- Home >
- Clinic services >
- Neurology >
- Cerebral vasospasm
In the human body, the brain is the most important organ, which not only regulates the functioning of all other organs and systems, but is also responsible for our consciousness, perception and memory.
The human brain, like any other organ, must be supplied with blood and receive the required amount of oxygen and metabolic substances. Therefore, the microvasculature of the brain is one of the most complex vascular networks in our body. Indeed, when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, pathological processes occur, many of which are irreversible. One of the common causes of circulatory disorders in various parts of the brain is vascular spasm. Nowadays, cerebral vasospasm is a condition that most often occurs in people over 30 years of age. What is a spasm, how and why does it occur in the vessels of the brain, and how should this condition be treated?
The definition is: a spasm is a case of sudden contraction of smooth or striated muscle. It is known that our vessels have a wall consisting of smooth muscle, when a vessel spasm (angiospasm) occurs, the lumen of the vessel closes, which is always fraught with complications.
Causes of cerebral vasospasm
Angiospasm often occurs due to:
- overwork;
- nervous or physical stress;
- sedentary lifestyle (for example, prolonged sitting at the computer);
- stress and strong emotions, even positive ones;
- lack of sleep;
- lack of oxygen in the room;
- abuse of coffee and strong tea;
- vitamin deficiency;
- smoking;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- hypothermia;
- atmospheric pressure fluctuations;
- age-related changes in the arteries.
Spasm of cerebral vessels can be a symptom of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, arterial hypertension, cerebral aneurysm, tumor formation, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and thyroid diseases.
The risk group includes elderly people and people sensitive to weather changes, smokers, abuse alcohol, often drink strong tea/coffee, suffer from insomnia, hypertension, angina pectoris, diabetes mellitus or dyscirculatory encephalopathy, and have a family history of stroke or myocardial infarction .
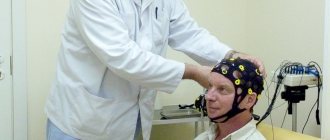
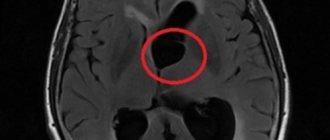
What does an EEG look like for epilepsy?
To obtain accurate EEG readings for epilepsy, it is necessary to prepare the patient for the procedure. You need to wash your hair thoroughly to keep your hair clean. Installation fixing agents are not allowed. This will allow you to get closer contact with the scalp. It is not recommended to eat two hours before the procedure, but also not to feel hungry. You should also remove all jewelry before the procedure.
Signs of epilepsy with EEG
EEG in epilepsy helps to identify foci of neuronal activity. EEG indicators determine the form of pathology. They can also be used to track dynamics and determine the dosage of medications. The greatest value of this method is that painful changes can be identified in the intervals between attacks.
The following types of EEG are distinguished:
- routine electroencephalography. Diagnostics, in which the recording and recording of brain biopotentials is carried out to determine epilepsy;
- using additional electrodes;
- during night sleep. EEG indicators are recorded during night sleep;
- long-term EEG in epilepsy. Recording indicators during the day;
- EEG with standard activation procedures. Hyperventilation, photostimulation and the use of other types of stimulation such as reading, watching movies, music;
- video monitoring;
- sleep deprivation procedure.
Quite often, changes in the EEG occur when eye movements, changes in breathing rhythm, vascular pulsation or motor reflexes. Therefore, it is very important to correctly interpret the signs of epilepsy in the EEG.
Signs of cerebral vasospasm
The main symptom of the pathological process is headache of varying localization and intensity. It usually occurs in the temples and forehead, sometimes felt all over the head.
You may also experience:
- dizziness;
- pain in the eyes, ear, neck;
- noise in ears;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- darkening of the eyes;
- nausea;
- changes in blood pressure;
- feeling tired;
- numbness of lips;
- tingling in temples.
If a spasm is a precursor to a stroke or rupture of an aneurysm, disturbances in speech, sense of orientation in space and coordination of movements, and loss of consciousness are possible.
Symptoms
With angiospastic syndrome, prolonged spasm of the vessels of the extremities occurs. Such patients react acutely to cold air. There is a feeling of coldness in the upper and lower extremities, the color of the skin changes, and numbness is felt. Spasm of the blood vessels in the hand leads to tremor. People with angiospastic syndrome take longer to warm up. Sometimes, with prolonged exposure to low temperatures, atrophic processes develop.
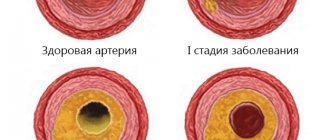
Obliterating atherosclerosis occurs due to thickening of the walls of blood vessels due to fat deposition. Atherosclerotic plaques form, narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels occurs, up to their blocking in certain areas. This does not allow blood to enter the tissues, they do not receive the necessary nutrients.
Symptoms of arterial insufficiency:
- pain in the legs that occurs when walking, which goes away after rest;
- the pain has a constraining, squeezing character;
- limitation of leg mobility;
- thickening of nails;
- hair loss or slow hair growth;
- feeling of coldness, tingling, numbness in the legs;
- ulcerative lesions on the skin;
- lameness.
With spasm of the blood vessels in the legs, the pain is localized in the lower part of the limbs, in the calves. When large blood vessels are blocked, discomfort occurs in the thighs and buttocks. It becomes difficult for patients to walk, run, or climb stairs. With atherosclerosis in the later stages, even painkillers do not help patients cope with pain.
With obliterating endarteritis, damage to small vessels occurs. This occurs due to autoimmune processes and leads to the proliferation of connective tissue. The disease develops quickly. The main symptoms of vascular spasm in the legs during endarteritis:
- leg fatigue;
- lameness;
- sensation of burning and coldness in the fingers of the lower extremities;
- increased sensitivity, pallor or cyanosis of the skin;
- convulsions;
- deterioration of hair and nail growth;
- ulcerative lesions.
With the onset of obliterating endarteritis, patients notice an increase in symptoms after walking a distance of about 200 meters. Over time, this figure decreases; it is difficult for a person to walk more than 60 meters.
If you have diabetes, there is a risk of vascular damage to the upper and lower extremities (microangiopathy). As a result, ischemia occurs, that is, oxygen starvation of tissues.
Treatment
If the problem is caused by external negative factors, they should be avoided if possible. If a spasm occurs against the background of any disease, therapy should be aimed at curing it.
At the same time, drugs are used to relieve spasms of cerebral vessels - No-Shpa, Halidor, Dibazol, Doverin, Papazol, Spazmol. They affect the muscular wall of blood vessels, reduce muscle tone, and expand the lumen of blood vessels.
You can also take painkillers for cerebral vasospasm - Analgin, Aspirin.
Antispasmodic analgesics are drugs of a combined composition that eliminate spasms and relieve pain. This group includes Pentalgin, Andipal, Baralgetas, Novigan, Spazgan, Spazmoblok.
To improve cerebral circulation, it is recommended to take nootropic drugs such as Actitropil, Gopantam, Idebenone, Nootropil, Recognan, Piracetam.
For the treatment of cerebrovascular disorders, medicines and dietary supplements based on ginkgo biloba leaf extract are widely used. This plant improves the rheological properties of blood and oxygen supply to the brain, normalizes microcirculation and metabolism in cells, reduces the permeability of vascular cells, and has antithrombotic and antihypoxic effects.
The patient is recommended physiotherapeutic procedures: oxygen therapy, kinesiotherapy, hydrotherapy, magnetic therapy, darsonvalization. Massages in the neck and back of the head help improve blood circulation.
First aid for seizures
Proper care for an epileptic seizure reduces the risk of complications and injuries. The person who happens to be next to the patient should catch him and prevent him from falling. You also need to do the following:
- Place a blanket, pillow or cushion of clothing under your head;
- Free your neck and chest from constricting objects and clothing (tie, shirt, scarf);
- Carefully turn the patient's head to the side to minimize the risk of inhalation or passive reflux of vomit or own saliva;
- Open your mouth and put a cloth or handkerchief in it to prevent the patient from biting his tongue;
- Do not forcefully open your mouth;
- If breathing stops for a long time, perform artificial ventilation from the mouth to the nose or mouth.
During an attack, the patient may experience involuntary urination or bowel movements. This manifestation of epilepsy should not cause fear in others. After an attack, patients usually experience drowsiness and severe weakness.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at maintaining the normal functioning of the circulatory system and strengthening blood vessels. These include:
- normalization of work and rest schedules;
- good sleep;
- moderate exercise;
- hardening;
- to give up smoking;
- reasonable alcohol consumption;
- adequate drinking regime;
- avoiding hypothermia;
- proper nutrition.
Doctors recommend eating more vegetables, fruits and herbs, and giving preference to fish and lean meats. Limit the consumption of butter, coffee, black tea, cocoa, sugar, chocolate, smoked meats, lamb and pork, mayonnaise and sauces, fried foods.
How to prevent an epilepsy attack
Epilepsy attacks occur differently depending on the form of the disease. The most severe course of the disease is accompanied by attacks with loss of consciousness, convulsions; the patient is often injured and does not remember anything after the attack. Another type of epileptic seizure occurs without loss of consciousness. The patient may freeze for a while, his gaze stops, his limbs begin to spasm, he may smack his lips. If the patient was standing, then a spasm of the limbs may force him to sit down, then he loses control and falls onto his back. In most cases, patients with epilepsy do not remember themselves at such moments.
Lack of sleep for a baby or schoolchild can lead to the development of an attack if the child has epilepsy. There are certain sleep standards that must be observed for a sick child:
- a newborn sleeps during the day from 8 to 9 hours, at night from 10 to 12 hours;
- from 3 months, the child sleeps from 6 to 7 hours during the day, and up to 10 hours at night;
- from six months at least 15 hours a day;
- from 10 months at least 14 hours a day;
- from one and a half years old at least 13 hours a day;
- from three to seven years at least 12 hours a day;
- from 14 to 17 years old at least 9 hours a day.
An adult with epilepsy should sleep at least 8 hours a day to prevent the development of an attack, and older people at least 7 hours.
How to prevent epilepsy in children and adults
To prevent epilepsy in a child, prevention should begin before birth. Do not drink alcohol, do not smoke during pregnancy or breastfeeding, eat rationally, follow all doctor’s recommendations.
In young children, the cause of epilepsy can be intrauterine hypoxia - this disorder is indicated by the results of studies during pregnancy. The pregnant woman will have to undergo treatment and be under the supervision of doctors. An epileptic attack in a child can be caused by a brain infection - this is one of the most common causes of epilepsy.
Popular questions about cerebral vasospasm
How to understand the cause of a headache?
First of all, it’s worth analyzing the situation - what could be causing the problem? Perhaps a headache occurs when the weather changes, after excessive physical exertion, hypothermia, stress, or frequent lack of sleep. If there is no explainable reason, you should definitely seek help from a doctor.
What drugs can be taken without a doctor's prescription?
Most non-narcotic analgesics and antispasmodics are sold without a prescription.
The most effective drugs?
The best tablets for cerebral vasospasm are combined drugs that have analgesic and antispasmodic effects, for example, Bralangin, Pentalgin and Spazmalgon. Antispasmodics that reduce vascular tone, for example, Papaverine and Drotaverine, are also effective.
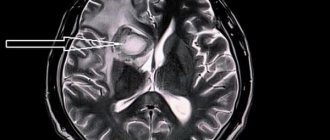
Diagnostics
If complaints arise about spasms of blood vessels in the arms and legs, diagnosis begins with a visual examination. The doctor pays attention to the appearance of the skin, its color and condition. Next, he performs manipulations with flexion and extension of the limbs so that the patient reports the degree of pain.
Special diagnostic methods are used:
- oscillography (determination of pressure in blood vessels);
- measuring temperature in various parts of the limbs;
- rheography (determining changes in tissue resistance);
- radioisotope study (determining the filling of blood vessels);
- capillary study;
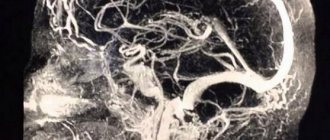
- angiography (detection of the degree of narrowing of the vessel and the size of the affected area);
- Ultrasound duplex scanning.