Tachycardia, which is characterized by increased heart rate, often has nothing to do with blood pressure readings. A high pulse with normal pressure, if it persists for a long time or occurs with a certain frequency, indicates the development of serious pathologies. To establish the cause and make an accurate diagnosis, you should undergo a full examination.
Validol
Validol belongs to the group of vasodilators and has a sedative effect. These tablets are good for high heart rate, but have virtually no effect on blood pressure levels.
Important! The product is indicated for sublingual (sublingual) use. Thanks to this, the therapeutic effect is achieved 3-5 minutes after the tablet is dissolved.
Contraindications:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- sugar intolerance;
- diabetes mellitus (with caution).
Side effects:
- allergic reaction - itching, skin rashes, urticaria, Quincke's edema;
- lacrimation;
- nausea;
- dizziness.
Adverse symptoms disappear on their own after reducing the dosage or stopping therapy.
Why does rapid heartbeat occur?
The occurrence of rapid heartbeat can be triggered by various factors, including both the body’s natural reactions to the influence of external stimuli and the presence of pathological changes in organs or systems.
Rapid pulse has two forms of occurrence: physiological and pathological. Physiological palpitations appear against the background of psychoemotional disorders, excessive physical exertion, prolonged exposure to sunlight, overeating, insomnia, consumption of alcohol, caffeine, drugs, hormonal activity with increased arousal. Heart rhythm disturbances due to such influence factors are a natural compensatory reaction of the body. Treatment of physiological tachycardia is not required. To stop an attack, just calm down and rest.
The pathological form of a rapid pulse occurs due to the presence of concomitant diseases, in which rhythm disturbance acts as a symptom, and treatment of cardiac tachycardia with tablets is an integral process.
Such pathologies include:
- hypertonic disease;
- heart disease (myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, heart failure);
- pathologies of the endocrine system (hypothyroidism, hypoglycemia, diabetes mellitus);
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs (anemia, leukopenia);
- renal failure;
- malignant neoplasms;
- internal bleeding;
- brain damage;
- infectious pathologies.
Treatment of palpitations, which is determined solely by the attending physician, directly depends on the etiology of the condition.
In pregnant women, the condition is diagnosed in 70%. The increase in pulse rate in this category of patients occurs by 10-20 units even in a normal state. This process is natural, since a woman gains weight and often succumbs to stress. As a medicine for discomfort during tachycardia, you can use sedative drugs with a natural composition, for example, valerian or motherwort.
Asparkam
Asparkam is a medicine from the group of antiarrhythmics. It also does not cause a decrease in blood pressure. The daily dose for an adult is no more than 6 tablets, which must be divided into three doses.
Asparkam should be taken after meals.
Contraindications:
- increased sensitivity to the component composition;
- cardiogenic shock;
- severe myasthenia gravis;
- dehydration;
- increased content of magnesium and potassium in the body;
- oliguria;
- anuria;
- metabolic acidosis;
- atrioventricular block 2–3 degrees;
- liver dysfunction;
- high risk of developing edema.
Side effects:
Causes of rapid heart rate with normal blood pressure
- nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain;
- loose stools;
- dry mouth;
- abdominal discomfort;
- decreased blood pressure;
- myocardial conduction disturbance;
- paresthesia;
- convulsions;
- skin rashes;
- itching;
- facial redness;
- feeling of heat.
Pathological causes
A rapid pulse can be observed against the background of normal blood pressure with congenital and acquired heart defects. These pathological conditions are characterized by a variety of manifestations and have varying degrees of danger. In most cases, the problem can only be eliminated surgically.
Another common cause of rapid pulse associated with the development of cardiac pathologies are inflammatory diseases that affect the structure of the heart muscle. These are myocarditis, endocarditis, rheumatism, etc. Without appropriate therapy, these diseases pose a threat to life.
Rapid pulse also occurs for the following pathological non-cardiac reasons:
- Dehydration. When the body loses a lot of fluid, the blood thickens. This increases the load on the heart muscle, which causes it to contract more intensely.
- Infectious diseases. When the temperature rises, the body becomes intoxicated. In order to quickly remove harmful substances from the body and normalize the condition, the heart begins to pump blood faster.
- Neurotic diseases. The level of stress increases in such cases due to the release of large amounts of stress hormones.
- Hormonal disorders. As a rule, they are associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. An increased amount of hormones leads to intoxication of the body. Against this background, the heart muscle begins to work more intensely.
- The occurrence of severe bleeding. This is due to a violation of the volume of blood circulating in the body. To provide tissues with the necessary amount of nutrients and oxygen, it is necessary to accelerate the pumping of hematological fluid through the vessels.
- Anemia. Most often, increased heart rate is observed with iron deficiency anemia. Additionally, increased fatigue with minimal physical activity and deterioration of the condition of the skin and nails are noted.
Bisoprolol
Bisoprolol is used to normalize pulse at high blood pressure. The active substance is bisoprolol fumarate. The drug belongs to the group of β1-blockers. It has the following effects: antianginal (elimination of symptoms of myocardial ischemia), antiarrhythmic (reduces heart rate), antihypertensive (normalization of blood pressure).
Important! The drug has a fairly large list of contraindications, so before you start taking it you need to make sure that they are absent.
During treatment, a person may experience:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- flushes of blood to the face;
- sleep disorders;
- depression, hallucinations (rare);
- paresthesia;
- disruption of tear production;
- conjunctivitis;
- pain in the abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting;
- stool disorders - diarrhea and constipation are possible;
- muscle weakness;
- convulsions;
- increased sweating;
- bradycardia.
The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with psoriasis, diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, predisposition to allergic reactions and those people whose work is associated with a high speed of psychomotor reactions.
Blood thinners for heart problems
Separately, it is worth considering blood thinners, which are prescribed to prevent the formation of dangerous blood clots. These medications include antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants, which have the side effect of increasing the risk of bleeding. If a doctor prescribes one of these drugs to a patient, this means that great care must be taken with any injury, surgery, or even dental procedures.
Antiplatelet agents
These drugs work by directly affecting the function of platelets in the blood. Platelets are special cells that help stop bleeding by sticking together and forming a clot.
List of drugs with antiplatelet action:
- clopidogrel (Plavix);
- prasugrel;
- tirofiban (aggrastat);
- dipyridamole.
Anaprilin
Anaprilin belongs to the group of beta-blockers. It has hypotensive, antiarrhythmic and antianginal properties. The active ingredient is propranolol. The drug is used if the blood pressure is high and the pulse is significantly increased.
The drug is effective in the initial stage of arterial hypertension, so the drug is used in young patients. A decrease in systolic pressure is accompanied by a decrease in the frequency of myocardial contractions.
Anaprilin is part of the group of beta-blockers
Contraindications:
- arterial hypotension;
- individual intolerance to the component composition;
- heart failure;
- atrioventricular block;
- sinus bradycardia;
- diabetes;
- predisposition to the development of bronchospasm;
- myocardial infarction;
- bronchial asthma;
- period of gestation and breastfeeding.
Side effects: bradycardia, bronchospasm, nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, hypoglycemia, blurred vision, decreased potency, heart failure. If the regimen and dosage of the drug are not followed, the development of the following conditions cannot be ruled out: arrhythmia, convulsions, difficulty breathing, bronchospasm, dizziness, heart failure.
In case of overdose, Anaprilin can greatly reduce the pulse. The drug should absolutely not be combined with alcohol intake. In this case, death cannot be ruled out. The medicine cannot be combined with antipsychotics and tranquilizers. In the case of long-term course treatment with Anaprilin, the use of cardiac glycosides is recommended.
Symptoms of increased heart rate
Usually, when the pulse increases, the patient feels some discomfort in the heart area. It manifests itself primarily in the heartbeat (with a normal pulse, a person does not feel the work of his heart). The heart is pounding, “jumping out of the chest.” Pain of various types may appear behind the sternum or in the left half of the chest.
Due to deterioration of blood supply to the whole body, symptoms such as:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- severe shortness of breath, with difficulty in inhaling;
- nausea;
- sleep disturbance;
- nausea and even vomiting;
- loss of consciousness.
All this precedes the detection of an increased pulse and very often requires the intervention of specialists.
Persen
Persen belongs to the group of herbal preparations. Extracts of valerian, lemon balm, and peppermint are used as active ingredients. Thanks to its complex composition, Persen has a calming (due to the presence of valerian), mild sedative and antispasmodic effect. The pulse-lowering ability is based on calming the human central nervous system.
Contraindications:
- individual intolerance to glucose, lactose;
- lack of sucrose;
- diseases of the biliary tract – gallstones, cholangitis and others;
- arterial hypotension;
- bearing a child and the period of breastfeeding;
- children's age - Persen is not prescribed to children under 12 years of age;
- intolerance to the component composition of the drug.
In the presence of gastroesophageal reflux disease, the drug is prescribed with caution. During treatment, allergic reactions and constipation may develop. The tablets should be taken orally with the required volume of any liquid.
Persen is a herbal preparation with a calming effect
The duration of the course is no more than 1.5 months. After stopping treatment, withdrawal syndrome does not develop. An overdose of Persen (in case of taking more than 60 or more tablets at the same time) is indicated by the appearance of nausea, general weakness, dizziness, and hand tremors. Treatment of the condition is symptomatic.
The drug should be taken carefully with antihypertensive and hypnotic drugs, since Persen enhances the effect of these medications. If such a need arises, dosage adjustments will be required.
Valerian
To normalize a rapid pulse with normal blood pressure, you can use valerian tablets. They contain an extract from the plant as the main active ingredient. The drug helps not only to lower the heart rate by reducing the degree of excitability of the central nervous system, but also has a hypnotic and sedative effect.
Important! The sedative effect develops slowly but is stable.
Contraindications:
- individual reaction to the components of the tablets;
- depression and other conditions accompanied by central nervous system depression;
- galactose intolerance;
- lack of lactase;
- glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Side effects:
- increased drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- feeling depressed;
- poor performance;
- headache;
- nausea;
- allergic reactions - skin rashes, itching, local swelling - in case of intolerance to the component composition of the drug.
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to reduce the dosage or completely stop taking Valerian. According to the instructions, adults and children over 12 years of age need to take one or two tablets three times a day. They must be swallowed without chewing, washed down with the required volume of any liquid.
The decrease in heart rate, due to a decrease in the excitability of the central nervous system, occurs slowly. For this reason, the drug is not suitable for emergency use. An overdose is indicated by:
- dizziness;
- drowsiness;
- headache;
- lethargy, general weakness;
- hand trembling;
- dilated pupils;
- visual and hearing impairment;
- feeling of tightness behind the sternum.
Treatment of the condition involves gastric lavage and taking activated carbon tablets. If necessary, carries out symptomatic therapy. Valerian enhances the effect of ethanol, antispasmodics and sedatives. If a person simultaneously takes synthetic sedatives, he needs constant medical supervision.
Features of the treatment of heart rhythm disorders
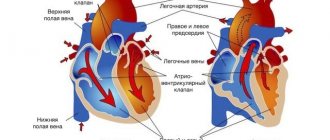
If patients experience irregular beating of the upper chambers of the heart, arrhythmia is diagnosed. For example, after a good amount of stress, the atria become out of sync with the lower chambers, called the ventricles. When this happens, not all the blood is pumped out of the heart. This can cause blood to fill the atria, which can cause clots to form. If one of these clots begins to move, it can restrict blood flow to the brain, which in turn can lead to a stroke.
Arrhythmia can lead to stroke
People with arrhythmia may suffer from strong and irregular heartbeats both on a regular basis and in certain abnormal life situations. Fortunately, modern pharmaceuticals offer many medications for the treatment of arrhythmia. Cardiologists usually do not recommend treating heart problems with natural remedies, but rather immediately start taking synthetic drugs.
Only tablets will quickly and effectively help regulate and control your heart rhythm and its speed. As a positive side effect, patients may notice a decrease in high blood pressure and an overall feeling of well-being. In addition, most of the following medications will also help prevent blood clots.
New generation of drugs
New generation drugs that reduce the pulse to normal but do not reduce blood pressure include Ivabradine and Coraxan
Ivabradin
Ivabradine belongs to the group of antianginal and anti-ischemic drugs. The decrease in heart rate at rest occurs by approximately at least 10 beats per minute. The myocardium works in a more relaxed mode. Additionally, there is a decrease in oxygen consumed by the heart muscle.
Contraindications:
- myocardial infarction;
- significant reduction in blood pressure;
- bradycardia;
- cardiogenic shock;
- sinoatrial block;
- chronic heart failure;
- lactation;
- presence of an artificial pacemaker;
- unstable angina;
- pregnancy;
- allergy to the active ingredient;
- age up to 18 years.
When using Ivabradine, the likelihood of developing bradycardia is minimal
Side effects:
- bradycardia;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- extrasystoles;
- fainting conditions;
- muscle cramps;
- nausea;
- diarrhea/constipation;
- shortness of breath, etc.
Coraxan
Coraxan belongs to the group of antianginal drugs. The active ingredient of the drug is ivabradine. The medicine helps normalize heart rate without having any effect on blood pressure.
Contraindications:
- acute period of myocardial infarction;
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- bradycardia (with heart rate less than 60 beats per minute);
- cardiogenic shock;
- renal/heart failure;
- arterial hypotension;
- non-adaptive artificial pacemaker;
- age up to 18 years.
Coraxan can be taken with caution and under constant medical supervision (in a hospital setting) in the following cases: congenital long QT syndrome, recent ischemic stroke of the brain, second-degree atrioventricular block.
Coraxan is a dose-dependent drug, therefore, if the prescribed dosage is exceeded, the development of the following side effects cannot be ruled out:
- feeling of heartbeat;
- atrioventricular block;
- acquired weakness of the sinus node;
- atrial fibrillation;
- headache;
- allergic reactions;
- increased drowsiness, fatigue;
- general malaise.
Causes of increased heart rate
The normal heart rate for a healthy person is 60-90 beats per minute. These figures are relatively arbitrary; they guide doctors in their work. Practice shows that people with a pulse of 55 or 98 can feel quite satisfactory, unless, of course, they are among those who look for sores in themselves only based on the numbers on the tonometer display.
Most often, the pulse quickens under the influence of emotional or physical stress. This is a normal process aimed at satisfying the body’s increased needs for oxygen. However, tachycardia can also occur under the influence of other factors:
- panic attack;
- taking certain medications;
- drinking excessive amounts of coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- taking amphetamines;
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- deficiency of potassium and magnesium in the blood;
- increasing the production of thyroid hormones;
- a sharp release of adrenaline and norepinephrine with pheochromocytoma;
- myocardial ischemia in coronary heart disease.
By the way, people often fall into a state close to panic when using automatic blood pressure monitors with a low-quality heart rate monitor. To avoid this, it is best to learn how to measure the pulse by feeling it on the radial artery of the hand. You need to feel the pulsation on your wrist with your index, middle and ring fingers, count the number of beats in 30 seconds and multiply by two.
Additional recommendations
High pulse and low blood pressure are a serious condition, since many drugs intended to normalize heart rate further reduce blood pressure. Beta-blockers, cardiac glycosides, medications intended to replenish magnesium and potassium deficiency, drugs with a sedative effect, and tranquilizers can stabilize the pulse and at the same time increase blood pressure.
For low pulse and high blood pressure, medications should be selected by the attending physician. With such a combination, there are no emergency remedies. The most commonly used long-acting antihypertensive (BP-lowering) drugs are:
- angiotensin receptor blockers – Valsacor, Lozap;
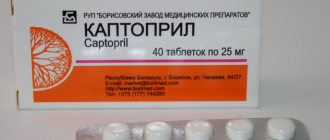
- ACE inhibitors – Capoten, Enalapril;
- alpha-blockers – Tonacardin, Doxazosin;
- diuretics – Hypothiazide, Furosemide.
The majority of these drugs are available only by prescription. Regardless of the type of problem that arises, medications should be selected by a specialist. Self-medication can only aggravate your well-being and provoke deterioration. This is why it is so important to obtain specialized medical advice.
How to quickly lower your heart rate at home
In cases of tachycardia, it is extremely important to provide assistance as quickly as possible. Complications of this condition can be quite serious: pulmonary edema and cardiogenic shock are deadly conditions that, without emergency assistance, lead to the inevitable death of the patient. Fortunately, more often the increase in heart rate occurs for physiological reasons, and in these cases you do not even have to take pills that lower your heart rate.
The first thing to do is to conduct one of the vagal tests. These are certain manipulations that cause an increase in the work of the vagus nerve, which inhibits the work of the heart:
- Valsalva maneuver - drawing air into the chest and exhaling it with the mouth and nose closed. Of course, you won’t be able to exhale, but that’s not the goal;
- deep, quick inhalation and slow exhalation;
- light massage of the eyeballs;
- washing your face with cold water or immersing your face in a basin of cold water (carry out only in the presence of another person);
- irritating the root of the tongue with a spoon, as when trying to induce vomiting (if an episode of vomiting occurs, it’s okay).
Each of the above actions can be carried out for no more than 30 seconds. In many cases, this is enough to reduce the heart rate by 20-30 beats.
However, situations also arise in which vagal tests alone are not enough, and then you have to take pills or administer medications intravenously. For tachycardia use:
- adenosine;
- beta blockers (metoprolol, bisoprolol, labetalol, etc.);
- calcium channel blockers (verapamil, amiodarone);
- cardiac glycosides (digoxin, corglycon, strophanthin);
- sodium channel blockers (procainamide, disopyramide);
- potassium channel activators (lidocaine).
All these drugs can only be used as prescribed by a doctor and in a clearly indicated dosage. The Dobrobut.com website strongly recommends not using them as self-medication - it can be dangerous!
For increased heart rate and low blood pressure, doctors usually prescribe one of the drugs that increases blood pressure along with an antiarrhythmic drug. In emergency settings, this is most often phenylephrine (Mezatone). In cases where a decrease in pressure is caused by a global disturbance of the systemic circulation (usually this occurs when the pulse increases to critical values - 150 and above), an intravenous drip infusion of dopamine, a specific agent for raising blood pressure, is possible.