According to statistical studies, 15% of menstruating women suffer from anemia of varying severity, and not every one of them notes signs of this insidious disease.
And among pregnant women, the percentage of those suffering from a lack of hemoglobin in the blood doubles, so during this period of a woman’s life it is important to regularly take blood tests to detect anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia is most often diagnosed when the hemoglobin protein contains an insufficient amount of iron. However, the human body is designed in such a way that when there is a lack of iron, internal reserves are primarily used, so anemia does not always manifest itself with characteristic symptoms in the initial stages of the disease.
Blood condition after menstruation
The amount of iron in a woman’s body after her period is over is an important indicator of health. To identify abnormalities and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, it is recommended to do blood tests before and after menstruation. In healthy women, the level of hemoglobin changes cyclically within acceptable limits. It is not recommended to do tests during menstruation, since their results do not reflect an accurate picture.
Together with menstrual flow, 15 to 30 mg of iron leaves a woman’s body. As a result of a natural process, the concentration of hemoglobin substance decreases. With heavy and prolonged bleeding, the body loses more valuable microelements. Then the concentration of red blood cells changes more strongly. But even with significant blood loss, the level of iron-containing protein is quickly restored.
To maintain the balance of red blood cells during menstruation, eat more foods high in iron. Then within 3-4 days the normal concentration of the necessary substances is restored. If, 2 weeks after the end of your period, your blood test still shows low levels of iron protein, consult your doctor.
On a note!
In addition to the usual symptoms of hemoglobin deficiency, the state of health is judged by the nature of the discharge. The presence of violations is indicated by abundant and prolonged discharge or too dark and scanty discharge. In case of these deviations, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
During menstruation, the concentration of iron-containing protein decreases. Therefore, during this period it is necessary to eat right, maintain a normal level of physical activity and avoid stress so as not to provoke a stronger decrease in hemoglobin levels. The composition of the blood returns to normal a few days after the end of menstrual flow. If this does not happen and you continue to feel unwell, you should consult a doctor.
Low hemoglobin during menstruation
Iron protein levels are usually low during menstruation. But this condition is normal. To accurately assess the result, it is not recommended to take a blood test during menstruation, since the interpretation may be incorrect. With iron deficiency in the body, monthly bleeding lasts a long time and is painful. This happens due to hormonal imbalance caused by insufficient oxygen supply to tissues.
Iron deficiency increases the likelihood of damage to blood vessels, which are found in large numbers in the uterus. When hemoglobin protein is low, the blood becomes too thin. Therefore, the discharge lasts longer, is more intense, and causes a lot of unpleasant sensations. With normal iron protein levels, a temporary drop is felt within a week after the end of menstruation. Sometimes complete restoration of blood composition occurs faster. If recovery does not occur within two weeks, you should consult a doctor. This condition indicates the presence of diseases and disorders in the body.
Before critical days
Most signs of PMS are obvious. But they all come from internal changes that are inevitable in the female body at a given time:
- Estrogens and progestins still exist in fairly high concentrations, but are decreasing;
- The vessels, including those in the endometrium, are compressed and somewhat spasmed;
- Hemoglobin before menstruation is higher than a few days ago, as the number of red blood cells carrying it increases.
All changes in the female body are cyclical. This also applies to blood; its indicators vary throughout the menstrual period. At the end of the cycle it becomes more viscous. The biological meaning of this is that the upcoming menstruation requires the energy provided by oxygen. And it is carried by red blood cells. Nature has taken care of this in such a way that women’s appetite increases before their critical days. Many foods help increase the amount of iron in the blood. Therefore, doctors attach great importance to nutrition these days and the critical ones that follow. A proper diet, that is, food with B vitamins, helps you survive them with the least amount of problems for your well-being. But this applies more to healthy women. If there are diseases, such measures are also necessary, but not sufficient.
How to change hemoglobin levels during menstruation
If a girl’s Hb readings are normal, to prevent a decrease in it during menstruation, the following rules must be followed:
- make friends with physical activity - it increases the body’s resistance to stress as a whole and increases Hb levels;
- eat right - the diet should contain a large amount of meat and other protein products, all by-products (especially liver), buckwheat, fish are useful;
monitor the volume of menstruation - a number of gynecological diseases are accompanied by heavy menstruation, in such cases, even taking medications will not help restore iron reserves and increase hemoglobin levels; treatment of the underlying disease is necessary.
With low Hb levels, diet and lifestyle alone will not help quickly normalize the values. It is necessary to take iron in tablet form or even by injection. The course of treatment is at least 3-4 weeks, sometimes longer. For example, there are such drugs - Gyno-tardiferon, Ferrum lek, Totema and others.
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
For women who take oral contraceptives, the hormonal pills themselves help maintain hemoglobin levels at the proper level - they sometimes contain iron. An example of a drug is Tri-Regol. Oral contraceptives with additional folic acid are equally useful - it is involved in the formation of hemoglobin. For example, Jess.
Hemoglobin level is one of the indicators of a woman’s health. Considering the characteristics of the body of representatives of the fair sex, fluctuations in indicators are possible throughout the menstrual cycle, especially if menstruation is heavy or there are some gynecological diseases.
A decrease in Hb levels affects not only a woman’s well-being, but also her appearance. Timely identification of the problem and correction of blood counts is the key to health and well-being.
To determine the level of hemoglobin in the blood, you should take a general blood test. This procedure must be performed on an empty stomach in the morning. Before the analysis, you should not drink alcohol for several days, as the result will be unreliable. Experts also do not recommend performing high-intensity physical exercises before taking the test.
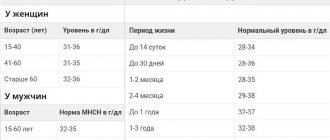
For a healthy woman, normal hemoglobin ranges from 120 to 140 g/l. If a woman plays sports, her norm will be 160 g/l. A low hemoglobin content in the blood is accompanied by symptoms:
- weakness, constant fatigue;
- brittle nails, hair without shine;
- dizziness, stars before the eyes;
- pale skin.
As a rule, such indicators require special attention. To independently increase your hemoglobin level without harm to your health, you need to eat foods high in iron:
- buckwheat porridge;
- apples;
- beef liver;
- pomegranate or pomegranate juice;
- rosehip tea;
- egg yolk;
- beans;
- nuts.
Very rarely, but still there are opposite cases when hemoglobin during menstruation exceeds the norm. A woman does not experience the usual signs of premenstrual syndrome; her period may begin earlier and last fewer days, usually about three. This happens because the blood becomes too thick.
Due to the fact that there is an excess amount of iron in the blood, too much oxygen reaches the heart, which leads to an increase in the functioning of the organ. Therefore, with high hemoglobin during menstruation, women feel discomfort in the heart area. Such a course of critical days is not considered normal. As a rule, this may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system or the development of diabetes mellitus.
source
How can a woman understand that she has anemia: symptoms and signs of anemia
Symptoms of this disease can manifest themselves in various conditions, ranging from malfunctions of the cardiovascular system to distortion of tastes and smells. But first of all, a woman should be concerned about the most specific signs for this condition, which most often accompany anemia:
- decreased labor activity;
- causeless weakness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- fatigue and apathy;
- depression;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- prevalence of bad mood;
- cold fingers;
- tendency to eat chalk, clay, toothpaste, raw cereals, etc.
It is worth paying close attention to your appearance. Often women explain their external changes by other reasons and do not always think about the fact that a serious disease, such as anemia, can greatly affect their appearance. So, it is recommended to consult a good gynecologist if external signs of anemia appear:
- pale, flabby, dry skin, sometimes with a greenish tint;
- haggard appearance;
- hair and nails are brittle, dull;
- White stripes or dots may appear on the nails, the nail plates themselves become concave;
- Trophic wounds appear on the tongue, which manifests itself as pain when eating salty and spicy foods.
It is worth urgently undergoing an examination if the above symptoms are accompanied by loss of consciousness, pain in the heart, shortness of breath, urinary incontinence or numbness of the extremities. Such manifestations may indicate advanced anemia that requires immediate treatment.
Fluctuations in hemoglobin during the cycle
During a woman's menstrual cycle, protein levels are allowed to fluctuate. This is due to the following facts:
- On the eve of menstruation, the body tries to protect itself and makes “reserves” of hemoglobin, as a result of which its numbers may increase slightly.
- During menstruation, a woman loses a small amount of blood, which contains red blood cells. Accordingly, iron reserves also decrease - with each cycle, about 10-30 mg of this trace element is lost. This leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels. If the discharge is very heavy, the fluctuations can be significant.
- After menstruation, protein levels are restored to the extent that the body's reserves allow.
Other factors also affect hemoglobin levels. Namely:
- Place of life - women who live in the highlands will always have higher rates.
- Lifestyle. Hemoglobin is higher in people who play sports - this is a healthy reaction; the level increases due to the fact that it is necessary to provide a large number of muscles with oxygen.
- Bad habits. Smoking is a risk factor for the development of erythrocytosis. The hemoglobin level will also be higher, but this is due to the fact that the body is in constant hypoxia - conditions of oxygen deficiency. So he tries to compensate for the shortage.
Watch this video about the dangers of elevated hemoglobin:
How dangerous is anemia for a woman from a gynecological point of view?
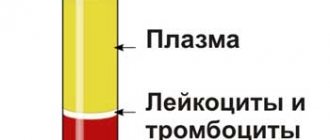
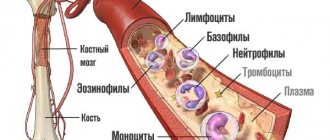
Anemia, if the start of treatment is delayed or the therapy is incorrectly selected, can seriously affect the functioning of the entire body. With this disease, the number of not only red blood cells in the blood decreases, but also leukocytes and platelets, which in turn inevitably leads to a decrease in immunity and even the development of immunodeficiency states. As a result, the woman begins to get sick often and for a long time.
Depression, low performance and chronic fatigue can provoke various neurological disorders. It becomes more difficult for such patients to concentrate, mental abilities decrease, and memory deteriorates. An advanced disease can negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system; the load on the heart muscle increases significantly.
An important factor for women is the deterioration of appearance due to anemia. The disease affects the condition of the skin, hair, and nails. Dark circles under the eyes and pale skin become companions of iron deficiency anemia.
If gynecological diseases leading to anemia are not treated, a woman is at risk of developing infertility. Some changes in the uterus that provoke recurrent bleeding and, as a result, anemia, are irreversible if treatment is not started on time.
It is worth understanding that insufficient or excessive production of sex hormones in the female body can become a provocateur of diseases like a chain reaction. Therefore, in case of anemia, it is so important to undergo a full course of gynecological examination and make sure that women’s health is stable, and if any pathologies are detected, undergo a course of treatment in a timely manner and thereby improve overall well-being.
Hemoglobin and the cycle
In connection with the above, there is no doubt about whether low hemoglobin can affect your periods. First of all, this will affect the woman’s well-being: weakness will increase, she will constantly want to sleep. Normally, these signs of PMS do not escape many people, but they are caused by hormonal changes and do not appear noticeably in everyone. Low hemoglobin before critical days can also change the duration of the period and the parameters of menstruation.
The negative impact that low hemoglobin and delayed menstruation can have on the cycle. A deficiency of the substance interferes with the normal functioning of the brain, which is responsible for the production of hormones. The ovaries will also be associated with it, which will also slow down their work. The reproductive cell will take longer to mature, and the endometrium will be delayed in development. This happens among supporters of strict diets, as well as those experiencing stress. In both cases, the formation of red blood cells is difficult. And if so, the amount of hemoglobin will also not correspond to the norm.
Treatment of heavy periods
The gynecologist must not only reduce the symptoms, but also eliminate the cause of the problem. Otherwise, it is impossible to get rid of hypermenstrual syndrome.
Conservative treatment methods are limited to normalizing hormonal levels, the functioning of the endocrine glands, restoring blood circulation and hematopoiesis.
To reduce blood loss, doctors prescribe ascorbic acid, rutin, and anti-inflammatory drugs. For heavy discharge, specialists use calcium gluconate. To restore hemoglobin levels, doctors choose drugs rich in iron.
The patient may be undergoing inpatient or outpatient treatment, but in both cases she is shown complete rest and a balanced diet. Immediately after the end of menstruation, the woman is prescribed physical therapy: electrophoresis, phonophoresis, diathermy, ozokerite.
Surgery
If the doctor has diagnosed injuries or other violations of the integrity of the tissues of the vagina, uterus or cervical canal, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. Endometriosis, neoplasms, and inflammatory processes also do not always respond to conservative therapy.
Surgeons excise the affected tissue and connect it by suturing the edges of the wound. In situations where a woman is over 40 years old, gynecologists often choose to remove the uterus in order to completely eliminate complications. Sometimes specialists perform supravaginal amputation of the uterus - removal of the genital organ while preserving the vagina.
Also, sometimes operations are performed to excise or remove organs of other body systems: for example, to restore hormone levels, part of the overgrown thyroid gland is removed.
Normal hemoglobin level during menstruation
Before menstruation, hemoglobin levels may decrease, but then they increase. Its amount varies depending on age; from the first months of their onset it is high, then returns to normal by the age of 18.
The rate depends on the following factors:
- up to 18 years – 110 – 135 g/l;
- up to 50 years – 110 – 120 g/l.
Women who smoke often have increased harmful hemoglobin in their blood, which does not carry oxygen, but affects test results. If you need to donate blood for testing, you should not smoke for 1-2 days to get the correct result. To balance its norm, smokers need to eat citrus fruits.
On a note!
During critical days, about 50 ml of blood is consumed per day, on average it is 200 ml.
How to determine hemoglobin level
The simplest and most common option is to go to the nearest clinic and get your blood tested. It is very important not to have breakfast on this day: this test must be taken in the morning and always on an empty stomach, 8-12 hours after the last meal. The doctor will take blood from your finger, after which it will be sent to the laboratory for testing. A few days later (sometimes on the day of the tests), you will be presented with a report - a form with the results, which will indicate the following data:
- hemoglobin concentration;
- total number of leukocytes and erythrocytes;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
We need exactly the first indicator, which can be presented in the following units of measurement: g/l, U/l or µmol/l. A woman’s blood should be saturated with this substance within 120-140 grams per liter, but if you were tested during your period, lower concentrations are possible. Moreover, the norm of the same results of a general blood test for people of different ages will be different. Only a doctor can evaluate and decipher the results obtained, so you should not rely only on your own conclusions.
Please note that to identify problems in the body or any diseases, a general blood test is required over time. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to do this at least once a year, however, if any suspicion of certain diseases is detected, the doctor may prescribe and more frequent laboratory visits.
It is noteworthy that you can check the level of hemoglobin in your blood even at home. Similar to visits to the doctor, the patient should be tested on an empty stomach in the morning. To get accurate results, avoid smoking or drinking alcohol the day before, as well as exercising or exercising. Women planning to find out their hemoglobin content at home have several “tools” to choose from:
- Rack with test tubes and glass scale. The blood is sent into a test tube and diluted with hydrochloric acid. After a few minutes, the solution will acquire a new shade, after which you need to add distilled water (no more than 10-40 milliliters) to it. The results obtained are compared on the scale provided in the kit.
- Test strips. Read the instructions for use carefully and use one test strip from the package to find out the result.
Normal hemoglobin during menstruation
It is well known that the norm of hemoglobin outside menstruation can vary from 120 to 140 g/l. The only exceptions are athletes or those who like to lift weights in the fitness room: for them this figure can easily reach 160 g/l, and this is not a sign of pathology. A deviation can also be observed in those who smoke: in this case, the protein concentration increases to 150 g/l.
A natural phenomenon is considered to be similar to other days of the menstrual cycle or reduced hemoglobin during menstruation: the norm is about 110-130 g/l, depending on the age of the woman. In particular, we present to your attention the average hemoglobin indicators by age, which are called normal:
- maturing organism (11-15 years) - 110-130 g/l;
- young girls (15-18 years old) - 115-135 g/l;
- girls aged 18 years and older - 120-140 g/l.
With large blood loss or prolonged menstruation, this indicator can be at the level of 105-115 g/l, which is understandable from a physiological point of view.
Young mothers whose hemoglobin level drops to a minimum level deserve special attention: to 110 g/l during the first and third trimester, and also to 105 g/l during the second. It is believed that pregnancy is proceeding normally if this indicator does not exceed 120 g/l. This is due to the fact that carrying a baby is accompanied by a more active consumption of iron, which goes towards the formation of the placenta and the development of the embryo. Moreover, the volume of blood in a woman’s body during pregnancy increases by at least 50%, due to which the bone marrow performs its functions slowly and cannot provide the blood with hemoglobin in the usual amount.
Causes of heavy menstruation
Gynecologists diagnose natural heavy periods and deviations from the norm. Hypermenstrual syndrome during puberty or the premenopausal period is considered natural, that is, normal. In this case, the reason is hormonal imbalance, but it is a consequence of the restructuring of the body. After a few months, the function of the genitourinary system stabilizes: the cycle normalizes or the performance of the ovaries decreases.
Much more dangerous are hormonal disorders associated with uncontrolled use of drugs (oral contraceptives, anti-inflammatory drugs) or diseases of the endocrine glands: diabetes mellitus, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
Deviations from the norm occur more often due to diseases of the genitourinary system:
- Endometriosis;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Benign, malignant neoplasms;
- Anomalies of organ development;
- Inflammatory processes.
Miscarriages or ectopic pregnancies, as a result of bleeding, are a normal phenomenon, but they are not classified as heavy menstruation: they do not occur on time and do not depend on natural physiological processes.
Hypermenorrhagia develops in the presence of other diseases:
- Blood clotting disorder;
- Hypertension;
- Neuralgia;
- Psychical deviations;
- Cardiovascular pathologies;
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys.
We must not forget about trauma: for example, careless insertion of a tampon or cup can increase the total blood volume during menstruation. Physical activity and stress also often cause an increase in the volume of menstruation.
High hemoglobin during menstruation
This situation is extremely rare, but it does happen. What happens to the female body. First of all, there are no obvious signs of PMS with weakness, dizziness, or sleep disturbances. But there is pain in the heart area. Due to the large amount of oxygen, the load on the organ increases. The heart works at an increased rate, which causes pain. Intestinal upset leading to constipation may occur.
Your period starts at the expected time or a little earlier than usual. But there is less blood discharge because the viscosity of the blood is increased. Repeating the situation several cycles in a row can lead to a reduction in menstruation to 2-3 days, with scanty discharge. In general, menstruation that lasts 3 days is also considered normal. But if she was like this from the beginning of the formation of the menstrual cycle. When the situation suddenly appears, it is better to get examined, donate blood, and get advice from specialists. To prevent this situation, doctors prescribe blood thinners. So that menstruation is complete.
Increased hemoglobin during menstruation
During menstruation, increased concentrations of iron-containing protein are rare. A large amount of iron in the body increases the flow of oxygen and increases the load on the cardiovascular system. This causes chest pain in the heart area. Unpleasant sensations develop due to heart rhythm disturbances and increased contraction frequency. Sometimes excess iron in the body provokes digestive problems.
With a high level of hemoglobin index, menstruation begins earlier than expected. Due to the high viscosity of the blood, the discharge is scanty. After symptoms persist for several months, the condition becomes normal. A high concentration of iron-containing protein is normal in adolescence, when the body has not yet fully formed. But if the hemoglobin factor increases in a woman of reproductive age, a doctor’s consultation is necessary. This condition may be a symptom of heart disease or diabetes.
Blood condition after menstruation
In a healthy female body, hemoglobin is quickly restored after menstruation. The norm is considered to be a decrease to 110 g/l.
In a woman without pathologies, it rises to the previous 120–140 g/l. This takes from 2 days to 2 weeks. It is also considered normal if the amount of iron-containing protein does not change during menstruation.
Since any changes in the composition of the blood can signal serious disorders in the body, tests must be taken and the results evaluated under the supervision of a doctor. Only a qualified specialist will adequately assess the woman’s condition and prescribe the necessary therapy. Tests can subsequently be taken over time to assess how effective the treatment was.
Hemoglobin is found in the blood and is responsible for circulating oxygen throughout the body, as well as removing carbon dioxide. Like many other health indicators, hemoglobin is subject to changes during menstruation. Every woman needs to know what happens to iron-containing protein at the beginning of the next menstrual cycle, how the body reacts to changes, and in what cases you need to worry about the dynamics of this indicator.
Normal hemoglobin during menstruation
To talk about whether the level of oxygen-containing protein has decreased or increased, you need to understand what its level is considered normal.
The average norm for hemoglobin in women is considered to be from 120 to 140 g/l. If a woman smokes, the norm rises to 150 g/l. For physically active people involved in sports, the normal value reaches 160 g/l.
A special case for measuring the concentration of this protein is during pregnancy. In the first trimester, its level, according to the results of the analysis, does not exceed 110 g/l; throughout the entire gestation period, this figure gradually decreases due to an increase in the volume of circulating blood and the consumption of iron reserves in the mother’s body. Therefore, if low hemoglobin is accompanied by a delay in menstruation, it is recommended to take a pregnancy test. In other cases, such a figure may be a sign of anemia.
Video: Everything you need to know about menstruation
Physical activity makes the blood function faster. As a result, the cells receive the required amount of oxygen. If a woman moves little, a signal is sent to the brain that there is a sufficient number of red blood cells; additional synthesis is not required. And when menstruation occurs, decreased hemoglobin appears.
Stress
The central nervous system is responsible for all processes in the body. Violation of its functioning entails a lot of negative consequences. Stress reduces appetite, which makes it impossible to replenish iron deficiency through nutrition. Disturbs the functioning of the digestive tract. The absorption of essential microelements and vitamins deteriorates.
Blood loss
How to correct low hemoglobin
Because the concepts of “low hemoglobin” and “menstruation” are interrelated. There is no way to avoid the situation. But it is possible to prevent the indicator from falling too low. To do this, you need to make it a rule to move more and be in the fresh air. For example, walk to work rather than using public transport or a car. Review your diet. Include the following products in your daily menu:
- liver;
- legumes;
- apples;
- dried fruits;
- beef;
- lamb;
- yolk;
- buckwheat;
- nuts;
- pomegranate juice;
- rosehip decoction.
If low hemoglobin and menstruation are not related, and other alarming symptoms are present, it is necessary to undergo an examination.
Attention, TODAY only!
Low hemoglobin levels during menstruation
Low hemoglobin during menstruation can be quite normal if the value does not deviate from the lower limit. If a woman has low hemoglobin on normal days of her cycle, then during menstruation its level will decrease even more, which is fraught with dangerous consequences. The woman’s health worsens, weakness, dizziness, and nausea occur. Fainting often occurs in this state. Due to the fact that hemoglobin drops during menstruation, the blood becomes too thin, which can cause bleeding that will be difficult to stop on your own.
Usually, with low hemoglobin, the duration of discharge increases, and the level of this important protein does not rise even after menstruation
The reasons for this condition can be very different. Most of them are associated with poor nutrition, but dangerous pathologies can also affect the level of protein in the body.
- Nutrition. Very often problems arise due to poor nutrition, strict diets, and a monotonous diet. To supply the body with a sufficient amount of useful microelements, you should eat foods rich in iron and avoid strong tea, coffee, and chocolate. They prevent the necessary substances from being absorbed normally.
- Vitamins. The most useful are folic acid and B vitamins. A deficiency of these components in the nutritional system leads to a decrease in hemoglobin and blood thinning.
- Red blood cell deficiency. This cause is often found in people with infectious diseases, hepatitis, tuberculosis, and lupus.
- Constant stress. It is often said that all diseases are caused by nerves, and this phrase makes sense. Stress leads to decreased appetite and improper bowel function during menstruation, as a result of which essential microelements do not enter the body.
- Bleeding. The fewer red blood cells in the body, the lower the hemoglobin level.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. This disease leads to impaired absorption of iron, which comes from foods. To avoid consequences, you need to consult a doctor who will identify the problem and prescribe therapy with an optimal diet and a complex of vitamins.
- An active lifestyle has a positive effect on the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Inactivity, on the contrary, leads to iron deficiency. The brain receives a signal that a constant increase in red protein is normal, and during menstruation there is a sharp drop in hemoglobin, which leads to anemia.
Due to iron deficiency in the body, the level of oxygen decreases, which leads to fragility of blood vessels, especially during menstruation. Due to the destroyed endometrial vessels, bleeding increases, and the thinned blood leaves the uterus much more abundantly and takes longer, which leads to very painful long periods.
Situations when the usual rhythm of the menstrual cycle changes arise for many reasons. Sudden hormonal...
If the hemoglobin level cannot be corrected with the help of iron-containing products, the protein drops during menstruation and does not rise after it, you should consult a doctor and get tested to find out how much lower the values are, so that a specialist can prescribe optimal therapy. Iron deficiency can have a detrimental effect on a woman's health.
Why does anemia develop more often in women?
The content of the article
The main factor influencing the prevalence of this disease among women is rather large monthly blood losses during menstruation. Even healthy girls and adult women without any abnormalities in the functioning of the circulatory system lose 50 mg of iron with every 100 ml of blood during menstruation. For this reason, after each menstruation, a physiological decrease in the level of iron in the blood appears for 3–5 days. At the same time, women who experience heavy menstrual bleeding are at risk for anemia.
The need for iron increases significantly during pregnancy, when this mineral is necessary not only for the normal functioning of the circulatory, cardiovascular and pulmonary systems, but also for the healthy development of the ever-growing fetus. It has been established that with each pregnancy, the internal reserves of iron in the body decrease significantly, which increases the risk of developing anemia if other provoking factors occur.
Women are more susceptible to this disease due to their adherence to a low-calorie diet. Monotonous diets and low intake of meat products affect hemoglobin levels and over time can provoke the development of anemia.
Other causes of anemia in women may include:
- chronic or acute blood loss: serious injury, diseases of internal organs, including cancer;
- helminthic infestations;
- stomach ulcer and chronic gastritis;
- gynecological diseases;
- polluted air with low oxygen concentration.
In addition, women often have a nutritional deficiency of iron. It occurs in strict vegetarians who deliberately exclude meat, protein and dairy products from their diet.
➡ Read more about the tests taken for anemia and their interpretation on the page:
Relationship between hemoglobin level and discharge intensity
The menstrual cycle has an average of 21-28 days. Before ovulation, that is, the release of an egg, the level of hemoglobin increases sharply. The blood becomes thick, which helps prevent blood loss. If the protein content is low, they will become abundant.
Short
During menstruation, from an average norm of 120 g/l, it drops to 85 - 90. If hemoglobin is significantly reduced, menstruation is very painful, all signs of anemia are observed:
- weakness;
- decreased blood pressure;
- nausea.
In this case, the cycle does not last 3-4 days, which is the norm, but is extended to 6-7. The ability to work decreases, to the point that it is difficult to get out of bed. With oxygen starvation, hormonal levels are disrupted, and a lack of iron increases the risk of vascular damage, including in the uterus. It will take longer to recover than at normal levels.
High
Cases of increased hemoglobin during menstruation are rare. They occur with increased physical activity due to a large volume of oxygen. Athletes often complain of painful and short periods, menstrual irregularities and constipation.
Blood condition after menstruation
After menstruation, the blood becomes less thick, since the capillaries of the uterus close, which are responsible for removing its residues and mucus. Low hemoglobin levels affect your period after it ends. They become scarce, gradually its quantity returns to normal, this takes about a week.
Why does blood sugar rise?
- Glucose norm
- Regulating sugar levels in the body
- Why is sugar high?
- Short-term increase
- Conclusion
The main source of energy necessary for human life is glucose. It enters the body with foods containing carbohydrates. It is formed as a result of the breakdown of food in the gastrointestinal tract as a result of the action of enzymes, then enters the blood, and from there into the cells. Disturbances in the complex process of transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells can cause high blood sugar.
Glucose norm
Its level is a very important indicator of the body’s functioning, namely carbohydrate metabolism. Normal sugar concentration should be constant and range from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol per liter. As a rule, this is true for blood taken from a finger. In blood obtained from a vein, the glucose concentration is usually slightly higher - from 4 to 5.9 mmol per liter.
For older people whose age has exceeded 60 years, higher values are allowed - up to 6.4 mmol per liter. Children tend to have lower sugar levels. It also increases slightly in healthy pregnant women, which is associated with glucose consumption by the fetus.
Regulating sugar levels in the body
Upward or downward changes can be dangerous. Hormones produced by various glands are responsible for maintaining normal levels. The main one is insulin, the synthesis of which occurs in the pancreas. As soon as the concentration of glucose in the blood increases, the production of insulin increases, which helps it penetrate the cells, resulting in a decrease in sugar levels. In this way its concentration in the blood is regulated.
Why is sugar high?
If your blood glucose level has increased, you need to find out why this happened. This condition is called hyperglycemia and is not a disease in itself. There are many reasons for high sugar levels. Among them are both natural and pathological.
Physiological increase
As a rule, it is impossible to judge the presence of any pathology based on a single blood test. Therefore, if an increase in sugar is detected, a repeat test is prescribed. Glucose concentration increases in healthy people in the following cases:
- for several hours after eating;
- under stress, severe anxiety, anxiety, overwork;
- after high physical activity;
- after smoking;
- before menstruation.
Increased glucose in pathologies
The most common cause of high sugar is such a common disease as diabetes. The mechanisms of increase differ depending on the type of diabetes.
In type I, the high concentration of sugar is due to the fact that the pancreas does not produce insulin, which is responsible for transporting glucose into cells. The disease has an autoimmune mechanism of development: cells involved in the synthesis of insulin are destroyed by cells by the immune system.
In type II diabetes, a sufficient amount of the necessary hormone is produced, but it does not interact with cells. Since the cells either do not perceive the hormone sufficiently or do not perceive it at all, glucose cannot enter them and accumulates in the blood, while the cells themselves experience starvation.
In addition to diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia can be observed in the following diseases:
- endocrine diseases: pheochromocytoma, Cushing's syndrome, thyrotoxicosis;
- pathologies of the pancreas: pancreatitis (acute or chronic), gland tumors;
- liver diseases: hepatitis, cirrhosis, malignant tumor;
- infections (in this case, the glucose level may change under the influence of the pathogen, as well as due to stress on the body, which causes the disease itself);
- taking medications: diuretics, glucocorticoids, hormonal, contraceptive, psychotropic and others;
- diabetes in pregnant women: this condition is classified as a separate category and is associated with insulin deficiency and elevated sugar during pregnancy; after childbirth, glucose levels return to normal.
The effect of hemoglobin on the female body
The name consists of two parts: hemo - which means iron, globin - protein. The main task is to supply cells with oxygen, ensuring the full functioning of all internal organs and systems. Iron deficiency affects the entire body as a whole, including the reproductive system.
During menstruation, a woman loses a certain amount of blood, and along with the secretions, iron. As a result, the indicator decreases during menstruation and several days after its completion. However, nature has provided for everything. A few days before the start of menstruation, hemoglobin levels increase. The blood becomes more viscous. This is necessary to prevent bleeding. But already with the onset of menstruation, hemoglobin drops. Liquid blood is easier to remove from the body. Full menstruation occurs.
A deviation of the indicator upward or downward leads to the failure of vital systems, since their activity depends on the full supply of oxygen. The menstrual cycle is disrupted.
Why should you go to the gynecologist if you have anemia?
When diagnosing anemia in women, it is mandatory to visit a gynecologist and undergo appropriate diagnostic procedures: examination using gynecological mirrors, colposcopy, ultrasound of the uterus and, if necessary, tests. First of all, anemia can develop in a woman due to heavy menstruation, when a large amount of blood is lost during menstruation, and the menstruation itself lasts longer than usual. In this case, properly selected hormonal therapy aimed at regulating hormonal levels in the body can help. A test for sex hormones can help identify dishormonal disorders.
When identifying anemia in a woman, it is important to find the cause that provoked this disease. It is its elimination that will allow you to quickly get rid of the pathology. In women, the following diseases often lead to recurrent uterine bleeding, which can affect the amount of iron in the blood:
- endometriosis – proliferation of cells of the inner layer of the uterine mucosa, their localization in atypical tissues or organs;
- fibroids and polyps - benign neoplasms in the uterine cavity;
- malignant changes in the uterus and other female genital organs.
Timely detection of these diseases is a factor in their successful treatment and, as a result, relief from anemia, subject to an integrated approach to therapy.