Sometimes problems with the cardiovascular system become so serious that conservative treatment methods no longer have the desired effect. If the patient is diagnosed with atherosclerosis, which has seriously affected one or more vessels, surgical intervention is indicated. In the problem area, certain manipulations are carried out aimed at restoring normal vascular patency and the correct functioning of the entire cardiovascular system.
If blood vessels are blocked by atherosclerotic deposits, the heart tissue experiences oxygen starvation. This leads to the occurrence of coronary disease. This condition is extremely dangerous for the patient’s life, especially in the case of complete blockage of the vessel, which entails myocardial infarction. However, today there are effective methods for treating coronary heart disease - stenting and bypass surgery.
What are coronary stents and why are they needed?
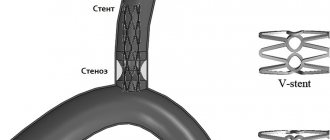
A coronary stent is a medical device that is a frame in the shape of a metal cylinder, installed in narrow places in the artery (with cholesterol deposits) to widen them, thereby ensuring normal blood flow.
Stents can combat arterial stenosis that occurs due to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques. Cholesterol is deposited on the walls of the arteries and narrows the lumen, thereby preventing blood flow. Poor blood flow causes oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients in the organs. One of several ways to relieve such bottlenecks in the arterial system is stenting. Installation of a stent is not always indicated for the patient, but only in some severe cases when there are no contraindications, but more on that later.
Relevance of the operation
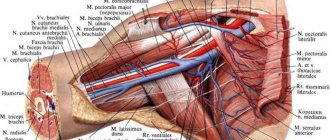
Coronary arteries are the arteries that supply the heart muscle.
There are 2 main vessels:
- Arteria coronaria dextra. This artery (blood, nutrients passing through the branches) supplies the right wall of the right ventricle, the septum, and the posterior wall. The vessel is small.
- Arteria coronaria sinistra. It supplies blood to the left parts of the myocardium, the anterior wall (almost all), most of the septum and the apical region.
Each artery has a large number of connections. Due to this, when the branches narrow, blood flows to the muscle from the pool of another vessel (in a smaller volume). This provides protection against coronary syndrome and acute heart attack. When small branches are blocked, muscle damage will be moderate. Coronary blood flow does not decrease significantly.
| Type of intervention | Price |
| Stenting of coronary arteries | 110,000 - 220,000 rub. |
However, it is important to understand that the coronary arteries play a major role in the functioning of the heart muscle. It is thanks to them that the blood supply to the heart is ensured. Blood flowing through the arteries supplies all heart cells with oxygen and essential nutrients, so that the organ functions properly. If the vessels narrow due to atherosclerosis or myocardium, the heart stops working at full capacity. Because of this, changes occur in tissues at the biochemical level. The consequence of obstruction of the coronary vessels is coronary artery disease. Ischemic disease involves damage to the myocardium.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Application area
One of the common causes of the development of heart pathologies is a decrease in vascular elasticity and vasospasm. The arteries gradually lose their ability to expand, which leads to local disturbances in blood supply. Also, if the process is chronic, this contributes to the accumulation of cholesterol deposits on the vascular walls. Scientists all over the planet are actively working to develop an effective method to combat this disease. Coronary stenting is one of the existing ways to solve the problem.
Stenting is a procedure for integrating a special dilating device into a vessel. It is a tube with a mesh texture that can take the desired shape when implanted. The device acts as a frame. As a result, the narrow or spasmodic section of the artery should expand, and the blood flow should return to its previous state.
This treatment method belongs to endovascular surgical interventions and is considered minimally invasive. It is performed exclusively by experienced surgeons of the highest category.
Let's consider the stenting algorithm using the heart as an example. The catheter on which the element is fixed is passed through the femoral artery through the introducer. The conductor must be moved to the designated area where it is planned to install the expander. As soon as the catheter is inserted, the artificial frame is fixed, inflated under the action of the balloon, and normalizes blood supply to the heart muscle.
The operation involves local anesthesia. The average duration is relatively short, from 20 minutes to 3 hours. If necessary, the surgeon installs several devices at once.
What symptoms should you look out for? When should I contact a doctor to schedule surgery?
Note that the disease can develop very slowly, over years. That is why there is a possibility that the pathology will not make itself felt. As a result, the disease is detected very late.
However, common symptoms include:
- Chest pain and discomfort.
- Swelling of the legs.
- Shortness of breath.
- Severe fatigue even after little physical activity.
- Excessive sweating.
- Pain in arms and shoulders.
- Nausea.
You should listen especially carefully to the symptoms if you are at risk:
- Gender: male.
- Age: over 45 years old.
- Genetic factors: predisposition (when close relatives have heart disease).
- Weight: overweight, obese.
- Lifestyle: sedentary, sedentary.
- Bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Nutrition: predominance in the diet of fatty, salty, spicy, sweet foods rich in cholesterol.
- Associated pathologies: hypertension, stress.
If you suspect a pathology, you should immediately undergo diagnostics.
How is the disease detected?
Several methods are used to diagnose pathology.
Among them:
- ECG. Often, not a one-time study is carried out, but daily monitoring. It allows you to evaluate all the features of the heart and problems that arise during the day and night.
- Echocardiography.
- Treadmill test.
- CT scan.
- Electron beam tomography.
Particular attention in diagnosis is paid to such a method as angiography. This technique is aimed at studying the functional state of blood vessels, circuitous blood flow and the extent of the pathological process. In the shortest possible time, the doctor will be able to detect the pathology, identify its nature, location and degree of development.
The patient’s story about his condition is also very important. When going to the doctor, be prepared to list all the symptoms and talk about past illnesses. Remember! Further diagnosis and the accuracy of the diagnosis will largely depend on your story.
Indications
Installation of coronary stents may be indicated by a doctor in the following cases:
- complete blockage of the coronary artery during or after myocardial infarction;
- narrowing or complete blockage of the arteries with a high risk of heart failure;
- narrowing or complete blockage of blood vessels with a high risk of severe angina.
Stenting is done only in cases where there are no contraindications to the operation. In another case, bypass surgery is performed.
Prognosis after treatment
Coronary angioplasty significantly increases blood flow through a previously narrowed or blocked coronary artery. In this case, chest pain (angina) should usually decrease, and the physical capabilities of the body, on the contrary, should increase.
You need to understand that angioplasty and stenting do not cure coronary heart disease, but only eliminate specific circulatory disorders of the heart muscle. To achieve a stable result, you must lead a healthy lifestyle and take medications prescribed by your doctor.
If the symptoms of angina return, then you need to contact your doctor again, and if you have chest pain at rest that does not respond to nitroglycerin, then call an ambulance.
After coronary angioplasty and stenting, the quality of life improves in 95% of patients, with many of them maintaining the effect for more than 5 years.
Contraindications for surgery
- If intervention is required in an artery with a diameter of less than 3 mm.
- If the patient has a large number of cholesterol plaques, more than 1 centimeter in length.
- If the patient is allergic to iodine-containing drugs.
- If the patient has a large number of cholesterol plaques, more than 1 centimeter in length.
- If the patient has poor blood clotting.
- If the patient has a serious condition, accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, impaired consciousness, shock, liver, kidney or respiratory failure.
- The patient has malignant tumors that cannot be treated.
If a patient is contraindicated for stenting, but still wants this operation, then in some cases he may insist on having it performed at his own risk.
Types and types of coronary stents
Stents differ from each other:
- Length. The size of the stents varies from 8 to 38 millimeters.
- Diameter. There are from 2.25 to 6 millimeters.
- By design. They differ in the shape of the elements from which they are created.
- Material. They are made from steel, cobalt-chrome, PLLA polymer and others.
- Coated. Stents are available without coating or with drug coating Sirolimus, biolimus and others.
- Method of disclosure. They can open either independently or with the help of a balloon on a catheter.
- By type of drug coating. The medications used are Sirolimus, everolimus, paclitaxel and others.
By lenght:
Stents are available: 8, 10, 13, 16, 18, 23, 28, 33, 38 mm.
By diameter:
Stents are available: 2.25, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.25, 3.5, 3.75, 4, 4.25, 4.5, 4.75, 5, 5.25, 5.5, 5.75, 6 mm.
By design:
- mesh (made of woven mesh);
- tubular (from a tube);
- wire (made of wire);
- ring (from separate rings).
According to the material from which the frame is made:
- stainless medical steel;
- cobalt-chrome alloy;
- alloy of platinum and chromium;
- polylactose acid (PLLA) polymer.
By type of coverage:
- Uncoated with bare metal.
- Drug-coated, which releases a drug that reduces the likelihood of future artery narrowing.
- With double coating - external and internal, to heal the artery itself and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Coated with antibodies, attracting endothelial cells, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Dissolving, made from a material that dissolves and releases a drug coating that prevents the recurrence of stenosis.
By opening method:
- self-expanding;
- opened by a balloon.
By drug coverage:
- Sirolimus;
- Zotarolimus;
- Everolimus;
- Biolimus;
- Paclitaxel.
Depending on the manufacturer, stents may differ in their characteristics and price. In Russia, the production of stents is carried out in accordance with GOST R ISO 25539-2-2012.
Stenting or bypass surgery: pros and cons
Let's start with the fact that each method of operation has its pros and cons. Stenting (angioplasty with stenting) is performed if the arteries are affected in 1-2 places. If three or more vessels are affected, and also if the plaque is long-lasting, then, of course, bypass surgery .
Rice. Angioplasty with stenting
Stenting
Stents are placed on balloons, which allows them to have very small dimensions when unexpanded, and after the balloon is inflated inside the coronary artery, they expand, remaining in this position forever.
When stenting blood vessels, the lumen of the affected artery is restored to normal diameter. Stenting is performed invasively, through a catheter with a stent at the tip. The catheter is moved to the desired area, after which a stent is installed, which forms the required width of the vessel, and as a result, blood flow is normalized. In addition to low morbidity - no need to cut the chest - this procedure has a number of other advantages. This operation does not require general anesthesia, it has a short rehabilitation period and a minimal number of complications.
Currently, a variety of stent models are used in interventional cardiology, differing from each other in certain design features. All of them are absolutely compatible with human organs and tissues, have a flexible structure and are elastic enough to support the artery wall.
Rice. Bypass surgery
Bypass surgery
Bypass surgery is performed through an open approach. This operation makes it possible to identify narrowing of the lumen of the vessel with higher accuracy. But at the same time, the postoperative period will be longer, since during the operation the chest cavity is opened. Like any surgical intervention, such an operation has its own risks; it should not be performed on patients of advanced age or with concomitant serious illnesses. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. It is more invasive and has a greater chance of complications, such as bleeding or infection.
Bypass or stenting?
Recently, cardiologists have given preference to stenting, which is performed without incisions in advanced medical centers.
Rice. Vessel stenting
Under X-ray control, a miniature balloon is inserted through a small puncture into the vessel affected by atherosclerosis, on which a thin metal tube-stent with a diameter of 2.5–4.5 mm is placed. The balloon moves into the narrowing area and inflates under pressure. The cholesterol plaque is flattened and the vessel expands to the desired diameter.
Rice. Coronary artery bypass surgery
With the development of stenting technology, the proportion of patients for whom bypass is only 5–10%. And this is understandable. Stenting is much less traumatic and the rehabilitation process after it is much faster (after 1–2 days the person is discharged home). It is not always possible to perform bypass surgery using minimal access. In addition, shunts made from your own veins inevitably age. They are susceptible to atherosclerosis and degenerative changes. At the same time, there are very few opportunities for re-restoring blood circulation. The same cannot be said about stents , which are now produced with a special drug coating that prevents restenosis (re-narrowing) of blood vessels.
Why is drug coverage important?
Drug coating of a stent plays a very important role in preventing restenosis (re-occlusion) of the coronary arteries at the site of its implantation. The drug coating (for example, sirolimus) consists of immunosuppressants, which in turn locally stop the growth of endothelial cells (the inner layer of blood vessels), thereby keeping the lumen of the vessel clear for blood flow.
Dr. BOSTI recommends high-quality stents Orsiro®, Magmaris® from BIOTRONIK (Germany)
The German company BIOTRONIK is a world leader in the production of coronary stents, introducing innovative and high-tech methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Rice. Orsiro® BIOTRONIK stent
Orsiro stent is indicated for complex patients and lesions, including:
- acute coronary syndrome;
- myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation;
- diabetes;
- high risk of bleeding;
- complex of lesions;
- small vessels;
- multi-vascular diseases.
Advantages and disadvantages of using stents
Stents are an outstanding invention that can save the lives of many patients. But it is not suitable for all patients suffering from stenosis. Like other medical instruments, stents have advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive, to eliminate the problem you do not need to make large surgical incisions on the body, but only a small hole on the body into which a catheter with a stent is inserted. Fast healing. The patient can be discharged on the 3rd day.
- Use of local anesthesia during surgery. There is no need to put a person to sleep. High percentage of successful cure (90%).
Flaws:
- There is a possibility of secondary stenosis, the appearance of blood clots and heart attacks. Occurs in 10% of patients.
- Complexity of the operation. The installation of stents in the heart is performed only by highly qualified surgeons.
- Some drug-eluting stents are expensive.
- Not all patients can undergo stenting - there are contraindications.
Bypass surgery and stent placement - is there a difference?
Coronary bypass surgery is performed for angina pectoris, restoration of blood circulation after a heart attack, and for its prevention. During the operation, healthy areas of the vessels are connected, bypassing the damaged ones. A kind of bridge is created. For bypass, an autovenous vein is used (usually the great saphenous vein of the thigh or leg). In some cases, coronary plastic grafts are installed to replace the damaged artery.
Bypass surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The chest is opened. The heart is stopped during the operation. A special device replaces the work of the organ and lungs. In some cases, bypass surgery has recently been performed on a beating heart.
Of course, there is a difference with the operation to install a stent. Your doctor will tell you about all the differences. He will also make a choice in favor of a specific technique.
The main indications for intervention for stent placement:
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Myocardial infarction.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Difference between stenting and bypass surgery
Both surgeries are performed to improve blood flow in areas where the arteries are narrowed due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. The difference between these methods is in the way they solve the problem of stenosis.
The bypass method involves creating a section of artery that bypasses the problem area. Normal blood flow is ensured through this new area. A section of the saphenous vein of the femoral, radial or internal mammary vein is used as a shunt. Bypass surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
Stenting involves installing a stent in a narrow place in an artery and expanding it, thereby normalizing blood flow. In this case, a shunt is not used, but the problem area in the artery is simply restored. The stent is inserted into the artery using a catheter with a balloon through a small hole in the body. At the desired location, the stent is expanded using a balloon and the catheter is pulled out. The operation takes place under local anesthesia.
Both methods are now used in medicine. Each patient is better suited to a certain method of operation based on his diagnosis and condition. Stenting is a more advanced method of treating stenosis, but it may be contraindicated for some.
What is cardiac stenting?
Stenting is a more modern, low-traumatic operation to restore the affected area of the vessel. The main direction of the intervention is restoration of the lumen of the vessel.
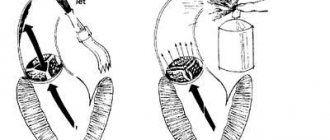
The essence of stenting is the introduction of a special balloon into the affected vessel, which opens under high pressure, destroys the atherosclerotic plaque and ensures patency of the vascular bed. The balloon is located in a stent - a special supporting structure made of a special alloy. When the balloon is deployed, the stent opens and remains in the vessel forever, fixing its walls and preventing the re-formation of atherosclerotic deposits. The balloon is removed from the artery.
Preparing for stenting
Before stenting, the patient is examined. They take basic tests, do echo and electrocardiography. Coronary angiography is performed by injecting contrast into the circulatory system and performing an X-ray examination. A map of the coronary arteries is obtained. The site of stent insertion is determined.
As a rule, to prepare for surgery, doctors may require:
- Avoid food and water 8 hours before surgery.
- Avoid taking blood thinning medications 3 days before stenting.
- Shave your groin and wash yourself.
- Eliminate or reduce the intake of glucose-lowering drugs 2 days before surgery.
Operation stages
- The operation is performed in an operating room equipped with an angiograph, which allows the doctor to observe the artery and the movement of the catheter on a monitor screen. The patient is placed on his back and sedated to keep him calm and relaxed.
- Doctors cover the patient with sterile linen and neutralize the stent insertion site.
- Local anesthesia is given.
- A thin wire is inserted into the artery through a needle, which acts as a conductor.
- An introducer is inserted along the guidewire, through which other instruments will be inserted into the artery and the wire is removed.
- Through the introducer, the doctor carefully inserts a thin catheter with a stent and a balloon.
- A contrast agent is injected into the coronary artery to accurately visualize the movement of the stent.
- The stent continues to be carefully moved to the desired location.
- The stent is expanded using a balloon on the catheter, thereby normalizing the diameter of the artery.
- After stent placement, the introducer and catheter are removed from the patient.
- A compressive bandage is applied to the catheter insertion site.
Hemostasis
What to do with a hole in an artery?
If the intervention was carried out through the radial artery (on the arm), a special bracelet with a cushion (hemostatic cuff) is put on the wrist, which will put pressure on the injection site and prevent bleeding. Depending on the situation, the cuff will remain on the arm from 3 to 12 hours.
In case of femoral access, there are 2 main options:
- Manual (manual) hemostasis. After the introducer is removed, the doctor presses with his hands on the injection site for 15 minutes. Then apply a pressure bandage for 6-8 hours. The patient should lie on his back with his leg straight.
- Closure devices are special “plugs” that allow you to close the artery from the inside. In this case, there is no need to put pressure on the leg and a pressure bandage is not needed. A special patch is applied to the injection site and several hours of bed rest are recommended.
Stenting is completed.
Is stenting possible during pregnancy?
Installation of stents is not recommended for pregnant women, as during the operation an X-ray is taken, which can be harmful during pregnancy. The operation can be stressful; the pregnant patient is given contrast, anesthesia and other drugs, which can also have a negative effect on the fetus. Some drugs may cause allergic reactions.
Surgery for pregnant women is prescribed only in extreme cases; the surgeon informs the patient in advance about the possible risks and consequences and performs the operation only with her consent.
Complications
In some cases, complications may occur after stenting. The reason may be an incorrectly performed operation or the characteristics of the patient’s body, how it reacts to the installed stent.
- Thrombus formation at the site of stent placement is the most common complication. To reduce the likelihood of blood clots, the patient is given blood thinning medications.
- Bleeding with hematoma. Occurs due to the introduction during surgery of drugs that reduce blood clotting. Rarely seen.
- Infection of the incision site where the catheter is inserted.
- Allergy to radiopaque contrast agent or drug coating on the stent.
- Re-narrowing of an artery in another location, as plaques carried by blood from a previously problematic area can break off and block another area in the artery.
- Restenosis is the body’s reaction to the installed stent, expressed in excessive growth of the inner lining of the vessel in the area where normal lumen was restored.
- Heart attack during stenting.
There is a greater risk of complications in patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes, kidney disease and blood clotting disorders. To exclude a number of complications, the patient is thoroughly studied before the operation and adjustments are made to the treatment, regulating blood clotting with medication, and selecting a stent with the desired drug coating. Carefully monitoring the patient's condition after surgery.
When is stenting performed?
Stenting is done when the lumen of the arteries is narrowed by more than half. This is an effective operation that is performed even in the presence of concomitant chronic diseases and infectious processes in the body. Initially, when deciding on surgical intervention, the question of stenting is almost always raised. If it cannot be done, then bypass surgery is performed.
Recovery period
During this period, a set of measures is formed for the patient that will help him recover faster and reduce the risk of complications and recurrence of the disease.
After the operation, the patient lies in bed for 1-3 days in the hospital. At this time, doctors closely monitor the patient. After this, the person is discharged home, where he must also be at emotional and physical rest and observe bed rest. He should not take a bath or shower or exert himself physically.
During the recovery period, drug treatment is prescribed for six months, designed to reduce the risk of re-stenosis, thrombosis and heart attack. And increase the length and quality of life.
During the recovery period, the doctor prescribes everything necessary to:
- Improve a person's physical abilities.
- Restore heart functionality.
- Slow down the process of ischemia.
- Bring laboratory parameters back to normal.
- Prevent possible complications after surgery.
- To form in the patient a correct lifestyle that ensures longevity.
- Provide psychological comfort.
Drug therapy
After stent installation, the patient is usually prescribed the following medications:
- Antiplatelet, reducing the risk of blood clots. (Aspirin, Aspicard, Aspinat, Trombogard, Acetylsalicylic acid, Clopidogrel, Detromb, Trombex and others. Prescribed by the doctor to each patient individually.)
- Statins, which lower cholesterol levels and reduce the likelihood of restenosis. (Simvastatin, Pravastatin, Pitavastatin, Lovastatin, Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin and others. Prescribed by the doctor to each patient individually.)
- Drugs that reduce the risk of heart attack.
The range of medications prescribed depends on the patient’s condition and health characteristics. It is necessary to strictly take in full all medications prescribed by the doctor for the period of treatment. After stenting surgery, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and take medications at your own discretion.
General recommendations after surgery
Patients after bypass surgery and stenting are advised to have a proper, varied diet. It is necessary to avoid eating fatty, fried and salty foods. Products with high cholesterol content are strictly prohibited. At the request of the patient, you can receive a referral to a nutritionist who will write out the optimal individual diet.
The rehabilitation period after surgery involves taking medications. In addition to the standard set of medications, you must take anticoagulants prescribed by your doctor. Many people refuse them due to the high cost. However, ignoring the cardiologist’s instructions can lead to the formation of a blood clot in the installed stent/replaced area of the vessel.
Lifestyle change
Atherosclerosis, as a rule, is caused by an incorrect lifestyle, and in order to fully recover after surgery and avoid arterial stenosis in the future, it is necessary to change your lifestyle to a healthy one.
The transition to a healthy lifestyle is:
- Do morning exercises, move and walk quietly for 30 minutes - 1 hour about 3-4 days a week.
- Completely eliminate active and passive smoking.
- You can safely enjoy swimming, skiing, use an exercise bike or treadmill evenly and measuredly for up to 6 hours a week.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks.
- Avoid fatty, fried and salty foods.
- Do not consume more than 4 grams of salt per day.
- Drink tea instead of coffee.
- Attend examinations by your attending physician.
- Eat more vegetables, fruits, fish, rye and bran bread.
The diet and exercise program is prepared by the attending physician. For successful recovery, you must fully adhere to the schedule he has drawn up.
All articles →
| Our company offers high-quality stents for coronary vessels. You can familiarize yourself with the entire range of manufactured medical equipment for cardiac surgery in the website catalog. We are pleased to present you a coronary stent at a price affordable for every consumer! | Go to catalog > |
What is bypass surgery?
To understand the difference between bypass surgery and stenting of cardiac vessels, let’s take a closer look at how the shunt is installed. The goal of surgery is to redirect blood flow away from clogged arteries.
The principle of the operation was developed by Soviet scientist Vladimir Demikhov in 1960. During the Great Patriotic War he worked as a pathologist. It was at this time that he came up with the idea of creating a bypass route to supply the heart with blood.
The scientist proposed suturing the thoracic artery to the cardiac artery in the area below the plug. Such a prosthesis is called a shunt. In surgery, they resort to suturing with the radial artery of the arm or the great saphenous vein of the leg.
Compared to stenting, this approach provides a long-term effect. It is rare for a patient to return with symptoms. A shunt is used if 3 or more arteries are blocked. In other cases, stenting or balloon angioplasty is performed.
Installing a shunt allows you to determine the location of the plaques. But the method has many contraindications and possible complications, and the cost is higher than stenting.