Photo: UGC When asked how many liters of blood are in a person, any student who is familiar with biology will answer: “5-6 liters.” And this will not be a complete answer. The numbers given are the average. This volume is theoretically observed in a man of average build and weight. In fact, the volume of blood depends on how old a person is, what weight he has, and what gender he belongs to. Let's look at the issue in more detail.
Why measure blood volume?
Blood volume is measured in order to identify various diseases, the development of which causes abnormalities associated with the volume of circulating blood. Blood volume is also measured for blood loss during surgery. Blood volume measurements are also performed to detect conditions such as hypercythemia (increased red blood cell count), anemia (decreased red blood cell count), hypovolemia (low blood volume), and hypervolemia (increased blood volume).
The blood will tell. What diseases can be calculated using conventional analysis?
How to make up for the loss?
Today this problem is solved with the help of donor blood transfusions. This procedure is necessary for severe injuries, surgeries, and childbirth. Most often, plasma is transfused, which makes up about 60% of the total volume. The donor's blood must match the patient's group and Rh factor.
According to the existing law, you can donate no more than 450 ml of blood (or 600 ml of plasma) at a time. In addition, there are restrictions on the frequency of donation and the weight of the donor (4 times a year for women, 5 times for men, the interval between donations is at least 60 days, the donor’s weight is at least 50 kg). This order is due to the fact that the loss of 10% of blood can lead to a deterioration in health and the development of anemia.
Blood volume in the human body
The volume of blood in the human body varies, and this is quite natural - there is no clear single indicator for all people. After all, in the end, height indicators and weights are different for all people. Blood volume changes with age, while many other changes occur in the body. On average, blood volume is 4-5 liters . At the same time, there is less blood in the female body, and its volume is about 3.5 - 4.5 liters .
But again, in pregnant women, blood volume increases rapidly, and there is significantly more of it. In addition, lifestyle also affects blood, its volume and quality. Those who regularly engage in physical activity, lead an active lifestyle, and choose sports have more blood. Those who have large muscle mass have more blood, while those who lead a sedentary lifestyle and do not have developed muscles have less blood.
How much blood is there in a person?
Functions
Blood performs essential functions in the human body. It constantly circulates in a system consisting of large and small blood vessels that penetrate all organs and tissues, with the exception of the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes, articular cartilage, cornea, hair and nails.
Red cells deliver oxygen to tissues due to the ability of hemoglobin to reversibly bind to its molecules. Platelets are directly involved in coagulation during bleeding: they rush to the site of vessel damage and form a blood clot at this site. Leukocytes are the body's main defenders from internal and external harmful agents.
Blood transports oxygen from the lungs to tissue cells, and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs, carries metabolic products, nutrients, hormones, enzymes, biologically active substances, and is also responsible for the delivery of final metabolic products to the organs of the excretory system. It regulates temperature and maintains water, electrolyte and acid balance in the body.
How much blood does a person lose in liters during mild, moderate and severe blood loss?
Compensated blood loss is considered to be a decrease in circulating blood volume by ten to fifteen percent. Such patients have normal or moderately low blood pressure, a compensatory increase in heart rate and slight weakness.
For reference. Moderate blood loss is considered to be a decrease in the amount of blood by fifteen to thirty percent.
Such blood loss manifests itself:
- decrease in pressure,
- weakness,
- thirst,
- heart rhythm disturbances and compensatory tachycardia,
- sweating,
- increased breathing,
- dizziness.
With a loss of thirty to thirty-five percent of circulating blood volume (CBV), moderate blood loss is noted. Patients are restless, there is severe pallor, blueness under the eyes, impaired skin turgor, profuse sweating, cyanosis, a sharp decrease in pressure, impaired renal function, arrhythmias, and significant tachycardia.
Symptoms of severe blood loss (severe cyanosis, arterial hypotension, respiratory, cardiac and renal failure, impaired consciousness, etc.) develop when the volume of blood volume decreases by thirty-five to forty percent;
- How many liters of blood are in the human body and how much can be lost without consequences?
Attention! The loss of more than forty percent of blood is accompanied by severe shock with the development of multiple organ failure.
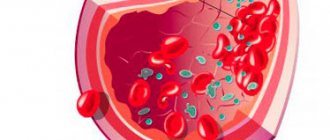
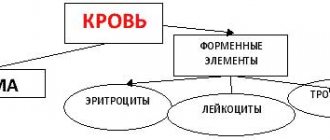
Blood composition
Blood consists of 4 main components:
- red blood cells - red blood cells that transport oxygen from the lungs to the human organs;
- white blood cells - leukocytes responsible for fighting infections that attack the body;
- blood platelets - platelets that ensure blood clotting, thereby protecting the body from fatal blood loss due to injuries and cuts.
All these cells are suspended in blood plasma, which not only serves as a transport medium for blood cells, moving them throughout the human body, but also contains proteins and salts necessary for the body.
How to determine a person's blood volume?
For this purpose, a certain amount of a contrast agent, usually a harmless dye, is injected into the blood. After it is distributed throughout the riverbed, a fence is made to determine its concentration.
Another way is to inject radioactive isotopes and count the number of red blood cells that contain them. The amount of blood is determined by the level of its radioactivity.
Blood transfusion is used to normalize blood volume in the body.
Blood test for ARVI
When a child has a fever, cough and runny nose, parents want to be sure that this is a common ARVI and not a bacterial infection. Sometimes it seems to them that a general blood test will dot the i's - as soon as they take it, it will immediately become clear what the child is sick with and whether they need to give him antibiotics. However, this is not quite true. In some cases, a blood test will actually help the doctor make a diagnosis, but most often it is not necessary. In addition, the result obtained, where half of the indicators go beyond the norm, only needlessly scares parents. Pediatrician Alexandra Zhukovskaya talks about why you shouldn’t rush to get a blood test at the first symptoms of the disease.
What indicators can change during infection?
First of all, the total number of leukocytes changes - these are the cells that protect the body from viruses and bacteria. There are several types of white blood cells that perform different tasks: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils. Their number and relationship to each other are displayed in the leukocyte formula - usually as a percentage. As soon as one indicator increases slightly, the rest will automatically decrease. This is why, with minor changes in the leukocyte formula, the forms look frighteningly red. In addition, in many laboratories, the forms indicate standards for adults, which differ from children. Thus, in children under 5 years of age, lymphocytes predominate, in older children - neutrophils, and the total number of leukocytes changes with age.
What do deviations mean?
With a bacterial infection, you usually experience:
- increase in the number of leukocytes (leukocytosis) - more than 15 × 10⁹/l;
- increase in the absolute* number of neutrophils - more than 10 × 10⁹/l;
- a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left - that is, the appearance of immature (band) forms of neutrophils - more than 1.5 × 10⁹/l.
*To estimate the absolute neutrophil count, you need to know the total white blood cell count and the percentage of neutrophils. For example: leukocytes are 9 × 10⁹/l, and neutrophils make up 72%, which is usually already highlighted in red. We count: 9 × 72/100%, we get 6.5 - that is, the normal absolute number of neutrophils.
With a viral infection, you usually experience:
- Decrease in the total number of leukocytes (leukopenia) - especially with influenza, measles, etc.
- Increased absolute number of lymphocytes (lymphocytosis).
- The appearance of “atypical” cells occurs in infectious mononucleosis.
Another nonspecific sign of inflammation is an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). High ESR is typical for both viral and bacterial infections.
What then causes difficulties?
The fact is that in the first days of the disease there may not yet be any characteristic changes in the general blood test, or vice versa - the leukocytes may “jump” significantly even for a banal viral infection, casting doubt on the diagnosis. Many viruses (adenovirus, Epstein-Barr virus) lead to a persistent increase in the number of white blood cells - leukocytosis - which is usually associated with a bacterial infection.
Conversely, some bacterial diseases occur without abnormalities in blood tests - for example, otitis media or atypical pneumonia, or even with changes characteristic of a viral infection - for example, lymphocytosis is observed in whooping cough.
There are quite a few such exceptions, which is why at the beginning of the disease a general blood test cannot be a universal diagnostic method - the doctor will receive much more information during a thorough examination of the child.
How else can you clarify the diagnosis?
If the doctor suspects streptococcal sore throat or influenza, a streptate test or rapid test for influenza is performed. Methods are available to detect many viruses in saliva, nasal secretions, etc. A chest x-ray is indicated to rule out pneumonia. If a urinary tract infection is suspected, urine test strips and urine tests are performed. In case of severe intestinal infections, feces are examined for the presence of bacteria belonging to the intestinal group (salmonellosis, dysentery, etc.). If the child has been feverish for a long time and there is no obvious source of infection, the levels of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin are looked at in a biochemical blood test. Some time after the onset of the disease, specific antibodies against various infectious agents can be detected in the blood.
Isn't it easier to give an antibiotic right away?
No.
- Antibiotics are ineffective against viruses and cannot prevent bacterial complications, but vaccination against pneumococcus and other bacterial infections can cope with this.
- Antibacterial therapy disrupts the vital activity of normal microflora involved in protection against foreign and dangerous microorganisms.
- Taking antibiotics without indications leads to antibiotic resistance—bacterial resistance. This means that the next time an antibiotic is actually needed, it will no longer be harmful to the bacteria, and the disease will be more difficult to cure.
- For some viral infections (for example, infectious mononucleosis), the administration of widely used penicillin antibiotics leads to the appearance of a rash. This is often interpreted as an allergic reaction, although there are no contraindications for further use of this group of antibiotics in a child.
- All medications, including antibacterial drugs, have side effects. The benefit of any intervention should be greater than the potential harm - you should not break this rule by giving antibiotics “just in case”.
What to do if bleeding starts
If bleeding develops, you must immediately call an ambulance. Before her arrival, the patient is given first aid.
If there is bleeding from the stomach, it is necessary to put cold on the stomach, provide complete rest to the victim, and give him cold water to drink in small sips.
If you have a nosebleed, you should tilt your head slightly forward and apply cold water to the bridge of your nose. You can't throw your head back.
In case of injuries to the extremities with arterial bleeding (scarlet blood flows out under pressure - “spouts”), a tourniquet should be applied or the artery should be pressed with fingers to the bone above the bleeding.
The tourniquet should be applied to fabric, not bare skin. The time for applying the tourniquet must be recorded! In winter, the tourniquet can be kept for no more than 50 minutes, in summer – 1.5 hours. After this time, the tourniquet should be loosened for 5-10 minutes. If necessary, it is applied again, above the previous place of application.
Venous bleeding is stopped by applying a tight bandage to the wound.
For reference. The main treatment is carried out in a hospital. The cause of blood loss is eliminated, depending on the severity of blood loss, infusion therapy is carried out to correct hypovolemia, restore blood volume, balance electrolytes, relieve arrhythmias, restore kidney function, etc.
According to indications, the patient is transfused with solutions of crystalloids, colloids, erythromass, albumin preparations, etc.
Benefits of donation
Many, for one reason or another, had to act as a donor and donate their blood or plasma, some had their own reasons for this, while others simply do this for charity for the sake of sick children. Of course, you won’t be able to just come to the blood transfusion center without an appropriate examination; first you will need to see doctors such as:
- Therapist.
- Venereologist.
- Dermatologist.
Only after you receive permission from each specialist, you can become a donor, and it does not matter whether you weigh 50 or 60 kg, the volume of red liquid taken will not exceed 450 ml - this is the indicator that will not affect the functions of the body. All new arrivals are necessarily checked against the database, and those who have recently suffered from certain diseases may not be admitted at all
Red liquid is donated no more than once a month, but plasma is allowed to be donated twice. The blood collection procedure takes no more than ten minutes, there is nothing complicated about it. If you come to donate plasma, you will have to lie on the couch for at least thirty minutes.
If you have the opportunity to donate blood or plasma for adults and children in need, take advantage of it, because donation can save the lives of most of them. Some people believe that donation is a life-threatening procedure; in fact, this is not the case; you can verify this by consulting a doctor.
References
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency anemia, 2015. - 58 p.
- Klochkova-Abelyants, S.A., Surzhikova, G.S. Iron deficiency anemia and anemia of chronic diseases: some aspects of pathogenesis and prospects for differential diagnosis. — Medicine in Kuzbass, 2021. — No. 3. — P.25-28.
- Tiglis, M., Neagu, T., Niculae, A. et al. Incidence of Iron Deficiency and the Role of Intravenous Iron Use in the Perioperative Period, 2021. - Vol. 56(10). - P. 528.