What complications can occur after stenting of the coronary arteries and heart vessels?
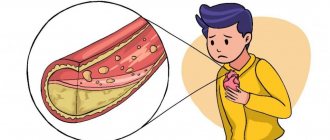
Complications after stenting can occur both immediately after surgery and in the long term. Immediately after implantation of the endoprosthesis, it is possible to develop allergic reactions to medications used during the intervention or over the next few days. Some stents have special coatings that contain substances whose action is aimed at preventing re-narrowing of the vessel. Patients predisposed to allergies may have a reaction to their release into the blood.
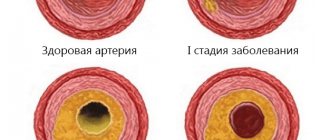
When performing stenting of cardiac vessels, complications may include repeated narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots. These are the most common complications, and the attention of medical scientists is currently focused on combating and preventing them. Complications after stenting cannot be excluded, such as the occurrence of perforation of the vessel walls, the development of bleeding and the formation of hematomas at the site of catheter insertion or other parts of the path of passage of the balloon with the stent.
Activities prohibited
Absolute contraindications to work after myocardial infarction are the following professions:
- Associated with high-risk vehicles (drivers of passenger, freight and railway transport);
- Those requiring increased attention and nervous tension (dispatchers of transport enterprises);
- Work at airlines (pilots, flight attendants, flight mechanics, dispatchers);
- Associated with prolonged walking or the need to be on your feet for a long time (postman, cook, courier, salesperson);
- If the workplace is remote from permanent residence and is located far from populated areas (geological, survey parties);
- Associated with toxic substances, harmful conditions in production (chemical, metallurgical, mining enterprises);
- With a variable work schedule, including night and daily shifts;
- Work at height.
If the patient worked in such conditions, he will be assigned a disability group with restrictions on work activity and a recommendation to change profession (groups 2 and 3), or with a complete ban on working (group 1).
How to avoid complications after stenting of heart vessels and coronary arteries
Patients most prone to complications after coronary artery stenting are those with various serious chronic diseases - kidney pathologies, diabetes mellitus, various disorders of hematopoietic and coagulation functions. Factors that increase the risk include old age and poor general condition of the patient’s body at the time of surgery.
In order to prevent the development of complications associated with the above reasons during coronary artery stenting, a thorough examination of the health status of the candidate for angioplasty is carried out even at the stage of preparation for the operation. This includes not only an assessment of the condition of the blood vessels, but also a comprehensive examination with attentive attention to all the patient’s complaints, taking into account all the medications he is taking and their possible reactions with medications administered during and after the operation.
Why can they refuse?
The commission's refusal to establish a disability group means that the patient's condition has improved and he can lead a full life.
- Types of arthrosis and their degrees for which a disability group is given
This may also happen for the following reasons:
- the patient’s rehabilitation was completed successfully and excludes relapses;
- the patient’s professional activity does not involve heavy physical exertion and psycho-emotional costs;
- full preservation of working capacity and ability to self-service in everyday life.
Important! If the commission’s response is negative, the citizen has the right to appeal the commission’s decision and demand an independent examination or appeal to the judicial authorities.
What is myocardial infarction
The disease is called an ischemic necrotic focus of the muscle tissue of the heart, which appears due to a violation of coronary blood flow. The patient complains of burning or squeezing pain behind the sternum. It radiates to the left shoulder blade and arm.
ICD code 10 I21 (Acute myocardial infarction).
Attention! In case of illness, it is necessary to urgently hospitalize a person in a cardiac intensive care unit. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, death may occur.
Re-examination: how often is it necessary to undergo an examination?
The commission has the right to issue the first group for life if the person is in serious condition and the likelihood of successful therapy is low. However, most often the patient has to undergo regular re-examination.
Read also: The procedure for declaring a citizen incompetent in Russia: where to start
The first group should undergo an examination every 2 years. From II and III once every 12 months.
The treating doctor must indicate the therapeutic regimen and rehabilitation that were carried out over the past year and failed to improve the patient’s condition. For the re-examination, the patient prepares the same list of documentation as for the initial examination.
A certificate of disability and IPR must be attached. In the latter, the doctor marks the implementation of rehabilitation measures that were prescribed during the previous examination. These include the work schedule that the employer provides for the patient, regular examinations by the attending doctor and the performance of examinations.
Attention! If there are no such marks, BMSE has the right to refuse to extend the disability.
Can I drink wine?
A heart attack and wine are completely compatible; even more, a glass of wine a day will help cope with problems with the cardiovascular system.
Flavonoids, which are one of the components of red wine, help with heart function. These elements produce good cholesterol and fight bad cholesterol. A large amount of them is found in dry red wine; the more sugar, the less antioxidants in wines.
Another important element that fights cancer cells and is present in dry red wine is resveratrol.
However, it must be remembered that not all wines contain these elements. Wines based on the Lydia and Isabella grape varieties do not contain flavonoids, so these types of wine should not be taken for therapy.
There is also a flip side to the coin; drinking large quantities of wine only causes harm.
The essence of therapy is how much and how to take wine. Taking a sip of wine after a meal will benefit the body. Be more careful when taking this ancient drink of the gods; an extra drop can cause great harm, especially after suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
Features of registration of disability
Before referring a patient for MSE (medical and social examination), the doctor sends him for research. They will show the need for examination.
The doctor should fill out form 088/у. He submits an application for a medical examination in order to assign a disability group and select an IPR (individual rehabilitation program).
The doctor specifies the date when you should appear for the examination. The commission has the right to conduct additional diagnostics, study the social and living situation or obtain a work history of the patient undergoing a medical examination.
Attention! All actions carried out by the commission are free. They are covered by compulsory medical insurance. The group is established from the moment an application is submitted to recognize the patient as disabled.
Is it possible to drink vodka
There is a lot of discussion around alcohol, namely around the permissible doses for use.
Vodka has a detrimental effect on the heart, but there is a fine line without crossing which the patient does not harm the body. However, this amount can only be calculated on an individual basis. It is necessary to know the history of the disease, lifestyle and age in order to make the correct calculation and not harm the body.
Therefore, theoretically, vodka can be consumed after a heart attack, but an individual approach is required to calculate the safe dose - it can be two tablespoons, or maybe one drop.
What group can you get?
A heart attack is a serious illness after which it is impossible to fully restore heart function. However, not everyone is eligible for the disability group. Moreover, the list of diseases requiring the assignment of disability does not include a heart attack.
The disability group after a heart attack is determined by the severity of coronary heart disease that occurs after a heart attack.
When assessing the post-infarction state, the person’s ability is taken into account:
- independently provide for your basic needs;
- move;
- navigate;
- communicate;
- control behavioral reactions;
- study;
- work;
- disturbances in the functioning of the body.
If the disease imposes varying degrees of restrictions on the patient’s abilities, the patient may be recognized as disabled.
- How to assign a disability group for coxarthrosis, where to go and what are the criteria for registration
First group
The first disability group after a myocardial infarction is awarded to people who are practically unable to work, move around, or take care of themselves. They require constant care. The history of such patients includes recurrent infarction, a large area of damage, and the presence of severe complications.
Criteria for assigning disability of the first group (one category is sufficient) (1).
| Basic Skill | Description |
| Self-service | The patient is unable to care for himself. Constant help is required. The patient is completely dependent on the assistants. |
| Movement | Unable to move independently. |
| Orientation | Unable to navigate without the help of others. |
| Communication | Unable to communicate independently. |
| Behavior control | Unable to control behavior. There are no correction methods. An assistant should constantly monitor the patient's behavior. |
| Education | Disabled to learn. |
| Job | Any work is contraindicated or the patient cannot perform it. |
Second group
The second disability group for myocardial infarction is assigned to patients who have had a heart attack and are unable to fully care for themselves or work without special working conditions. It is difficult for them to walk, it is difficult for them to learn new things, and they require periodic help from other people. Usually the second group is given to people who have experienced a massive heart attack after which serious heart failure has developed.
Group 2 is also assigned to patients with:
- the need to implant a pacemaker;
- signs of blood stagnation inside the heart (dilation of chambers, aneurysm);
- decreased cardiac output;
- a pronounced decrease in cardiac exercise tolerance.
Criteria for assigning a disability of the second group (one category is sufficient) (1).
| Basic Skill | Description |
| Self-service | The patient can take care of himself, but sometimes he needs the help of other people or technical devices. |
| Movement | It is difficult for the patient to move independently. However, if the patient is helped or has technical means of support (walkers, crutches), this is possible. |
| Orientation | A person is able to realize himself as a person, his spatial, temporal position only with the help of third parties or technical means. |
| Communication | The ability to communicate is preserved. However, a person requires auxiliary means to convey his thoughts. For example, he can show what he needs. The ability to perceive information is preserved. |
| Behavior control | The ability to control behavioral reactions is limited. |
| Education | Conventional teaching methods are useless. The use of special techniques allows the patient to acquire skills, abilities, and knowledge. |
| Job | The patient can work subject to special equipment at the workplace, an assistant, and special working conditions. |
Third group
People who receive it live full lives. They can work, study, judge themselves, and move around. However, they require aids or special conditions to perform normal activities. The third group of disability is given to people who have experienced a large or micro-infarction and have an initial degree of heart failure.
Other markers that influence the decision to assign a group:
- a slight decrease in the heart's ability to pump blood;
- moderate expansion of the heart chambers;
- reduced exercise tolerance.
Criteria for assigning disability of the third group (the presence of restrictions on work activity or a combination of violations of other basic skills is mandatory) (1).
| Basic Skill | Description |
| Self-service | The patient can fully support himself if he has auxiliary equipment: handrails, restraints. |
| Movement | The patient is able to walk short distances. Perhaps at a slower pace, with more breaks, with a stick. |
| Orientation | The patient is precisely aware of himself, his spatial and temporal position. He requires aids that improve sensory perception (hearing aids, glasses). |
| Communication | The speed, intensity of communication, and the volume of assimilation decreases. Full understanding of the semantic content of speech. |
| Behavior control | Periodically, the patient is unable to control his behavior. |
| Education | The ability to learn is preserved. The patient can receive education and new skills. However, he requires a special study regime, possibly auxiliary aids. |
| Job | The patient cannot work in his main profession. However, if the nature and/or duration of work changes, further employment is possible. |