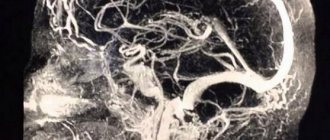
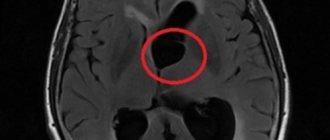
What is the essence of the EEG procedure?
An electroencephalogram records electrical signals from brain cells and allows us to identify epilepsy, trauma, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and changes in blood vessels. Pathology is indicated by disturbances in the electrical activity of neurons, which are recorded using special sensors placed on the patient’s head.
Using an electroencephalogram, the doctor can:
- analyze the performance of the brain;
- identify foci of pathologies;
- assess the nature and extent of damage;
- confirm or clarify the diagnosis;
- monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
Benefits of Electroencephalography
Today, electroencephalography is widely used in neuropathological practice. It makes it possible to clarify a huge number of problematic situations that are associated with the diagnosis and differentiation of neurological diseases. One of the undeniable advantages of encephalography is the fact that it not only helps to identify certain problems, but also helps to distinguish true disorders from hysterical manifestations or simulation.
In addition, the procedure is not as expensive as examination using a tomograph or other similar devices. EEG equipment is available in most hospitals.
The procedure does not have any negative impact on human health and condition. The patient remains fully functional. The study can be carried out even on patients in serious condition, children and adults of any age, since it does not cause deterioration of the condition, discomfort or pain.
In what cases is EEG prescribed?
After a conversation with the patient and studying the medical history, the specialist decides to prescribe encephalography. Typically, indications for an EEG are frequent headaches, sleep problems, fainting, fatigue and chronic fatigue.
Deterioration in well-being may be a sign of disorders in the functioning of the brain. The above ailments often arise due to:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head;
- inflammatory processes in meningitis and encephalitis;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant or benign neoplasms.
For patients suffering from epilepsy who have undergone neurosurgical interventions and head injuries, EEG monitoring is mandatory.
Contraindications
It is noteworthy that there are no absolute contraindications for electroencephalography. If a person suffers from convulsive attacks, is diagnosed with coronary heart disease, hypertension, or mental disorders, an anesthesiologist must be present during the diagnosis.
The procedure should be postponed if there are open wounds, traumatic injuries, postoperative sutures or any signs of an inflammatory process in the area where it is necessary to install electrodes. Also, the study is not carried out for patients with ARVI.
How to prepare for an electroencephalograph examination?
Monitoring the electrical activity of the brain does not require complex training. During the examination, it is important to simply follow the doctor's instructions and remain calm. Flashes of light and noise are part of the procedure.
Three days before the examination, it is recommended to stop taking tranquilizers, anticonvulsants and sedatives. 24 hours before the examination, do not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, or eat chocolate. The day before monitoring, wash your hair. Have a snack an hour before the examination. Before starting, loosen your hair and remove metal jewelry.
Rhythms of a waking person
Brain activity recorded on the EEG in an adult has several types of rhythms, characterized by certain indicators and states of the body.
- Alpha rhythm. Its frequency remains in the range of 8–14 Hz and is present in most healthy individuals – more than 90%. The highest amplitude values are observed when the subject is at rest, in a dark room with his eyes closed. It is best identified in the occipital region. It is fragmentarily blocked or completely subsides during mental activity or visual attention.
- Beta rhythm. Its wave frequency fluctuates in the range of 13–30 Hz, and the main changes are observed when the subject is active. Pronounced fluctuations can be diagnosed in the frontal lobes under the obligatory condition of active activity, for example, mental or emotional arousal and others. The amplitude of beta oscillations is much less than alpha.
- Lambda rhythm. It has a small range - 4–5 Hz, and is triggered in the occipital region when it is necessary to make visual decisions, for example, when searching for something with open eyes. The vibrations disappear completely after concentrating your gaze on one point.
- Mu rhythm. Defined by the interval 8–13 Hz. It starts in the back of the head, and is best observed in a calm state. Suppressed when starting any activity, not excluding mental activity.
How is an EEG performed?
The examination takes place in several stages.
Preparatory stage
- the patient enters the office, protected from light and sound;
- an encephalograph “cap” consisting of special sensors is put on it;
- The sensor wires are connected to a device that records the bioelectric impulses of the brain.
Diagnostic stage
- the encephalograph transmits data to the monitor in the form of a graph;
- the power of electric fields and its distribution in different parts of the brain are recorded;
- Functional tests are carried out: the patient is asked to blink, look at flashes of light, breathe less often or deeper, listen to a sharp sound.
Final stage
- the electrodes are removed from the patient;
- print out the results.
Historical reference
One of the founders of the electroencephalography method is considered to be the physiologist and psychiatrist from Germany Hans Berger. In 1924, using a device for measuring small currents called a galvanometer, he was the first to perform a procedure resembling an EEG recording.
Later, a special device called an encephalograph was created to conduct electroencephalography. Today, there are stationary encephalographs, which make it possible to conduct research exclusively in a special room, and portable ones, which are designed for long-term monitoring and can be moved.
It is noteworthy that initially EEG was considered exclusively as a method for identifying mental disorders in a person. Only over time it became clear that the technique also makes it possible to detect deviations not related to psychiatry.
How long does the electroencephalogram procedure take?
A regular encephalogram (routine EEG or diagnosis of a paroxysmal state) takes from 20 to 30 minutes.
During the examination, a number of tests are carried out:
- rhythmic photostimulation;
- hyperventilation;
- load in the form of slow blinking.
If it is necessary to evaluate certain brain functions, the specialist adds additional tests, which he informs the patient about in advance. Such tests include:
- clenching your fingers into a fist;
- being in the dark;
- sleep deprivation for a certain period;
- night sleep monitoring.
Price
The cost of EEG video monitoring depends on the qualifications of doctors, the quality of equipment, the quality of service and the room in which the patient is located during the study, and the clinic’s experience in the field of neurophysiology. The clinic's specialization in neurology provides a great advantage for the patient who wants to receive an accurate and definitive diagnosis.
Medical has been operating since 1988 - it has vast experience and a scientific base, as well as the best specialists. Video-EEG monitoring is carried out on elite neurophysiological equipment “Grass Telefeaktor” in special rooms with all the necessary equipment in compliance with world standards of EEG video monitoring
The diagnostic price may include consultation with specialists with analysis of the electroencephalogram in complex cases - participation in deciphering the results of the medical consultation examination. The cost also depends on the time of the study - multi-day EEG video monitoring is more expensive.
The diagnostic price may include consultation with specialists with analysis of the electroencephalogram in complex cases - participation in deciphering the results of the medical consultation examination. The cost also depends on the time of the study - multi-day video-EEG monitoring is more expensive.
Interpretation of survey results
Even a qualified specialist is not always able to accurately name the cause of the patient’s poor health and immediately make a diagnosis. The doctor may be alerted to focal changes on the EEG. In this case, magnetic resonance imaging will be required to exclude a tumor or cyst.
When you contact a medical doctor, you will be able to undergo all examinations as quickly as possible, without delaying your visit to specialists.
If you need to do an EEG of the brain and you want to do it using modern expert-class equipment and in the shortest possible time, call the phone number listed on the website or leave a request in the feedback form.
Medical staff will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!
Electroencephalographic montages
➥ Main article: Installation of EEG leads
The basis of electroencephalography is the registration of the potential difference between two points. The recorded and graphically displayed potential difference between the two electrodes is called the electroencephalographic lead . It is believed that the activity recorded under one electrode reflects the functional state of a cortical area with an area of 10 x 10 to 15 x 15 mm. To record the bioelectrical activity of all parts of the convexital cortex, it is necessary to use a sufficient number of leads for this task. Switching EEG leads into a specific system constitutes installation . Based on the method of recording activity, montages can be divided into bipolar and monopolar (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Classification of EEG montages
In bipolar montages, the leads are switched in successive “chains” either along the sagittal line or across it. Accordingly, such installations are described as longitudinal and transverse (Fig. 1). The name of the leads in bipolar montages corresponds to a pair of switched electrodes: for example, Fp1-F3, F3-C3, C3-P3, P3-O1, etc.
Rice. 2. Bipolar EEG montages
a-longitudinal, b-transverse
One of the common longitudinal montages is a montage representing sequential switching of electrodes over each hemisphere into two fronto-occipital circuits: a circuit through the parasagittal leads and a circuit through the temporal leads (Fig. 2, a). The scheme of such an installation has a characteristic appearance, which made it possible to give the installation an appropriate name: “double banana” (English), “doppelte Wapape” (German). When switching electrodes along the frontal lines, a transverse bipolar montage is formed (Fig. 2, b).
Monopolar montages can be divided into two types depending on the method of obtaining an “indifferent”, i.e., “zero” lead. In the first case, the reference electrode is located at a point so far from the brain that its activity tends to zero. The second method is based on “averaging” the signal from all active electrodes. This signal becomes the “averaged electrode” against which activity over each lead is assessed.
In referential montages , the location of an indifferent electrode on the earlobe, as experience shows, is a completely justified method, given the relatively low power of the EEG signal. The reference electrode is placed on the ipsilateral earlobe: electrodes A1 and A2, respectively (Fig. 3). Very often, a lead from two ear electrodes connected to each other is used as a reference electrode (AA is a combined ear referent), which makes it possible to reduce the influence of interhemispheric asymmetry on the referent (do not forget that the ear electrode is not so far from the temporal lobe, and when location in the temporal lobe of a powerful pathological source, for example an epileptic focus, a false hemispheric or diffuse spread of activity can be obtained).
Rice. 3. Monopolar EEG montages
a - referential montage; b - installation with separated ear electrodes; c - installation relative to the vertex (Cz)
In some clinical cases, for example, with an epileptic focus in the temporal lobe, the ear referent ceases to be an “indifferent” inactive electrode. In such a situation, electrodes “remote” from the skull, for example on the acromion process of the scapula, can be used as a reference. However, placing a reference electrode on distant parts of the body encounters a number of difficulties, mainly due to interference from other electrically active organs: the heart and striated muscles. The location of the “remote” reference electrode on the chin, bridge of the nose, and cheekbone is extremely rare and is, perhaps, only of historical interest. However, in situations where placing the electrode on the earlobe is undesirable for some reason, such a location of the referent is possible.
The vertex electrode Cz can be used as a reference electrode. The paradox is that, despite the obvious active nature of this electrode, due to its topographical central location, it has a level of activity that can be conditionally considered to be a certain average total level. The use of the Cz electrode with an average activity level marked the beginning of another method: the mathematical formation of a virtual averaged electrode
In installations with an averaged electrode (Av), a “point” (“source”) is used as such an electrode, to which all active electrodes located on the scalp of the subject are connected in parallel through identical, fairly large resistances. Connecting a large number of electrodes in parallel “averages” the activity and provides a relatively low amplitude of the total signal of the averaged electrode. As follows from the technical rationale for this technique, the number of averaged electrodes must be large enough so that the activity of an individual electrode does not make such a large contribution that it will distort the average signal. In practice, installations with an averaged electrode are used with a total number of electrodes of at least 16.
The average electrode can be formed separately for each hemisphere: the average electrode of the right hemisphere (AvR) and the left hemisphere (AvL). Since each active electrode is included in the mathematical model of the averaged electrode, the active electrodes are switched with the averaged electrode of the ipsilateral hemisphere.
When averaging, mathematical transformation procedures, for example Laplacian or Lemos, can be additionally used to level out disturbances from individual electrodes. Such a reference is designated as an “averaged weighted electrode” (AvW).
In the most general case, a monopolar lead is designated as a lead relative to the reference electrode. For example, Ol-Ref, O2-Ref. However, the referent is usually indicated. As a result, the lead name looks more specific, for example O1-A1, or O1-AA, or Ol-Av, or 01-AvW.
A variety of montages during EEG serves to solve the inverse problem of EEG - localization of the source of pathological activity. This section, dedicated to the EEG research methodology, does not imply a discussion on which montage - monopolar or bipolar - is better and, therefore, in what montage to record the EEG. In the era of paper-based encephalographs, specialists adhered to the rule of recording the EEG in several mandatory montages. The switching of 6-8 such installations was already “hardwired” into the device. Computer encephalography allows the EEG recorded in any montage to be switched to any other montage. The software of the encephalographic complex includes a so-called montage library. It is quite extensive. In addition, there is always the opportunity to create your own montage or your own library. A necessary condition is a sufficient number of electrodes. When using an EEG helmet (EEG-cap), the optimal number of leads is recorded. When working with bridge or cup electrodes, you should strive to apply at least 19-21 electrodes so as not to rob yourself during subsequent analysis of the data obtained.
The graphical representation of the EEG pattern (EEG screen images) implies the order in which the leads are presented “from top to bottom.” The graphical representation depends on the tasks being solved. In a general assessment of neurodynamics, the hemispheric leads are alternately reflected from top to bottom. When identifying interhemispheric differences, homologous leads of the right and left hemispheres can be displayed in pairs. The lowest channel, as a rule, records the ECG in standard lead II.
The neuroscience community has not developed standard requirements for screen imagery. Equally often one can find the representation of screen images as a sequence of leads from the frontal to the occipital, and vice versa. The order of presentation of the leads of the left and right hemispheres, as well as the sequence of hemispheric leads, are, perhaps, determined by established traditions in the laboratory and reflect the individual style of perception of the specialist (“I see it this way”). Still, you shouldn’t impose your style on others. A novice specialist needs to choose a style, develop it and stick to it. The sequence of leads should be logical, expedient, and should not be pretentious.