When we breathe easily, we don’t even notice this process. This is normal, since breathing is a reflex act that is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Nature intended it this way for a reason. Thanks to this, we can breathe even in an unconscious state. This ability in some cases saves our lives. But if even the slightest difficulty appears with breathing, we feel it immediately. Why does constant yawning and shortness of breath occur, and what to do about it? This is what the doctors told us.
Dangerous symptoms
Sometimes difficulty breathing occurs for physiological reasons, which are quite easily remedied.
But if you constantly feel like yawning and taking deep breaths, this could be a symptom of a serious illness. It’s even worse when, against this background, shortness of breath (dyspnea) often occurs, appearing even with minimal physical exertion. This is already a reason to worry and see a doctor. You should go to the hospital immediately if difficulty breathing is accompanied by:
- pain in the chest area;
- changes in skin color;
- nausea and dizziness;
- severe coughing attacks;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling and cramps of the limbs;
- feeling of fear and internal tension.
These symptoms usually clearly signal pathologies in the body, which need to be identified and eliminated as soon as possible.
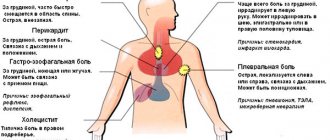
Tetanus
Tetanus is an acute infectious disease caused by the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium tetani. The occurrence of tetanus is caused by the action of an exotoxin (tetanospasmin), which is produced during the lysis of bacteria. The toxin enters peripheral nerve endings, binds there irreversibly, then moves in the opposite direction along axons and synapses and ultimately enters the central nervous system. As a result, the secretion of inhibitory transmitters from nerve endings is blocked, thereby leading to unopposed muscle stimulation by acetylcholine and spasticity, usually superimposed by periodic tonic spasms. Disinhibition of autonomic neurons and loss of control over the processes of catecholamine release by the adrenal glands leads to instability of the autonomic nervous system and a hypersympathetic state. Once bound, the toxin cannot be neutralized.
Most often, tetanus is generalized, affecting skeletal muscles throughout the body. However, sometimes tetanus is limited to the muscles at the entrance to the wound.
The time for symptoms to appear is from 2 to 50 days (on average 5-10 days).
There is a vaccine called diphtheria-tetanus or DT. It is vaccinated in a child in childhood to protect against the disease. But although it is rare, tetanus is found in statistics of diseases to this day.
Causes of lack of air
All the reasons why a person may go to the doctor with the complaint: “I can’t breathe fully and I’m constantly yawning” can be roughly divided into psychological, physiological and pathological. Conditionally - because everything in our body is closely interconnected, and the failure of one system entails disruption of the normal functioning of other organs.
Thus, prolonged stress, which is attributed to psychological reasons, can provoke hormonal imbalance and cardiovascular problems.
Physiological
The most harmless are physiological reasons that can cause difficulty breathing:
- Lack of oxygen. It is strongly felt in the mountains, where the air is thin. So if you've recently changed your geographic location and are now significantly above sea level, it's normal to find it difficult to breathe at first. Well, ventilate the apartment more often.
- Stuffy room. Two factors play a role here - a lack of oxygen and an excess of carbon dioxide, especially if there are many people in the room.
- Tight clothes. Many people don’t even think about it, but in pursuit of beauty, sacrificing convenience, they deprive themselves of a significant portion of oxygen. Clothes that strongly compress the chest and diaphragm are especially dangerous: corsets, tight bras, tight bodysuits.
- Poor physical shape. Lack of air and shortness of breath at the slightest exertion are experienced by those who lead a sedentary lifestyle or have spent a lot of time in bed due to illness.
- Overweight. It causes a whole bunch of problems, in which yawning and shortness of breath are not the most serious. But be careful - if you significantly exceed normal weight, heart pathologies quickly develop.
It is difficult to breathe in the heat, especially if you are severely dehydrated. The blood becomes thicker, and it is harder for the heart to push it through the vessels. As a result, the body does not receive enough oxygen. The person begins to yawn and try to breathe deeper.
Medical
Shortness of breath, yawning and a regularly felt lack of air can cause serious illnesses. Moreover, often these signs are the first symptoms that allow diagnosing the disease at an early stage.
Therefore, if you constantly have difficulty breathing, be sure to go to the doctor. The most common possible diagnoses are:
- VSD – vegetative-vascular dystonia. This disease is the scourge of our time, and it is usually triggered by severe or chronic nervous overstrain. A person feels constant anxiety, fears, panic attacks develop, and fear of enclosed spaces arises. Difficulty breathing and yawning are warning signs of such attacks.
- Anemia. Acute iron deficiency in the body. It is necessary to carry oxygen. When there is not enough of it, even with normal breathing it seems that there is not enough air. The person begins to constantly yawn and take deep breaths.
- Bronchopulmonary diseases: bronchial asthma, pleurisy, pneumonia, acute and chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis. All of them, in one way or another, lead to the fact that it becomes almost impossible to take a full breath.
- Respiratory diseases, acute and chronic. Due to swelling and drying of the mucous membranes of the nose and larynx, it becomes difficult to breathe. Often the nose and throat are clogged with mucus. When yawning, the larynx opens as much as possible, so when we have the flu and ARVI, we not only cough, but also yawn.
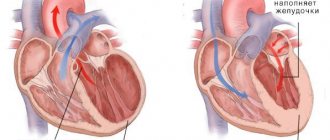
- Heart diseases: ischemia, acute heart failure, cardiac asthma. They are difficult to diagnose early. Often shortness of breath, coupled with difficulty breathing and chest pain, is a sign of a heart attack. If this condition occurs suddenly, it is better to immediately call an ambulance.
- Pulmonary thromboembolism. People suffering from thrombophlebitis are at serious risk. A detached blood clot can block the pulmonary artery and cause part of the lung to die. But at first it becomes difficult to breathe, there is constant yawning and a feeling of acute lack of air.
As you can see, most diseases are not just serious - they pose a threat to the patient’s life. Therefore, if you often feel short of breath, then it is better not to delay your visit to the doctor.
Psychogenic
And again, we cannot help but recall stress, which is one of the main causes of the development of many diseases today.
Yawning under stress is an unconditioned reflex inherent in us by nature. If you observe animals, you will notice that when they are nervous, they yawn constantly. And in this sense, we are no different from them.
When stressed, a spasm of the capillaries occurs, and the heart begins to beat faster due to the release of adrenaline. Because of this, blood pressure increases. In this case, taking a deep breath and yawning perform a compensatory function and protect the brain from destruction.
When you are very frightened, there is often a muscle spasm, which makes it impossible to take a full breath. It’s not for nothing that the expression “takes your breath away” exists.
Origin of yawning
Many people mistakenly think that the cause of yawning is a lack of oxygen in the body; this is not entirely true. Physiologically, when yawning, the neck muscles relax, thereby compressed vessels can transport more blood to the brain and, naturally, oxygen.
Also, at the moment of deep inhalation, the air cools nearby brain tissue. When we breathe through our nose, our brain cools down, but when we just wake up, we start yawning to cool our brain after sleep. We see the same thing when we are tired or want to sleep, our brain heats up and requires cooling. In this article we will look at the main causes of excessive yawning in adults and analyze their features in detail.
What to do
If you find yourself in a situation where frequent yawning and shortness of breath occur, do not try to panic - this will only worsen the problem. The first thing you need to do is to provide an additional flow of oxygen: open a window or vent, if possible, go outside.
Try to loosen as much as possible the clothing that prevents you from fully inhaling: take off your tie, unbutton your collar, corset or bra. To avoid dizziness, it is better to take a sitting or lying position. Now you need to take a very deep breath through your nose and an extended exhalation through your mouth.
After several such breaths, the condition usually improves noticeably. If this does not happen, and the dangerous symptoms listed above are added to the lack of air, call an ambulance immediately.
Before medical professionals arrive, do not take medications on your own if they are not prescribed by your doctor - they can distort the clinical picture and make it difficult to make a diagnosis.
Treatment options
Treatment of respiratory neurosis requires complex therapy with medications and psychotherapeutic methods in combination with breathing exercises:
- Working with a psychotherapist . The main task is to teach the patient to quickly take control of his own emotions, without allowing them to dominate the intellectual assessment of the situation and become a stressful event. The best results for solving this problem are demonstrated by cognitive behavioral therapy.
2. Taking antidepressants . Helps reduce the intensity of negative experiences, depression, anxiety and more. Only the attending physician can prescribe a specific type of antidepressant. 3. Electrolyte balance . It is ensured by taking magnesium and calcium supplements. 4. Hardware therapy . Using special equipment, patients are taught how to control physiological processes such as breathing rate and muscle relaxation. 5. Breathing exercises . Developing correct breathing skills by regularly performing special breathing exercises.
Supportive techniques include physiotherapy, relaxing baths, autogenic training and general health spa treatment.
First aid for acute respiratory neurosis
Separately, 4 rules of first aid for the development of acute hyperventilation syndrome should be described:
- Allow the patient to breathe in a paper or plastic bag. By inhaling his own CO₂, the patient increases the level of carbon dioxide in the blood, which allows the blood pH level to remain normal.
- Reassure the patient to the extent that the situation allows.
- Provide a visual flow of fresh air - for example, open the windows wide (this is very calming for many).
- If the patient has previously undergone a course of psychotherapy and breathing exercises as part of the complex treatment of DN, remind him what to do, since in a moment of panic, some patients forget to use the skills they have learned.
Diagnostics
Emergency doctors usually quickly determine the cause of sudden difficulty breathing and the need for hospitalization. If there are no serious concerns, and the attack is caused by physiological reasons or severe stress and does not recur, then you can sleep peacefully.
But if you suspect heart or lung disease, it is better to undergo an examination, which may include:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- bronchoscopy;
- computed tomogram.
What types of research are needed in your case will be determined by your doctor during your initial examination.
If lack of air and constant yawning are caused by stress, then you may need to consult a psychologist or neurologist, who will tell you how to relieve nervous tension or prescribe medications: sedatives or antidepressants.
Autonomic disorders
We will talk about such a vegetative disorder as HVS (Hyperventilation syndrome). It occurs against the background of neurological and psychological disorders of the central nervous system. Rarely due to other metabolic disorders. It has quite a few symptoms, one of which is frequent yawning and lack of air.
Often, hot water provokes emotional tension and severe stress, which is why it is also called respiratory neurosis. When a stressful situation arises, say at work, in order to realize it, the body needs oxygen. At this moment we breathe quickly and shallowly. Signals begin to arrive in the brain that there is a lot of oxygen and not enough carbon dioxide. Then the brain sends another signal, it begins to suppress breathing. Therefore, neurotics have the feeling that they cannot breathe deeply, that they are suffocating, even to the point of a panic attack.
Only pulling yourself together can help him.
He begins to breathe even faster because he thinks he is suffocating. Signals enter the brain with even greater force, and the brain presses the breath with even greater force.
A kind of vicious circle of hyperventilation arises, from which it is very difficult for a neurotic to escape. After yawning, he wants to yawn some more. This can go on for quite a long time. A person tries to inhale through yawning. Because he can no longer breathe deeply.
A good mood is the enemy of yawning
From all of the above, we can conclude that this reflex can be a cause for concern if it occurs frequently and is accompanied by breathing problems. From autonomic disorders to cancer, various manifestations of yawning are possible. It is important to note that monitoring your psychological state helps eliminate many causes of this reflex. Therefore, you should not immediately think about serious illnesses. The best way out is healthy sleep and a good mood. Then hormones return to normal, our organs do not require cooling, we feel vigorous and healthy people.
CNS lesions
Brain lesions come in various etiologies. They can lead to breathing problems and frequent yawning. Moreover, a person may not even suspect that he has serious disorders in his body.
A stroke is a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, which is accompanied by damage or death of part of the brain. Because due to blockage or rupture of the vessel, oxygen no longer reaches a certain area and a heart attack occurs. The affected area can no longer function normally, which results in many symptoms. The occurrence of pneumonia during a severe stroke is common and entails additional stress on the respiratory system. Yawning as a symptom of stroke can be caused by many factors, including damage to the central nervous system and various breathing disorders.
One of the symptoms of multiple sclerosis in adults may be frequent yawning. As with a stroke, damage to the brain stem leads to breathing problems. The brainstem is located at the base of the skull, connecting the spinal cord and the cerebral cortex. Providing the function of interaction of the nervous system, being responsible for many reflexes, including breathing. When damage to this department occurs, its functions are naturally disrupted. This is where frequent yawning occurs as a result of damage to the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis.
Oncological diseases can also have a huge range of symptoms. Depending on the affected areas and the disruption of their functions, frequent yawning and breathing problems may appear.
Hormone imbalance
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter responsible for conducting nerve impulses. It is also called the “happiness hormone”, because it plays a big role in shaping our mood. It plays an indispensable role in the functioning of the central nervous system.
Cortisone is a biologically active glucocorticoid hormone of a steroid nature, that is, it has a sterane core in its structure. Cortisol is secreted by the outer layer (cortex) of the adrenal glands under the influence of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH - a pituitary hormone). It takes part in many processes in our body and is called the “stress hormone”.
It turns out that excessive yawning indicates depression due to an imbalance of serotonin and cortisol.
When the correct balance of these hormones is disturbed, depression occurs and in this state a person may yawn. Subsequently, pathological fatigue occurs, and this reflex occurs more often.
In addition, it indicates obesity, which can be caused by hormonal imbalance. Since overweight individuals are in a sleepy state in most cases, they yawn accordingly more often. Scientists noted that in the case of anxiety disorder, the symptom manifests itself in a similar way.
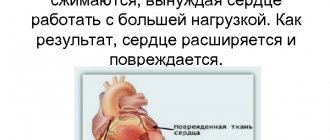
Cardiovascular diseases
Doctors believe that if the number of yawns exceeds 25 per day, you need to pay attention to this. If this phenomenon continues for more than 3 days, then this is a reason to do an ECG. You may have some kind of heart disease. This fact is confirmed by research by American doctors. This is also confirmed by domestic doctors. Prolonged frequent yawning can cause serious heart disease.
As is known, diseases of the cardiovascular system can lead to impaired blood pressure. If the pressure is low, then blood flows poorly to the brain and it suffers from oxygen starvation. With high blood pressure, this respiratory reflex is also noted. Heart disease can cause stimulation of the vagus nerve, which connects the central nervous system to the heart and other organs. Then yawning may occur.
List of sources
- Apchhi... Cheers! Sneezing, hiccups, yawning / Author-comp. L. Cheremukhina; M.: "Eksmo" 2010. - 128 p.
- S.V. Shushkov, Voluntary yawning as a hypoxic procedure / Bulletin of physiology and pathology of breathing, Issue 77, 2021. - p. 69-76.
- Yankovsky A.E., Andermann F., Dubos F. Postictal forced yawning in a patient with non-dominant hemisphere epilepsy. Epileptic disorder. 2006; 8:65–9.
- Corey T.P., Shoup-Knox M.L., Gordis E.B., Gallup G.G., Jr. Changes in physiology before, during and after yawning. Front Evol Neurosci. 2011; 3:7. [
- Guggisberg A.G., Mathis J., Schnyder A., Hess K.W. Why do we yawn? Neurosci Biobehav Rev.2010; 34: Nudelman R. Our unknown body. Why do we yawn? – M.: Lomonosov, 2014. – P. 20‒30. 1267–1276.
Liver and kidney dysfunction
For many, liver and kidney dysfunction is associated more with digestive or urinary problems. Yes, this is true, but there are situations when diseases of these organs can cause difficulty breathing in a person and frequent yawning. To understand how this happens, it is important to understand the meaning and functions of these organs.
The liver is a vital filter that passes through a huge amount of blood. Its structure and blood supply characteristics help to perform the important biological function of detoxification. In general, the liver has the following functions:
- removal of poisons, toxins, antibiotics from the body, turning them into less harmless compounds;
- removal of excess hormones;
- provides energy functions of the body;
- synthesizes some hormones;
- synthesis of various enzymes.
When the liver becomes ill, it can no longer perform some of its functions as needed. These include cirrhosis, cancer, hepatitis and other diseases. Toxins formed in the body are no longer neutralized. Then other organs begin to suffer, especially the central nervous system. Intoxication of the body can manifest itself in many symptoms and cause a person to have difficulty breathing and yawn a lot.
A similar situation is observed when the kidneys and their excretory function are impaired. Harmful substances accumulate, the blood transfers them to other organs, slowing down the metabolic processes of the latter. Therefore, disruption of the body’s filters (liver, kidneys) becomes an indirect cause of respiratory dysfunction.