Arrhythmia: types, diagnosis and treatment
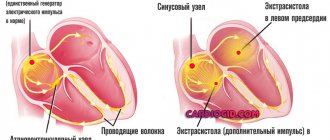
What is a heart rhythm disorder called arrhythmia and why does its type, tachycardia, occur? - says Ekaterina Radikovna Perminova, a cardiologist at the CORDIS Medical Center. ⠀ Heart rate (HR) at rest is affected by age, physical fitness and other factors. A normal rhythm should be in the range of 60 to 100 beats per minute. The sinus node, which is located in the anterior upper part of the right atrium, is responsible for its regulation. Arrhythmia is a disturbance in heart rate, firing sequence, and conduction. It may feel like a sinking heart or appear as extraordinary contractions.
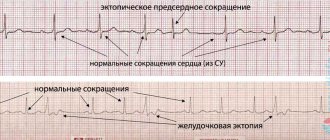
Arrhythmia has several types that differ from each other. The three main types include sinus, ventricular and atrial arrhythmia. They are further distinguished by heart rate:
- atrial fibrillation is considered the most common type. Cardiac muscle fibers work asynchronously due to twitching or “flickering” of the atria. Their reduction simply disappears. At the same time, the ventricles also stop working normally.
- tachycardia - in this condition, a person’s pulse exceeds 100 beats per minute. Tachycardia that occurs during heavy physical exertion is considered normal. But if you are completely calm and your pulse is high, we can talk about pathology.
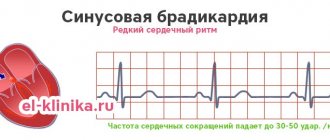
- bradycardia - with this type of arrhythmia, the heart rate is less than 60 beats per minute. It often appears when you feel normal. But if you constantly feel unwell, the pathological process has already started.
- extrasystole usually appears for no apparent reason. A premature contraction seems to be woven into the normal heart rhythm. The cause of the attack can be severe stress.
- paroxysmal disorders are expressed in a sharp increase in pulse rate, strong heartbeat with the inability to count its beats. Sometimes their frequency reaches 200 beats per minute. This is a special type of tachycardia, leading to sudden weakness and even loss of consciousness. The condition is considered extremely dangerous. Immediate medical attention is needed here.
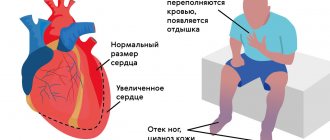
CAUSES OF ARRHYTHMIA Arrhythmia does not always occur due to problems related to the functioning of the heart. It can be a consequence of other cardiac pathologies: - heart attack - coronary heart disease - cardiomyopathy - myocarditis - arterial hypertension - heart failure - heart defects (congenital and acquired) - cardiosclerosis - injuries and wounds of the heart These diseases lead to damage to the heart muscle and complicate normal propagation electrical impulse of the heart to its parts. ⠀ HOW ARRHYTHMIA MANIFESTS
- sudden weakness
- headache
- dizziness to the point of loss of consciousness
- shortness of breath, lack of air
- fast or slow heartbeat
- chest compression, pain
BRADYCARDIA
indicates various cardiac pathologies. Most often it appears due to blockage of the sinus node and is characterized by a slowing of the heartbeat to 30-50 beats/min. Other causes of bradycardia include: - heart attack, coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, heart disease - age-related changes in the heart muscle - reflex effects (cold water, blow to the chest or neck) - increased intracranial pressure, pressure on the carotid artery or eyeballs - stomach and duodenal ulcers - use of drugs that replace heart rate - consequences of poisoning with chemical or organophosphorus substances - disturbances in potassium balance and calcium levels
SYMPTOMS OF BRADYCARDIA If you have a heart rate less than 40 beats per minute, this may lead to the development of heart failure. Common symptoms of bradycardia include:
- general weakness, cold sweat
- pale skin and mucous membranes
- dizziness
- swelling
- convulsions
- dyspnea
- low blood pressure
- fainting or momentary loss of consciousness
- absent-mindedness
WHAT TO DO Unfortunately, arrhythmia can be either an independent pathology or a manifestation of another disease. Therefore, if you begin to sleep poorly, wake up with shortness of breath in the middle of the night, if you have tremors in your hands and you panic more and more often, you have heart problems. With sinus bradycardia, a rare pulse and respiratory arrhythmia are observed. To diagnose it, daily ECG monitoring, cardiac ultrasound, and exercise bicycle ergometry are prescribed. The sooner you see a doctor, the lower your risk of developing cardiovascular problems. Sinus bradycardia requires constant prevention. Quit smoking and alcohol, normalize blood pressure and weight, eat right. Worry less and exercise.
TACHYCARDIA
is not considered a severe pathology. Rather, it is a symptom when the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute. It is usually caused by increased physical activity in those who do not regularly engage in heavy physical labor or sports. But sometimes the CAUSES of tachycardia can be: - dehydration - increased sensitivity to coffee, strong tea, nicotine, alcohol - high temperature - sleep problems - anemia - obesity - strong emotions, stress, fear - old age - hypertension or hypotension - taking certain medications (from a runny nose or cough) - intoxication - in some cases - heart disease
In a completely healthy person, the heart rate can reach 150-200 beats/min. and higher. It happens that an attack lasts from several minutes to several hours. Your norm for tachycardia and arrhythmia is quickly passing symptoms without weakness, sweating and decreased blood pressure.
SYMPTOMS OF TACHYCARDIA You should consult a doctor when:
- heart rhythm disturbances occur frequently and for a long time
- you begin to experience shortness of breath, lack of air
- if you feel dizzy and sweat
- you urinate often
- you feel scared for no reason
- you stop sleeping normally, you lose your appetite
- there is pain in the heart area
- general health and mood are at zero
WHAT WE DO If you suddenly feel ill, apply a cold compress to your forehead, wash with cool water, and then take one of the sedatives: Corvalol, Valocordin, valerian, motherwort or peony infusion. Of course, if you discover symptoms of arrhythmia, you need to undergo an ECG examination. It shows the consequences of rhythm disturbances, even if you are already fine and the attack has passed. But it may happen that tachycardia is accompanied by loss of consciousness, severe chest pain or shortness of breath. Then call an ambulance immediately. Tachycardia should be treated only after its cause has been determined. To reduce the likelihood of unexplained tachycardia, avoid caffeine, spicy foods, chocolate, alcohol and cigarettes. Also, avoid serious physical activity and be less nervous.
AFIBLIRATORY ARRHYTHMIA
As you know, the heart must contract in a strictly ordered rhythm. And one of the deviations from it is atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation). ⠀ The prevalence of this rhythm disorder increases with age: approximately 6% of men and women over 60 years old suffer from atrial fibrillation. ⠀ What happens to our heart during an attack of atrial fibrillation? The atria begin to contract rapidly and erratically, and the sinus node does not coordinate the heart rhythm. These fibrillations can reach 300-600 per minute when the norm is from 60 to 90. Scary, right? ⠀ If atrial fibrillation lasts for a long time, blood clots may occur, and hence ischemic strokes and acute arterial insufficiency of the arteries of the upper or lower extremities. ⠀ REASONS This disease is caused by a number of reasons related to both cardiac pathologies and diseases of other organs or external factors affecting the body: - heart attack - arterial hypertension - tachycardia - myocarditis - severe heart failure - intoxication - cardiosclerosis - rheumatic heart defects - cardiomyopathy - thyrotoxicosis - diabetes - psycho-emotional overload - previous surgical interventions - hypokalemia ⠀ Atrial fibrillation in itself does not threaten your life. But atrial fibrillation interferes with the synchronous functioning of the heart and increases the risk of developing chronic cardiovascular failure and thromboembolic complications. ⠀ SYMPTOMS So, we can talk about atrial fibrillation if you find the following symptoms: erratic heartbeat
- feeling of heart fluttering
- chest pain
- weakness and sweating
- labored breathing
- dizziness and fainting
- shiver
- frequent urination
- feeling of fear
⠀ But as soon as you restore your heart rate, these symptoms disappear. Atrial fibrillation is of three types: - paroxysmal from 30 seconds to 7 days - persistent - longer than 7 days - constant
HOW TO DETECT The following are considered the most accurate diagnostic methods for identifying atrial fibrillation and the causes leading to it: ECG Ultrasound of the heart MRI of the heart Bicycle ergometry and treadmill test 24-hour Holter monitoring Blood test, which can be used to confirm or rule out other diseases You can measure your pulse yourself and assess the regularity and frequency of heart contractions. A fast, slow, or arrhythmic pulse indicates that your heart rhythm is abnormal.
WHAT TO DO First of all, make an appointment with a cardiologist. The doctor will prescribe you treatment to prevent “rhythm disruptions” and their complications, and correct diseases that lead to paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. In some cases, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation may require hospital treatment and electrical pulse restoration of rhythm. We will have to reconsider our lifestyle. If you abuse smoking, alcohol and fatty foods, give up everything that can have a bad effect on your health. Strong tea and coffee can also cause heart rhythm disturbances, so reduce their consumption.
*Prices are presented for informational purposes only. The current price list can be found here
Sick sinus syndrome
What is this . Sick sinus syndrome is damage to the sinus node (the part of the heart that conducts impulses). Due to damage, the sinus node no longer controls the heart correctly, and arrhythmia occurs.
Sick sinus syndrome manifests itself:
- dizziness, fainting;
- loss of consciousness with convulsions;
- constant weakness, inability to concentrate;
- a rare pulse, which is replaced by a rapid heartbeat.
Diagnosis and treatment . To diagnose the disease, an examination is carried out, general blood and urine tests, an ECG, and an echocardiogram are prescribed. To eliminate sick sinus syndrome, treat the underlying disease that caused it. If the syndrome is accompanied by constant complaints, a pacemaker is installed, which artificially sets a normal heart rhythm.
Atrial flutter
Atrial flutter is a rapid, uniform rhythm of the atria, which contract at a frequency of up to 200-400 beats per minute. An attack of atrial flutter lasts from 1-2 seconds to several days.
Symptoms . For atrial flutter:
- general weakness develops, endurance decreases;
- discomfort appears in the chest, angina pectoris - pain behind the sternum;
- sudden attacks of rapid heartbeat develop;
- shortness of breath increases.
Diagnosis and treatment . The problem is diagnosed by ECG and ultrasound of the heart. Drug treatment is aimed at normalizing atrial contractions, preventing attacks and reducing the risk of blood clots. Beta blockers, potassium supplements, and anticoagulants are prescribed.
The Medicenter clinic diagnoses and prescribes effective treatment for all types of arrhythmia. Drug therapy is used and surgery is prescribed.