- Types and causes of diabetes
- What happens in the body of a diabetic?
- Is it possible to determine at home that a person has diabetes?
- What happens to your appearance with diabetes?
- How does the disease progress in children?
- What examinations should I undergo if a person suspects that he has high blood sugar?
- Tests for diabetes
Diabetes mellitus (DM) or “sugar disease” is a common endocrine disease. It is caused by a decrease in the function of the pancreas (PG), which is responsible for the secretion of insulin, or the inability of its effect on cells. Insulin is a hormone that is responsible for processing glucose that enters the body with food. Glucose is necessary to fuel muscles and brain function. Carbohydrate metabolism directly depends on the production of insulin.
Its violation entails health and life-threatening conditions. Sugar disease is a chronic disease that affects the entire body and is incurable. Readers will learn from this article how to understand that you have diabetes and where to turn if you have alarming symptoms.
Types and causes of diabetes
Diabetes is a group of endocrine pathologies. All of them provoke impaired glucose tolerance. Doctors use the following classification of diabetes:
- diabetes types 1 and 2 (insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent);
- gestational (in pregnant women);
- diabetes as a symptom of pancreatitis or destruction of pancreatic cells after surgery, injury, poisoning.
Each disease has its own nature, development mechanisms and methods of treatment. Experts name many different reasons that influence the development of pathology. The main ones are:
- disorders of the immune system, in which the immune system attacks pancreatic cells and destroys them;
- unfavorable heredity: presence of diabetes in close relatives;
- pregnancy;
- developmental anomalies and diseases of the pancreas;
- improper diet, excess of fast carbohydrates, fatty foods;
- physical inactivity;
- excess body weight;
- endocrine pathologies that cause metabolic disorders;
- psycho-emotional overload, prolonged stress.
Some causes are congenital, but most factors that trigger diabetes are lifestyle factors. This allows you to monitor your health and take measures to prevent diabetes.
Preparing to visit the doctor
If you suspect diabetes, you should consult a doctor. Before visiting an endocrinologist’s office, you need to pay attention to:
- arterial pressure. It needs to be checked periodically (preferably twice a day), and then the data must be recorded. The same applies to the pulse;
- ambient temperature that a person feels comfortable;
- calculate the number of hours for sleep and how effective it is;
- weight changes recently (within the last 3 months or even a year);
- regularity of the menstrual cycle, since diabetes mellitus can also appear during pregnancy.
When visiting a doctor, you need to describe in detail all the sensations you have had recently, as these may be symptoms of diabetes. Also, in the future, this will help determine what type of diabetes the person has. You also need to write down your daily routine in detail, especially pay attention to your diet and diet, and also mention the amount of fluid you consume. Moreover, it is important to indicate in what form the body receives it: pure water, coffee or tea, any drinks.
If you suspect diabetes mellitus, no special preparations are required before going to the endocrinologist. The studies that the doctor prescribes for diagnosis also do not require such preliminary measures. The patient’s task when diabetes is suspected is to correctly assess his condition and describe everything to the doctor as accurately as possible.
What happens in the body of a diabetic?
In diabetes, the secretion of the hormone by pancreatic cells is disrupted (type 1) or its absorption becomes difficult (type 2). For this reason, the blood sugar level increases. This phenomenon is called hyperglycemia, which is chronic in diabetics. A short-term increase in sugar - nutritional hyperglycemia - occurs when a person has eaten. Eating food increases glucose levels due to the carbohydrate content and, accordingly, activates the production of insulin. Insulin is responsible for delivering amino acids, glucose and fats into cells, thereby maintaining blood glucose levels at a safe level. A normal level is considered to be around 80–100 mg/deciliter.
If the pancreas is healthy, sugar levels decrease after a while. Its excess under the influence of insulin is deposited in the muscles and liver in the form of glycogen.
In patients with diabetes, this physiological process is disrupted. Chronically elevated blood sugar has a negative impact on the functioning of all body systems. If this condition is not compensated for by taking medications and diet, irreversible pathological changes occur. In severe cases, they can be fatal.
Tests to detect diabetes symptoms
People with diabetes have a lot of symptoms, but first you should pay attention to extreme thirst and frequent bladder emptying. These signs indicate that the kidneys are working at a high rate. This happens because the concentration of sugar increases and the kidneys try to remove excess sugar from the body. This process requires large volumes of fluid, which the kidneys take from body tissues. As a result, the patient is constantly thirsty and goes to the toilet more often.
Unquenchable thirst and frequent urination are characteristic symptoms of diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by other symptoms:
- xerostomia (dry mouth);
- constant feeling of hunger;
- headache, vertigo (dizziness) with diabetes or prediabetic condition;
- tingling or numbness in the legs;
- increased nervous excitability;
- chronic fatigue;
- rapid weight loss;
- increased blood pressure;
- the appearance of wounds or ulcers that heal slowly;
- dry skin, itching;
- sexual disorders in men (due to increased glucose levels, testosterone decreases);
- menstrual irregularities.
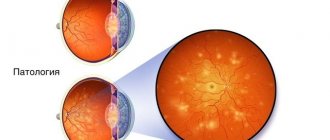
With the development of diabetes, the blood vessels of the brain are severely affected. Cells cannot absorb glucose without the participation of insulin, and as a result, they starve. For this reason, the patient has trouble concentrating, has a headache, and constantly feels tired.
If you notice at least a few symptoms of diabetes, then go to an endocrinologist. After all, complications of diabetes can be life-threatening, so there is no need to hesitate. In addition, there is hidden (latent) diabetes mellitus, so it is recommended to test 2-3 times a year.
Is it possible to determine at home that a person has diabetes?
Only an endocrinologist can make such a diagnosis after the necessary laboratory tests. However, there are signs that may indicate chronic excess glucose in the blood and the need to seek medical help. Here are the main symptoms that diabetics experience:
- Severe fatigue persists even after sleep, with reduced loads.
- Body weight begins to increase or decrease sharply. In type 1 diabetes, it decreases, although the person has a good appetite and a plentiful diet. With type 2 diabetes, you constantly want to eat, so the person consumes more calories and body weight increases.
- Excess blood sugar leads to dry mouth and unpleasant odor.
- Some patients experience such phenomena as dizziness, headache, and darkening of the eyes.
- Men may experience decreased libido. Up to a third of young and middle-aged patients report signs of erectile dysfunction.
- Itching in the vagina, frequent thrush, burning sensation when urinating - this is how diabetes manifests itself in women. High sugar levels increase the risk of yeast infection. Candida is a yeast-like fungus that uses sugar as a nutrient medium that is optimal for their growth and reproduction.
- On the part of the nervous system, diabetes can manifest itself not only as lethargy, but also as excessive irritability, anxiety, tearfulness and decreased academic performance in children.
- Diabetics are constantly thirsty, which is also caused by hyperglycemia. This condition is accompanied by frequent urination and increased load on the kidneys.
The absence of alarming symptoms does not negate the need to monitor your diet and periodically take glucose tests. At first, the disease may be asymptomatic, so the person is unaware of the danger and leads a normal lifestyle. Up to 50% of cases of diabetes remain undiagnosed! The disease is discovered during medical examinations or after the patient urgently calls an ambulance due to problems with well-being due to the development of complications.
In addition, many of the above signs are symptoms of diabetes and a number of other diseases.
Test strips
To detect the concentration of sugar in urine, the analysis is carried out with special test strips. However, this diagnostic method raises doubts among most doctors. The strip can only detect high levels of sugar in urine. Normally, the glucose concentration ranges from 0 to 0.02%. If after passing the test the amount of sugar is high, then it is recommended to undergo additional tests. Thus, test strips are used as part of a comprehensive diagnosis of diabetes.
Test strips help detect high concentrations of glucose in urine
Many patients are interested in the question of how many strips diabetics should take. According to the order of the Ministry of Health, it is planned to provide patients with test strips in the amount of 730 pieces per year for type 1 diabetics and 180 pieces for type 2 diabetes.
Based on all of the above, tests to detect diabetes mellitus are an excellent opportunity to diagnose the disease and begin treatment. The most effective method for diagnosing diabetes at home is a glucometer with test strips. If you detect an increased concentration of sugar, you should consult a doctor who will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe proper treatment.
What happens to your appearance with diabetes?
Diabetes is a serious disease that affects your health and appearance. If a person’s skin and hair condition has worsened for no apparent reason, the cause may be a carbohydrate metabolism disorder.
A specific sign of diabetes is itching of the skin and mucous membranes, which appears for no apparent reason. Diabetic skin not only itches, but also becomes drier. This is caused by increased fluid loss, disruption of the sweat and sebaceous glands. High blood sugar slows down the healing of skin wounds and reduces local immunity. Damage to small vessels also occurs, causing the skin to lose its elasticity.
Diabetics have an increased risk of infectious skin diseases, diaper rash, and fungal infections. Scratching allows the infection to easily penetrate the skin.
It is worth checking your sugar level if your hair begins to noticeably fall out, or if it becomes thinner and thinner. Since diabetes provokes metabolic disorders, hair immediately reacts to such changes. Diabetics are at risk of experiencing alopecia areata, in which hair falls out completely in certain areas of the scalp. This most often occurs in type 1 diabetes as a consequence of an autoimmune reaction. Experts also cite damage to the blood vessels through which blood and nutrients flow to the hair follicles as a reason for the deterioration of hair with high sugar levels.
How does the disease progress in children?
Type 1 diabetes is almost always diagnosed in childhood. The cause of the pathology is a violation of the immune system, which is caused by a hereditary predisposition. The immune system mistakenly attacks the body and damages the pancreatic cells that produce insulin. The disease can manifest itself already in the first year of life. In many young patients, it occurs after the child has had rubella, or due to antigens entering the body with food.
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas stops producing insulin, so the child needs regular injections of the drug and daily monitoring of glucose levels. Therefore, this type of diabetes is called insulin-dependent.
Neonatal diabetes mellitus is also known - a rather rare type. It occurs in an infant. In the first six months of life, the child already exhibits symptoms of diabetes. The pathology occurs due to disturbances in intrauterine development caused by a lack of insulin in the mother.
Can children and adolescents develop type 2 diabetes? Unfortunately yes. In recent years, the disease has become significantly younger. The main reason is the abuse of sweets and lack of exercise. The signs of diabetes in children are the same as in adults: increased thirst, fatigue, itchy skin, and others.
Endocrine or cardiac?
This disease literally destroys the entire body, but the high mortality rate from diabetes is not very obvious, since it is attributed mainly to cardiovascular mortality. But the truth is that it is possible to distinguish between both pathologies very conditionally. Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases are twin brothers. In any hospital cardiology department you look in, there will be approximately 40% of patients with diabetes or prediabetes. And in any endocrinology center where patients with diabetes are treated, there will be at least 70% of people with cardiovascular pathologies (heart attacks, strokes, intermittent claudication, limb amputations due to vascular thrombosis).
Covid diabetes. Soon this diagnosis will be made very often Read more
Tests for diabetes
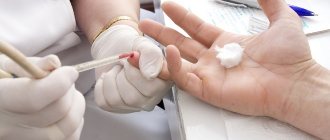
Laboratory testing of blood and urine helps determine sugar levels. In young and middle-aged patients, the glucose norm is 3.3-5.5 mmol/l if blood is donated in the morning before meals. People without diabetes should not have sugar in their urine.
For preventive purposes and if there is an increased risk of developing the disease, a blood glucose test should be taken twice a year. When glucose levels are from 5 to 7 mmol/l, a glucose tolerance test is performed. It includes two stages. First, sugar is measured on an empty stomach, then the person must drink sweet water. Two hours later, a blood test is done again to track changes and thereby assess how the cells respond to insulin. The most accurate is a blood test for glycated hemoglobin. It is used to determine sugar levels for the last three months.
Online test and glucometer
You can determine the “sweet disease” at home. There are special online tests for this purpose. To pass them, you need to enter the request “take an online test for diabetes.” After opening the site, you will need to answer questions: age, body mass index, glucose level, genetic predisposition to the disease, etc. After passing the test, you will receive a result indicating the likelihood of developing the disease. It is recommended that you print out the test with answers and take it with you to the doctor before professional diagnosis. This is necessary, since the results of online tests are quite questionable and require additional research.
You can monitor your sugar levels using a glucometer
A glucometer is a device for measuring blood sugar levels. Using this device, you can quickly and accurately determine your glucose concentration. Normal fasting blood sugar levels range from 70 to 130 mg/dL. Often the device comes with test strips and scarifiers (a knife for making scratches).
Instructions for using a glucometer to detect diabetes:
- Before the examination, thoroughly clean your hands with antibacterial soap.
- Massage your finger and wipe with an antiseptic solution at the puncture site.
- Use a scarifier to pierce the side of the fingertip.
- Wipe off the first drop of blood, squeeze the second onto a strip and place it in the glucometer.
- The results will appear on the device monitor.
The A1C kit allows you to accurately determine the concentration of glucose in the body. This technique is recommended to be used for 3 months, after which the patient receives an average value.