Medical editor: Strokina O.A. - therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. November, 2021.
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome (EVRS) is a medical concept that includes only ECG changes without characteristic external symptoms. It is believed that SRRS is a normal variant and does not pose a threat to the patient’s life.
However, recently this syndrome has become viewed with caution. It is quite widespread and occurs in 2-8% of cases in healthy people. The older a person gets, the less likely it is that he or she will have SRR; this is due to the emergence of other cardiac problems that are similar in electrocardiographic signs as they age.
Most often, early ventricular repolarization syndrome is diagnosed in young men who are actively involved in sports, in men who lead a sedentary lifestyle, and in people with dark skin (Africans, Asians and Hispanics).
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome - what is it? General information
Specific cardiac syndrome is found not only in patients with heart pathology, but also in absolutely healthy people. Early repolarization of the ventricles is called premature repolarization syndrome. Very often, WPW syndrome confused with premature repolarization, despite the fact that these are completely different pathologies.
Pathological changes on the ECG were considered normal for a long time, until a clear relationship with heart rhythm disturbances was revealed. The disease is asymptomatic, which greatly complicates timely diagnosis.
The syndrome of early (premature, accelerated) repolarization of the ventricles of the heart is characterized by specific changes in the electrocardiogram in the absence of obvious causes. ICD-10 code: I45.6
QT shortening
The syndrome is also very rare and may be associated with certain congenital diseases with gene mutations. Improper functioning of potassium channels leads to changes in QT duration. The shortened repolarization process is accompanied by constant arrhythmia, and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest always remains.
Short QT syndrome
Factors that allow diagnosing a shortened repolarization phase:
- Frequent attacks of arrhythmia and ventricular tachycardia, fainting.
- Sudden slowing of heart rate at any time of the day.
- ECG data. If the QT duration is less than 0.33, then this pathology will most likely be confirmed.
- Heredity. If there have been cases of sudden cardiac arrest in your family, there is a risk.
In children, the shortened repolarization process occurs in the same way as in adults. A qualified diagnostician may suspect this disease even if there are no direct symptoms.
Non-cardiac symptoms of short QT phase:
- elevated potassium or calcium levels in a blood test;
- elevated temperature;
- the initial stage of acidosis (the pH level is shifted to the acidic side);
- Digoxin use.
Pathogenesis
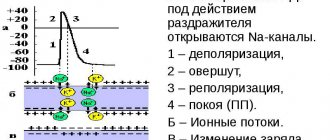
Contraction of the chambers of the heart occurs as a result of changes in the electrical charge in myocardial cells - cardiomyocytes . As a result, sodium, calcium and potassium ions move into the intercellular space and back. The process is carried out in alternating main phases:
- depolarization – contraction;
- repolarization is relaxation before a new contraction.
Early repolarization of the ventricles is formed as a result of improper conduction of the impulse through the conduction system of the heart from the atria to the ventricles. To transmit the electrical impulse, abnormal conduction pathways . The development of the phenomenon is due to an imbalance between repolarization and depolarization in the basal regions and apex of the heart. Characterized by a significant reduction in the period of myocardial relaxation. On the ECG, along with the SRRS, a disturbance of repolarization processes in the myocardium is often recorded, in particular, a violation of the repolarization of the lower wall of the left ventricle.
Tracking phase changes on an ECG
Diffuse changes in the repolarization process cause changes in the T wave. But it will be too early to talk about an exact diagnosis, since this is typical for any metabolic disorders, and not just in the heart muscle. If deviations of not only the T wave, but also the ST segment are observed, then there is a diffuse imbalance of cell electrolytes.
When deciphering the ECG results, the duration of the intervals between its components is measured
Prescribing treatment and making a diagnosis based on ECG results is difficult. It is necessary to collect a complete clinical picture and conduct additional studies. It is impossible to interpret the results of the electrocardiogram curve unambiguously, since the nature of the bioelectric processes is heterogeneous.
The repolarization process can be disrupted by a very serious pathology - hypersympathicotonia. This disease begins in childhood and is accompanied by increased levels of adrenaline in the blood.
Also, the reasons for deviations in the repolarization phases on the ECG curve may be due to heavy physical labor or constant stressful situations. Women during pregnancy or menopause are susceptible to the disease. A huge number of people have changes in the lower wall of the heart muscle, but are not aware of it.
Classification
In children and adults, early ventricular repolarization syndrome can have 2 development options:
- without damage to the cardiovascular system;
- with defeat.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- transitory form;
- permanent form.
Depending on the location of the ECG signs of SRGC, they are divided into 3 types.
- I characteristic signs are observed in a healthy person. ECG signs are recorded only in chest leads V1, V2. The likelihood of complications developing is extremely low.
- II ECG signs are recorded in the inferolateral and lower sections, leads V4-V6. The risk of complications is increased.
- III ECG changes are recorded in all leads. The risk of complications is the highest.
How deviations are determined
The main and only method for diagnosing ventricular repolarization disorders is electrocardiography. The film shows nonspecific changes in the T wave (mainly in the chest leads) - it becomes high, pointed, or, conversely, its amplitude decreases, it may be negative.
Of much greater interest is the ECG diagnosis of SRGR, in which the following main signs are noted:
- ST segment elevation;
- point j, “camel hump”, “Osborne wave” – a notch on the descending part of the ST segment;
Shortening of the PQ and QT intervals may also occur.
Decoding the cardiogram requires special care from the doctor, since ST segment elevation occurs in other, more serious pathologies - angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pericarditis, etc. Most often, the clinical picture does not help in differential diagnosis, because SRS is not accompanied by any symptoms.
However, if I find the above changes on film in an adult (especially after 40 years), then I additionally prescribe stress tests, i.e. taking an ECG while the patient is performing moderate physical activity - on a bicycle ergometer or treadmill (treadmill). With SRRH, the cardiogram returns to normal. This helps me make a differential diagnosis between the silent form of angina and heart attack.
In case of an unclear ECG picture, I use special tests with drugs. The patient is administered potassium chloride or Novocainamide. After 30 minutes, an ECG is taken. With SRR, the signs become more distinct.
To detect possible arrhythmias, I perform daily (Holter) ECG monitoring on my patients.
Since SRHR can develop against the background of organic heart disease, I prescribe echocardiography to assess the morphological structure of the myocardium.
Causes
The true reasons have not been fully studied. There are only hypotheses for the occurrence of early repolarization:
- Genetic predisposition. Mutation of genes that are responsible for balancing the processes of the entry of certain ions into the cell and their release out.
- Disruption of the processes of contraction and relaxation of individual areas of the myocardium, which is characteristic of type I Brugada syndrome .
- Changes in cardiomyocyte action potentials. The process is associated with the mechanism for the release of potassium ions from cells. This also includes increased susceptibility to a heart attack during ischemia .
According to statistics, accelerated repolarization syndrome is typical for 3-10% of healthy people of all ages. Most often, changes are recorded in young people aged 30 years, in people leading a healthy lifestyle and in athletes.
Nonspecific factors influencing the development of early ventricular repolarization syndrome:
- congenital form of hyperlipidemia , which provokes the development of atherosclerotic changes ;
- long-term use of certain medications, or overdose (for example, beta-agonists);
- connective tissue dysplasia , which is characterized by additional chordae in the ventricular cavity;
- high blood cholesterol
- electrolyte imbalance;
- neuroendocrine changes;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects : congenital, acquired;
- disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system;
- hypothermia of the body;
- excessive physical activity.
Disturbance of repolarization processes in the myocardium
Disturbance of repolarization processes - main symptoms:
- Headache
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Fever
- Cardiopalmus
- Dyspnea
- Memory impairment
- Heart rhythm disturbance
- Rapid pulse
- High blood pressure
- Malaise
- Pale skin
- Tingling in the heart
- Fluctuations in blood pressure
- Deterioration of general condition
- Slow heartbeat
Disturbance of repolarization processes is a disease during which the repolarization phase is reduced or becomes longer in time. Such a disorder may be symptomatic, but this can only be determined by carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures.
Diffuse disorders of cardiac repolarization are changes that are clearly visible on the cardiogram. They can occur in older people, as a marker of cell involution, or in people of all ages, as a marker of external influences on the heart.
Danger of condition
Diffuse disturbances of repolarization processes in the myocardium are dangerous because there is a high probability of additional contraction occurring before the end of the repolarization process.
Clinically, this is manifested by the occurrence of extrasystoles (in the best case, supraventricular, in the worst - ventricular).
In severe cases, polymorphic polytopic ventricular tachycardia may develop, which turns into ventricular fibrillation and becomes the cause of human death.
Diffuse disruption of the cardiac repolarization process does not always lead to such complications. Sometimes the condition simply remains an ECG phenomenon that does not affect hemodynamics or cause other rhythm disturbances.
Unfortunately, when a doctor sees a person and their electrocardiogram with a repolarization disorder, they cannot predict whether that person will develop complications or not.
Therefore, it is necessary to constantly be under the supervision of a cardiologist and periodically take new cardiograms.
Reasons for changes
Diffuse changes in repolarization processes can occur with the development of the following conditions:
- Myocarditis of any etiology.
- Cardiomyopathies – hypertrophic, dilated, restrictive.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Electrolyte imbalance associated with changes in the concentration of potassium, calcium, sodium, chlorine in the body.
- Development of metabolic acidosis or alkalosis.
- Respiratory failure with the formation of alkalosis or acidosis.
- Severe pulmonary hypertension.
- Shock of various etiologies.
Particular attention should be paid to coronary heart disease. It is generally accepted that this disease leads to infarction of the local area of the left ventricle. This complication is indeed characteristic of this pathology. However, at the same time, all parts of the heart suffer from constant ischemia (lack of blood flow and oxygen), and not just certain areas of the left ventricle.
Of course, the degree of tissue ischemia varies - it depends on the degree of narrowing of the coronary arteries and the provision of collateral blood flow. But all cardiomyocytes will suffer to one degree or another from coronary heart disease, and diffuse repolarization disorders can develop in all of them. Moreover, the severity of such changes will also depend on the degree of ischemia.
To identify changes, you will need to record a cardiogram or a series of them. To identify possible complications, it is necessary to conduct Holter monitoring. But to identify the causes of this condition, other diagnostic methods are needed.
- Complete blood count - identifying markers of the infectious process.
- Blood test to determine electrolyte composition.
- Echocardiography to assess the condition of the heart chambers.
- Dopplerography of heart vessels. If necessary, angiography.
- Treadmill test in a department where there is a resuscitation kit.
The latter technique allows you to identify hidden cardiac ischemia and make a diagnosis of coronary artery disease. This method should never be used first, especially if there is even the slightest suspicion that a person has myocarditis. Incorrect diagnosis with load can be fatal!
Treatment tactics
Before starting to treat the pathology, it is necessary to find out the cause of the condition and eliminate it as quickly as possible. Otherwise, all therapeutic measures will be ineffective.
If the cause is identified at the initial stage and quickly eliminated, there is a possibility that the diffuse disturbance of the repolarization process will disappear.
If the cause is eliminated, but the changes remain, it is necessary to use special cardioprotective drugs.
The heart is the main organ of the human body. Many of us do not even suspect how complex its structure is, how important the processes occurring here are.
Any disturbance in the normal functioning of the heart can cause diseases, of which there are a huge number today.
What’s worst is that most of them pose a great threat to human health and life, therefore, we must be extremely attentive to the main “motor” and pay attention to any problems in it.
One of the fairly common and very serious ailments is considered to be a violation of repolarization processes in the myocardium. The title is quite complex, so it can cause confusion among many readers. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Myocardial repolarization is a procedure during which the normal state of the membrane of the nerve cell through which the nerve impulse passed is restored. During its passage, the molecular structure of the membrane is disrupted, and after repolarization, accompanied by the reverse movement of ions, the electrical charge is restored.
Having studied the definition, we can say that myocardial repolarization is a very important procedure for the body; any disturbances in this process can provoke health problems. That is why it is worth considering the main reasons for their occurrence.
Reasons for violation
Numerous studies have shown that impaired myocardial repolarization can be caused by hundreds of reasons. All of them are divided into several main groups, depending on their characteristics:
- diseases associated with disruption of the neuroendocrine system. It is she who partly regulates the functioning of all organs of the cardiovascular system;
- heart disease - these include ischemia, hypertrophy, electrolyte imbalance;
- pharmacological effects - uncontrolled use of medications that have a negative effect on the heart.
There are also known nonspecific causes that can provoke changes in myocardial repolarization processes. In this case, they mean diagnosing it in adolescents.
Doctors do not yet know the exact list of factors that provoke these disorders.
But practice shows that in adolescence, impaired repolarization of the ventricular myocardium occurs quite often, in most cases it goes away on its own, without requiring drug treatment.
Interesting! In recent years, there has been a tendency to increase the number of cases of diagnosing myocardial repolarization disorders in adolescents. In this regard, the problem requires increased attention.
Symptoms
What is dangerous in this situation is the almost complete absence of symptoms of the disease. Often, repolarization of the left ventricle is detected only during an ECG, which the person was referred for for a completely different reason.
What can the doctor see on the electrocardiogram, getting the opportunity to make such a diagnosis as a violation of the repolarization processes occurring in the myocardium:
- changes in the P wave, indicating the presence of atrial depolarization;
- the QRS complex will show depolarization of the ventricular myocardium. On the cardiogram you can see that Q and S are negative, R is positive. In this case, there may be several last teeth;
- The T wave provides information about the features of ventricular repolarization; based on its deviations from the norm, disorders are diagnosed.
From the general picture of the disease, its form is very often isolated - early myocardial repolarization syndrome. This means that all processes of restoring the electrical charge start earlier than they should be. On the cardiogram such a change will be displayed as follows:
- the ST segment begins to rise from the J point;
- in the descending portion of the R wave, peculiar notches may be found;
- against the background of ST elevation, concavity is observed. It is directed upward;
- The T wave is characterized by narrowness and asymmetry.
Of course, there are many more nuances, and only a qualified specialist can read them from the ECG results, as well as prescribe effective treatment.
Features of treatment
If we consider repolarization disorders, treatment will depend primarily on the cause that provoked these disorders. If it is identified, then the main goal will be its elimination with re-diagnosis after the patient has completed the course of treatment. If there is no root cause as such, therapy is carried out in the following directions:
- vitamin preparations - they will support the full functioning of the heart and will be able to ensure the supply of all the vitamins and microelements it needs;
- corticotropic hormones – the main active ingredient is cortisone, which has a beneficial effect on processes occurring in the body, including the heart;
- cocarboxylase hydrochloride – helps restore carbohydrate metabolism, improve the trophism of the central and peripheral nervous system, has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system;
- anaprilin or panangin are drugs from the group of beta blockers. They are used to treat many heart ailments.
Before selecting a drug and its dosage, the doctor will carefully study the test results, obtaining a complete assessment of the patient’s health condition.
Only if the disorder really poses a threat to health, for example, if early myocardial ventricular repolarization syndrome is diagnosed, will the doctor select the most effective therapy.
In most cases, it is based on vitamin preparations and means to maintain heart function. If we talk about beta blockers, they are used only as a last resort.
Contact a specialist
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms are observed only in the form of the disease that is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system:
- loss of consciousness, fainting ;
- rhythm disturbances ( tachyarrhythmia , extrasystole , ventricular fibrillation );
- vagotonic, hyperamphotonic, tachycardial, dystrophic are formed under the influence of humoral factors on the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the heart caused by its hemodynamic disorders ( pulmonary edema , hypertensive crisis , shortness of breath , cardiogenic shock ).
Tests and diagnostics
The main changes are recorded precisely on the electrocardiogram. Some patients simultaneously experience clinical symptoms of cardiovascular diseases, but most often patients feel absolutely healthy and do not notice any changes.
Early ventricular reoplarization syndrome on ECG:
- elevation of the ST segment above the isoline;
- the convexity when raising the ST segment is directed downwards;
- an increase in the R wave with a parallel decrease in the S wave or its complete disappearance;
- point J is located above the isoline, at the level of the descending knee of the R wave;
- expansion of the QRS complex on the ECG;
- a “notch” is recorded on the descending limb of the R wave.
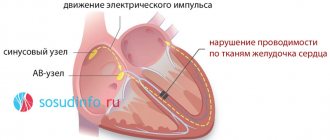
Basic methods for diagnosing cardiac conduction disorders
1. ECG (electrocardiogram)
A standard 12-lead ECG at rest can identify all the main types of cardiac conduction disorders: sinoatrial and atrioventricular block, bundle branch block. Drug tests in combination with ECG are almost never used at present.
2. Holter monitoring (monitoring) ECG
This type of study allows you to record an ECG for a day or more. It allows you to determine whether the patient has significant pauses (cardiac arrest). Pauses longer than 3 seconds are considered significant. If there are no significant pauses, installation of a pacemaker is almost never indicated.
3. Electrophysiological study of the heart (EPS)
This is the most reliable, but complex and expensive method for diagnosing arrhythmias. EPI is performed only in a hospital and requires the installation of several catheters in the veins of the arms and legs. Electrodes are inserted into the heart through these catheters and cardiac stimulation is performed—arrhythmias are caused and eliminated, and their parameters are examined.
To detect the most common types of cardiac conduction disorders, there is a simpler type of EPI - transesophageal EPI. In this case, a thin wire (probe-electrode) is inserted through the mouth or nose into the esophagus and the left atrium is stimulated through it. This type of study is performed on an outpatient basis. In particular, transesophageal EPI makes it possible to determine how long after cessation of stimulation the function of the sinus node (that is, its own pacemaker) is restored - this is necessary in order to make a diagnosis of sick sinus syndrome, one of the most common types of conduction disorders in the elderly.
Early ventricular repolarization syndrome in children
The reasons for the development of early repolarization syndrome in children can be very different:
- lack of sleep and irregular daily routine;
- excessive emotional stress;
- physical overload;
- constant anxiety, stress or nervous fatigue;
- isolation, lack of healthy emotional contact with parents;
- hypothermia;
- poor quality and unbalanced nutrition.
A similar syndrome can be recorded on an ECG in any child who reacts too emotionally to the assessment of his knowledge at school, takes current events to heart, and is overloaded in extracurricular activities. Lack of proper rest and intensive training in sports clubs can negatively affect the child’s well-being.
Data correction
If a comprehensive examination is carried out and an accurate diagnosis is established, the specialist will prescribe treatment aimed at eliminating the causes that caused the disruption of the repolarization phases. In cases where the disease is life-threatening, surgery is prescribed - cardiac ablation.
A person who has been found to have abnormalities in the repolarization process must:
- discuss the possibility of physical activity with your doctor;
- register with a dispensary;
- do ECG regularly;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- Take medications/vitamins prescribed by your doctor.
Control the functioning of your heart by keeping it healthy!
Forecast. What is the danger of early ventricular repolarization syndrome?
Modern cardiologists work to prevent and prevent the development of pathology, which can lead to death. That is why patients with early ventricular repolarization syndrome should be regularly monitored by a cardiologist to monitor the dynamics of the ECG and to identify hidden symptoms of other pathologies. It is not the syndrome itself that is dangerous, but the consequences it can lead to in the absence of proper treatment of the causative disease.
Persons who play sports are recommended to undergo examination at specialized physical education clinics, assessing their condition before and after intensive training, as well as before competitions.
There is no clear data on the transition of SRGC to a serious pathology. The risk of death increases significantly with alcoholism , abuse of fatty foods and smoking. A timely and complete competent examination will help to identify or exclude the true cause and avoid problems in the future.
Normal indicators and reasons for changes
The process of repolarization is a state during which the initial (before contraction) potential of the cell membrane is restored and its electrical charge is restored. Nerve impulses (potassium ions) must leave the membrane , energy, enzymes and oxygen saturation accumulate in the cell.
The interpretation of the electrocardiogram is very individual. The specialist must pay attention to many factors and indicators. It is almost impossible to independently determine the violation of repolarization processes , since in their presence several indicators are changed at once, and these changes may be insignificant or non-specific.
However, some deviations from the norm may be indicative when making a diagnosis. Some normal ECG readings:
- Prongs.
- T. _ VR is a negative value. Pointed upward. If the indicator changes, hyper- or hypoglycemia may be present. The relationship of this tooth to others is of paramount importance for determining violations of repolarization processes.
- Q. _ The norm is 1/4 R at 0.3 s. Enlargement indicates the presence of myocardial pathologies.
- R. _ The norm is determined at each lead. If absent, ventricular hypertrophy may be present.
- S. _ Normal height is 20mm. The ST segment is important.
- P. _ The first and second leads are positive. VR - negative. The norm is 0.1 s.
- Intervals.
- QT - up to 0.4 s.
- PQ - 0.12 s.
- R.R. – 0,62 – 0,66 – 0,6.
- QRS complex - up to 0.1 s.
- General information.
- Heart rate is within 60-85 beats per minute.
- The rhythm is sinus.
- Normal location of the electrical axis of the heart (without deviations to the right or left side).
Usually, in the conclusion, the specialist writes a transcript based on these indicators. But if the patient already has a diagnosis or is suspected of having one, more detailed data is indicated, where attention is paid to specific violations of certain indicators (for example, the length of specific teeth or intervals, distance from certain points).