March 12, 2018
Transfusion of whole blood from a donor to a recipient is not currently used. This procedure has been replaced by more
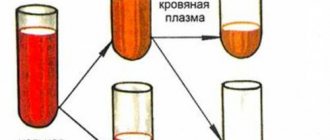
safe and effective methods of transfusion, in which a sick person receives donor plasma, red blood cells or platelets. They can be isolated from whole blood that a donor gives at a transfusion station, but a more modern method is the selective collection of individual components. With it, a person who has expressed a desire to help in the treatment of seriously ill people also donates blood, but at the same time it is filtered by special devices and its individual fractions are returned back to the bloodstream. Thus, it is possible to separately collect blood plasma, red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes.
Basic questions about donation
Who can donate blood and its components?
Citizens of the Republic of Belarus, as well as foreign citizens and stateless persons permanently residing in the Republic of Belarus, aged 18 to 60 years, who have full legal capacity and do not suffer from diseases and conditions in which donating blood and its components are contraindicated, are allowed to perform the donor function. . In exceptional cases established by the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, the medical advisory commission of the organization of blood transfusion may decide to allow persons over the age of sixty to perform the donor function.
What is the procedure for enrolling as a donor?
When registering to donate blood, the donor must provide:
- passport of a citizen of the Republic of Belarus with residence permit or registration for at least 6 months at the specified address. Those living in the dormitory must provide a certificate from the commandant (passportist) indicating the specific room of residence (at least 6 months);
- a medical certificate about the state of health (form 1 health/u-10), previous diseases, injuries, operations (taken at the clinic at the place of residence) is provided every six months;
- Chest fluorography data is provided once a year;
- a conclusion from a gynecologist (female), provided once every 6 months;
- a general urine test at the request of the medical registrar no later than 10 days before donating blood;
- military ID (for initial application);
- photograph (upon initial application).
How often can you donate blood and its components?
Men can donate whole blood no more than 5 times a year. Women – no more than 4 times a year. The interval between blood donations is at least 60 days, after the 5th donation - at least 90 days. After donating plasma, at least 14 days must pass before the donor can donate plasma again.
What medical examination do I need to undergo to become a donor?
All necessary tests are usually done directly at the blood transfusion station. Determined: blood type and Rh factor; general blood test data (hemoglobin, leukocytes, erythrocytes, ESR, etc.); as well as markers of pathogens of blood-borne (blood-borne) infections: human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B and C viruses; the causative agent of syphilis. In addition to the blood test, the potential donor undergoes a medical examination at the blood transfusion station, during which the doctor measures blood pressure, temperature, pulse, and asks about his health. Before the blood donation procedure, each potential donor fills out a special “donor questionnaire” in which he answers questions about his state of health and previous diseases. The final decision on admission to blood donation is made by a transfusiologist, who also evaluates the psychoneurological status of the donor and can reject him if he is suspected of using drugs, alcohol, or leading an antisocial lifestyle.
How is donating blood different from donating plasma?
When donating plasma, the donor's blood is taken, part of the plasma is separated, and the red blood cells are returned to the donor. Plasma can be donated at intervals of at least 2 weeks, and whole blood can be donated no more than 3-5 times a year at intervals of 60 days. After five regular blood donations, it is better to take a break for 3-4 months.
How long do you really need to wait after a risky situation (when you can become infected with HIV or viral hepatitis) for the tests to be informative?
At least 6 months. In no case should you hide existing risky situations from the doctor at the donor point. Hidden information can be dangerous for the recipient.
Can a smoker be a donor?
Smoking is not a contraindication to donation. Experts recommend refraining from smoking one hour before donating blood and not smoking for two hours after donating.
What types of blood donation are there?
The most common method is to donate whole blood. It is taken from a vein in the arm with an average of 450+/-50 ml at a time and lasts 7-10 minutes. You can donate not whole blood, but its components, for example, plasma - the procedure is called plasmapheresis, or platelets - thrombocytapheresis. During these procedures, only the component necessary for clinical use is selectively extracted from the donor's blood, and all other components are returned to the bloodstream. Plasmapheresis procedures are performed much more often. There are two ways to carry them out: manual (manual) or also called “intermittent”, when a dose of blood is taken from a donor and immediately centrifuged, separating it into red blood cells and plasma. The red blood cells are returned to the donor, and the plasma is quarantined. With automatic plasmapheresis, the process occurs continuously using a special device. The whole procedure takes 30-40 minutes.
How to prepare for donating blood?
1 - 2 days before blood donation, exclude fatty, fried, spicy foods from the diet (butter and vegetable oil, cream, milk, sour cream, cottage cheese, lard, mayonnaise, nuts, seeds, eggs). Blood supply is carried out after a light breakfast (not on an empty stomach! ), it is advisable not to eat fatty, fried and dairy products the previous evening; sweet tea, crackers, cookies, fruits are recommended. You must refrain from:
- drinking alcohol 48 hours before donating blood,
- as well as from the use of aspirin, analgin and medications containing aspirin and analgesics 72 hours before the procedure,
- If possible, refrain from smoking an hour before the procedure,
- you also need to get enough sleep.
Donors in a state of alcoholic intoxication or hangover will not be accepted and no supporting documents will be issued.
How long should it take after drinking alcohol before donating blood?
It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol 2-3 days before and on the day of blood donation.
What needs to be done to restore the body after donating blood?
On the day of blood donation, heavy physical and sports activities and heavy lifting are not recommended. For two days, it is recommended to eat well and regularly, drink at least 1-2 liters of liquid per day (alcohol is not recommended). Then lead your normal lifestyle. To restore your blood composition faster, it is recommended to drink more fluids - juices, tea. Proper nutrition is necessary: the donor’s diet should always contain protein, which determines the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Products containing protein - meat, lentils, beans and all legumes, fish, etc.
Is it possible to become addicted to donation?
There is no habituation to donation: hematopoiesis in the body of a healthy person is a complex self-regulating process that is not affected by periodic blood donations.
How is the record of blood donated by a donor and, in general, the record of donors kept?
Records of blood donated by a donor and donor records are maintained in the medical institution where blood donation is carried out. Information about the donor is simultaneously entered into an electronic database. For now, electronic databases are maintained in each region independently and are not interconnected. In the future, they will all be united into a single information network of donors in Belarus. When registering, each donor is also given a “Donor Questionnaire”, which he or she fills out independently or with the help of a medical registrar. Registration forms are stored for 5 years, except for the “Donor Registration Card”, which must be stored for 75 years. When a donor is deregistered, a record is made of the reason for the donor’s deregistration in the “Medical Card of an Active Donor” and in the “Donor Registration Card” and the total amount of withdrawn blood or its components for the entire period of donation is summed up.
What is the single dose for donating blood?
The volume of blood donation should not exceed 13% of the circulating blood volume, which is 7 – 7.2% of the donor’s body weight. The dose of standard blood donation is 450±50 ml. For modern medicine, it is very important that as many people as possible weighing more than 55 kg give blood in a full dose of 450 ml, and plasma 600 ml. Doctors have to transfuse blood components in large doses to one patient, and the fewer number of donors the blood is taken from, the more safe and effective its action as a therapeutic agent.
Is it harmful to donate blood? Is the human body adapted for this?
Donating blood is not harmful. The human body is evolutionarily adapted to bloodletting: this is a universal reaction mechanism in case of injury, and in women, in general, it is part of the functioning of the body.
Who needs donor blood?
Every third person on earth needs blood donors at least once in their life. There are several categories of people who need donor blood. There are people who need blood products for life. These are, first of all, patients with hemophilia. If there are enough clotting factors, and the patient has received adequate supportive therapy since childhood, then he is no different from an ordinary person and leads the life of an ordinary person. And without blood clotting factors, the life of such patients is simply impossible. Patients with cancer need donated blood. Modern treatment of malignant tumors involves killing tumor cells. Along with the tumor cells, normal hematopoiesis also stops for some time. It is during this period that the patient needs maintenance therapy with components of donor blood, in particular, platelets, for which there is no replacement, and is not even theoretically expected in the near future. Donor blood is needed for patients with surgical pathology. These are people who need joint replacements, these are cardiac surgery patients. Surgical operations involve trauma to blood vessels and tissues, and the need to restore lost blood components. Blood transfusions are often required for women during childbirth. A certain number of women in childbirth are always at risk of blood loss, which also needs to be properly compensated in order to save the life of the mother and child.
What sensations may arise when donating blood? I want to help, but I'm terribly afraid of all these procedures.
As for sensations, everything is very individual. There may be a slight sensation of pain when inserting the needle into the vein, but only for a couple of seconds. Sometimes during blood donation, more often in men, fainting occurs. Women, due to their physiology, are better adapted to small blood losses. Moreover, fainting speaks more of psychological fear. Many donors do not observe any changes in their well-being and do not cancel the reduction in their usual activity on the day of donating blood - they go to work, etc. And for many, there is euphoria from the consciousness of a good deed done.
What is plasmapheresis?
Plasmapheresis is the selective removal of plasma from the body. Plasma is the liquid part of blood. It contains a wide variety of substances: proteins (including coagulation factors), fats, carbohydrates, hormones, vitamins, salts, which are necessary for building body tissues and maintaining their vital functions, as well as organic substances that regulate metabolism. Plasma is widely used for medicinal purposes in surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, oncology and other areas of medical practice. Donor plasmapheresis is a method of obtaining plasma from a donor with the return of one’s own blood cells (erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes).
What should I do if I want to donate blood for a specific patient?
If you know the first and last name of the person for whom you want to donate blood, then it is enough to come to the medical institution where such a patient is located and go to the donor point, which is usually located at the hospital. You can also contact the blood transfusion station that serves this medical institution and inform that you are going to donate blood for a specific patient, indicating his name and place of treatment. You must first coordinate blood donation with the doctors who are treating the patient for whom you want to donate blood.
What can and cannot be done after donating blood?
Immediately after donating blood, sit for 10-15 minutes. Refrain from smoking for an hour before and after blood donation, and refrain from drinking alcohol for 24 hours. Do not remove the bandage for 3-4 hours, try not to get it wet. Try not to undergo intense physical activity during the day. Try to eat plentifully and regularly for two days. Drink increased amounts of fluid for two days. Do not plan to give blood immediately before exams, competitions, a project, during a particularly intense period of work, etc.
Why is a donor registered in one region not allowed to donate in another region?
This is due to security issues. The ban on not taking blood from people arriving from other regions is caused by the hypothetical assumption that in one region the donor is listed as a person exempt from donation, and in another region there is no way to verify the opposite. With the introduction of a unified information base, which will contain a register of persons exempted from donation in all regions of the republic, this problem will be eliminated.
How does donating blood affect your health?
Donating blood on a regular basis is useful for the prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system and, in addition, promotes self-renewal of the entire body. Scientists, in the course of examining a large number of men, found that those who regularly donate blood have heart attacks ten times less often. American researchers from the Kansas Medical Center confirmed that men who are regular donors are 30% less likely to suffer from heart attacks. Moreover: donating blood and subsequent renewal most directly influence the improvement of a person’s emotional state. And in serious situations, for example, in an accident, the donor has a better chance of survival, since his body is more adapted to blood loss.
Will I be infected with anything?
No. Everything necessary for blood collection is disposable and is opened in front of the donor. It is possible to become infected with hepatitis and HIV infection during a manicure, in a hairdresser, in a tattoo parlor, during acupuncture, but not at a blood transfusion station.
Could I faint?
You can. But according to statistics, only every tenth donor experiences illness. Most often - men. It is psychologically more difficult for them. Fainting is rare. Basically everything gets done with dizziness. They pass quickly.
I have a tattoo...
A tattoo is not an absolute contraindication. This is reinsurance. In a tattoo parlor you can become infected with HIV and hepatitis. After getting a tattoo, you can donate blood only after 1 year. The number of tattoos does not matter. The same applies to acupuncture treatment.
What are the requirements for blood (plasma) donors?
- the donor must lead a healthy lifestyle;
- have proper, sufficient sleep and rest, do not come for donation after a night shift;
- do not hide from the doctor information about previous diseases, about casual sexual relations that can lead to infection with HIV, hepatitis, and sexually transmitted infections;
- do not drink alcohol (including beer) for three days before donating blood;
- do not come for blood donation if there are signs of an acute illness (runny nose, cough, headache, sore throat, etc.) the day before and on the day of blood donation, do not take fatty foods;
- exclude significant physical activity, psycho-emotional stress.
What guarantees and compensation are provided to donors of blood and its components?
After donating blood or its components, the donor receives monetary compensation and a “Certificate of guarantees and compensation to the donor”, according to which he is exempt from work, study, service on the day of the medical examination and donation of blood (plasma) while maintaining the average salary. Maintaining average earnings is carried out by organizing blood transfusions in the manner determined by the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus. Full-time students upon provision of a certificate from the dean's office of the relevant educational institution. Article 31 guarantees provided to a donor who donated blood and its components on a reimbursable basis. Article 311 guarantees provided to a donor who donated blood and its components free of charge.
Attention to donors who donate blood for the first time in their lives!
At the choice of the donor, the donor function in the institution “Gomel Blood Transfusion Station” (Ilyich St., 286-b) can be performed either on a paid or free basis. Reception of donors and blood donation is carried out by appointment from 8:15 to 11:00. Collection of blood tests for preliminary examination is carried out by appointment (for primary donors donating on a reimbursable basis) from 11:00 to 12:00. 10-20 ml of venous blood is taken from a potential donor to be tested for markers of infectious diseases (HIV, hepatitis, syphilis); ALT activity. A donor is allowed to donate blood only if there are negative test results. Registration of primary donors who donate blood free of charge is carried out directly on the day of application for the near future, and no preliminary examination of blood for markers of viral infections is required.
Where can I get additional information regarding performing a donor function?
Phone number of the registry of the donor department of the Gomel blood transfusion station.
Is it harmful to donate plasma?
Everyone is interested in the question of how often you can donate plasma without causing damage to the donor’s body. According to American studies, it turned out that it is allowed to take it 12 times a year with absolutely no consequences, which turns out to be every 28 days. For comparison, platelets are taken 24 times in one year, once every 8 days.
Modern medical technologies are so developed that the need for whole blood sampling is no longer necessary. It is much more efficient to obtain all its components as needed, each separately:
- platelets;
- leukocytes;
- red blood cells;
- plasma
This technology allows the donor to be renewed faster, as opposed to whole blood collection. Once obtained, the biomaterial becomes safer for its recipient (recipient). In addition, a particular patient does not always need the presence of all blood components.
Is it dangerous to donate blood plasma?
As with any medical procedure, there is always risk:
- the possibility of infection if sanitary standards and rules are not observed;
- donate plasma more than 12 times in one year;
- There may be problems with the body's absorption of calcium.
Disadvantages of donating plasma
There is a preparation process: you are not allowed to eat fatty, salty, or spicy foods for at least a day. For some foodies, this restraint brings a number of inconveniences. Also, you should not drink drinks containing alcohol for a week. And the most important thing is not to smoke, as much as two hours before the procedure. The disadvantages include the duration of plasmapheresis, approximately 40 minutes, and the need to stay in the hospital for two hours. Under observation after plasma collection.
Benefits of donating plasma
Doctors have found that the process of plasma donation is beneficial for the donor, since blood fractions are restored after donation. This has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system, and also increases efficiency and allows the body to stay in good shape. For this reason, many become long-term donors.
In addition, plasma donors experience the following positive results after the procedure:
- The components of the biological fluid are renewed, as a result of which health improves and the body functions better.
- Those who donate plasma on a regular basis reduce the risk of diseases such as heart attacks and strokes and improve cerebral circulation.
- Donating blood plasma implies that the donor cares about his health.
- Experts have found that the average life expectancy of donors is approximately five years higher.
- Female donors have a much lower risk of serious bleeding during childbirth.
- Before donating plasma, the donor undergoes a thorough examination - even if the plasma donation procedure is delayed, basic information about the condition of the body can be obtained.
Despite the positive effects, we must not forget that donating plasma is a traumatic procedure that requires compliance with certain rules. Ignoring them on the part of a doctor or patient can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Harm from donating plasma
It often happens that a donor who decides to donate blood for plasma does not find the opportunity to carefully read the donation rules, which is why he may encounter complications after the procedure. In other cases, problems arise due to incorrect actions of doctors during plasma collection.
Donating plasma may pose a health risk in the following situations:
- The patient forgot to warn the doctor about chronic diseases that are a disqualification from the procedure - in this case, the disease may worsen or give unexpected complications.
- With an increase in the number of subsidies during the year, the body weakens, immunity decreases, and hemoglobin levels decrease.
- When using reusable instruments or violating aseptic rules, there is a risk of infection. In modern clinics this is practically impossible.
- Complications can occur in the absence of a thorough examination of the patient before the procedure. This usually happens in emergency situations when many donors want to donate blood or plasma at the same time.
If all the rules of donation are observed, both on the part of the patient and on the part of the doctor, it is possible to avoid harm from the procedure.
Where can I donate plasma?
Most often, blood transfusion stations do not accept plasma donors; you must contact large clinics or institutes. Plasma is also accepted by central hospitals and clinics that specialize in treating trauma patients.
When donating whole blood, you usually only need a passport and registration, but you can donate blood for plasma only after undergoing an outpatient examination. In this case, the donor independently makes an appointment with the doctor and brings the necessary certificates - as a rule, this is the conclusion of an infectious disease specialist, therapist and gynecologist (for women). This is not always practiced - the exact information needs to be clarified at the clinic where you are going to donate blood or plasma.
Is it harmful to donate blood plasma?
A number of limitations have been discovered under which this procedure is harmful:
- Eye diseases (only after consultation with your doctor).
- If a tooth was removed, less than 10 days ago.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages two days before the test.
- Women during menstruation, as well as those who gave birth less than a year ago.
- Citizens who have returned from tropical countries within 3 years (risk of contracting malaria).
- Patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Infectious patients.
- Severe somatic diseases.
- Mental disorders.
- High blood sugars.
Attention! It is strictly prohibited to donate blood or any of its components to patients with AIDS, hepatitis, tuberculosis, syphilis, as well as to homosexuals and illegal immigrants.
Benefits and harms
Plasma donation looks like a regular blood draw, during which only plasma is taken from it, and the remaining useful components are returned back to the donor. To do this, the blood is passed through a special disposable system. The body immediately reacts to cell loss and engages in self-healing. Other benefits of donating plasma include:
- prevention of various types of ischemia and atherosclerosis;
- reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke;
- prevention of inflammatory diseases of the liver and pancreas;
- correct lifestyle (blood is not taken from drinkers, drug addicts, patients with AIDS, hepatitis or tuberculosis);
- extension of life by approximately 5 years (scientifically proven)
In addition, regular donors who have donated blood more than 60 times for charitable purposes and have received the status of an honorary donor are provided with a number of benefits:
- the right to choose the time for vacation at the desired period of the year;
- extraordinary receipt of vouchers for health improvement in sanatoriums and health centers every year;
- annual receipt of a cash bonus, which is constantly increasing;
- constant medical examination and observation.
Important! Donating blood and its components is not just useful - it is necessary to save the lives of dozens, and maybe hundreds of people.
Harmful manifestations of donation include:
- risk of developing anemia;
- possibility of calcium leaching;
- weakness and flu-like condition for several days after the procedure;
- risk of infection due to violations of aseptic and antiseptic rules.
What do you need to donate blood plasma?
First of all, the future donor should familiarize himself with information about what is required for donation, who has the opportunity to donate blood plasma, and how to prepare for this procedure.
- The donor's age must be between 18 and 60 years.
- Weight must be at least 50 kilograms. Many people are interested in whether it is possible to donate plasma to donors with a lower weight - in some cases, this rate can actually be reduced to 47 kilograms. However, this is the exception rather than the rule.
- You must be a citizen of the country in which you want to donate plasma (Ukraine, Russian Federation), or have a residence permit. You need to have your passport with you.
- There should not be a single medical contraindication - there is an approved list of diseases for which donation is contraindicated, as it can pose a threat to both the donor and the recipient.
- If the patient has a tattoo, you need to wait a year from the moment it was applied.
- Women need to wait at least five days after the end of menstruation.
The procedure for donating blood plasma
It is better to go to the procedure well prepared and know exactly what is needed to donate plasma, so that there are no obstacles to donation at the last moment.
Preparation for the procedure includes the following steps:
Before donating blood, it is recommended to get a good night's sleep; it is not allowed to donate plasma after a sleepless night or a shift at work - this can lead to loss of consciousness.
Before donating plasma, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle: alcohol should be eliminated at least two days, smoking - three hours before the procedure. The blood should not contain alcohol breakdown products.
It is not recommended to drink tea and coffee on the day of donation - it is best to drink juices, fruit drinks, and clean water. Breakfast doesn't have to be heavy.
In many clinics, before donating blood, the donor will be offered a cup of tea with something sweet.
So, the preparation is completed, the documents are with you, you can go to the clinic to donate blood plasma.
Is donating plasma beneficial?
The benefits of donating blood plasma are mutual. The patient receives substances vital for the regeneration of the body after severe injuries, burns or operations. In the donor’s body, in turn, natural protective forces are activated, and the person himself can, without outside intervention, recover from many of the ailments that tormented him.
Doctors explain this by saying that immediately after the procedure for taking plasma, the body is engaged in rapid recovery. Simply, the blood is restored, stimulating the functioning of the immune system.
Regular donation allows blood cells to be regularly renewed, relieving the body of excess ballast. It is useful to donate plasma to people:
- with impaired iron excretion (genetic disease);
- high in fat and cholesterol (few people know that expensive plasmapheresis in private clinics and free donor plasmapheresis are the same thing);
- age 50 and older, well-being improves and youth prolongs, prevents heart attacks, strokes, thrombosis;
- for the moral pleasure of saving the life of a complete stranger.
Which is more useful: donating blood or plasma?
During the plasma removal process, the body is simultaneously cleansed of unnecessary fat and cholesterol, reducing the chances of early development of cardiovascular diseases. Young cells reproduced by the body stimulate defense mechanisms and improve the functioning of the immune system. Also, thanks to the selective selection of biomaterial, the donor loses less blood volume than with general sampling, and the recovery period is faster and almost imperceptible.
Blood plasma donation procedure
Those who plan to become donors very often experience psychological stress before the first donation, because they have no idea how donors donate plasma and what happens in the process. We will tell you in detail about what happens before the procedure, during plasma donation and after the donation.
Arriving at the clinic or blood transfusion center, the donor goes to the reception desk. At the initial appointment, they give him a card with basic information.
Then a preliminary medical examination is performed. It includes a general blood test, testing for antibodies to HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, identifying blood type, Rhesus and Kell antigen.
After the tests are completed, the donor is sent to a physician, who will review the test results, measure blood pressure and temperature, and decide whether the donor is eligible to donate plasma. After this, the doctor will briefly tell you how blood plasma is donated and answer all your questions.
After this, the donor proceeds directly to donating plasma. The procedure is carried out in a lying position, blood is drawn from one arm, it enters a special centrifuge, where it is divided into individual components: platelets and red blood cells are separated from the plasma cells themselves. Blood cells separated from the plasma are transferred to the second arm.
Donation lasts from 40 minutes to an hour, after completion it is recommended to lie down for a while, do not make sudden movements, drink a glass of strong sweet tea to restore strength. You should not leave the clinic for half an hour in case problems such as dizziness or loss of consciousness arise.
After donating plasma, a bandage is applied that cannot be removed for about two or three hours to prevent bleeding.
For two days after donation, it is better to avoid physical activity, hard work, and not to go to the gym.