Treatment under the compulsory medical insurance policy is possible!
Submit your application
Follow the news, subscribe to our social networks
Details
Angioplasty and stenting of the heart arteries is a method of treating coronary heart disease (CHD), which is performed without incisions under X-ray control and consists of restoring the patency of blocked coronary vessels. The essence of coronary angioplasty is to install a special catheter with a small balloon in the narrowing area. After inflation of the balloon, the lumen of the coronary artery is restored. To maintain the lumen of the coronary artery, it is necessary to install a metal frame - a stent.
Coronary angioplasty is a treatment that saves thousands of lives in patients with acute myocardial infarction. The advent of this technology has made it possible to reduce the mortality rate of a heart attack by 10 times and improve the quality of life in most patients with coronary artery pathology.
Long-term results of coronary angioplasty and stenting depend on follow-up and the stents used. Modern stents significantly improve the prognosis of the further course of the disease.
The endovascular clinic of the Innovative Vascular Center has achieved excellent results in emergency and planned operations for coronary heart disease. To correct stenoses and occlusions of the coronary arteries, we use the most modern endovascular instruments (balloons and stents). Every month, the clinic performs about 100 interventions on the coronary arteries in patients with acute coronary syndrome and elective angina.
- Our surgeons managed to achieve a minimum number of adverse outcomes in patients with myocardial infarction, and this figure remains the lowest in the Moscow region over the past years.
- Coronary angioplasty is performed using the latest Philips Allura Xper FD20 angiographic unit.
- Our endovascular surgeons use the safest radial approach on the arm.
- Our cardiac stenting technology often eliminates the need for coronary artery bypass grafting.
- We use the best stents to achieve optimal results.
- We have the most understandable and affordable prices for cardiac stenting.
How is coronary stenting different from open surgery?
Coronary stenting is a type of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Unlike open-heart surgery, coronary stenting is characterized by a minimal degree of trauma to the patient: the stent is implanted through a small puncture in a vessel of the thigh or upper limbs. This type of surgery does not require the use of general anesthesia: the patient is conscious and watches what is happening on the angiograph screen. In addition, treatment using endovascular surgery techniques is quick and comfortable, and the patient goes home the very next day after stenting the heart vessels.
If the stent implantation is successful, the patient feels relief almost immediately. Since normal blood flow to the heart is restored, heart pain, shortness of breath and other unpleasant signs of IHD disappear. Coronary artery stenting normalizes blood flow by widening and opening up narrowed and blocked arteries. As a result, chest pain decreases or completely disappears; physical activity does not provoke painful conditions.
Successful surgery minimizes the need for coronary artery bypass graft surgery in the future, where a vein or artery is removed from a part of the body and sutured directly to the heart to avoid affecting the affected area. Such an intervention requires an incision in the chest, but the risks are greater and the recovery period is longer. In addition, the price of cardiac stenting is much lower than bypass surgery.
Advantages of carotid artery stenting at the Innovative Vascular Center
Our clinic has extensive experience in treating patients with carotid artery pathology. In recent years, stenting has almost replaced open carotid endarterectomy in our practice, as we have become convinced that this method has undeniable advantages and is suitable for most cases.
We perform stenting of the internal carotid artery after assessing the intracerebral vascular bed in order to eliminate the risk of stroke as much as possible. The price for carotid artery stenting in our clinic is affordable, although a disposable instrument is used to perform the operation in our clinic - a recognized world leader in the development of peripheral endovascular products.
During the use of carotid artery stenting in our clinic, we have not noted a single case of serious complications (stroke, bleeding, thrombosis). The clinic’s vascular surgeons have a differentiated approach to the choice of method for restoring arterial patency. We try to perform open endarterectomy in young patients, and ICA stenting in older patients.
Indications
In what cases is stenting of coronary vessels performed? Often the reason for this is atherosclerosis. It begins due to the accumulation of cholesterol molecules on the walls of the arteries, gradually forming plaques. This complicates blood flow in this area, and the heart muscle experiences a lack of oxygen. As a result, the patient develops coronary disease, the symptom of which is angina pectoris. Retrosternal pain or pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, weakness, make themselves felt during physical activity. Read more about the characteristic signs of an angina attack here.
Cardiac stenting helps prevent the dangerous consequences of coronary artery disease: heart attack and acute coronary syndrome. Coronary stenting is a help for advanced stages of the disease or for emergency treatment of acute coronary syndrome. However, if both vessels are affected or the diameter of the vascular lumen is too small, bypass surgery, an open operation, will give better results.
conclusions
Coronary stenting eliminates the consequences of atherosclerotic lesions of the heart vessels, blockage and stenosis of the arteries. This procedure does not completely eliminate coronary disease, the main causes of which are metabolic disorders, metabolic diseases, smoking, alcohol abuse, and progressive atherosclerosis. Each patient after stenting should be aware of the need to follow the doctor’s recommendations and not violate the medication schedule. If therapy is stopped and preventive measures are not followed, the risk of sudden thrombosis and blockage of the stent in the heart artery increases several times.
A mandatory condition for monitoring the patient is a medical check-up and regular preventive examination by a cardiologist or therapist. This makes it possible to identify the slightest signs of a developing relapse and, as soon as possible, take measures to eliminate coronary stenosis, refer the patient to a cardiac surgeon and perform re-stenting.
Possible complications:
Coronary stenting rarely causes complications, but there are certain risks associated with it:
- Repeated narrowing of blood vessels (stent restenosis). If angioplasty is performed without stent implantation, the probability of restenosis reaches 30-40%. Installation of a bare metal stent reduces the possibility of relapse to 20%, and drug-coated stents - to 1%.
- The occurrence of blood clots. After some time, blood clots can form inside the stents, which are dangerous because they lead to a heart attack. To reduce the likelihood of their occurrence to a minimum, we recommend taking antiplatelet medications prescribed by your doctor: Plavix, aspirin, etc.
- Bleeding from the catheter site (arm or leg). In most cases, there will only be a slight bruise, but there is still a risk of serious bleeding.
Postoperative period
The patient is discharged on the 2nd day after surgery with a mandatory follow-up ultrasound scan.
After carotid artery stenting, combination antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel 75 mg/day and aspirin 100 mg/day is prescribed for up to 12 months. Subsequently, aspirin and anti-cholesterol drugs - statins remain.
A control ultrasound scan is performed one month after stenting surgery. The patency of stented segments should be assessed at intervals of 6 months. If signs of restenosis are detected, the patient is prescribed a multislice computed tomography scan with contrast.
Rare complications:
- Myocardial infarction or heart attack.
- Coronary artery rupture or dissection. Damage requires coronary artery bypass grafting or emergency stent graft implantation.
- Impaired kidney function. The contrast agent administered during stenting and angioplasty has a detrimental effect on the kidneys. If the patient already has problems with their functioning, the doctor prescribes medications for protection.
- Stroke. During surgery, blood clots may form on the catheter. If they fragment, break off and travel to the brain, the patient will suffer a stroke. To reduce the risk of developing this complication, blood thinning medications are used.
- Arrhythmia. Manifested by heart rate disturbances: bradycardia or tachycardia. This is a temporary complication that goes away after the medication is administered. A temporary pacemaker is rarely required.
Types of stents
A stent is a high-tech design, which is a tubular frame made of a medical alloy (cobalt, steel, chromium, tantalum, platinum and nithiol), absorbable materials or polymers with improved biocompatibility, which, when placed in the lumen of a narrowed vessel, expand it and resume blood flow on it.
There are about 400 types of stents, differing in manufacturer, composition, cells, coating and placement system.
Types of stent designs:
- Balloon-expandable:
- tubular;
- spiral;
- wire;
- sinusoidal (ring).
- Self-expanding (mesh).
Cells are divided into closed, open, with tanks, various thicknesses of beams and lintels.
Stent shapes:
- cylindrical;
- conical;
- bifurcation;
- ultra-low profile (for narrow vessels).
Types of stents by type of coating:
- "Passive":
- carbon;
- titanium oxynitride;
- "artificial endothelium".
- Mechanical:
- stent grafts;
- with micro mesh.
- Medicinal:
- limus;
- paclitaxel;
- others (“Tacrolimus”, “Trapidil”, “Dexamethasone”, “Heparin”).
- Hybrid (combination of active and passive).
Hybrid stents have a polymer coating that releases a substance that resists endothelial fouling of the structure. The second layer encapsulates the stent, preventing metal particles from penetrating into the tissue.
The newest models have an asymmetric coating of the drug, which prevents it from entering the systemic bloodstream.
A new development in cardiology is biodegradable stents made in the USA, which provide temporary mechanical support for opening the coronary artery with subsequent resorption for 24 months. This group is intended for implantation in young patients or with non-calcified plaque.
Preparing for stenting
After reviewing your medical history and performing a physical examination, the surgeon performs a coronary angiogram to determine whether atherosclerosis can be treated with stenting. A coronary angiogram makes it clear whether the arteries are narrowed or occluded (completely blocked). A contrast agent is injected through a catheter (a thin long tube passed to the coronary vessels through the artery of the leg or arm. When the substance fills the lumens of the arteries, X-rays are turned on. The image is displayed on the monitor, and the doctor determines exactly where the coronary arteries are affected. Having scheduled heart surgery, The doctor will give recommendations regarding nutrition. It is usually recommended to avoid drinking water and food after dinner the night before stenting. If you are undergoing preparation in the hospital, the instructions may be different.
The evening before surgery you should:
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor. If you are taking diabetic or blood thinning medications, your surgeon may ask you to stop taking them that evening.
- Prepare the necessary medications that you will take with you to the hospital.
- You will stay in the hospital until the next morning. Driving is contraindicated, so you should arrange your delivery home in advance.
When is bypass surgery performed?
Shunting is performed in the following cases:
- it is impossible to install a stent without surgery;
- the affected vessel has a miniature diameter;
- large extent of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- two or more vessels are affected, which is accompanied by multiple blockages of the lumens.
The operation has a number of contraindications. Bypass surgery should not be performed on elderly patients with severe concomitant diseases. Sometimes doctors are forced to urgently perform an operation even if there are contraindications, but then the risk of death increases significantly, of which the patient’s relatives must be notified.
Progress of percutaneous coronary intervention:
1. The site of exposure is treated with an antiseptic. The patient is given a local anesthetic and blood thinning medications to prevent the formation of blood clots. Small electrodes are attached to the chest to help the surgeon monitor the heart rhythm and pulse rate. 2. The operation is performed through the femoral artery (on the leg) or the radial artery (on the arm). Through a small puncture, a catheter-port for carrying instruments (introducer) is installed. Through it, a catheter is delivered to the mouth of the coronary artery, with the help of which surgical intervention is performed. 3. Angioplasty of the coronary arteries with stenting is performed in an angiographic operating room equipped with high-tech medical equipment. Contrast liquid is injected through the installed catheter. Using a coronary angiogram, the doctor evaluates the affected area. 4. A balloon catheter is passed to the site of the lesion, expanding the narrowed area. As the balloon inflates, the patient may feel discomfort in the chest. This is due to the blocking of blood flow through the artery - after the balloon is deflated, the unpleasant sensation stops. Stent implantation: 1. The stent, mounted in a closed state on a balloon, is advanced to the narrowed area of the artery. 2. The surgeon inflates the balloon in the affected area, thereby expanding the stent. 3. The wire remains in the artery to keep it open and improve blood flow to the heart. 4. The surgeon removes the catheter and makes control coronary angiograms to assess the strength of blood flow through the dilated artery. 5. The doctor applies a pressure bandage to the area of the leg or arm where the catheter was inserted.
Coronary stenting takes from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the severity of atherosclerosis. As prescribed by your doctor, after surgery you should take medications that minimize the possibility of blood clots. For a video of stenting of cardiac vessels, follow the link.
How does the installation work?
The full name of the procedure is percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty (PTBA).
Before the intervention, the patient must undergo coronary angiography (X-ray contrast of myocardial vessels), based on the results of which the vulnerability of the plaque is determined, a decision is made on the advisability of installing a stent, and its type, diameter and size are selected.
Additionally, the fractional reserve of the coronary circulation (FFR) is measured - the ability of this vessel to supply the heart with blood in sufficient quantities. Sometimes an MRI is required.
CTBA stages:
- Under local anesthesia, a puncture of a large artery (femoral, radial, brachial, ulnar) is performed. The most common is the femoral approach. Below the inguinal fold, the skin is incised, the vessel is punctured with a needle, a conductor is inserted and an introducer is installed for inserting instruments.
- The mouth of the coronary artery is catheterized, a special conductor is inserted below the narrowing of the vessel, through which the necessary instrument will be delivered to the site of the lesion.
- A catheter balloon is delivered through a guidewire to the lesion, and a preliminary expansion of the area with the atherosclerotic plaque is performed.
- The catheter balloon is replaced with a balloon with a stent and brought to the insertion site under X-ray control.
- The balloon with the stent is inflated under a pressure of 10-14 atm.
- The balloon is deflated and slowly removed from the artery.
- A control coronary angiography is performed to ensure that the stent is placed correctly inside the vessel.
- The introducer is removed, a suture and an aseptic bandage are applied to the incision area.
After the procedure, you need to stay in bed for 24 hours. The condition of the puncture site is carefully monitored throughout the day. After this period, the bandage is removed, and for another two days the patient is allowed to move only around the department.
Video of stent installation:
Rehabilitation
The patient spends the first few hours in the intensive care unit, where the doctor monitors blood pressure levels and heart parameters. If there are no contraindications, during rehabilitation it is recommended to drink more fluid (about two liters per day) so that the body quickly removes the contrast fluid. It is better to avoid heavy lifting and intense exercise. A few days after discharge from the hospital, the patient returns to his normal life.
After surgery, it is important to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and attend scheduled cardiologist appointments on time. Taking blood-thinning drugs: aspirin (Cardiomagnyl, thrombo ACC, Cardiasca, etc.) and clopidogrel (Plavix) requires special attention.
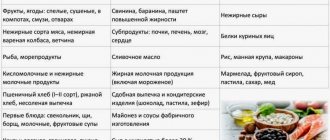
Diet
A diet after a heart attack is prescribed not only for the period of recovery and rehabilitation, but for the rest of your life. In most cases, the patient is recommended to undergo therapeutic diet No. 10 I , which includes three diet options.
The diet can be very varied, but it is necessary to prepare dishes following certain rules:
- It is necessary to significantly reduce the consumption of salt and products containing it. Salt leads to stagnation of fluid in the body, which contributes to the appearance of edema and shortness of breath. The daily norm is assigned to each individual, but on average the amount should not exceed 1 teaspoon per day .
- It is recommended to exclude fatty and fried foods, and also avoid pickles and smoked foods. The best cooking methods are: baking, steaming, boiling.
- The amount of additional fluid per day should not exceed one liter. You should not drink a lot of water after 5 pm. The maximum allowable amount at this time is 250 ml (1 mug).
- Some drinks should be avoided altogether. These include alcohol in any form, coffee and soda. The desired caffeine can be replaced with more gentle chicory.
- It is also necessary to enrich the diet with dried fruits containing potassium and magnesium: dried apricots, raisins, prunes.
The optimal amount of calories per day is 2300 Cal (the female norm is slightly lower, no more than 2000). However, it is important to follow a diet, dividing the total number of calories into 4-7 small meals . Products also need to be selected carefully. The diet must be composed of:
- berries, vegetables and fruits;
- plenty of fresh herbs;
- fermented milk products;
- lean fish (required);
- seafood;
- poultry meat with the addition of vegetable oil, preferably olive;
- lean meats;
- cereal crops.
It is recommended to reduce the amount of sugar and fast carbohydrates consumed as much as possible. There is little benefit to the body, but the harm after surgery may be much greater.
If you are overweight, it is recommended to follow a calorie deficit diet to bring your body weight back to normal. Heavy weight significantly increases the load on the heart muscle.
Recommended products for diet I-III:
- pureed vegetable and cereal soups (during diet III, they can be prepared in light meat broth);
- lean fish;
- veal;
- chicken meat (without fat and skin);
- cereals (semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat and rice);
- steamed egg white omelette;
- fermented milk drinks;
- low-fat sour cream for seasoning soups;
- butter (with a gradual increase in its quantity to 10 g by the third period);
- skim milk for adding to tea and porridge;
- wheat crackers and bread;
- low-fat sour cream for seasoning soups;
- refined vegetable oils;
- vegetables and fruits (initially boiled, then it is possible to introduce raw salads and purees from them);
- rosehip decoction;
- fruit drinks;
- compotes;
- jelly;
- weak tea;
- honey.
It is necessary to exclude foods from the diet:
- fresh bread;
- baking and baked goods;
- fatty meat dishes;
- offal and caviar;
- canned food;
- sausages;
- fatty milk products and whole milk;
- egg yolks;
- barley, pearl barley and millet;
- legumes;
- garlic;
- White cabbage;
- turnips and radishes;
- cucumbers;
- spices and pickles;
- animal fats;
- margarine;
- chocolate;
- grapes and juice from them;
- cocoa and coffee;
- alcoholic drinks.
Condition assessment
After carrying out exercises and various activities, a number of parameters are assessed:
| Index | Change |
| General state | Moderate fatigue Severe fatigue that does not go away for a long time |
| Angina pain | No Moderate, goes away on its own Severe, require medicinal correction |
| HELL | The increase for the upper one is no more than 40 mm Hg. Art., lower - no more than 12 Or a decrease in indicators of no more than 10 units |
| Heart rate | Increase by no more than 20 per minute or decrease by 10 units maximum |
| Breathing problems | An increase of no more than 6 per minute is acceptable. |
| Changes on the cardiogram | Signs of impaired blood flow (decreased ST segment) Violation of the rhythm of contractions Blockade of impulse conduction |
Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of the disease?
Undoubtedly!
Experts recommend:
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Move more. The most useful sports are cross-country skiing and swimming. You can also just walk, do simple gymnastics in the morning.
- Get rid of excess weight.
- Eat properly. Minimize your intake of full-fat dairy products, animal fats and eggs.
- Use medications that can effectively combat a number of concomitant diseases.