Blood is the connecting thread between the entire human body. She is like rivers that feed and give life to man. Almost every event that occurs in our body affects the circulatory system. Pregnancy rebuilds a woman’s entire body, including the circulatory system. The composition of the blood also changes. As a result, the expectant mother may develop thrombophilia. When pregnancy occurs, a woman suffering from thrombophilia should immediately discuss with her doctor medication support and a test regimen that will allow her to monitor her blood condition and prevent complications in time.
Why is thrombophilia dangerous during pregnancy and what kind of disease is it?
Planning pregnancy with thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is a disease in which blood clotting is significantly increased, which entails a risk of developing thrombosis.
The blood clots themselves, under normal circumstances, protect the human body and do not cripple it: if a vessel is damaged, a blood clot forms, which clogs the damaged vessel. But with thrombosis, blood clots can form in completely healthy vessels, blocking the flow of blood and nutrients to the tissues.
A woman may have thrombophilia and plan to become a mother. This is quite natural. But it is not so rare that the disease develops during pregnancy.
In both cases, thrombophilia can become dangerous for both the fetus and the pregnant woman, so it is necessary to monitor the blood condition in order to monitor the development of the disease in time and begin treatment as early as possible.
Folic acid preparations
Today, no one doubts that folic acid should be used two months before the planned pregnancy by the patient when she is planning a pregnancy, in order to reduce the risk, namely, chromosomal abnormalities, neural tube defects, and microcephaly. Low doses, 400 mcg, are usually recommended for this purpose. The maximum is 800 mcg.
If we are talking about patients with high homocysteine levels, that is, this is a moderate and severe form of hyperhomocysteine, of course, such doses are not enough to reduce homocysteine levels. Such patients should receive doses of at least 5 milligrams per day, along with vitamins B, B6, B12. We start with injection therapy, then move on to tablet forms of B vitamins and antiplatelet agents.
Hereditary thrombophilia and pregnancy
A disease that affects the circulatory system cannot but affect the body as a whole. Thus, thrombophilia contributes to a woman’s ability to conceive a child. Due to insufficient blood supply to the uterus and pelvic organs, the embryo may not take root or may soon be rejected by the body.
The disease may be hereditary. During pregnancy, the development of genetic thrombophilia will be influenced by genes responsible for blood clotting and genes of enzymes that control folic acid metabolism.
If among your closest relatives there are people suffering from this disease, you should undergo a molecular genetic study when planning a pregnancy. And, if it turns out that the disease is inherited, it is advisable to immediately begin treatment in order to avoid problems with the health of the expectant mother and fetus.
Causes
In recent decades, there has been an increase in the number of patients who suffer from congenital and acquired forms of thrombophilia. Scientists explain this by the following factors:
- deterioration of the environmental situation in the world;
- "population aging;
- failure to seek professional medical help in a timely manner.
At CELT you can get advice from a phlebologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
The division into genetic and acquired thrombophilia is carried out based on the cause of the disease. Thus, genetic thrombophilia is the result of structural features of certain genes that lead to disturbances in the functioning of the blood clotting system. The most common hereditary thrombophilias are:
- polymorphism (Leiden mutation) of blood clotting factor V;
- polymorphism in the prothrombin II blood clotting factor gene;
- protein S deficiency;
- protein C deficiency;
- antithrombin deficiency.
They arise due to:
- increased levels of lipoproteins in the blood;
- lack of antithrombin III;
- lack of prothrombins S and C;
- thalassemia;
- factor V gene mutations;
- prothrombin mutations.
Unlike congenital thrombophilia, acquired forms develop against the background of other diseases, including cancer, as well as when taking certain medications. It is customary to highlight the following reasons:
- long-term venous catheterization;
- heart defects;
- cancerous tumors, the treatment of which involves massive chemotherapy;
- autoimmune diseases;
- dehydration of the body, accompanied by an increase in the number of red blood cells.
What are the dangers of thrombophilia during pregnancy?
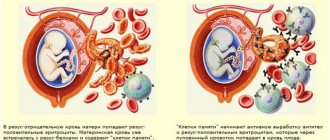
Why is thrombophilia dangerous for a pregnant woman? Because a new life with its own circulatory system is born in her body. A person has two circles of blood circulation - large and small. A pregnant woman has another blood circulation, called the placental, through which blood, along with nutrients, flows directly to the fetus. If the blood is too viscous, then its flow rate will be lower than it should be to properly provide the unborn child with oxygen and all other useful substances.
In addition, to protect a woman during childbirth from extensive blood loss, the body increases blood clotting. But in case of illness, blood already coagulates very quickly, so the risk of blood clots increases several times. A thrombus can completely block even large vessels, or significantly reduce its lumen. This will also prevent blood from flowing freely to the fetus.
As a result, with thrombophilia during pregnancy, the consequences for the child may entail the threat of a frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, or the birth of a child with developmental defects. Oxygen starvation can cause developmental delays in the newborn and weak immunity. But the disease can also damage the body of the pregnant woman herself. The consequences may be the appearance of varicose veins, very severe toxicosis that threatens the woman’s life, premature placental abruption with heavy blood loss. If a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, the disease can be fatal.
Antiphospholipid syndrome - chameleon syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome is extremely characterized by early reproductive losses, but for the same syndrome, which is also called chameleon syndrome.
Due to various clinical multiple effects, it is called chameleon syndrome, because traumatic complications, early losses, and late losses, up to placental abruption and severe preeclampsia, are possible.
Any obstetric pathology can be a consequence of the circulation of antiphospholipid antibodies, therefore, the basic therapy for antiphospholipid syndrome today is anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy.
If earlier, even before the discovery of the effect of antiphospholipid antibodies on the hemostatic system, preference was given to immunosuppressive drugs (glucocorticoids), then today glucocorticoids are not first-line drugs in the prevention and treatment of complications associated with antiphospholipid syndrome.
Nevertheless, glucocorticoids remain drugs that are prescribed to patients with antiphospholipid syndrome in the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus or other severe autoimmune connective tissue diseases that require the prescription of glucocorticoids for health reasons on the part of the mother.
Diagnosis of thrombophilia in pregnant women
It is difficult to diagnose thrombophilia during pregnancy, so at the slightest symptoms of the disease you should consult a specialist. There are not many signs, and they are not always interpreted in favor of the disease.
Severe toxicosis, blood clotting disorders (a network of burst vessels or bruises under the nails), high blood pressure, and convulsions are indicative.
Blood clots can form in any vessels and cause pain in various parts of the body, even a pre-infarction condition. The diagnosis of “thrombophilia” can also be suspected by the reaction of the fetus: if it does not receive a sufficient amount of nutrients, it may become excessively active or, on the contrary, freeze.
Antiplatelet agents
The antiplatelet agents we use in pregnant women are low doses of aspirin. The small doses that are currently used throughout the world in pregnant women include doses of no more than 100 milligrams. Although in practice we, as a rule, do not increase the dose of aspirin above 75-80 milligrams. But in some cases, the issue of aspirin resistance arises, which occurs in almost 30-40% of the population.
It is possible to check the presence of aspirin resistance only by studying platelet aggregation activity. This is also an extremely painful issue of modern diagnostics and the modern so-called “hemostasiogram” in quotes. Because today, each laboratory understands coagulogram and hemostasiogram as its own set of parameters of the coagulation and anticoagulation system.
The process of studying platelet aggregation activity is labor-intensive.
It is extremely necessary for pregnant women, especially in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome, thrombocytopenia, and thrombocytopathy. Because both high platelet function and low platelet function are two ends of a big problem. On the one hand, there is a risk of thrombosis, and on the other, there is a risk of bleeding. The correct selection of antiplatelet agents is extremely important.
Analysis for thrombophilia during pregnancy and its planning
In order to detect or exclude the disease, two blood tests are taken - a general blood test and a coagulogram, a comprehensive analysis of blood clotting indicators.
Blood for a coagulogram is taken from a vein on an empty stomach (it is advisable not to eat 12 hours before taking the test). Before a blood clotting test, you should not:
- smoke;
- take alcohol and psychotropic substances;
- eat fatty and spicy foods;
- Warn the laboratory assistant about taking medications if it is not possible to refuse the medications.
It is especially important to undergo tests for thrombophilia when planning pregnancy, if there are cases of the disease in the family, so that the diagnosis of a hereditary disease will help start treatment on time.
Our services in phlebology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Appointment with a cardiovascular surgeon (phlebologist), MD. Malakhova Yu.S. with ultrasound examination (primary) | 4 500 |
| Duplex scanning of the veins of both lower extremities | 6 000 |
| Duplex scanning of the veins of one lower limb | 3 500 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Treatment of thrombophilia when planning pregnancy
Medicines, diet and strict regimen are the three main directions in the treatment of the disease.
Medicines for thrombophilia are anticoagulants, drugs to reduce blood clotting, they are prescribed individually and exclusively by specialists.
Additionally, for the treatment of thrombophilia when planning pregnancy, it is recommended to take Omega-3. Taking Omega-3 reduces blood viscosity, reduces the production of thromboxane, which constricts blood vessels, and improves the fluidity of red blood cell membranes. All this has an antithrombotic effect when taken on a regular basis. Therefore, doctors recommend a continuous course of Omega-3 to prevent thrombosis, especially for women with high blood clotting rates.
The Pregnoton Mama complex, recommended for pregnant women and preparation for pregnancy, contains Omega-3 in an effective dosage. You can take the drug throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
Prevention of thrombosis
Prevention of thrombosis in thrombophilia in most cases is based on lifestyle changes. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous exercise and injury while maintaining the same amount of physical activity. An important preventive measure is wearing compression stockings. Doctors always decide on preventive measures strictly individually after assessing the thrombotic risk.
Bibliography
- Kyrle PA, Rosendaal FR, Eichinger S. Risk assessment for recurrent venous thrombosis //Elsevier.2010;376(9757):2032–2039.
- Khan S., Dickerman JD Hereditary thrombophilia. // Thromb. J. BioMed Central. 2006;4:15.
- Vasiliev S.A., Vinogradov V.L., et al. Thrombosis and thrombophilia: classification, diagnosis, treatment, prevention // RMZH - 2013.- No. 17. - P.896.
- Robertson L. et al. Thrombophilia in pregnancy: a systematic review // Br. J. Haematol. Blackwell Science Ltd.2006;132(2):171–196.
- Sibai BM, How HY, Stella CL Thrombophilia in pregnancy: Whom to screen, when to treat. 2007;19(1):50–64.
- Battinelli EM, Marshall A., Connors JM The role of thrombophilia in pregnancy. // Thrombosis. Hindawi.2013; 2013:516420.
- Andriyashkin A.V. Russian clinical recommendations for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolic complications // Phlebology - 2015. -T. 9. – No. 2. – P.1–52.
SARU.ENO.19.03.0436
Micronized progesterone preparations
During pregnancy, micronized progesterone preparations are used due to the fact that this group of drugs does not have any pathogenic effect on intrauterine development.
Let me step aside a little from the problem of thrombophilia. A huge number of researchers are specifically studying the problem of intrauterine programming of a child. There is no doubt that intrauterine development is nothing more than a certain program, which has its own laws and which is laid down very early.
But during intrauterine development, this programming can be disrupted, and this can be a consequence of the occurrence of various fetal deformities and behavioral disorders.
This is the same diabetes, metabolic syndrome and so on. The use of drugs during pregnancy, especially in the early stages of pregnancy, requires a very careful approach. To date, mechanized progesterone preparations have been recognized as absolutely safe: Utrozhestan, Crinon and an oil solution of progesterone.