cells destroyed by the pathogen.
The most frequently asked questions about syphilis tests
02.08.2018
Quantity
The most frequently asked questions about syphilis tests
How to get tested for syphilis for free?
To do this, you need to go to the clinic at your place of residence and visit your local doctor, who will give you a referral for testing. Testing for syphilis is free for all residents of the Russian Federation under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Where can I get tested for syphilis anonymously?
Tests can be done anonymously in any paid laboratory; skin and venous dispensaries often offer this service themselves. It is also possible to test for syphilis at home using rapid tests that are sold in pharmacies. However, it must be remembered that such a test does not give an accurate result, and if you suspect syphilis, you should consult a doctor.
How many days after sexual intercourse can you donate blood for syphilis?
If infection has occurred, the test for syphilis will be positive no earlier than ten to fourteen days later. This period may be longer, so if the results are negative, the test should be repeated after 2 weeks.
Where is blood taken for syphilis?
Blood for syphilis is most often taken from a vein, but can also be taken from a finger. It depends on the type of analysis.
Preparation. How to get tested for syphilis?
Before donating blood for syphilis, you should not eat for four hours—blood must be donated on an empty stomach. In addition, you should not drink alcohol 12 hours before the test. This is important because liver damage from alcohol can cause false positive tests.
How long does it take to test for syphilis on average?
The results are usually known the next day. Conducting rapid tests takes no more than 30 minutes.
What test is taken for syphilis and what is it called?
For screening, when there is no suspicion of the disease, either RMP (microprecipitation reaction) or RPR (rapid plasma-reagin test). Sometimes such screening tests are called the Wasserman reaction. If there are any real suspicions or doubts, they are never limited to one analysis. At the same time, one of any of the screening group (RMP or RPR) and one of any of the more specific testing group (RPGA or ELISA) are performed, then they act depending on the results and the patient’s history.
Can a syphilis test be wrong?
Maybe!
The probability of error in different methods depends primarily on the period of illness and the general condition of the body. Non-treponemal tests are most sensitive at the height of the disease - in the secondary period. Due to their low specificity, they often give false-positive results. This can happen due to fever, flu or other infectious disease, recent vaccination, chronic diseases and a number of other reasons. Treponemal tests are more sensitive in the later period. They can also give false-positive results, but only if there are pathogenic bacteria similar to Treponema pallidum in the body that cause other diseases: non-venereal treponematoses pinta (rare in Russia) or Lyme disease (transmitted through a tick bite).
False negative test results are possible with all diagnostic methods. They depend on the body's immune response: no response - no reaction to syphilis. This is possible in people infected with HIV, as well as those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. In addition, there is a reverse reaction: hyperproduction of antibodies, the “prozone” effect, in which there are so many antibodies that they prevent each other from reacting with the antigen. The result is a false negative result.
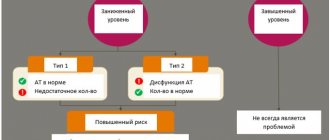
For a simpler understanding of the material, here is a table of deciphering the results of a clinical and laboratory examination of a patient:
• If the non-treponemal test (one of the RMP/RW/RPR) and the treponemal test (RPGA/ELISA) are positive, an additional alternative treponemal test is performed (ELISA if the first test was RPGA, and vice versa - RPGA if there was an ELISA). If the test becomes negative, the patient's blood is sent to an expert laboratory and additional tests are performed. If the second treponemal test becomes positive, a diagnosis of “latent syphilis” is made. This condition may persist for some time after treatment. If the patient has been treated before, then in order to confirm the diagnosis, an additional test for IgM is performed. If the results are positive, the diagnosis is confirmed, but the test is still recommended to be repeated after 2 weeks. If the results are negative, syphilis is refuted. • If the non-treponemal test (RTP/RW/RPR) is negative and the treponemal test (RPGA/ELISA) is positive, then the condition can be assessed as “late syphilis” or “no syphilis” if the patient has previously been fully treated. To distinguish between these two conditions, an additional IgM test is performed (IgM ELISA, RIF-abs-IgM, Immunoblotting-IgM). If IgM is present in the blood, they diagnose “late syphilis” and treat it. If not, the patient is considered healthy. • If RPR (or RW/RMP) is positive, RPGA is positive, and ELISA is negative (or vice versa: RPGA “-” and ELISA “+”), then the test results are questionable and it is recommended to send the blood to an expert laboratory or conduct alternative tests (RIF , Immunoblotting). • If the non-treponemal test (PMP/RW/RPR) is positive and the treponemal test (RPGA/ELISA) is negative, then an additional treponemal test (ELISA/RPGA) is performed. If it gives a positive result, the blood is sent to an expert laboratory. If negative, then the diagnosis is refuted, and the result of the non-treponemal test is considered false positive.
| RPR/ RW/ RMP | RPGA | Treatment was carried out | Diagnosis | Further tactics | |
| + | + | + | — | Hidden syphilis | ELISA/RIF for IgM |
| + | + | + | + | Condition after treatment | Observation by a doctor is recommended, repeat tests after 2 weeks |
| + | — | + | — | Questionable test result | It is recommended to send the blood to an expert laboratory |
| + | + | — | — | Questionable test result | It is recommended to send the blood to an expert laboratory |
| — | + | — | — | Questionable test result | It is recommended to send the blood to an expert laboratory |
| + | — | — | — | False positive result. The patient is healthy | No treatment required |
| — | + | + | + | Condition after treatment, the patient is healthy | Removal from the register |
Preparation for delivery
When preparing to take the test for bladder cancer, you need to follow several recommendations:
- Blood must be donated on an empty stomach. You are allowed to drink plain water before the collection.
- It is recommended to eat your last meal 8 hours before donating blood.
- On the eve of the analysis for bladder cancer, it is recommended to remove fatty, spicy or fried foods, as well as alcoholic beverages from the daily diet.
- Before the analysis, try to avoid heavy physical activity.
- Be sure to notify your doctor about taking medications, the presence of diseases or pathologies, or feeling unwell.
To test for bladder cancer, blood is taken from a vein.
What it is
During hospitalization or preoperative examination, the patient should be aware of the blood test for bladder cancer, that this is a routine procedure that everyone must undergo.
The principle of microprecipitation is the detection of antibodies in the blood to the cardiolipin antigen found in the membranes of the causative agent of syphilis, Treponema pallidum and other microorganisms from the genus Treponema of the order Spirochaetales. The reaction is based on the phenomenon of precipitation—precipitation of a mixture of blood serum and reagent. If a precipitate forms, the test is considered positive. A reaction with the formation of a precipitate is considered positive.
Syphilis infection
Antibodies to treponema begin to be produced in the early stages of syphilis infection. RMP is carried out in the blood or the contents of a lymph node. Analysis for bladder cancer allows you to diagnose the disease at its onset.
What does it mean to donate blood for breast cancer?
This study is the first in the chain of necessary tests to diagnose syphilis. The principle of its operation is based on the recognition of antibodies to cardiolipin (an element located inside the membranes of bacteria). These antibodies begin to form at the initial stage of the disease (after several weeks of illness). To carry out the analysis, blood is taken from the patient or a lymph node is punctured. In 80% of cases, such a study makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage.
A blood test for bladder cancer is prescribed strictly according to indications
Total antibodies to Treponema pallidum: explanation
A positive reaction to antibodies to Treponema pallidum indicates different clinical stages of syphilis (primary, secondary, latent). Also, a positive test result for total antibodies to Treponema pallidum may persist for some time after a course of treatment for syphilis (“serological scar”).
The test result is negative in the absence of infection or early primary syphilis.
The test for total antibodies to Treponema pallidum may have an equivocal result. Then a repeat analysis for total antibodies is carried out a couple of weeks later.
When is a test ordered?
The main indications for blood sampling for RMP are:
- examination before surgery or admission to hospital;
- mandatory examinations for syphilis of pregnant women, donors and people of certain professions;
- the appearance of the first signs of the disease (enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area, rash on the skin);
- completion of drug treatment of the disease.
Also, a study of breast cancer is mandatory for a child born from an infected mother.
Important! Don’t be afraid to donate blood for bladder cancer; it is best to diagnose the disease in the early stages than to deal with complications later.