In our heart there is a group of special cells that produce electrical impulses and cause the atria and ventricles to contract in a certain rhythm and sequence.
Thanks to special cells and its own electrical conduction system, the heart works in a certain rhythm and sequence
The brain is not able to give the heart the command to stop, work faster or, conversely, slower. However, it is wrong to say that the heart works completely autonomously. The heart rate is influenced by the autonomic nervous system, which consists of two divisions - sympathetic and parasympathetic.
Physiology of the autonomic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the heart’s reaction to physical activity, stress, the entry of nutrients or toxic substances into the blood, and other external or internal stimuli. It dominates during the waking period, during daylight hours. The stronger the stimulus, the higher the heart rate.
The parasympathetic department prevails during rest and, especially, night sleep, allowing the “perpetual motion machine” - the heart muscle - to work in a more relaxed mode. Doctors figuratively call the night the “kingdom of the vagus,” the vagus nerve (vagus, lat.) – the “chief manager” of the parasympathetic system.
The functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system can be disrupted for a number of reasons, one of which is poor quality sleep at night. Only if sleep goes through all its phases (stages) and cycles, the autonomic system does not suffer and the heart gets the opportunity to fully rest.
Stages of the sleep cycle
Normally, in an adult, the difference between the average daytime and nighttime heart rates reaches 7-10 beats per minute, and the heart rate during sleep depends on age and gender.
Symptoms
The complaints of people who have suffered such an attack are similar to one another: “I sleep terribly, I suddenly wake up at night from a strong heartbeat, I can’t breathe normally, I can’t sleep, I break out in a cold sweat.” The essence of the complaints is disturbance of night sleep and a feeling of a racing pulse.
Frequent interruption of night rest, when the heart beats strongly, leads to the fact that a person gets up after sleep without a feeling of freshness, broken, and unable to concentrate during the day. Insomnia often occurs.
The somatic side of the attacks - increased heart rate - is combined with the psychological - panic attacks. They frighten a person, but since they occur at night during sleep, they take the form of disturbing or nightmare dreams. Having awakened, a person does not regard dreams, even terrible ones, as a reason for concern about health.
You can do nothing if sleep is disturbed by attacks of tachycardia only occasionally. When your heart beats at a frantic rhythm from night to night, you cannot remain careless: you cannot do without the help of a competent doctor. Ignoring the problem of a strong heartbeat is fraught with aggravation of attacks.
The following signs indicate a deterioration of the situation and the transition of night palpitations to a more severe form:
- the appearance of chest compression;
- heartache;
- feeling dizzy
- loss of consciousness.
These symptoms join existing night attacks and signal the need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms of seizures during sleep
Changes in heart rate cause patients to feel palpitations, anxiety or sudden panic, discomfort or pain in the heart area, and difficulty breathing. Sudden awakenings and nightmares may be signs of heart rhythm problems. When extrasystole occurs, there may be tremors in the chest or “turning over” of the heart.
In the morning, patients experience typical manifestations of poor sleep quality:
- severe weakness, weakness;
- dizziness when getting out of bed;
- irritability;
- memory impairment;
- difficulty doing work that requires concentration.
These signs may be accompanied by pale skin, coldness of the extremities, blurred vision in the form of flashing dots before the eyes, and fainting due to ineffective cardiac output with serious heart rhythm disturbances.
- Drugs for rapid heartbeat: effective remedies for tachycardia
Types of arrhythmia
The first examination performed for any heart rhythm disturbance is an electrocardiogram. Analysis of ECG curves made it possible to divide rhythm disturbances present in patients with night-time tachycardia into several types:
- extrasystoles;
- migration of the pacemaker to the AV node;
- blockade of pathways;
- sinus arrhythmia.
Tachycardias at night, accompanied by a lack of breathing (apnea), are observed strictly in a state of sleep
Upon waking up and throughout the day, the heart continues to beat at a normal rhythm, there is no discomfort. With successful treatment of sleep apnea, nocturnal tachycardia stops.
Obstructive sleep apnea is one of the causes of heart rhythm disturbances at night
Poor quality of night sleep is very often associated with obstructive sleep apnea. In apneics, sleep mechanics disturbances are combined with oxygen starvation. The lack of oxygen is also felt by the heart. This forces the heart muscle to work in an economical mode, that is, to contract less frequently than usual - a person periodically experiences bradycardia (a decrease in heart rate to 35 beats per minute or less).
At the same time, the sympathetic nervous system constantly “spurs” the worn-out heart, causing tachycardia and overwork of the heart muscle, which is already suffering from a lack of oxygen. As a result, the heart begins to beat irregularly, contract chaotically - “flicker”. Atrial fibrillation is a very serious rhythm disorder that, without treatment, leads to the development of heart failure, coronary artery thrombosis and heart attacks.
The alternation of atrial fibrillation with compensatory bradycardia is usually also accompanied by episodes of cardiac arrest - asystole. After stopping, the “engine” may no longer start, so such patients are often fitted with a device that artificially affects the heart rhythm - a pacemaker.
Timely effective treatment of obstructive apnea allows you to normalize night sleep, rebuild autonomic function and eliminate oxygen starvation of the heart, which will again begin to work correctly and without overload.
Polysomnography allows you to comprehensively analyze the functioning of the respiratory organs, heart and blood vessels during night sleep
To understand whether sleep apnea is the cause of heart rhythm problems, a special examination - polysomnography or cardiorespiratory monitoring - will help.
Cardiorespiratory monitoring makes it possible to identify episodes of apnea and rhythm disturbances
Causes of tachycardia
The transition of the body into a state of sleep is accompanied by the transfer of control from the cerebral cortex inward - to the department of the reticular formation. The active state of the retinal formation inhibits the sympathetic department and increases the tone of the parasympathetic part of the nervous system.
Parasympathetic has a multifaceted influence on all life processes. If there are hidden health deviations under parasympathetic nighttime influence, they become aggravated. This happens with nocturnal tachycardia.
Low vagal tone
The vagus nerve (nervus-vagus), part of the parasympathetic division, reduces the pulse by suppressing the activity of the sinoatrial node. For this reason, at night, a healthy person’s heart beats at a slow pace and blood pressure is reduced.
But insufficient vagal tone allows the sympathetic nerves to remain in a position of dominance. The effect of sympathy on the heart rhythm is exactly the opposite - an increase in the heart rate. The smooth muscles of the intestine are affected by the vagus nerve; in response to increased vagal tone, peristalsis (movement) of the intestinal loops increases.
Neuroses, panic attacks
Frequently observed causes of nocturnal tachycardia are prolonged stress, driven inside the consciousness, and long-standing fears. Each process that occurs in the cerebral cortex and is not completed forms a focus of pathological excitation in it with stable neural connections.
In a state of sleep, the cerebral cortex tries to remove the pathological focus - and the person dreams that he is trying to cope with repressed fear. Sometimes a dream ends with victory over fear. This means that the brain destroyed the pathological focus in the cortex.
In psychiatric practice, such dreams are referred to as “catharsis” - liberation from fears repressed into the subconscious. In a cathartic state, there is a huge release of emotions - a constant sign of getting rid of the pathological focus. Night tachycardia, along with other symptoms, is the physiological side of cleansing catharsis.
In the morning, a person does not remember why he suffered from night terrors. A similar mental defense mechanism is designated by the psychoanalytic term “repression.” The specialist’s goal is, together with the patient, to find repressed thoughts and fears and help the patient destroy them in a state of consciousness.
Nocturnal hypertension
Why does blood pressure rise at night during sleep?
Attacks of palpitations at night can be caused by a rise in blood pressure in hypertensive patients, if the effect of blood pressure-lowering drugs has ended earlier than expected.
This happens when a patient misses a dose of an antihypertensive drug or takes an insufficient dose. Regular repetition of cases when the heart is pulsating strongly, closer to the onset of morning, means that it is time to see a doctor to adjust drug therapy.
After the examination, the doctor will delve into the complex pathogenesis of the nocturnal rise in blood pressure and prescribe new doses or new antihypertensive drugs. In people suffering from hypertension, a characteristic rise in blood pressure occurs in the morning and signals the need to seek medical help!
Apnea syndrome
Suspending breathing while a person is sleeping is a common cause of an attack of nocturnal tachycardia. The most banal option: the lack of breathing is caused by obstruction of the respiratory tract - the tongue simply relaxes and closes the throat.
Breathing disappears for a few seconds - minutes. Oxygen deficiency causes activation of the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata - breathing movements become more frequent and deeper, the heart beats loudly. At the moment when the inhalation force is higher than the air resistance in the respiratory tract, snoring occurs. The sleeper wakes up from his own snoring or the REM sleep phase begins.
Snoring people not only disturb their loved ones, but also harm themselves. Because of snoring, the sequence of rapid and slow-wave sleep is confused, and as a result, the person is not able to get a good night's sleep. During apnea, the heart muscle suffers from a lack of oxygen. This is fraught with the development of angina, when there is pain in the chest area and the heart is pounding.
The state of lack of breathing at night creates stress for the cerebral cortex, which results in disturbing and nightmare dreams
At the start of apnea, the heart slows down and beats more slowly. When the period of apnea has passed and the person has woken up, breathing and heart rate increase to compensate for oxygen deprivation.
Other causes of nighttime palpitations
Types of pathology that can lead to the appearance of a strong night pulse:
- organic disease of the heart muscle, pathology of the endocrine glands (diabetes, thyrotoxicosis);
- uncontrolled use of cardiac medications, alcohol and nicotine poisoning, acute viral infections;
- reduced hemoglobin content in the blood - anemia.
The reason remains unknown? Such cases are called “idiopathic”.
Causes of physiological tachycardia
In a healthy body, the heart rate increases in many situations.
- Getting physical activity. This includes sports, physical work, muscle tension of various origins.
- A moment of emotional stress. Emotions - any - must be strong.
- Being in a threatening external environment. This is dirty air, lack of oxygen at altitude or in a stuffy room, increased ozone content in the post-storm air.
- A rise in body temperature, for example, during a cold. Surely it is angina that gives you the feeling that you are shaking. After all, there is a “10 to 1” rule: the heart rate increases by 10 beats for every rise in temperature by 1 degree.
- Overeating attacks. Excessive eating often causes an increase in heart rate.
- Allergy attack.
- Menopausal flushing of the face and upper body.
- Taking energy liquids. Heart palpitations can also increase from strong tea or coffee.
What is tachycardia?
The human heart beats at a frequency of 60-90 beats per minute. A condition in which the heartbeat reaches 90 beats or higher is called “tachycardia” in medicine. It can be physiological, or it can be pathological - a symptom of various diseases. Physiological tachycardia is a variant of the norm, does not cause significant discomfort to the patient, occurs in completely healthy people, and goes away after a short rest.
Emotional experiences
It can be observed during significant physical exertion, in stressful situations, during fear, emotional experiences, both positive and negative, after drinking coffee and caffeine-containing drinks. This physiological increase in heart rate can also occur at night. If before going to bed a person, for example, watched a horror movie, decided to do physical exercise, drank a couple of cups of coffee, if the day was emotionally intense, there were stresses at work. All these factors do not go unnoticed and can cause increased heart rate at night.
If such a condition occurs once and is associated with any of the above reasons, after rest the person feels well, this condition is regarded as a variant of the norm, and there is no reason for concern. Perhaps an attack of rapid heartbeat occurred due to overstrain of the body and nervous system. But if such attacks occur regularly at night, then they are pathological and dangerous to health. And it is imperative to find out the reason for their occurrence.
Diagnostic methods
The main methods for diagnosing nocturnal tachycardia are:
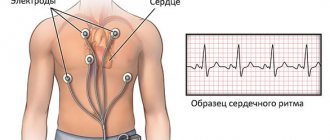
ECG
The main method for detecting nocturnal tachycardia is to take an ECG. Performed when you first seek medical help.
An ECG helps to study the work of the myocardium during the day and exclude the presence of daytime heart rhythm disturbances
Holter cardiogram
To document the fact of nocturnal tachycardia when a person goes to bed gives a chance to take a Holter electrocardiogram. The mobile device is attached to the patient for a day. A Holter ECG will not only detect nocturnal palpitations, but will also make it possible to determine its type and severity.
Echocardiogram
Another name is ultrasound of the heart. Allows you to “see” on the screen all the structures of the heart: chambers, valve apparatus, vessels. The functioning of the endocrine glands is checked using blood biochemistry, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and pancreas.
Diagnostics
Holter ECG monitoring
The following methods are used in diagnosis:
- ECG. It may not be informative in case of paroxysmal arrhythmia, which bothers the patient only at night and not during the daytime. When taking an ECG, the attack may not be recorded. In this case, Holter ECG monitoring helps.
- ECG Holter monitoring - electrodes are fixed to the human body and an ECG is recorded all day long, even during sleep. After recording, the data is output to a computer and decrypted by specialists. Such a study makes it possible to record nocturnal tachycardia and assess the form, frequency and duration of episodes.
- Transesophageal electrophysiological study. This is a study of the conduction system of the heart using electrodes that are inserted through the esophagus.
- EchoCG is a method that allows you to visualize the chambers of the heart, valves, great vessels, and the condition of the heart muscle.
Also, to find out the causes of tachycardia, the following are used: ultrasound of the thyroid gland, general, biochemical blood tests, MHO analysis, determination of blood glucose levels.
Treatment
It is a common situation when cardiac pathology is the basis of the nightly “pranks” of the pulse. In this case, treatment aimed at getting rid of cardiac pathology will help. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the number of attacks and their severity. Indeed, in the presence of myocardial pathology, a violation of the rhythm of contractions gradually turns into a factor aggravating heart disease.
When the cause of night attacks is high blood pressure, the doctor prescribes antihypertensive drugs and determines the dose individual for the patient. As a rule, the evening dosage of the medication is increased. If the issue is sleep apnea, then everything is more complicated. Therapeutic measures in relation to it have a weak effect.
In all cases, doctors advise sleeping on your side. But sleeping people usually do not control the position of their own body in their sleep. For this reason, the only effective method is the use of special devices for ventilation. Such gadgets pressurize oxygen through a mask into the lungs of those sleeping.
To prevent your tongue from closing your windpipe at night, you can lose excess weight and cure ENT pathology. One hundred percent option: the doctor selects a gadget that fixes the position of the lower jaw while you sleep. Straining, changing body position, and taking a hot-cold shower will help quickly (but not for long) make tachycardia disappear.
Psychotherapy
The trigger for an increase in heart rate at night can be a mental injury, after which the patient wakes up for a long time, attacked by panic attacks. A qualified psychotherapist will help eliminate this problem. Beta-blockers and sedatives are indicated as medications.
General recommendations for nocturnal tachycardia - normalize sleep, increase the overall tone of the body
Blood pressure and pulse jump: reasons
If the pulse periodically quickens or slows down against the background of a decrease/increase in blood pressure, then the causes of this condition may be:
- myocarditis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- infectious diseases;
- hyperthyroidism (thyroid disease);
- heart defects;
- pathological changes in the upper chamber of the heart;
- obesity 2-3 degrees;
- pulmonary or heart failure;
- benign tumors;
- cardiac ischemia.
The listed conditions are exclusively pathological in nature; they require long-term and targeted treatment.
Signs and warning signs
Conditions when you need to pay attention to your health and immediately consult a doctor:
- the appearance of shortness of breath (I can’t breathe);
- noise in the ears, cranium;
- dizzy;
- it becomes dark in the eyes;
- there is weakness up to loss of consciousness;
- heartache.
You must immediately call an ambulance, and while waiting for it you must:
- free the patient’s neck and chest from tight clothing;
- provide air access to the patient (open the window);
- apply cold to your forehead, rinse your face with very cold water.
Prevention
To prevent attacks of nocturnal tachycardia from occurring, the best way out is to reduce the load from both physical labor and emotions, adhere to an active lifestyle that can enhance the reserve capabilities of the human body and bring the pulse back to normal.
You need to take control of the number of hours spent motionless (at the computer), remove all “nicotine poisoning sessions” from the regime, and avoid drinking 8 cups of coffee a day, especially before going to bed.
It is better to avoid heavy meals before bedtime and reduce the amount of quickly digestible carbohydrates. The body should receive almost the entire daily dose of calories in the first half of the day. Before going to bed, you should not engage in physical activity; it is better to take a walk or take a relaxing shower.
What causes your heart rate to fluctuate at rest?
If your heart rate fluctuates at rest, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- age of the person - in the elderly, an increase in heart rate is considered normal if it is not accompanied by pain and shortness of breath;
- ambient temperature - if it is high, then vasodilation will certainly lead to an increase in heart rate, thus the body simply cools down;
- lack of fluid in the body - banal dehydration makes the blood thick, reduces the amount of plasma, and the heart has to work with redoubled force to maintain blood circulation;
- stressful situations - even at rest a person is able to worry, remember, look for solutions to problems and an increase in heart rate against the background of stress is also possible;
- excessive physical activity - if a person is specifically involved in sports and his pulse increases at rest, then he needs to either reduce the time of training and its intensity, or increase the rest time between them;
- emotional state - even slight excitement automatically leads to an increase in heart rate.
The listed factors relate to the physiological causes of pulse fluctuations at rest; they are quite easy to correct.
But if, against the background of the main symptom, a person is bothered by headaches, a feeling of pressure in the chest (the anatomical location of the heart), periodic increases in blood pressure, and dizziness, then it is worthwhile to undergo examination by a cardiologist. It is possible that pathologies such as microinfarction, heart failure, malignant neoplasms, infectious or inflammatory processes will be diagnosed - they may occur for some time without pronounced characteristic symptoms.