Elevated blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs for a variety of reasons. Normally, the sugar level should not be higher than 5.5 mmol/l. The severity of hyperglycemia is determined by two main factors: the total amount of glucose in the blood and the rate at which it increases. In medical practice, the pathological condition in question is classified according to two criteria: fasting hyperglycemia and afternoon hyperglycemia.
Glucose is necessary for the cells of the human body, but if its level exceeds the norm, this can lead to irreversible consequences. The person himself may not notice the symptoms of this condition for a long time if it is mild. If the sugar level is significantly elevated, characteristic signs appear that are important to recognize in time and consult a doctor. In our clinic you can always get advice from competent specialists, take the necessary tests and undergo a course of treatment.
Causes of high blood sugar
High blood sugar may be associated with certain diseases:
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies;
- liver diseases;
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- severe infectious diseases;
- obesity.
Diabetes mellitus is considered the most common cause of hyperglycemia, which is long-lasting and negatively affects almost all internal organs and systems of the body.
Factors that contribute to hyperglycemia that are not associated with pathologies of the body are also identified:
- overeating, predominance of simple carbohydrates in the diet;
- stress;
- severe premenstrual syndrome in women;
- alcohol abuse;
- hereditary predisposition.
Causes of diabetes
There can be quite a few causes of diabetes, so let’s highlight the most significant:
- heredity;
- age (the older the person, the greater the likelihood of getting sick);
- obesity;
- nervous tension;
- diseases that destroy beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin: pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, etc.;
- viral infections: hepatitis, chickenpox, rubella, influenza, etc.
In addition, diabetes mellitus can develop against the background of:
- hyperfunction of the adrenal glands (hypercortisolism);
- tumors of the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased levels of hormones that block insulin;
- liver cirrhosis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- poor digestibility of carbohydrates;
- short-term increase in blood sugar levels.
According to the severity of the disease:
Diabetes mellitus 1 degree (mild form). Characterized by a low level of glycemia (blood sugar) - no more than 8 mmol/l (on an empty stomach). The level of daily glucosuria is no more than 20 g/l. May be accompanied by angioneuropathy. Treatment at the level of diet and taking certain medications.
Diabetes mellitus 2 degrees (moderate form). Characteristic is a relatively small, but already with a more obvious effect, increase in glycemic levels at the level of 7-10 mmol/l. The level of daily glucosuria is no more than 40 g/l. Manifestations of ketosis and ketoacidosis are periodically possible. Severe disturbances in the functioning of organs do not occur, but at the same time, some disturbances and signs in the functioning of the eyes, heart, blood vessels, lower extremities, kidneys and nervous system are possible. Possible signs of diabetic angioneuropathy. Treatment is carried out at the level of diet therapy and oral administration of sugar-lowering drugs. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe insulin injections.
Diabetes mellitus stage 3 (severe form). A typical average glycemic level is 10-14 mmol/l. The level of daily glucosuria is about 40 g/l. There is a high level of proteinuria (protein in the urine). The picture of clinical manifestations of target organs—eyes, heart, blood vessels, legs, kidneys, nervous system—is enhanced. Vision decreases, numbness and pain appear in the legs, and blood pressure increases.
Diabetes mellitus stage 4 (super severe form). A typical high level of glycemia is 15-25 mmol/l or more. The level of daily glucosuria is over 40-50 g/l. Proteinuria increases, the body loses protein. Almost all organs are affected. The patient is prone to frequent diabetic comas. Life is maintained purely on insulin injections - at a dose of 60 OD or more.
Associated symptoms
A pronounced increase in blood sugar levels manifests itself with characteristic symptoms, which are especially clearly visible in patients with diabetes:
- constant thirst and dry mouth;
- increased urge to urinate;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- increased appetite, weight gain or sudden weight loss (this symptom is typical mainly for patients with type 1 diabetes);
- skin itching, furunculosis, prolonged wound healing;
- increased blood pressure due to impaired renal function;
- increased irritability;
- drowsiness;
- apathetic state;
- difficulty concentrating;
- decreased vision;
- susceptibility to infectious diseases.
Having noticed such manifestations in yourself, you may suspect hyperglycemia, but only a qualified doctor will make an accurate diagnosis. In our clinic you can undergo a full range of examinations to identify acute and chronic diseases. An experienced endocrinologist will develop effective treatment tactics to eliminate pathological symptoms and return you to good health.
Diagnostics in our clinic
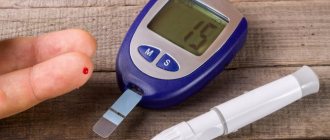
Diagnosis of hyperglycemia includes taking a medical history, analyzing clinical symptoms and a number of laboratory tests. A blood sugar test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. In some cases, it becomes necessary to repeat the analysis after a few days to exclude possible stress factors.
In modern medicine, several methods of testing blood for sugar are used:
- rapid test for determining the approximate glucose concentration - can be carried out at home, but does not provide one hundred percent accuracy;
- analysis for glycated hemoglobin - allows you to determine the average glucose level over a certain period of time (1-3 months);
- Glucose tolerance test is a comprehensive study that involves taking blood from a finger prick four times over two hours (on an empty stomach and after taking glucose).
In a healthy person, the glucose level is 3.5-5.5 mmol per liter of blood. An indicator of 6 mmol is considered a prediabetic state. If the glucose concentration exceeds this value, the doctor has reason to diagnose diabetes mellitus.
When performing a glucose tolerance test, a result of up to 7.9 mmol/l is considered as normal. Diabetes mellitus is indicated by a value of over 11 mmol per liter.
Diabetes mellitus: who is at risk
According to WHO, the number of people with diabetes has quadrupled over the past 40 years. What are the risk factors and the first symptoms of diabetes, how serious are the consequences and is it possible to prevent the disease? Endocrinologist Elena Anatolyevna Koroleva spoke about all this on a live broadcast on the website Apteka.ru. Here are the main points of the broadcast.
What is diabetes mellitus and how does it manifest?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot use the insulin it produces effectively (insulin resistance).
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. A common result of uncontrolled diabetes is hyperglycemia, or elevated blood levels, which over time leads to severe damage to many body systems, especially nerves and blood vessels.
The normal blood sugar range is from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol/l. If a laboratory test shows a higher blood sugar level, it means that carbohydrate metabolism is disturbed in the body.
Classic symptoms of diabetes: increased thirst, frequent urge to urinate. However, they appear at very high sugar levels (10-15 mmol/l); with moderately high sugar levels (5.5 to 10 mmol/l), symptoms may not appear immediately.
What types of diabetes are distinguished today?
Modern medicine distinguishes three types of diabetes.
For type 1 diabetes
(previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood) the cells that produce insulin die in the body. The cause of this type of diabetes is unknown, so it cannot currently be prevented. You can develop type 1 diabetes before the age of 30.
Symptoms: excessive urination, thirst, constant hunger, weight loss, vision changes and fatigue.
These symptoms may appear suddenly.
On the one hand, this is a very severe type of diabetes, the only way to treat it is insulin therapy. On the other hand, this is a fairly rare type of disease - only 10% of people with diabetes suffer from type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes
(previously called insulin-independent or adult-onset) develops as a result of the body's ineffective use of insulin. Most patients suffer from type 2 diabetes. It is largely the result of excess weight and physical inertia. Most often, people develop type 2 diabetes after age 40. The peak of the disease is 60-70 years.
Symptoms may be similar to those of type 1 diabetes, but are often less severe. As a result, the disease can be diagnosed several years after its onset, after complications have arisen.
Until recently, this type of diabetes was observed only among adults, but in recent years it has also affected children.
is also distinguished .
Gestational diabetes is hyperglycemia that develops or is first detected during pregnancy. Women with this form of diabetes also have an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth, and they have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Most often, gestational diabetes is diagnosed during prenatal screening rather than based on reported symptoms.
It is important to note that this type of diabetes is more dangerous for the baby than for the mother (chronically high sugar can lead to problems during pregnancy and after birth). However, having gestational diabetes during pregnancy increases a woman's chances of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Gestational diabetes ends with pregnancy, but it is important to identify and treat it early for the well-being of mother and child.
Prediabetes
Increased glucose tolerance (HTG) and impaired fasting glucose (IFG) are intermediate conditions between normal and diabetes.
People with PTH and IFN are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but this may not happen.
The task of doctors should be to identify and prevent PTG and NGN. For prevention purposes, you should not neglect a medical examination and donate blood for sugar at least once every three years.
Risk factors (type 2 diabetes): obesity, presence of diabetes in relatives, presence of diabetes in a pregnant woman, presence of concomitant hypertension, smoking.
Consequences of diabetes
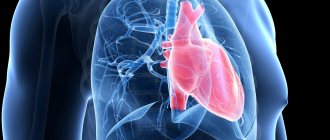
Over time, diabetes can affect the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nerves.
Adults with diabetes have a 2-3 times higher risk of heart attack and stroke.
Combined with decreased blood flow, neuropathy (nerve damage) in the legs increases the likelihood of leg ulcers, infection, and ultimately the need for limb amputation.
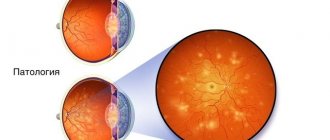
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the important causes of blindness. It develops as a result of long-term accumulation of damage to the small blood vessels of the retina. Diabetes may be responsible for 2.6% of global cases of blindness.
In addition, diabetes is among the leading causes of kidney failure.
Is it possible to control the consequences of diabetes if the disease can no longer be prevented?
The severity of the consequences correlates with sugar levels. The most important thing is to control your sugar level and reduce it. The easiest way to do this is at an early stage of the disease.
Prevention recommendations:
- achieve and maintain a healthy body weight
- Be physically active - at least 30 minutes of regular moderate-intensity activity on most days; Additional activity is required to control weight. The minimum prevention of the disease is to try to walk 10,000 steps a day. If your life is spent in front of a computer, you need to start small - take a break from work, walk around the room, use the stairs instead of the elevator, etc. Children and adolescents from 5-17 years old are supposed to get 60 minutes of moderate and high-intensity exercise every day.
- Eat a healthy diet and reduce your intake of sugar and saturated fat
- refrain from using tobacco – smoking increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases
Addition to the point about physical activity: women are in a more vulnerable position - due to the greater number of responsibilities (home duties are added to work), it can be very difficult to find time for yourself and for physical activity.
However, it is important to plan ahead and make time for physical activity - women are more likely to develop diabetes.
Modern methods of diagnosing diabetes
The main method remains donating blood for sugar. In addition there are:
- glucose tolerance test
— determination of glycated hemoglobin
- hormonal and genetic studies
— 24-hour glucose monitoring system
— Holter ECG monitoring
Modern methods of treating diabetes
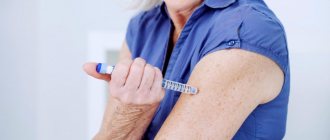
Type 1 diabetes is treated only with insulin therapy.
Continuous infusion of insulin using insulin pumps is a new method of insulin therapy that delivers insulin continuously in very small doses.
For the treatment of type 2 diabetes:
- adherence to nutritional rules, physical activity
— modern hypoglycemic drugs (tablets/injections)
— physiotherapeutic effects (physical therapy)
- high-tech medical care (pump therapy is also high-tech; this also includes vascular operations)
Do people with diabetes receive support from the government?
Yes. Patients have the right to receive free medications. You can view the list of vital medications on the website of the Ministry of Health (list of vital and essential drugs).
One of the requirements for the patient is to carry out self-monitoring using a glucometer (hours for measuring sugar are discussed between the patient and the doctor individually - different types of diabetes require different measures).
Do you need a special diet for diabetes?
Diet is required. The most important thing is to give up sweets. It is necessary to eat in such a way as to lose weight, if you are overweight - for this you need to rebuild your diet, you should start by at least reducing the amount of food consumed.
- It is worth limiting foods containing animal fats and carbohydrates. You can eat carbohydrates in moderation: bread, porridge, pasta, fruits, but do not overdo it, otherwise the sugar will rise too much again.
- You need to increase the amount of dietary fiber in your diet - the more vegetables, the better.
- It is not recommended to eat dried fruits; you should limit nuts and seeds - all these are almost pure fatty foods.
- Be careful with meat: if you eat fatty meat every day, you can gain weight. The same thing with fish - limit fatty, high-calorie varieties.
- Sausage is a bad product for a diabetic.
- Milk contains carbohydrates, so the amount should be limited.
- Vegetable oil is better, it is saturated with beneficial acids. But it affects body weight in the same way as cream. So again you have to be careful. The best option is to use olive or flaxseed.
Questions and answers
Q: Is insulin resistance reversible?
A: Insulin resistance is partly genetic. You can reverse it - you need to make efforts to reduce body weight, you need physical activity, exercise.
Q: If I smoke, my blood pressure periodically rises, and I am overweight, how often should I donate blood?
A: Once a year.
Q: What are the normal blood sugar levels?
A: Blood from a vein – up to 6 mmol/l, from a finger – up to 5.5 mmol/l.
Q: Are the drugs that are given at a discounted rate modern, or is it better to buy them yourself?
A: One of the free drugs is metformin. It is the first-line drug in the treatment of diabetes mellitus around the world. Not the most expensive product, but very effective. On the other hand, today new, innovative drugs have appeared. They do not always work when they should, sometimes they cause side effects, sometimes, on the contrary, additional positive effects. If a doctor recommends buying something extra during a consultation, and you can afford it, it’s better to listen.
Q: How expensive is it to have diabetes?
A: Diabetes is a catastrophic financial burden. Diabetes is expensive, but if treated well, it can cost up to 12,000 rubles a month for just one drug. Consumables (needles, test strips) also cost a lot. Therefore, it is worth focusing on preventing the disease.
Q: Is it possible to measure sugar once every 2-3 days? Every day is very expensive.
A: Depends on how you are being treated. Sometimes they are treated only with diet or medications that do not reduce sugar levels. Then it's better once a day. If the sugar is stable - once a week, maximum - once every two weeks, at least. But if constant self-monitoring is necessary, then it is worth measuring up to several times a day. Sometimes self-control is more important than even the therapy itself.
Recorded by Nina Timonova
Photo deposiphotos.com
The opinion of the author may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Principles of treatment
If you have high blood sugar, you will need treatment to avoid life-threatening conditions. The complex of therapeutic measures includes:
- adherence to the principles of proper nutrition;
- regular monitoring of blood sugar levels - for this you can purchase a special device for home use - a glucometer. It is recommended to carry out the test several times a day. Urgent consultation with an endocrinologist is required if sugar levels increase repeatedly over a short period;
- regular physical activity;
- weight normalization;
- regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels;
- taking medications to reduce blood glucose concentrations (insulin secretagogues, alpha-glucosiade inhibitors, etc.).
Treatment tactics are always selected individually depending on the reasons that led to the increase in blood sugar.