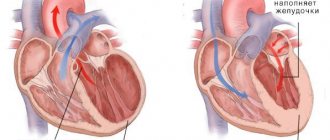
A healthy person does not feel the work of his heart in any way. And if heart rhythm disturbances occur, he may feel palpitations, interruptions or “loss of pulse.” The normal heart rate of an adult is from 60 to 90 beats per minute.
Tachycardia is an increase in heart rate to values exceeding 90 beats per minute. Often in such situations, patients complain of increased beating, “fluttering” or “jumping out” of the heart, they say that “the heart is pounding.” Of course, such a condition is a deviation from the norm.
Causes of simultaneous tachycardia and shortness of breath
The causes of rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath are different: from hyperthermia to oncological processes.
Usually these symptoms are compensatory in nature and appear to quickly saturate the body with oxygen. Tachycardia and rapid breathing are also observed in healthy people (in newborns, a heart rate of 110-120 beats per minute and the number of respiratory movements of 40-60 per minute are considered normal, and physical activity - pregnancy, stress - is also classified as a reflex rapid heartbeat).
Cardiovascular problems
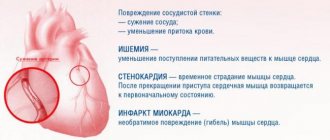
The function of the cardiovascular system is to provide all organs and tissues of the body with oxygen. If for some reason the normal blood flow is disrupted, a state of hypoxia appears and compensatory mechanisms are activated to restore adequate oxygenation. Causes:
- Cardiac ischemia . With IHD, atherosclerotic plaques form on the walls of blood vessels, which impair blood flow to the heart, brain and other organs.
- Arrhythmia is a disturbance in the rhythm and frequency of the heartbeat that impairs blood circulation.
- Hypertonic disease . High blood pressure does not immediately manifest itself as tachycardia and shortness of breath. With a long course and lack of treatment, the load on the heart increases and atherosclerosis develops, and this is the basis for the appearance of such symptoms.
- Congenital and acquired heart defects , in which the structure of the valves, walls, and septa is disrupted and, as a result, the normal flow of blood becomes difficult.
- Heart failure is usually a complication of the above diseases and is characterized by weakness and ineffectiveness of the heart.
Pathologies of other organ systems
In addition to diseases of the cardiovascular system, tachycardia and difficulty breathing also appear due to other diseases:
- Diseases of the respiratory system most often occur with the manifestation of dyspnea (breathing disorder). The reason is obstructed passage of air through the airways (broncho- or laryngospasm, bronchial foreign body, asthma, obstructive bronchitis) or gas exchange disorders caused by dysfunction of the lung tissue (pneumonia, lung cancer, pneumosclerosis).
- Anemia - develops due to a lack of hemoglobin in the blood, the cause is a deficiency of iron, vitamin B 12, bleeding, oncology, hereditary diseases.
- Endocrinological diseases : diabetes mellitus, pheochromocytoma, thyroid dysfunction.
- Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system (VSD).
- Infectious diseases with increased body temperature.
- Allergic reactions (Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock).
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, drugs). With a sharp refusal of these substances, withdrawal syndrome develops.
Anemia
A disease that develops due to insufficient hemoglobin in the body. It is provoked by problems with the intestines, various infectious diseases, deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
Classification of anemia
Thus, vitamin deficiency anemia can cause shortness of breath and a number of other unfavorable symptoms, including:
- increased heart rate;
- impaired coordination and reflexes;
- general weakness;
- temperature increase.
Anemia - symptoms
Problems such as an increase in liver size and various types of mental disorders may occur.
What diagnostics do you need to undergo?
If the patient notices the appearance of tachycardia and shortness of breath at rest or accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
The first thing the doctor will do is take a thorough history. It is important to find out under what circumstances the patient notices symptoms (physical activity, stress, rest), whether there is heart pain, cough, general weakness, whether the person is taking any medications. Next, the doctor examines the patient in detail, including a visual examination of the mucous membranes and skin, measures pulse, blood pressure, palpation and auscultation.
Laboratory tests include a general blood and urine test, blood biochemistry; from instrumental - ECG, X-ray of the lungs. If necessary, an additional ultrasound of internal organs is performed and a consultation with specialists is prescribed. A carefully collected anamnesis and a properly selected examination are the main conditions for making a diagnosis.
Diagnostics
A general urine test will help identify renal pathology. To make a correct diagnosis, a complete history and examination of the cause of shortness of breath are fundamentally important. This will help to establish the factor that provokes this condition without resorting to additional research and analysis. Depending on the initial cause, examinations are carried out:
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- general urine and blood tests to identify pathologies in the kidneys and determine hemoglobin levels.
Return to contents
Treatment and assistance to the patient
A person who complains that his heart is beating quickly and is having difficulty breathing is often prone to panic and fear of death. The causes of these symptoms are dangerous, so the patient needs immediate help and proper treatment.
Pre-medical support: improvised methods
If shortness of breath or tachycardia begins suddenly and gets worse, immediately go to the hospital or call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, they do everything to alleviate the condition with a rapid heartbeat and lack of oxygen - they give you a semi-sitting position with support on your hands, provide access to fresh air. Further methods and techniques of assistance depend on the cause of the attack.
When a person begins to choke due to a foreign body entering the throat, it is removed as quickly as possible: the Heimlich maneuver is used; in case of an allergic reaction, remove the irritating factor and take antihistamines.
If the heartbeat increases sharply, it is recommended to perform vagal tests, which reduce the activity of the sympathetic nervous system and have a therapeutic effect:
- massage of the carotid sinus (the branching point of the carotid artery) for three to five minutes;
- sudden straining after a deep breath (Valsalva maneuver);
- holding your breath.
Taking medications
If the cause of an attack is unknown, do not take the medicine without a doctor’s prescription. To select adequate and effective therapy, additional examinations are performed.
What does the treatment regimen depend on?
Frequent pulse and shortness of breath are usually not an independent disease, but a sign of other diseases. Therefore, the underlying pathology is treated, not the symptom.
For heart failure, a large number of drugs are prescribed that normalize blood pressure (ACE inhibitors, sartans, beta blockers), antiarrhythmics and diuretics, which remove excess fluid from the body and reduce swelling. With proper treatment, normal pulse and breathing levels are quickly achieved.
If increased breathing and heart rate are caused by diseases of the bronchopulmonary system (an asthma attack), short-acting bronchodilators are used in the form of an aerosol. On inhalation, the drug enters the bronchi and eliminates the spasm. When necessary, the treatment regimen includes inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators.
For pneumonia, the emphasis is on antibiotics and detoxification measures. When a patient has trouble breathing and severe manifestations of respiratory failure, he is prescribed treatment in the intensive care unit.
For anemia, iron supplements and vitamins are used, and in severe cases, blood transfusions are used. If the cause of shortness of breath is a tumor that mechanically prevents the patient from inhaling, surgical treatment and chemotherapy are used.
Duration of therapy
The duration of treatment depends on the diagnosis and the severity of the concomitant pathology, the age of the patient (an elderly patient with non-hospital pneumonia and heart failure caused by coronary heart disease receives inpatient treatment for an average of two to three weeks. After discharge, the patient continues maintenance therapy for a certain time) .
For pulmonary tuberculosis, a person is treated with antibiotics for a long time (from six months). Since anti-tuberculosis drugs are very toxic, they cause allergies, joint pain, and weakness. To protect the liver, hepatoprotectors and other medications are added to therapy.
If a young patient complains of elevated body temperature, sore throat, runny nose and notes a rapid pulse, slight weakness and shortness of breath, then most likely the cause of the malaise is a cold. In this case, treatment is performed on an outpatient basis. When there are no complications, recovery occurs within a week.
Cardiac causes of sinus tachycardia
The main way to regulate heart rate is an electrical impulse sent by the sinus node located in the heart.
This impulse spreads to all the muscle fibers of the heart and causes them to simultaneously contract: thus, the main function of the organ is realized - to push portions of blood through the great vessels. Disturbances in the functioning of the sinus node are caused by the influence of various substances (hormones, chemical compounds). With sinus tachycardia, the number of heartbeats usually ranges from 90 to 120 beats per minute, in some cases it reaches 150 to 160. Sinus tachycardia sometimes appears during eating, during physical activity or emotional stress. It occurs in various diseases and is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of them.
Thus, rapid heartbeat is a common occurrence with myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) of various origins. In this case, along with rapid heart contractions, the following appear:
- sensations of heart failure,
- arrhythmia of heart contractions,
- dyspnea,
- chest pain,
- weakness and fatigue,
- joint pain (not always),
- slight increase in body temperature.
Also, sinus tachycardia often occurs with heart failure, which may be a consequence of coronary disease or heart defects. In such cases, rapid heartbeat is also combined with shortness of breath, weakness and increased fatigue, which is often accompanied by swelling of the lower extremities. If such symptoms appear, you should contact a cardiologist as soon as possible. Once the underlying disease is eliminated, the tachycardia will also disappear.
In addition, rapid heartbeat is one of the symptoms of anemia. With anemia, due to a lack of hemoglobin, the delivery of oxygen to the tissues is reduced. As a compensatory response, the sinus node begins to generate more electrical impulses, the heart beats faster, and blood begins to circulate faster to bring the missing oxygen to the tissues. Tachycardia with anemia is accompanied by a number of additional symptoms:
- shortness of breath,
- weakness and dizziness,
- "flies" before the eyes,
- pallor (sometimes cyanosis) of the skin,
- chilliness,
- hair loss and brittle nails,
- tingling on the tip of the tongue,
- numbness of the limbs.
If you have tachycardia and most additional symptoms, you should first consult a physician. After donating blood to determine the level of hemoglobin and serum iron, the doctor will accurately determine whether there is anemia. If anemia occurs, consultation with other specialists may be required to determine the true cause of the disease.
Arterial hypotension is a condition in which sinus tachycardia occurs. It is often preceded by severe emotional stress, disturbances in sleep and wakefulness, and malnutrition. In addition to increased heart rate, hypotension is characterized by drowsiness, irritability, apathy, memory loss, headache, nausea and dizziness. In this case, you should pay attention to your lifestyle: normalize your diet, daily routine and physical activity.
An increase in heart rate is associated with intoxication. Abuse of drinks containing caffeine (coffee, tea, energy drinks), as well as certain medications, leads to sinus tachycardia.
Tips for preventing heart palpitations and shortness of breath
A patient with complaints of rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath should carefully monitor his health and follow the doctor’s advice. In order to prevent the occurrence of new episodes, avoid factors that increase heart rate and breathing, follow these recommendations :
- quit smoking;
- regularly take maintenance medications for ischemic heart disease, hypertension, bronchial asthma;
- avoid strong physical exertion and emotional stress;
- adhere to the principles of rational nutrition;
- control body weight.
After treatment, physical activity is gradually increased. If training in the gym is an integral part of your life, then increase the load little by little, monitoring your well-being.
Elderly people with a large number of chronic pathologies should be responsible for following medical prescriptions (taking medications in the morning, monitoring sugar levels and blood pressure) to increase the length and quality of life.