Against the background of coronavirus infection, blood oxygen saturation may drop sharply, and serious health problems will begin. In case of lack of oxygen, doctors often talk about hypoxemia. What is it?
Hypoxemia is a word derived from the ancient Greek “hypo” (a prefix denoting weakness) and the New Latin oxygenium - oxygen. In fact, this term, experts note, hides a decrease in the oxygen content in human blood. The causes of this condition can be various options - from circulatory disorders to a decrease in hemoglobin. With hypoxemia, pressure often decreases, and saturation also drops below normal values.
Blood saturation - what is saturation?
In order to understand how to increase oxygen in the blood at home, you will have to understand several terms. So, blood saturation 0₂ (saturation, Sp0₂) is an indicator that determines the amount of oxygen circulating in the bloodstream. This value is relative and is expressed as a percentage. Normal saturation for an adult is 95-100%. This means that the body receives enough oxygen to function. The easiest way to measure oxygen levels in the blood is to use a pulse oximeter: this is a small device that attaches to your index finger and determines saturation within 1-2 minutes.
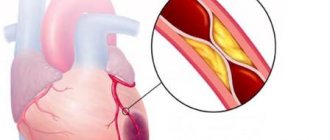
A drop in blood oxygen saturation is most often caused by respiratory diseases, such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchial asthma, etc. If saturation drops to 90-95%, the patient may be faced with the question of how to increase oxygen in the blood at home, but when the value drops below 90%, you need to go to the hospital. A decrease in Sp0₂ may be accompanied by shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness, cardiovascular problems, cognitive decline, fainting and more serious problems.
What is the normal saturation level for a healthy person?
The norm for a healthy person is considered to be SpO2 = 95-99 (or 100)%. The rate of blood oxygen saturation depends on the individual characteristics of the human body, for example, on the presence or absence of anemia, apnea, chronic diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, bad habits, and age. At night, each person's saturation decreases, and the differences can be significant. For example, in people with chronic diseases of the respiratory system (COPD, apnea), who have adapted to a constant lack of oxygen, the rate can drop to 90% (in the deep sleep phase).*
According to the observations of doctors working in hospitals with seriously ill patients who are on oxygen, the most dangerous time is from 3 to 7 am. At this time, the largest number of deaths are recorded due to decreased saturation, or more precisely due to oxygen hypoxemia.
Almost all residents of megacities suffer from hypoxia to one degree or another. The fact is that in modern cities, oxygen from the air is increasingly replaced by carbon dioxide, nitrogen and sulfur dioxides and other substances. So, if in rural areas the oxygen content in the atmosphere is 21%, then in megacities it is 17-18%.
Other factors that lead to hypoxia are diseases of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system, anemia, carbon monoxide poisoning, pregnancy, intense physical activity, and being in a stuffy, unventilated room.
What are we talking about?
The brain coordinates and regulates the functioning of the entire body. It provides a balance of processes, protection from negative influences, and adaptive mechanisms. The brain perceives and processes information, provides a person with thinking and other higher functions.
Nerve cells need a lot of oxygen and nutrients to work. Cerebral circulation is different from blood flow in other tissues of the body. It's much more complicated:
- numerous bends of the brain vessels - to smooth out the pulsation of blood flow and maintain pressure stability;
- the richest network of capillaries - so that all tissue areas and cells without exception receive nutrition;
- developed collateral circulation - brain vessels are connected to each other by collaterals - “bridges”, which help restore blood flow when the main vessel is blocked.
The brain has an autonomous regulation system: with a general increase in blood pressure, it remains stable in the brain for the longest time. But excess or insufficient blood circulation sooner or later leads to negative consequences: fluid accumulation and the development of tissue edema, lack of oxygen, stroke and other complications.
Symptoms of decreased saturation
The list of symptoms of decreased saturation usually includes:
- Try holding your breath for a few seconds - if you can't help but breathe as long as before, and this action is causing difficulty, it makes sense to measure your saturation.
- Your breathing and heart rate have increased.
- The skin turned pale and acquired a bluish tint (face, lips, fingertips).
- You feel very tired and sleepy.
- My head hurts and feels dizzy, I have problems with memory and concentration.
- You are experiencing some symptoms of a respiratory system disease: shortness of breath, discomfort and unusual sensations in the chest, coughing.
What are the dangers of lack of oxygen?
- sleep disturbance or drowsiness;
- headaches and migraines;
- weakness and muscle pain;
- depressive states;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- decreased immunity and susceptibility to colds;
- decreased concentration and reaction speed;
- skin problems and premature aging;
- disruption of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
We live while we breathe! In an oxygen-free environment, the brain cannot withstand even 5 minutes. Therefore, it is important that oxygen constantly and in the required quantities enters our body. For the smooth functioning of the body and proper breathing, the surrounding air must contain 20–21% oxygen. But in cities the situation is aggravated due to emissions from industries, fumes from asphalt roads, etc. A decrease in this concentration leads to the development of ailments or exacerbation of chronic diseases.
What to do if saturation has decreased?
Don't panic about low saturation - normal vital signs can be quickly restored, and even a reading of 70% within a few days is compatible with life, and the chances may be even higher if the patient has, for example, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and to a low level oxygen, his body has already adapted. Saturation may drop for several days.
However, if during coronavirus the saturation drops to 95%, 93, 90...%, and all measurements are made correctly (it is important to check that the pulse oximeter has an adequate battery level, and that the device itself is registered as a medical device and not purchased from dubious manufacturer) - you need to call an ambulance.
How many breaths should you take?
Usually, to return to normal well-being and to relieve symptoms of oxygen deficiency, 2 to 5 deep breaths within 10 minutes are enough.
Just 5 breaths and here you have clarity of thinking and a clear head!
To prevent diseases and strengthen the immune system - 2 sessions of 5-10 breaths daily.
In a stressful situation, as well as to improve performance, 2–3 sessions with an interval of 10 minutes, consisting of 8–10 breaths, are recommended.
How to increase blood oxygen levels in an adult?
There are several ways to train your body to receive more oxygen, thereby increasing the level of oxygen in your blood. Cardio exercise is one of them, but simply focusing on your workout is not enough when you want to increase your oxygen levels. By practicing cardio exercises, you train your cardiovascular and respiratory systems, but this does not mean that your breathing is optimal. We will list 5 important ways to increase your oxygen supply.
Breathe fresh air
Open the windows or go outside. Fresh air will give you energy and bring extra oxygen to your lungs.
Drink water
To saturate cells with oxygen and remove carbon dioxide, our lungs must be hydrated, that is, saturated with water. Therefore, drinking enough water affects your oxygen levels. We lose on average about 400 ml of water per day through breathing and it is important to adequately replenish it.
Eat foods rich in iron
Certain foods can help improve blood oxygen levels. Iron is a mineral essential for red blood cells, which carry blood throughout the body. This is why we can be tired and exhausted if we don't have enough iron.
Great sources of iron-rich foods include green leafy vegetables, cabbage and broccoli, fruits, apples, legumes, lean proteins such as eggs, poultry and fish.
Do exercises
The better we obtain and use oxygen, the more energy our cells are able to produce. Thus, increased use of oxygen will strengthen our endurance.
There is a clear correlation between performance and the amount of oxygen inhaled. This is measured in VO2 max, your maximum oxygen consumption. The higher the VO2, the greater the endurance. Interval training and sprinting are the best methods to increase oxygen levels.
Train your breathing
Exercise alone is not enough if you want to improve the quality of your breathing, as exercise does not guarantee that you are actually using your lungs' capacity. However, breathing is vital for increasing oxygen levels.
Slow and deep breathing increases oxygen levels in the blood. If you have breathing problems, your doctor will recommend a range of breathing exercises.
For the same reason, many people with infections and athletes feel a huge difference when they start working on their breathing through breathing training. Breathing exercises not only strengthen our stamina, but also help reduce stress levels through increased focus and calmer breathing.
Stop smoking
Even passive smoking, i.e. Inhaling tobacco smoke from a smoker near you causes serious damage to the lungs and negatively affects the alveoli.
Drink more water
Firstly, it thins the mucus in the respiratory tract and facilitates the removal of phlegm. Secondly, it thins the blood. It is advisable to drink in small sips separately from meals. The water should be clean, without additives, at room temperature.
Give yourself oxygen therapy courses
The procedure has virtually no contraindications, and the effect on the body is amazing: the immune system is strengthened, metabolism is accelerated, toxins are eliminated, the nervous system calms, sleep quality improves, vitality increases, etc. Oxygen therapy at home can be carried out by inhaling oxygen from oxygen cylinders or taking oxygen cocktails.
The Prana company produces and sells oxygen cylinders with a capacity of 8 to 16 liters. Inside there is a mixture of nitrogen (20%) and oxygen (80%), which does not dry out the respiratory tract, is tasteless and odorless. There are options for cans with an individual mask included. Affordable cost, long service life, convenient lightweight packaging make KISLOROD oxygen cylinders the optimal choice for relieving symptoms or preventing hypoxia and increasing oxygen levels in the blood.
Covid as trauma
Specialists from the National Medical Research Center named after. V. M. Bekhterev believes that after COVID-19, patients experience symptoms characteristic of the so-called post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
PTSD is a mental disorder that occurs after events that have a traumatic effect on the individual’s psyche. At the same time, the traumatic nature of the events that occurred is associated with a person’s feeling of helplessness, the inability to influence what is happening, and to resist danger. Characteristic symptoms of PTSD include flashbacks, nightmares, partial amnesia, emotional instability and panic attacks. These manifestations can occur not only immediately after a traumatic event, but also months and even years later.
PTSD is well known to psychiatrists - this disorder can occur after any event that traumatizes the individual’s psyche. And Covid may well be one of them.
Photo © Pixabay
Is it possible to quickly increase the saturation on your own?
Before the ambulance and oxygen therapy arrive, the patient can take the following measures:
- Do breathing exercises. Sit up straight, lower your shoulders, straighten up and try to relax. Exercise 1
- Raise one hand up and grab the floor lamp/beam/door handle to secure the position of your hand.
Place your other hand on the diaphragm. Breathe deeply, lifting your diaphragm as you inhale.
Exercise 2
- Continue to hold one arm up while keeping the other extended forward.
- As you inhale, turn your body towards your outstretched arm (if your left hand is raised, turn your body to the left and vice versa).
Exercise 3
- Breathe deeply with one arm raised up. The hand is fixed on any object (floor lamp) or wall.
Due to individual anatomical characteristics, elderly patients should not lie on their stomach - compression of the respiratory organ is possible.
There is no evidence that any medications can effectively increase saturation in a coronavirus patient. However, in the absence of individual intolerance and the presence of aspirin in the home medicine cabinet, the use of this drug is acceptable.
The anticoagulant aspirin is associated with a reduction in the need for mechanical ventilation and admission to the intensive care unit, as well as a reduction in mortality in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
In general, doctors who worked with seriously ill patients have repeatedly noted that oxygen therapy, or rather the constant stay of the patient “on oxygen,” is less effective than breathing exercises. The patient must breathe independently, under the supervision of medical personnel, “kneading” and stimulating the lungs.
Performing the popular exercise with “inflating” balloons is not permissible in cases of lung damage KT-2, KT-3, KT-4 and especially in elderly patients, since the damaged and overstretched pulmonary matrix may simply not withstand the load.
When is hospitalization and oxygen support necessary for low oxygen levels?
Emergency hospitalization for low oxygen levels and oxygen support:
- If the indicator has dropped to 93% and the patient feels unwell (hypoxemia, respiratory failure, respiratory symptoms are severe).
- With a significant percentage of lung damage on CT (> 50%, with CT-3, CT-4).
- Old age of the patient.
- Concomitant chronic diseases of the respiratory system.
- Concomitant chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Initially low saturation due to anemia.
- Pregnant women.
- Patients with immunodeficiency.
- Obese patients.
- For diabetes mellitus.
A decrease in saturation is dangerous primarily for these groups of patients.
If a hospitalized patient's saturation is low and does not rise even with oxygen, then, according to the current recommendations of resuscitators, the patient undergoes tracheal intubation.
Types of oxygen therapy
Depending on the route of oxygen administration, oxygen therapy methods are divided into two main types:
- inhalation (pulmonary) - through catheters, endotracheal tubes, masks;
- non-inhalation - enteral, intravascular, subcutaneous, intracavitary, intraarticular, subconjunctival, cutaneous (general and local oxygen baths).
Carrying out oxygen therapy
The most common methods of oxygen therapy:
- administration of oxygen through a nasal catheter
- use of an oxygen tent, awnings, incubator for newborns;
- hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO);
- carrying out procedures in baths with oxygen supply;
- the use of aerosol cans, pillows with a gas mixture;
- the use of oxygen cocktails based on juices and herbal decoctions.
Technique for oxygen therapy procedure:
- preliminary preparation of equipment and patient;
- supply of gas mixture;
- constant monitoring of the patient's condition;
- care and monitoring of the patient after the procedure.
Who is oxygen therapy indicated for?
The use of oxygen cartridges has no restrictions on their use. Inhalation of the mixture can be indicated for both healthy people and those with various diseases. Oxygen inhalations are useful for city residents, athletes, schoolchildren during periods of increased mental and physical stress, and weakened children. Oxygen therapy helps pregnant women cope with toxicosis and reduce the risks of fetal development associated with hypoxia.
When is oxygen therapy contraindicated?
In neuromuscular diseases, oxygen is contraindicated, including oxygen therapy procedures. Let's look at the reason for this using amyotrophic lateral sclerosis as an example.
This is a disease in which the nervous system (the so-called motor neuron) is affected, which leads to disruption of the most important systems of the body, including weakening of breathing. It becomes more superficial, as a result of which saturation often decreases. But despite this, oxygen cannot be prescribed.
What does the body do when it realizes that breathing has become shallow, which means there is little oxygen for the body? Of course, we begin to breathe more often. Albeit superficially. Such shortness of breath allows the body to live even with reduced saturation numbers. If oxygen therapy is prescribed, the body cancels this protective mechanism - shortness of breath. And then the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood increases. Human consciousness is oppressed. For this reason, oxygen therapy can seriously harm a person with a neuromuscular disease.
In any case, the indications and contraindications for oxygen therapy are determined by the doctor.
Effects of oxygen therapy
If oxygen therapy is prescribed according to indications, the person notices an improvement in well-being, a decrease in shortness of breath, palpitations, and less fatigue.
Quite often, relatives ask whether oxygen therapy will have an effect when a loved one is in the terminal stage of the disease. There is only one answer: there are no indications in the terminal stage: oxygen therapy can have an effect only when saturation is reduced; oxygen does not treat shortness of breath. Rather, oxygen therapy can have positive psychological effects.
How to increase saturation after viral pneumonia?
If even after suffering from coronavirus the saturation is slightly reduced, then this is normal - the lung tissue needs time to restore the previous vital capacity of the respiratory organ. Breathing exercises (see Strelnikova’s set of breathing exercises) and walks in the fresh air with moderate physical activity are extremely useful.
To prevent aggressive adhesions in the lungs in patients with fibrous changes evident on CT; usually with CT-4, CT-3, less often with CT-2 and very rarely with CT-1, antioxidant therapy for pulmonary fibrosis is prescribed, which includes a diet enriched with antioxidants, acetylcysteine, and vitamins E (if there are no allergies).
To clarify the diagnosis and causes of reduced saturation after coronavirus, CT control is important.
When else does a person have low saturation?
There are also the following cases when a person has reduced saturation:
- For heart defects;
- With hypoventilation of the lungs (with a slowdown in the frequency of exhalations and inhalations);
- For anemia;
- For chronic diseases of the lungs and bronchi (COPD, emphysema);
- If the oxygen concentration in the air is reduced;
- For diffuse disorders;
- Under excessive loads;
- When smoking;
- If you are overweight;
- When there are changes in atmospheric pressure;
- At night (from 3 to 7 o’clock) and in the deep sleep phase;
- When he is under general anesthesia.
How is oxygen inhalation performed?
The oxygen cartridge, which is used for oxygen inhalation, is equipped with a simple, convenient dispenser. Thanks to the dispenser, the cylinder can be used by several people.
Individual use of a can with a mask provides control over the flow of the mixture and prevents the ingress of impurities from the surrounding air. The procedure is performed with the help of a mask for children, the elderly and people with disabilities.
If a person has a serious illness and requires constant oxygen therapy, it is recommended to purchase not an oxygen canister, but a concentrator. A special device that produces high concentration oxygen from 1 to 3 liters per minute. In this case, the patient breathes through a mask or nasal cannula. The number and duration of procedures is determined by the attending physician. This therapy is prescribed for patients with pulmonary pathology, heart disease, cancer, and nervous system disorders. Sessions can be performed at home or in a hospital setting.
What is he like?
The oxygen cartridge contains a concentrated breathing mixture consisting of 80% oxygen and 20% nitrogen. This composition ensures maximum absorption of oxygen during inhalation. Cans are available in different volumes: 8, 12 and 16 liters. They weigh from 140 to 180 grams. The oxygen cartridge does not take up much space in your purse, which allows you to carry it with you.
How is saturation measured?
Saturation is measured with a pulse oximeter. Ambulance teams are equipped with mobile devices. You can also purchase it for home monitoring. The device resembles a clothespin that is attached to your finger.
Within a minute, a sensor with LEDs reads data, namely the color of the blood (hemoglobin), which changes depending on the saturation, as well as a specific pulsating light signal that changes depending on changes in blood pressure.
The pulse oximeter display shows two numbers - the top one shows the percentage of oxygen in the blood, the bottom one shows the pulse.
Saturation is measured in a sitting or lying position, the patient's hand should lie on the surface and not hang in the air.
Hospitals also use invasive devices to help laboratory technicians measure blood gases. To do this, it is taken from an artery or vein.
Is the pulse oximeter wrong?
A pulse oximeter can indeed make mistakes, the result will be false or distorted if:
- The device is of poor quality and has low sensitivity;
- The device's batteries run out;
- A person's saturation was measured immediately after exercise or hard work;
- The patient has cold hands;
- Nails are covered with gel polish;
- The patient is wearing a mask that does not allow air to pass through well.
It is important to understand that the result of pulse oximetry can be influenced by: the sensitivity of the device (including battery charge), lighting, and the color of the patient’s skin (the darker, the higher the indicator, which does not reflect the real state of affairs).
The concept of “saturation rate” is very arbitrary. It happens that patients with signs of coronavirus infection and a mobile non-invasive device for measuring saturation begin to panic and call an ambulance if the oxygen in the blood drops, for example, to 93%.
Anxious expectations
Already in the first wave of the pandemic in 2021, psychiatrists drew attention to changes in the mental health of the population. Lockdowns, other coronavirus restrictions, remote work, a person constantly being at home - all this has already provoked negative psychological effects. Add to this anxious expectations - fear of becoming seriously ill, fear for loved ones, the possibility of losing a job - and here it is, a set that places a heavy burden on the human psyche.
At the same time, some researchers have started talking about the increase in suicidal and depressive feelings among completely healthy citizens in different countries of the world. Moreover, data began to appear about increasing cases of domestic violence and divorce.
Photo © Pixabay
When a person gets sick, his anxious expectations intensify. The patient begins to monitor his condition, symptoms, temperature, and breathing with fear. No one wants to end up in a hospital under strict quarantine. Even more fears are caused by the possibility of developing severe complications, the use of ventilators and other procedures. Now doctors already know that the most severe psychological consequences occur precisely in patients who have undergone artificial ventilation.
Questions and answers about blood oxygen levels
Below are popular questions and answers regarding oxygen levels in human blood.
- Can blood oxygen levels be too high?
The oxygen level in the blood may be 100%, but what matters is what kind of oxygen we inhale. There is only 20% of it in the air. And if you breathe pure oxygen, for example from an oxygen cylinder (which, unfortunately, many began to do at home due to COVID-19), this can lead to very dangerous conditions and even death. Oxygen poisoning, lung burns, and the development of free radical oxidation with toxic reactions are some of the main risks.
- What should the blood oxygen level be during coronavirus?
Many people with COVID-19 have low oxygen levels even when they feel well. Low oxygen levels can be an early sign that people need medical attention. Normal oxygen levels are at least 95%. Some patients with chronic lung disease or sleep apnea may have normal levels of around 90%. If your home SpO2 value is less than 95%, call your doctor.
- At what level of oxygen in the blood should you call a doctor at home?
Oxygen levels measured by a pulse oximeter are not the only way to tell how sick you are. Some people may feel very sick and have good oxygen levels, and some may feel fine but have low oxygen levels. You may also have low oxygen levels if you feel short of breath, breathe faster than usual, or feel too sick to do your normal daily activities. If you have these symptoms, call your doctor immediately.
Are there traditional means of measuring blood oxygen levels?
No, there are no traditional methods for measuring oxygen levels in the blood.
- What complications can occur with low blood oxygen levels?
They are possible when the oxygen pressure in the air changes at high altitudes. In addition to pilots, aircrew, and airplane passengers, athletes, travelers (lowlanders) to ski resorts, mountaineering expeditions, and people making pilgrimages to monasteries, abbeys, shrines, or temples are at high risk of developing acute mountain sickness or altitude sickness.
If left untreated, low blood levels can lead to progression of severe manifestations: high-altitude pulmonary edema and high-altitude cerebral edema. Oxygenation at high altitudes may help such individuals or their companions to acclimatize to high altitudes and therefore prevent or alleviate symptoms of altitude sickness or the progression of severe illnesses.
Sources:
- https://prana.moscow/o_kislorode/articles/kak-podnyat-kislorod-v-krovi-v-domashnikh-usloviyakh
- https://kt-spb.ru/medical-articles/saturatsiya-pri-koronaviruse
- https://www.ortix.ru/wiki/chto_takoe_kislorod_i_dlya_chego_on_nuzhen
- https://peredelkinokardio.ru/articles/kislorodoterapiya-lechenie-i-profilaktika-zabolevanij
- https://pro-palliativ.ru/blog/dlitelnaya-i-situatsionnaya-kislorodoterapiya-na-domu
- https://www.kp.ru/putevoditel/zdorove/uroven-kisloroda-v-krovi-u-vzroslogo
Post-Covid syndrome?
The entire diverse set of consequences in people who have survived a new coronavirus infection has already been called “post-COVID-19 syndrome.” Among its symptoms are mental disorders that are already well known to us: “fog in the head,” disorientation in space, panic attacks and cognitive disorders. However, some researchers say that mental problems in Covid survivors are not unique consequences of the new disease, but complications that cause any severe infectious disease.
So, back in 2021, an article appeared in the authoritative medical journal The Lancet, which analyzed 72 studies of the consequences of epidemics - the predecessors of COVID-19 - SARS-1 and MERS viruses. Mental disorders in those who recovered from these infections turned out to be identical: confusion, depressed mood, anxiety, memory impairment, insomnia and even delirium. Thus, we can draw a preliminary conclusion: the COVID-19 virus does not necessarily have any unique properties that affect the psyche.
Photo © Pixabay