13.11.2017
Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases of the endocrine system that develop due to the lack or absence of insulin (hormone) in the body, resulting in a significant increase in the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood (hyperglycemia).
Diabetes mellitus is mainly a chronic disease. It is characterized by metabolic disorders - fat, carbohydrate, protein, water-salt and mineral. In diabetes mellitus, the functions of the pancreas, which actually produces insulin, are impaired.
Insulin is a protein hormone produced by the pancreas, the main function of which is to participate in metabolic processes - the processing and conversion of sugar into glucose, and the further transport of glucose into cells. In addition, insulin regulates blood sugar levels.
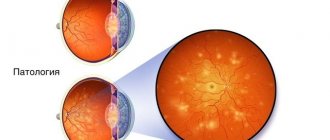
In diabetes, cells do not receive the necessary nutrition. It is difficult for the body to retain water in the cells, and it is excreted through the kidneys. Disruptions occur in the protective functions of tissues, the skin, teeth, kidneys, and nervous system are affected, the level of vision decreases, atherosclerosis and hypertension develop.
In addition to humans, the disease can also affect some animals, such as dogs and cats.
Diabetes mellitus is inherited, but it can also be acquired in other ways.
How does diabetes develop?
The hormone insulin converts sugar into glucose, which is an energy substance necessary for the normal functioning of body cells. When there is a failure in the production of insulin by the pancreas, disturbances in metabolic processes begin. Glucose is not delivered to the cells and settles in the blood. The cells, in turn, starving, begin to malfunction, which externally manifests itself in the form of secondary diseases (diseases of the skin, circulatory system, nervous and other systems). At the same time, there is a significant increase in blood glucose (hyperglycemia). The quality and effect of blood deteriorate. This whole process is called diabetes.
Why is high blood sugar harmful?
High blood sugar levels can cause dysfunction of almost all organs, including death. The higher the blood sugar level, the more obvious the result of its action, which is expressed in:
- obesity;
- glycosylation (sugarification) of cells;
- intoxication of the body with damage to the nervous system;
- damage to blood vessels;
- the development of secondary diseases affecting the brain, heart, liver, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, muscles, skin, eyes;
- manifestations of fainting states, coma;
- lethal outcome.
Symptoms of diabetes
Diabetes mellitus in most cases develops gradually, and only occasionally does the disease develop rapidly, accompanied by an increase in glucose levels to a critical level with various diabetic comas.
The first signs of diabetes
- constant feeling of thirst;
- constant dry mouth;
- increased urine output (increased diuresis);
- increased dryness and severe itching of the skin;
- increased susceptibility to skin diseases, pustules;
- prolonged wound healing;
- a sharp decrease or increase in body weight;
- increased sweating;
- muscle weakness.
Signs of diabetes
- frequent headaches, fainting, loss of consciousness;
- blurred vision;
- heart pain;
- numbness in the legs, pain in the legs;
- decreased skin sensitivity, especially on the feet;
- swelling of the face and legs;
- liver enlargement;
- prolonged wound healing;
- high blood pressure;
- the patient begins to smell of acetone.
Complications of diabetes
Diabetic neuropathy - manifested by pain, burning, numbness of the extremities. It is associated with disruption of metabolic processes in nervous tissue.
Edema. Swelling in diabetes can spread locally - on the face, legs, or throughout the body. Swelling indicates a disturbance in the functioning of the kidneys, and depends on the degree of heart failure. Asymmetrical swelling indicates diabetic microangiopathy.
Leg pain. Pain in the legs with diabetes, especially when walking and other physical activity on the legs, may indicate diabetic microangiopathy. Leg pain during rest, especially at night, indicates diabetic neuropathy. Often, leg pain in diabetes is accompanied by burning and numbness in the feet or some parts of the legs.
Trophic ulcers. Trophic ulcers in diabetes mellitus, after pain in the legs, are the next stage in the development of diabetic angio- and neuropathy. The types of wounds differ greatly from each other, so treatment of trophic ulcers in diabetes is prescribed after an accurate diagnosis, noting the smallest symptomatic details. The negative impact of ulcers is a decrease in the sensitivity of the affected feet, which occurs due to damage to the nerves when the foot is deformed. In some places, this results in corns, under which hematomas are formed with further suppuration. All these processes often occur unnoticeably, so people, as a rule, go to the doctor whose leg is already very swollen, red, and has a trophic ulcer.
Gangrene. Gangrene in diabetes mellitus in most cases is the result of diabetic angiopathy. The onset of gangrene occurs due to damage to small and large blood vessels in the area of the lower limb, most often the big toe. In this case, the patient feels severe pain in the foot. Redness of the damaged area occurs, which over time gives way to bluish skin, and after some time, this area becomes covered with black spots and blisters with cloudy contents. The process is irreversible - amputation of the limb is necessary. The optimal level of limb amputation is the lower leg.
High and low pressure. High and low pressure in diabetes mellitus is observed simultaneously in two points of the body. In the upper part of the body (in the brachial artery) there is increased pressure, which indicates kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy). In the lower part of the body (in the vessels of the legs) there is low pressure, which indicates the degree of diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities.
Coma. Coma with diabetes occurs extremely quickly. A sign of coma in diabetes is the patient's lethargy and fainting. Before this, a person may smell of acetone coming from the mouth when breathing, which is due to extreme intoxication of the body. In addition, the patient may break into a cold sweat. If the patient exhibits at least one of these signs, he must be taken to a medical facility immediately.
Causes of diabetes
There can be quite a few causes of diabetes, so let’s highlight the most significant:
- heredity;
- age (the older the person, the greater the likelihood of getting sick);
- obesity;
- nervous tension;
- diseases that destroy beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin: pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, etc.;
- viral infections: hepatitis, chickenpox, rubella, influenza, etc.
In addition, diabetes mellitus can develop against the background of:
- hyperfunction of the adrenal glands (hypercortisolism);
- tumors of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased levels of hormones that block insulin;
- liver cirrhosis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- poor digestibility of carbohydrates;
- short-term increase in blood sugar levels.
According to the severity of the disease:
Diabetes mellitus 1 degree (mild form). Characterized by a low level of glycemia (blood sugar) - no more than 8 mmol/l (on an empty stomach). The level of daily glucosuria is no more than 20 g/l. May be accompanied by angioneuropathy. Treatment at the level of diet and taking certain medications.
Diabetes mellitus 2 degrees (moderate form). Characteristic is a relatively small, but already with a more obvious effect, increase in glycemic levels at the level of 7-10 mmol/l. The level of daily glucosuria is no more than 40 g/l. Manifestations of ketosis and ketoacidosis are periodically possible. Severe disturbances in the functioning of organs do not occur, but at the same time, some disturbances and signs in the functioning of the eyes, heart, blood vessels, lower extremities, kidneys and nervous system are possible. Possible signs of diabetic angioneuropathy. Treatment is carried out at the level of diet therapy and oral administration of sugar-lowering drugs. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe insulin injections.
Diabetes mellitus stage 3 (severe form). A typical average glycemic level is 10-14 mmol/l. The level of daily glucosuria is about 40 g/l. There is a high level of proteinuria (protein in the urine). The picture of clinical manifestations of target organs—eyes, heart, blood vessels, legs, kidneys, nervous system—is enhanced. Vision decreases, numbness and pain appear in the legs, and blood pressure increases.
Diabetes mellitus stage 4 (super severe form). A typical high level of glycemia is 15-25 mmol/l or more.
The level of daily glucosuria is over 40-50 g/l. Proteinuria increases, the body loses protein. Almost all organs are affected. The patient is prone to frequent diabetic comas. Life is maintained purely on insulin injections - at a dose of 60 OD or more.
Causes of high blood sugar in the morning
The minimum glucose values are observed in the patient in the morning, when after the night there is a physiological decrease. In the case of high levels of morning sugar on an empty stomach, progression of insulin-dependent diabetes is noted. Severe hyperglycemia in the morning is observed even when a sufficient dose of insulin is administered before bedtime. As a rule, such sugar surges are a systematic condition of a diabetic.
This phenomenon is quite common and, due to its characteristics, is called “dawn syndrome”. The phenomenon is due to changes in hormonal levels, since in the morning a large amount of hormones are secreted that counteract insulin. Thus, high concentrations of cortisol and glucagon cause high sugar levels between 4-8 am.
It is recommended for a diabetic to keep a self-monitoring diary in which he notes glucose levels and the dosage of insulin administered
Factors contributing to the phenomenon:
- Insufficient dose of insulin administered before bedtime.
- Abuse of carbohydrate foods at night.
- Acute viral disease or development of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Mental and emotional stress during the day.
- Incorrect selection of the dose of insulin against the background of its chronic overdose.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient needs to measure sugar throughout the night. To establish an accurate picture, it is recommended to carry out a measurement: control at 00:00, then from 3:00 to 7:00 every hour. If during this period of time an increase is observed compared to the control, then the presence of the syndrome can be assumed.
Treatment of the syndrome consists of adjusting the dose of administered insulin and changing the injection time to a later time, so that the drug will act at the peak of the production of antagonist hormones.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
The following methods and tests have been established for diagnosing diabetes mellitus:
- measuring blood glucose levels (determination of glycemia);
- measurement of daily fluctuations in glycemic levels (glycemic profile);
- measuring insulin levels in the blood;
- glucose tolerance test;
- blood test for the concentration of glycosylated hemoglobin;
- blood chemistry;
- urine test to determine white blood cell, glucose and protein levels;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- Rehberg's test.
In addition, if necessary, carry out:
- study of blood electrolyte composition;
- urine test to determine the presence of acetone;
- fundus examination;
- electrocardiography (ECG).
Control Features
Daily monitoring of circulating blood glucose levels is an integral part of successful diabetes management. This allows you to achieve compensation for the disease, look at the dynamics of sugar levels and control its concentration at the optimal level.
As a rule, most diabetics feel their condition worsening in the morning before meals, and some at lunchtime or in the evening
Monitoring glucose levels is necessary in the following cases:
- 4.00 to prevent hypoglycemia;
- in the morning after a night's sleep;
- before the first breakfast;
- before each meal;
- 2 hours after a meal;
- 5 hours after insulin administration;
- after severe emotional and physical stress;
- before going to bed at night.
To monitor the dynamics of the disease, you need to record glucose levels, since when visiting a specialist, they will be taken into account when assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus requires compliance with certain rules in measuring glucose:
- The measurement should be carried out at a strictly defined time, since the norm may fluctuate within 30 minutes.
- It is not recommended to measure sugar after physical activity, since during exercise a large amount of energy is consumed and the results will be poor.
- Glucometer readings may be elevated after mental and emotional stress.
- During pregnancy, sugar readings fluctuate, so its measurement should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
To achieve good compensation for the disease, measurements should be taken at least twice a day.
Treatment of diabetes
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct an accurate diagnosis of the body, because a positive prognosis for recovery depends on this.
Treatment of diabetes is aimed at:
- decreased blood sugar levels;
- normalization of metabolism;
- preventing the development of diabetes complications.
Further, treatment varies depending on the type of diabetes. Let's look at them separately.
Treatment of type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent)
As we already mentioned in the middle of the article, in the “Classification of Diabetes Mellitus” section, patients with type 1 diabetes constantly need insulin injections, since the body cannot produce this hormone itself in sufficient quantities. There are currently no other methods of delivering insulin to the body other than injections. Insulin-based tablets will not help with type 1 diabetes.
In addition to insulin injections, treatment for type 1 diabetes includes:
- diet;
- performing dosed individual physical activity (DIPE).
Treatment of type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent)
Type 2 diabetes is treated by following a diet and, if necessary, taking antihyperglycemic drugs, which are available in tablet form.
Diet for type 2 diabetes mellitus is the main method of treatment due to the fact that this type of diabetes develops due to improper nutrition of a person. With improper nutrition, all types of metabolism are disrupted, therefore, by changing their diet, a diabetic in many cases gets better.
In some cases, with persistent types of type 2 diabetes, the doctor may prescribe insulin injections.
Diet for diabetes
When treating any type of diabetes, diet therapy is a must.
A nutritionist for diabetes mellitus, after receiving tests, taking into account age, body weight, gender, lifestyle, outlines an individual nutrition program. When dieting, the patient must calculate the amount of calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements consumed. The menu must be followed strictly as prescribed, which minimizes the risk of developing complications of this disease. Moreover, by following a diet for diabetes, it is possible to defeat this disease without additional medications.
The general emphasis of diet therapy for diabetes is on eating food with minimal or no content of easily digestible carbohydrates, as well as fats, which are easily converted into carbohydrate compounds.
Prevention of type 2 diabetes
The most important thing is to remain positive and be ready for change. Try to wean yourself from possible bad habits and think about what gives you pleasure - this will help you move towards a healthier lifestyle. You can start walking more or try new, healthier recipes - whatever you like, as long as you do it with enthusiasm.
If you are in an age group at higher risk of developing diabetes or have a poor family history, there is no need to worry too much. Just check out this article and try to enjoy a healthy lifestyle.
The relationship between glucose levels, cholesterol and body weight
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is almost always accompanied by obesity, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. When performing a venous blood test in diabetics, cholesterol levels are assessed, with a mandatory distinction between the amount of low-density lipotropes (“bad cholesterol”) and high-density lipotropes (“good cholesterol”). BMI (body mass index) and blood pressure (blood pressure) indicators are also determined.
With good compensation of the disease, normal weight is recorded, according to height, and slightly exceeded blood pressure measurement results. Unsatisfactory (poor) compensation is a consequence of the patient’s regular violation of the diabetic diet, incorrect therapy (the glucose-lowering drug or its dosage is incorrectly selected), and non-compliance by the diabetic with the work and rest regime. The glycemic level reflects the psycho-emotional state of the diabetic. Distress (constant neuropsychological tension) causes an increase in glucose levels in the blood.
How to adjust indicators?
The measures taken depend on the causes of sugar surges. Your doctor will help you identify them. Once the cause is established, you can begin to take active action.
Recommendations for the Somogyi effect: regular monitoring of sugar levels using a glucometer, following a diet, avoiding alcohol, and avoiding physical overload.
Those suffering from the dawn phenomenon should:
- avoid eating after 7 p.m.;
- in the evening, limit the consumption of foods rich in plant fiber;
- administer long-acting insulin between 1:00 a.m. and 3:00 a.m.;
- in severe cases, the use of an insulin pump is recommended.
The described conditions can be easily corrected if a competent treatment regimen is prescribed and the patient complies with all the doctor’s instructions. To prevent morning hyperglycemia, it is important to use properly selected medications that lower sugar, adhere to a balanced diet and moderate physical activity.