How did the fourth group appear?
It is believed that during the formation of human society, gene mutations occurred. This also applied to blood type. The fourth one arose last as a variant of the second and third. About a thousand years ago there was a mixing of the genetic groups of Indo-Europeans and Mongols.
It has been established that there are spots of this particular group on the Shroud of Turin. This makes it possible to classify Jesus Christ as a bearer of rare blood.
Children can get AB (IV) if the parents have the second or third group, and this type will never be formed if one of the parents has the first group.
The laws of inheritance are studied by medical genetics and used in judicial practice.
What kind of blood can be transfused?
Transfusion of fresh blood is prohibited by the Instructions of the Ministry of Health. Only red blood cells or other blood products are allowed to be used. But doctors know emergency situations in case of injuries, heavy bleeding, when a person’s life depends on the urgency of replenishing the bloodstream. In such cases, even direct transfusion from donor to recipient is justified.
In an emergency, the blood transfusion station prepares its supplies of blood substitutes and calls donors
Since it is very difficult to find a single donor for an AB (IV) Rh (-) case, transfusion of any Rh-negative blood is suitable. In this sense, people with the fourth group are considered “universal”. Because they already have agglutinogens A and B, additional administration from the second and third groups will not cause a reaction, and in the first group there are none at all.
A test for individual compatibility is mandatory, even with a planned transfusion.
INHERITANCE OF BLOOD TYPE BY A CHILD
Often in the maternity hospital, mothers are asked the question: “What cut group does my child have?” And then they think long and painfully: “Why did they say that my baby has the first blood type, if my husband and I have the second?”
To answer this question, let us remember what blood groups are and what laws of nature they “obey”.
At the beginning of the last century, scientists proved the existence of 4 blood groups.
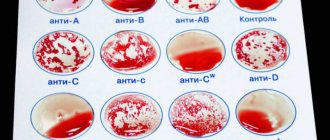
The Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner, mixing the blood serum of some people with red blood cells taken from the blood of others, discovered that with some combinations of red blood cells and serum, “gluing” occurs - red blood cells stick together and form clots, but with others - not.
While studying the structure of red blood cells, Landsteiner discovered special substances. He divided them into two categories, A and B, highlighting a third, where he included cells that did not contain them. Later, his students - A. von Decastello and A. Sturli - discovered red blood cells containing A- and B-type markers simultaneously.
As a result of research, a system of dividing blood groups emerged, which was called ABO. We still use this system today.
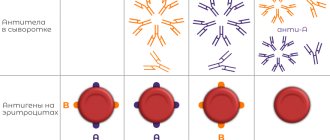
- I (0) – blood group is characterized by the absence of antigens A and B;
- II (A) – established in the presence of antigen A;
- III (AB) – B antigens;
- IV(AB) – antigens A and B.
The AB0 system has revolutionized scientists' understanding of the properties of blood. Genetic scientists began to study them further. They proved that the principles of inheritance of a child's blood type are the same as for other characteristics. These laws were formulated in the second half of the 19th century by Mendel, based on experiments with peas, familiar to all of us from school biology textbooks.
So how are blood groups inherited by a child according to Mendel’s law?
- According to Mendel's laws, parents with blood group I will give birth to children who lack A- and B-type antigens.
- Spouses with I and II have children with the corresponding blood groups. The same situation is typical for groups I and III.
- People with group IV can have children with any blood group, with the exception of I, regardless of what type of antigens are present in their partner.
- The inheritance of a blood group by a child is most unpredictable when the union of owners with groups II and III occurs. Their children are equally likely to have any of the four blood types.
- The exception to the rule is the so-called “Bombay phenomenon”. Some people have A and B antigens in their phenotype, but do not manifest themselves phenotypically. True, this is extremely rare and mainly among Indians, which is why it got its name.
TABLE OF INHERITANCE OF BLOOD TYPE BY A CHILD DEPENDING ON THE BLOOD GROUPS OF THE FATHER AND MOTHER
| MOM + DAD | CHILD'S BLOOD TYPE : POSSIBLE OPTIONS (%) | |||
| I+I | I (100%) | — | — | — |
| I+II | I (50%) | II (50%) | — | — |
| I+III | I (50%) | — | III (50%) | — |
| I+IV | — | II (50%) | III (50%) | — |
| II+II | I (25%) | II (75%) | — | — |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | — | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III+III | I (25%) | — | III (75%) | — |
| III + IV | — | I (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) |
| IV + IV | — | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
INHERITANCE OF RH FACTOR
The birth of a child with a negative Rh factor in a family of Rh-positive parents causes deep bewilderment at best, and mistrust at worst. Reproaches and doubts about the fidelity of the spouse. Oddly enough, there is nothing exceptional in this situation. There is a simple explanation for such a delicate problem, which is based on the same laws of genetics.
The Rh factor is a lipoprotein located on the membranes of red blood cells in 85% of people (they are considered Rh positive). If it is absent, they speak of Rh-negative blood. These indicators are denoted by the Latin letters Rh with a plus or minus sign, respectively.
The gene for a positive Rh factor is designated D, it is a dominant trait (always appears). The Rh negative gene is recessive and is designated d (appears only in the absence of D). Therefore, people with a set of DD or Dd chromosomes will have Rh positive blood, and only those with a dd chromosome set will have Rh negative blood.
Consequently, parents with a homozygous absence of the Rh factor (dd) can only give birth to children with Rh negative blood.
Parents with homozygous Rh positive factor (DD) will only give birth to children with Rh positive blood.
But in the union of people with Rh positive blood with heterozygous presence of Rh (Dd), their children will have Rh positive in 75% of cases and negative in the remaining 25%.
So, parents: Dd x Dd. Children: DD, Dd, dd – these are Rh negative children of Rh positive parents! .
Inheritance of the blood type of the Rh system, possible in a child, depending on the blood groups of his parents.
| Mother's blood type | Father's blood type | |
| Rh(+) | rh(-) | |
| Child's blood type | ||
| Rh(+) | Any | Any |
| rh(-) | Any | Rh negative |
And some more interesting things from geneticists...
INHERITANCE OF CHARACTERISTICS
For centuries, parents have only wondered what their child would be like. Today is an opportunity to look into the future. Thanks to ultrasound, you can find out the gender and some features of the anatomy and physiology of the baby.
Genetics will make it possible to determine the likely color of the eyes and hair, and even whether the baby has an ear for music. All these characteristics are inherited according to Mendelian laws and are divided into dominant and recessive.
Brown eye color, hair with small curls, and the ability to roll the tongue into a tube are dominant signs. Most likely, the child will inherit them. Unfortunately, dominant signs also include a tendency to early baldness and graying, myopia and gaps between the front teeth.
Gray and blue eyes, straight hair, fair skin, and a mediocre ear for music are considered recessive. These signs are less likely to occur.
BOY OR...
For many centuries, the blame for the lack of an heir in the family was placed on the woman. To achieve the goal of having a boy, women resorted to diets and calculated favorable days for conception. But let's look at the problem from a scientific point of view. Human sex cells (eggs and sperm) have half the set of chromosomes (that is, there are 23 of them). 22 of them are the same for men and women. Only the last pair is different. In women these are XX chromosomes, and in men they are XY.
So the probability of having a child of one sex or another depends entirely on the chromosome set of the sperm that managed to fertilize the egg. To put it simply, the father is entirely responsible for the gender of the child!
Head of the department for newborn children Ilkevich N.G.
Neonatologist of the department for newborn children Valentyukevich T.S.
Problems during pregnancy
For a pregnant woman with positive Rh and blood type IV, problems can only arise with bleeding during childbirth. Because there are difficulties with selecting donors.
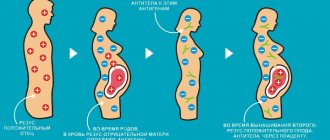
During pregnancy, special conditions arise only if the mother does not have Rh in the blood and the father is Rh positive. In this case, the child can choose the man’s genes, and the mother’s body will begin to produce antibodies to the fetus.
If the child prefers the maternal genes, then this will not affect the pregnancy at all.
This reaction is called a “Rh conflict”. It is dangerous for both the mother and the unborn baby. The formation of organs and systems of the fetus is disrupted. There is a predisposition to interruption in the early stages.
During the first pregnancy, a sufficient level of antibodies accumulates only towards the end of the term, and the child’s body is minimally affected. The situation is especially dangerous during the second and subsequent pregnancies, which do not necessarily result in childbirth. Even after an abortion, antibodies have already appeared in the body of a Rh-negative woman. They begin to attack the unprotected fetus and cause complete rejection.
Rh factor
During scientific research in 1940, an antigen was found in the blood of macaques, which later received the name Rh factor. It is hereditary and depends on race. Those people who have this antigen in their blood are Rh positive, and if it is absent, they are Rh negative.
Transfusion compatibility:
- Rh negative is suitable for transfusion to people with Rh negative;
- Rh positive is compatible with any Rh blood.
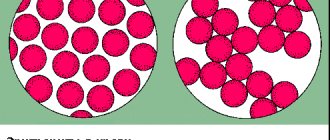
If you use Rh-positive blood for a patient with a Rh-negative category, then special anti-Rhesus agglutinins will be produced in his blood, and with another manipulation, red blood cells will stick together. Accordingly, such a transfusion cannot be carried out.
Any transfusion is stressful for the human body. Whole blood is transfused only if the loss of this biological fluid reaches 25% or higher. If less volume is lost, blood substitutes are used. In other cases, transfusion of certain components, for example, only red blood cells, is indicated, depending on the type of lesion.
Prevention
To prevent such unexpected situations, obstetricians and gynecologists check whether the parents are matched by Rhesus. All adults are advised to know their blood type and Rh.
Antibodies are examined by immunological tests
During pregnancy, it is necessary to determine the onset of antibody production as early as possible. To do this, the woman is sent for a specific blood test.
Women with group AB (IV) Rh (-) are recommended to administer anti-Rhesus globulin in the first three days after abortion or childbirth. The technique has proven itself and allows you to have two or more children.
In the case of AB (IV) and positive Rh, the expectant mother does not have such problems, even if the father does not have Rh.
Question 2:
I have a negative Rh factor. I recently had an abortion. Will I be able to have children? Is there a chance that the baby will be sick during the next pregnancy?
Answer
: The presence of a negative Rh factor does not directly affect conception. During an abortion (if it was performed at 9-10 weeks of pregnancy), there was a possibility of sensitization of the body to the Rh factor. Before a planned pregnancy, it is advisable to do a blood test for the presence of antibodies to the Rh factor.
Features of people with a rare group
The Japanese especially believe in the characteristics of people with different blood groups. Many followers have appeared in Russia, so we will try to characterize a person of only group AB (IV).
How long can you think without being considered indecisive?
In contrast to the first group, the fourth makes a person soft and patient. He is respected for his knowledge, philosophical way of thinking, and ability to offer a unique way to solve a problem.
Such people are good in humanitarian professions and science. They are purposeful and friendly. The ability to empathize and sympathize leads them to medicine and acting.
Weaknesses include indecision, procrastination when it is necessary to act immediately, and the need for support and attention from others.
Dietary recommendations
For those who use D'Adamo's theory of the dependence of healthy nutrition on blood type, we will present product recommendations for creating your individual diet.
It is important to cook fish dishes
- The preferred meat products are lamb, rabbit, turkey, and liver.
- Tuna, sturgeon, and trout are considered especially useful. Limit crabs, crayfish, and shellfish.
- Egg no more than one per day, up to four per week.
- Low-fat fermented milk products (kefir, cottage cheese) are well absorbed. It is recommended to limit whole milk. Only hard varieties of cheese are shown.
- Fruits and vegetables are needed fresh, compotes. Bananas, oranges, bell peppers, pomegranates, and persimmons are not recommended.
- It is necessary to eat porridge made from rice, buckwheat, and oatmeal.
- Attention is drawn to the need for nuts and vegetable oils. Olive oil is recommended, but sunflower, sesame and flaxseed oils are not recommended.
- Drinks include fruit and vegetable juices, black and herbal teas, coffee is limited.
- Legumes, corn, and seeds are not recommended in the diet.
Attention is drawn to the tendency of people with the fourth group to be overweight. Therefore, the theory calls for monitoring blood sugar and preventing high cholesterol.
We note the absence of unusual combinations or beyond the requirements. The products are quite accessible to everyone who wants to eat in accordance with the theory. We must not forget about rational physical exercises.
We get our blood type from our parents. We are not able to change it. All that remains is to adapt and come to terms with the peculiarities.
Blood group compatibility
In the 20th century, the idea of transfusion arose. Blood transfusion is a useful procedure that restores the total volume of blood cells; plasma proteins and red blood cells are replaced. The compatibility of the blood groups of the donor and recipient during transfusion is important, affecting the success of the blood transfusion. Otherwise, agglutination will occur - a fatal gluing of red blood cells, resulting in the formation of a blood clot, which leads to death. Blood compatibility for transfusion:
| Blood type | Recipients | Which ones can you transfuse from? |
| 0(I) | I, II, III, IV | I |
| A (II) | II, IV | I, II |
| B(III) | III, IV | I, III |
| AB(IV) | IV | I, II, III, IV |
First
The first blood group is considered to be the foundation of human civilization. Our ancestors developed the habits of excellent hunters, brave and persistent. They are ready to spend all their strength to achieve their intended goal. Modern first-bloods need to be able to plan their actions in order to avoid rash actions.
Main character traits:
- natural leadership;
- extroversion;
- better organizational skills.
Strengths:
- strong digestive system;
- physical endurance;
- increased ability to survive.
Weaknesses are considered:
- Types of arthrosis and their degrees for which a disability group is given
- increased acidity (risk of peptic ulcer);
- predisposition to allergies, arthritis;
- poor clotting;
Second
City dwellers. Evolution moved forward and people began to engage in agriculture. When plant protein became the source of human energy, the vegetarian second blood group arose. Fruits and vegetables began to be used as food - the human digestive system began to adapt to changing environmental conditions. People began to understand that following the rules increases their chances of survival.
Main character traits:
- communication skills;
- constancy;
- composure.
Strengths:
- good metabolism;
- excellent adaptation to change.
Weak sides:
- sensitive digestive system;
- weak immune system.
Third
People with the third blood group are called nomads. It is difficult for them to experience an imbalance within themselves, in the team. It is better to live in mountainous areas or near water bodies. They suffer from a lack of motivation because their bodies produce large amounts of cortisol when they are stressed.
Main character traits:
- flexibility in decisions;
- openness to people;
- versatility.
Strengths:
- strong immunity;
- tolerate changes in diet well;
- creative.
Weak sides:
- Is disability allowed for arthrosis of the knee and other joints?
- susceptible to autoimmune diseases;
- lack of motivation and self-confidence.
Fourth
Holders of the rarest, fourth blood group occurred as a result of the symbiosis of the second and third. A bohemian, easy life is what characterizes its representatives. They were tired of everyday decisions and devoted themselves to creativity. The total number of people with such a group is only 6% on the planet.
Main character traits:
- mysterious;
- individual.
Strengths:
- resistant to autoimmune diseases;
- resist allergic manifestations.
Weak sides:
- fanatics, capable of going to extremes;
- Drugs and alcohol should be avoided.