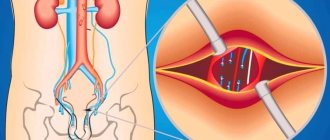
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries as a cause of stroke
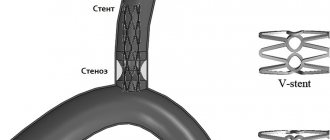
Atherosclerosis is a lesion of the arteries, in which dense growths (atherosclerotic plaques) appear on the inner wall, which narrow the lumen of the artery and impair blood flow through it.
The disease usually develops after 40 years of age, especially in patients with high blood cholesterol levels, as well as in smokers. The carotid arteries are no exception. With the development of atherosclerosis, plaques also appear in them, the lumen of the vessel narrows (this is called stenosis), and with stenosis of more than 60%, there is a high risk of developing such a formidable complication as a stroke. With atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries and increased blood pressure, plaques can break off from the vessel wall and enter the cerebral vessels with the blood flow. When large vessels are blocked, the blood supply to a certain area of the brain is cut off and an ischemic stroke develops. When small vessels are blocked, a microstroke occurs (also called a transient ischemic attack).
For small, less than 50% of the lumen of the vessel, stenoses, it is possible to carry out conservative therapy aimed at lowering cholesterol levels in the blood, improving cerebral circulation, and improving metabolic processes in brain tissue. With more significant stenoses, and especially in the presence of neurological symptoms, conservative therapy is not enough, and to avoid stroke, surgical treatment is required - carotid endarterectomy or endovascular interventions.
Differences from surgery
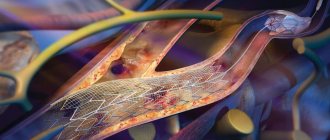
Angioplasty and stenting of the internal carotid artery (ICA) is considered a high-tech, minimally invasive endovascular intervention, performed under local anesthesia.
There are no scars left on your body on your neck, except for a very small cut - about 2-3 mm (puncture site) in a blood vessel in the groin or on the wrist.
There is no need for general anesthesia; everything is done under local anesthesia, so you are awake during the procedure. Fluids and medications are given through an IV.
Before the procedure
- You will be taken on a gurney to the cath lab operating room. You will place your head in a comfortable cup-shaped area on the operating table.
- Your wrists and groin should be shaved on both sides and prepared with an antiseptic solution.
- A local anesthetic is injected into the puncture site for pain relief.
- To monitor the ECG of the heart, electrodes will be connected to the chest.
During the procedure
Once you are calm, your operating x-ray surgeon will puncture an artery, usually the femoral artery in the groin area. The angioplasty and stent procedure are described below.
- A special catheter with a unique bend (tube) is inserted into the artery . Under X-ray control, a catheter with the necessary instruments and a balloon is brought to the narrowing of the carotid artery. You will not feel the catheter going through the arteries because the insides of the arteries do not have nerve endings. The entire instrument is guided through this catheter to the narrowed section of the artery.
- A radiopaque contrast agent (RCS) is injected into the carotid artery through a catheter . RCV may cause a temporary feeling of warmth on one side of your face. The RCV gives a detailed view of the narrowed artery and blood flow to the brain.
- The filter is opened in the artery . A filter, called an embolic protection device, is inserted beyond the narrowing to catch any particles that may break off from the narrowed section of the artery (plaque) during the procedure.
- A balloon catheter on the delivery system is positioned at the site of narrowing and inflated to dilate the vessel.
- A small metal mesh tube (stent) may be placed in the newly opened vessel . A self-expanding metal frame with a specially designed closed cell or double-layer stents that incorporate all the advantages of previous generations. The expanded stent provides support that helps prevent the artery from narrowing again.
- The filter, balloon and stent delivery system, and the catheter itself are removed.
When the procedure is complete, you lie still in one position and the bleeding stops at the site where the tube was inserted. You will usually not have stitches, but a bandage will be placed over the small incision. You are then transferred to a recovery room.
After the procedure
To avoid bleeding from the catheter site, you will need to lie relatively still for several hours. You will either be in the recovery area or in your hospital room. After the procedure, you may be given an ultrasound of the carotid artery. Most people are discharged from the hospital within 24 hours of the procedure.
The catheter site may be sore and swollen for several days. There may be a small hematoma in the puncture area. You can take medications in the recommended dose needed to relieve discomfort as prescribed by your doctor.
You may need to avoid vigorous activity and heavy lifting for a week after the procedure.
Examination before carotid endarterectomy
Before hospitalization, the patient must have the following results of laboratory and instrumental examinations with him:
- Clinical blood test
- General urine analysis
- Blood biochemistry (AST, ALT, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, urea, creatinine, total protein)
- Blood test for hepatitis B, C, HIV, syphilis.
- Chest X-ray or fluorography
- ECG
- Already in the hospital, before the operation, the patient undergoes:
- Duplex ultrasound angioscanning
- Computed tomography of the brain
- Angiography
These examinations help to find out how narrowed the lumen of the vessel is, the size and location of atherosclerotic plaques, the speed characteristics of blood flow through the carotid arteries, and the characteristics of cerebral blood flow.
After operation
In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed antiplatelet therapy - drugs that “thin” the blood. These drugs should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor with strict adherence to the dosage and regimen. Self-cancellation or replacement with other drugs without a doctor’s prescription is unacceptable.
Otherwise, the postoperative period after surgery on the carotid arteries does not differ significantly from any other operations: limiting physical activity, wound care.
In the vast majority of cases, the operation is quite comfortable and well tolerated by patients.
A timely operation saved the lives of many thousands of patients. Remember, there is nothing more expensive than your life and health.
Technique for carotid endarterectomy
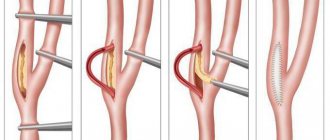
At its core, the operation is the removal of atherosclerotic plaque from the carotid artery.
The operation in Moscow is performed under local anesthesia, but anesthesia is also possible. Local anesthesia is preferable, with fewer complications and faster recovery.
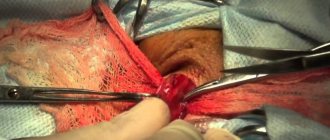
During the operation, a small incision is made in the artery with “scraping” of its inner wall along with atherosclerotic plaques. A suture is placed on the wall of the vessel, blood flow is restored. In some cases, replacement of the damaged vessel wall is required, which is performed from a fragment of a vein taken from the patient.
Some aspects of the operation are shown in the photo below:
WELCOME!
GBUZ JSC "AOKB" provides planned, urgent, emergency specialized and consultative and diagnostic medical care to patients in the city of Arkhangelsk and the Arkhangelsk region in the following areas:
| Chief physician Petchin Igor Vasilievich |
cardiology, neurology, gastroenterology, pulmonology, rheumatology, allergology, hematology, nephrology, endocrinology, neurosurgery, surgery (including purulent surgery), urology, traumatology, orthopedics, combustiology (burn medicine), otorhinolaryngology, maxillofacial surgery, vascular surgery , cardiac surgery, thoracic surgery, infectious diseases, obstetrics and gynecology, neonatal pathology, intensive care (including neonatal intensive care).
The institution's 24-hour hospital has 877 beds. Intensive care unit with 40 beds. 10 beds have been deployed in the Solovetsky District Hospital branch. Every year, more than 20 thousand patients are treated in the 24-hour hospital.
Up to 500 patients per shift and more than 100 thousand people annually seek advice from specialist doctors at the clinic. There is a day hospital. The structure of the hospital includes specialized centers for patients, as well as schools and offices in which regular meetings of patients are held with the participation of their relatives, friends and medical specialists.
In total, the institution employs almost 2 thousand medical and general hospital personnel.
For a long time, the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution JSC "AOKB" has been participating in a joint Russian-Norwegian project to reduce road traffic injuries in the Arkhangelsk region.
The hospital operates under the federal program “M8 Highway” as a first-level trauma center. All people injured as a result of road accidents on the Kholmogory highway are taken to the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution JSC "AOKB". This work involves ambulances equipped with the GLONASS system - a system for determining the location of a vehicle involved in an accident.
To help the population of the Arkhangelsk region and the city of Arkhangelsk, an emergency consultative emergency medical care department (ECMC) was created on the basis of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution JSC "AOKB" in order to improve medical care for adults and, in some cases, children with emergency conditions.
In 2014, a new surgical building was put into operation, which greatly improved the living conditions of patients and the working conditions of doctors in surgical departments.
Read more…
Endovascular interventions on the carotid arteries
Such manipulations include balloon angioplasty and stenting. With balloon angioplasty, the lumen of the vessel is expanded from the inside using a special catheter inserted through the subclavian artery. When stenting, a special metal stent is placed in the lumen of the vessel in the area of stenosis, which expands the lumen of the vessel and prevents it from narrowing.
These interventions are used in patients with severe concomitant pathology who cannot undergo standard carotid endarterectomy. This is due to the fact that with balloon angioplasty there is a high risk of vessel rupture, and with stenting the service life of the stent is usually no more than 5 years, after which a more complex operation is required.
Preparing for a non-surgical procedure
Before elective stenting, your endovascular surgeon will review your medical history and perform a physical examination. Can be assigned:
- Ultrasound . To obtain images using sound waves of the narrowed artery and the speed of blood flow to the brain.
- Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (MSCT) or Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) . This diagnostic produces highly detailed images of blood vessels using radiofrequency waves in a magnetic field or X-rays injected with a radiopaque contrast agent.
Food and medicine
You will receive instructions about what you can eat or drink before your angioplasty and ICA stenting. Preparation may be different if you are already in the hospital before the intervention.
The night before your endovascular surgery:
- Follow your doctor's instructions about adjustments to your current medications. Your doctor may tell you to stop taking certain medications before having angioplasty, especially if you take certain diabetes medications or blood thinners.
- Arrange transportation home in advance. Angioplasty usually requires a hospital stay, and you may not be able to go home the next day due to the lingering effects of the sedation.
Complications during stenting
- Transient cerebrovascular accidents
Transient ischemic attacks occur in 0.5% of patients during or immediately after carotid artery stenting. May be associated with tiny pieces of plaque entering the brain as the conductor passes through the narrowed area. These may be transient visual or speech disturbances, weakness in an arm or leg, which disappear within the next 3 hours after the intervention.
- Ischemic stroke
The development of stroke, according to the literature, occurred in 1% of patients after stenting, but in recent years, due to the advent of new technologies for protecting the brain, this complication is much less common.
- Reflex bradycardia and hypotension
These phenomena are associated with the effect of the balloon on the vagus nerve passing next to the carotid artery. They manifest themselves as a decrease in heart rate and a drop in blood pressure. With a timely response from the anesthesiologist, this complication is quickly relieved with medications.
- Bleeding from the puncture site
A rare complication, accompanied by the formation of a tense hematoma in the area of access to the vessel. Sometimes open surgery may be necessary to stop bleeding.
Postoperative period
In the early postoperative period, medical supervision is necessary until the next morning. The main attention is paid to the level of blood pressure, the absence of neurological disorders, swallowing and voice disorders. It is imperative to monitor the discharge from the drainage and the condition of the dressing (dry or wet with blood). Pain after surgery is mild and easily relieved with conventional analgesics. The day after surgery, the drainage is removed. The day after surgery, if the course is smooth, the patient can be discharged. Sutures are removed on the 7th day after surgery.
Tips for everyday life
During recovery, you may find it more difficult to do everyday activities. The tips below should help you.
- Maintain good posture: shoulders back and relaxed, head slightly tilted back. This will help relax your pectoral muscles and take pressure off your neck and shoulder muscles.
- If you feel weak on the side you had surgery on, rest your arm on a table or armrest while you sit. When you stand, rest the hand on your operated side on your hip or keep it in your pocket to relieve pressure from that hand on your shoulder. This will take the stress off the muscles and other parts of your neck and shoulder.
- When sleeping, lie on your back as much as possible. If you need to lie on your non-surgical side, you can place the arm on your surgical side on a pillow in front of you to avoid accidentally pulling your shoulder. Do not lie on your surgical side until your doctor or nurse tells you to do so.
- Do not lift or carry anything heavier than 3 pounds (1.4 kg) on your operated side until you no longer experience any pain. For comparison, an iron weighs approximately 3 pounds (1.4 kg), and a 1/2 gallon bottle of milk (approximately 2 liters) weighs 4 pounds (1.8 kg). Check with your doctor or nurse before lifting or carrying anything weighing more than 3 pounds (1.4 kg).
- Refrain from carrying a heavy briefcase on a belt or a bag on the side undergoing surgery. Check with your doctor or nurse before wearing a backpack or backpack.
to come back to the beginning
Progress of the operation
The incision is made along the inner edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the neck, the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and subcutaneous muscle are sequentially dissected. The edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is retracted outward. The bifurcation (bifurcation) of the common carotid artery is highlighted. The latter is divided into internal and external. The external carotid artery is distinguished by the presence of branches, the internal one does not have them. After this, the internal carotid artery is carefully isolated up to and above the tortuosity. Care must be taken when isolating the superior section, as this is where the hypoglossal nerve and pharyngeal plexus are located. After identifying the tortuosity, it is straightened out and a decision is made on the correction method. After excision of the excess artery, the course of the artery is restored. After starting the blood flow, the restored vessel is examined using an ultrasound scanner, and the nature of the blood flow (laminar, turbulent) and its speed are studied. After making sure that blood flow has been restored, they begin to suture the wound. The operation ends with the installation of drainage.
Indications for intervention
- Narrowing of the vascular lumen by more than 50-60%.
- Symptoms of microstroke and stroke.
- High risk of complications with other vascular interventions.
The operation is also performed for patients who have already undergone surgery to remove plaques, but are faced with a relapse of narrowing of the arterial lumen.
Stenting is not performed if:
- complete blockage of the carotid artery,
- allergies to the drugs used.
Also, surgery is not prescribed for cerebral hemorrhages that occurred within the last 2 months or for heart rhythm disturbances.
| Type of intervention | Price |
| Stenting of cerebral vessels | 300,000 - 450,000 rub. |
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Our advantages
Surgeons at the Innovative Vascular Center have been dealing with the problem of treating pathological tortuosity of the carotid arteries since 2001. During this time, a lot of scientific work was carried out to determine indications for treatment and a diagnostic algorithm. The technique of surgical interventions was developed. Since that time, more than 200 surgical interventions for pathological tortuosity have been performed without complications with good immediate and long-term results. The results of operations in all patients were analyzed. Constant postoperative monitoring of the patency of the operated arteries and neurological functions is carried out.