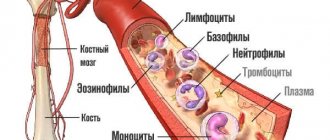
Of course, blood tests play a significant role in diagnosing diseases. Knowing the participation of different types of leukocytes in the life of the body allows us to timely identify abnormalities and suspect pathology.
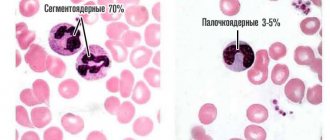
Band neutrophils are part of a large group of granulocytes and are precursors or younger (they are also called “young”) cells of the segmented type. They differ from their successors by having an undivided core of an oblong or twisted structure.
Doctors call them “sticks”, and if they are angry, “sticks”. Doctors of all specialties are familiar with the indicator.
Methods for counting quantities
Band neutrophils, like all blood cells, are counted in the finished smear after staining. They react to both acidic and alkaline reactions of paints. That's why they are called neutrophils.
A total count of cells of each type contained in a unit volume is carried out. For “rods” the absolute amount is normal from 1.8 to 6.5 x 109/liter of blood.
A more important indicator is the percentage of band forms in the total number of leukocytes. A detailed calculation of all types is the leukocyte formula.
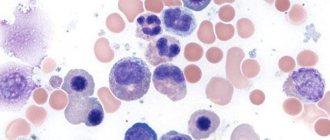
On the right are the final cells: all with “freckles”, which means “granulocytes”, in the middle row the penultimate one is a band neutrophil
How are they indicated in the analysis?
The relative abundance of neutrophils is indicated in a line beginning with the character set NEUT% (NE%) (neutrophils). The designation for the absolute content of neutrophils in a blood test looks somewhat different. The form contains a ciphergram in which the % sign is replaced by #: NEUT# (NE#) (neutrophils).
Form with blood test results
Norms
The norm of young neutrophils differs only in the first two weeks after the birth of children. The newborn gets rid of the mother's blood cells and begins to produce their own. During this period, there is a violation of the ratio between band and segmented neutrophils: the level of “segments” is 50–70%, and “rods” is from 3 to 12%.
Such a “distortion” quickly normalizes and throughout the rest of the child’s life and in adulthood it will be in normal conditions from 1 to 6%.
The level does not depend on the age of the adult; it is the same in men and women.
Reasons for the increase
An increase in the number of segmented neutrophils is usually observed in the following cases:
Infectious and inflammatory processes
Classics of the genre. This should include all possible disorders that relate to the penetration of foreign agents into the body. Bacteria, viruses or fungi.
The intensity of the increase in cellular structures, the speed and final volume of leukocytes depend on the specific disorder. The stronger the disease, the more abnormal agents and their waste products, the higher the level of neutrophils.
Symptoms depend on the pathological process. In general, there are always such deviations from the norm:
- Temperature increase. To what extent - you need to look at the situation.
- Weakness.
- Drowsiness.
- Feeling very tired.
- Manifestations of intoxication of the body: nausea, headache. Plus or minus. Everything is determined by the diagnosis.
- There are also focal signs of the pathological process. If it is tonsillitis - sore throat. Pneumonia, bronchitis - shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and so on.
The treatment is specific and is carried out under the supervision of a therapist and a specialized specialist (depending on the disease).
Antibiotics, antivirals, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics are prescribed to bring down the temperature.
Next, the course of treatment is adjusted based on the dynamics of the patient’s condition. This applies to both dosages and the names of the drugs themselves.
Autoimmune inflammation
They occur no less often, but are fundamentally different from infections. In this case, there are no traces of pathogenic structures. The body begins to react to its own tissues and cells inappropriately and attacks them.
Segmented neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils also participate in this process. All formed cells of the immune system.
The most common diagnoses are:
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Myocardial damage.
- Gout.
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Thyroiditis.
And much more. This also includes allergic reactions, which will be discussed below.
Treatment is provided by rheumatologists and immunologists. Glucocorticoids are prescribed. Prednisolone is used as a starting point.
Further, the strength of the drug is varied based on the essence of the pathological process and its severity.
In the most extreme cases, if the condition is resistant and does not respond to therapy, immunosuppressants are used. They inhibit the production of protective cells and thereby eliminate the negative impact.
Sepsis
Occurs against the background of a long-term infection or open injury. The second, not entirely accurate name for this pathological condition is blood poisoning.
In fact, we are talking about a generalized inflammatory process. It covers the entire body, systems and organs suffer. If nothing is done, there is a high probability of rapid death.
Segmented neutrophils are increased to eliminate bacteria, viruses, fungi, and their metabolic products, slow down the inflammatory process and somehow achieve a state of balance. Therefore, the growth is significant, clearly visible and rapid.
Attention:
The combination of speed and high rates often indicates either sepsis or gangrene.
Infectious disease specialists provide treatment. At first, the patient has to be placed in intensive care in order to provide the victim with thorough medical care and provide supervision: the condition can worsen at any moment.
Loading doses of antibiotics are prescribed, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs, medications for viruses and fungi.
Even these measures are sometimes not enough. They resort to hardware blood purification using plasmapheresis methods. But this is more of an auxiliary measure.
Rehydration solutions are administered and infusion therapy is prescribed in order to quickly remove waste products of abnormal agents and toxins from the body’s structures.
The prognosis is vague even with high-quality treatment. It all depends on the moment the correction begins.
Malignant oncology
Often the reason for the increase in segmented neutrophils is the poisoning of the body with tumor decay products: formed cells, leukocytes act as a kind of scavengers that utilize waste substances and particles. These include dead malignant cells.
You can expect tumor destruction starting from the second or third stage of the pathological process. Because there are so many cytological structures that there is no longer enough “food” for everyone. Some cells die from “gluttony”, others from nutritional deficiency. The bottom line is one thing: tissue breakdown and poisoning of the entire body.
By the way, hence the regular or even constant increase in body temperature, weakness, drowsiness, symptoms of general intoxication, sudden weight loss and other “delights” of this condition.
As for neutrophils, their concentration increases in parallel with the growth of the tumor. The further it goes, the worse the patient will become.
Thermal injuries
An increase in segmented neutrophils in the blood occurs with massive burns, since the products of protein destruction, which were located in the thickness of the dermis, enter the channel. The “garbage” needs to be removed. Granulocytes do this job.
The larger the affected area, the worse the situation overall. But that's not the problem. If nothing is done, fatal complications for the patient are very likely.
With burns of more than 20% of the body, there is a high probability of the following problems:
- Kidney failure from too much protein.
- Cardiac arrest due to overload.
- Heart attack.
- Coma.
To prevent this from happening, the patient is placed in a burn department or intensive care unit. Depends on the condition. But no one gives guarantees of survival.
Allergic reactions
Segmented neutrophils increase due to an autoimmune response, a false attack of the body's own defense cells on the body's tissues. There are no objective reasons for this.
As a rule, allergies develop to food dyes, natural pigments of natural origin, dust particles and other harmless substances.
Usually this is the result of hypersensitization of the body. Increased sensitivity to the limit after an infection.
Allergies can manifest themselves in different ways. In some cases it is a common skin rash or urticaria. In others - anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema. That is, very dangerous, potentially fatal violations.
Immunologists treat patients. The goal is to restore the body's normal sensitivity and reduce the degree of sensitization.
Corticosteroids like Pridnisolone are prescribed. As in other cases, immunosuppressants may be required. Fortunately, this is a relatively rare option.
Attention:
It is impossible to completely cure allergies. All that remains is to stop exacerbations and prevent relapses of the pathological process.
Parasitic infestations
Simply put, worms. Not necessarily in the classical sense. Those located in the intestines. There are different worms.
- Some prefer the hepatic ducts (giardia, flukes).
- Others, like echinococci, even settle in the lungs, brain, and also in the structures of the digestive tract.
- Opisthorchis, found in river fish, can potentially infest any organ that has a sufficient blood supply. Even the human eye. There are many options.
Be that as it may, parasites release waste products into the bloodstream. This is a kind of signal for the body to start an immune reaction.
Neutrophils attack intruders and destroy them along with eosinophils, which are more adapted for the purpose of combating helminths.
The more worms there are, the more active they are, the more intense the immune response itself. It is necessary to check for parasitic infestation almost in the first place.
The treatment of the pathological process is carried out by specialists in parasitology. Special medications are prescribed. The doctor will choose the exact name; there are many of them and they are usually specific. That is, they act on parasites of a certain type and origin.
It is strongly recommended to undergo treatment in a hospital. Because when they decay, worms poison the body and can cause complications.
Myocardial infarction
Oddly enough, an acute circulatory disorder in the myocardium can become the culprit for the growth of segmented neutrophils.
If you take a closer look, there is nothing unusual. The fact is that in this emergency condition, myocardial cells are destroyed. The accumulated substance known as myoglobin is released. This is protein.
Like all chemical components of this type, it has an increased allergenic potential. The body reacts to the compound as potentially dangerous and produces more formed cells.
In addition, you need to cleanse the body of waste products. These two goals provoke an increase in the content of segmented neutrophils in the blood.
There is no need to do anything special. High levels of formed elements and white blood cells will disappear on their own as soon as the acute condition passes.
It is important to focus on myocardial infarction. Conduct a course of maintenance therapy and prescribe rehabilitation measures. A cardiologist is dealing with the problem.
All symptoms of a pre-infarction condition are described in detail here.
Severe forms of renal failure
{banner_banstat9}
Normally, it is the excretory system that eliminates waste products, cellular debris, and waste proteins.
If the filtering paired organ fails, these poisons are absorbed back into the blood and poison all systems. The increase in neutrophil concentration is due to a reflex attempt to eliminate toxic components.
The most common causes of renal failure are long-term infectious-inflammatory and autoimmune processes. You can also name parasitic type disorders, oncology, anatomical changes (prolapse of the kidney, wrinkling, etc.).
Treatment is carried out by specialists in nephrology (not neurology). Diuretic drugs are prescribed, which stimulate the natural functioning of the paired organ.
If the state is neglected, they cannot be used. Doctors resort to hardware methods of blood purification, hemodialysis.
The only radical and effective way of recovery is a kidney transplant. Finding a suitable donor is not an easy task. That's why patients wait for years.
Many do not have time for the operation and die before the right moment arrives.
Some forms of poisoning
Intoxication with heavy metals. For example, lead, mercury. This also includes pathological processes provoked by volatile compounds. For example, sulfur fumes or other agents.
Most often, employees of hazardous chemical enterprises and people living in areas that are unfavorable from an environmental point of view encounter such problems.
The treatment is specific. It is dealt with by toxicologists or therapists if there are no specialized doctors nearby. A detoxification course is prescribed. When possible, use specific antidotes.
The correction takes place within the walls of the hospital to provide the patient with sufficient supervision.
By the way, some drugs can also lead to poisoning. For example, corticosteroids. The probability must be assessed based on the annotation. Information from the instructions for use.
Injuries suffered
{banner_banstat10}
After any injury, even a bruise, even a fracture, the inflammatory process begins.
So the body, on the one hand, eliminates a possible infection, a secondary septic phenomenon. On the other hand, it increases the local regenerative abilities of tissues and helps restore anatomical integrity.
Granulocytes also participate in this process. In particular, neutrophils. The degree of growth depends on the nature of the pathological condition.
A bruise will practically not provoke changes. The same cannot be said about an open wound with extensive tissue damage.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a traumatologist and surgeon. Specific measures are required: operational or conservative. The question remains at the discretion of the doctors.
These are the main, but not all possible provoking factors.
Quantity changes
The change in the number of band neutrophils depends on the general fluctuations of leukocytes and granulocytes. All five varieties are connected by the function of providing immunity and protecting the body from harmful influences.
The need for an increased level of protective reaction and the beginning of the fight against infectious agents causes an adequate response, accompanied by an increase in the production of “rods” and their maturation into segmented finished cells. The “segments” die after a few days, and new cells take their place from the rod forms.
The general decrease in neutrophils is also reflected in the reduction of “rods” until they completely disappear in the blood. Neutropenia (low) neutrophil levels or an increase in neutrophilia always affects progenitor cells.
Causes in children
In younger patients, the list of diseases will be approximately the same. There are some additions. A number of conditions occur only in young patients and appear immediately.
Pediatric infectious diseases
Scarlet fever, rubella, chicken pox, whooping cough, mumps (mumps) and much more.
They are not fundamentally different from other infectious pathologies. All white blood cells rush to fight foreign agents.
Pediatricians are involved in recovery. Antibiotics are prescribed in strictly controlled dosages. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also drugs for viral infections, antipyretics. An individual regimen is prescribed.
Regular monitoring of the condition is indicated.
Congenital bone marrow disorders
Segmented neutrophils in a child can be increased as a result of hyperfunction of the bone marrow, when too many formed cells are produced: including leukocytes in different variations.
This is usually a genetically determined disorder. It is difficult to correct. All that remains is to deal with the symptoms.
Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are prescribed. The disease often occurs in periods. The violation is replaced by remission and so on in a circle. You need to be constantly monitored by a hematologist.
When band neutrophils are absent
The main causes of neutropenia are associated with suppression (excess) of the production of leukocyte cells. This occurs in severe pathology:
- bacterial infections (typhoid and paratyphoid fever, chronic brucellosis, tularemia);
- viral infection leading to the predominant synthesis of monocytes and lymphocytes and suppression of neutrophils (rubella, diphtheria, scarlet fever, influenza, measles in children, viral hepatitis);
- toxic effect of medications on the processes of blood cell synthesis (sulfonamides, analgesics, interferon, immunosuppressive drugs);
- aplastic anemia and associated with deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12;
- the effects of radiation, radiation and chemotherapy for tumors, leukemia.
In all cases, a decrease in the number of neutrophils and the absence of their band forms indicates suppression of the immune system and a general weakening of the body.
If absent in the blood
A number of diseases and factors lead to a quantitative decrease in immature defender cells. For example:
- viral diseases (measles, rubella, etc.);
- mycoses;
- anemia;
- chemical poisoning;
- oncological processes and consequences of radiation;
- hyperthyroidism;
- taking certain medications.
The absence of band neutrophils in the blood of an adult does not always mean that he is sick or is under the influence of factors leading to neutropenia.
In most cases, 0 in an adult is a laboratory error. 1 percent in an adult is an indicator of health.
Why do band neutrophils increase?
Against the background of common reasons for an increase in the level of segmented neutrophils in bacterial and fungal diseases (rheumatism, infectious arthritis, genitourinary inflammatory diseases), severe intoxications, and blood diseases, special attention is paid to the role of “rods” in diagnosis.
Physical activity, pregnancy and labor can cause a temporary increase in neutrophils, but the level of band forms remains within normal limits.
Band neutrophils are increased when:
- septic conditions;
- severe tonsillitis;
- purulent diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (abscesses, phlegmon);
- hematopoietic diseases.
An increase in the level above 6% is called a shift of the formula to the left (towards younger forms).
With such purulent plugs on the tonsils, the number of “sticks” increases significantly