- Home /
- Branches /
- Cardiology /
- Dyspnea
01.11.2021 The article was checked by a cardiologist, Ph.D. Zhelyakov E.G. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Specialists at the Clinical Hospital on Yauza diagnose the causes of shortness of breath (assessment of respiratory function, X-ray, ECG) and treat the diseases that cause it at the modern level. Treatment of shortness of breath always involves treating the underlying disease and eliminating its causes (for example, achieving compensation for heart failure, etc.).
- Shortness of breath is the main symptom of chronic heart failure, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Up to 27% of people worldwide suffer from some form of shortness of breath
- Spirography is the gold standard for assessing external respiration
sign up for a consultation
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) - a violation of the rhythm, frequency, depth of breathing, a subjective feeling of lack of air, difficulty breathing - this is a complaint with which the patient first of all turns to a doctor. This symptom can be a manifestation of various diseases.
Respiration is an important body function that ensures that all cells have enough oxygen to survive and that toxic carbon dioxide is removed. Any problems that arise during the breathing process and cause shortness of breath may be a sign of serious illness. Therefore, there is a need for immediate medical attention.
Sudden shortness of breath may be caused by the development of heart pathologies or an asthma attack. Long-term shortness of breath is usually associated with pulmonary pathology.
Types of shortness of breath
The sensation of shortness of breath occurs when a signal from receptors located in the epithelium of the respiratory tract enters the respiratory center located in the brain stem. Respiratory signals are processed taking into account behavioral, intellectual and situational signals.
Shortness of breath is a symptom of the disease, not the disease itself. Therefore, its etiology can be defined as arising from four main categories:
- Central – diseases of the nervous system with impaired functioning of the respiratory center, with neuroses and other functional pathologies of the central nervous system.
- Pulmonary – observed in diseases of the lungs (pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, pulmonary fibrosis) and chest.
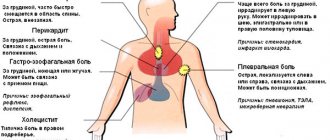
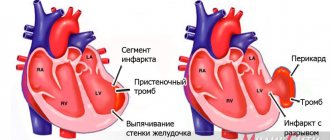
- Cardiac – a symptom of heart failure during myocardial infarction, myocarditis, cardiomyopathies, heart defects, etc.
- Hematogenous - any type of anemia, the effect on the respiratory center of changes in blood acidity and toxic metabolic products in case of poisoning, liver failure, decompensated diabetes mellitus, etc.
For different diseases, shortness of breath is perceived differently, but in any case it differs from increased breathing, which occurs during physical activity in healthy people.
Note!
Differences between cardiac and pulmonary dyspnea:
- With cardiac dyspnea, the heart cannot cope with the load, stagnation occurs and gas exchange is disrupted, which provokes rapid breathing.
- Pulmonary shortness of breath appears due to the accumulation of sputum in the organs of the respiratory system and is accompanied by a cough.
Cardiac dyspnea, unlike pulmonary dyspnea, occurs without expiratory difficulties (short inhalation and difficult exhalation). In an upright position and at rest the condition improves. With pulmonary dyspnea, hypoxemia (low oxygen in the blood), respiratory acidosis (accumulation of large amounts of carbon dioxide in the blood) and hypercapnia (excessive amount of CO2 in the blood) are observed.
Shortness of breath is a subjective sensation. Only the patient himself can differentiate its intensity. However, in any case, if you feel short of breath, it is better to consult a doctor and determine the cause of the ailment. Shortness of breath is often a symptom of a serious pathology that can lead to disability. To avoid serious illnesses, make an appointment with a doctor and get tested without delay.
Content:
- Symptoms of pathology
- Options for shortness of breath after Covid-19
- How to assess lung function after COVID-19 3.1. Difficulties in self-diagnosis
- How to treat shortness of breath after coronavirus 4.1. Medicines for shortness of breath 4.2. Oxygenation 4.3. Inhalations 4.4. Physiotherapeutic procedures 4.5. Breathing exercises
- Ways to improve lung function on your own
COVID-19 takes its toll throughout the body, but it most commonly affects the lungs. Shortness of breath after Covid is common. It occurs both in people who have had pneumonia and in those who have not encountered serious complications during their illness.
Scientists have found that in approximately 20% of those recovering, the function of the lung tissues has worsened. Patients gasp for air if they are in a hurry, are unable to lie on their back for a long time, and quickly get tired when doing even simple physical work. Things are especially bad for people diagnosed with pulmonary fibrosis, which leads to scarring of the paired organ.
Under normal conditions, fibrosis is rare. It is most often encountered by people over the age of sixty. With this diagnosis, shortness of breath is a concern. It can be so strong that it is difficult for a person to talk and move.
We suggest you figure out why difficulty breathing after coronavirus bothers you, and how to recognize and eliminate dangerous symptoms. It is important to know this information to prevent complications from Covid-19 from progressing.
Causes of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air can be associated with disturbances in external (oxygen supply through the lungs) or internal (tissue) respiration:
- Impact on the respiratory center of toxins, metabolic products in severe infectious diseases.
- Respiratory impairment due to exposure to toxic chemicals at the cellular level.
- Chest injuries that violate the tightness of the pleural cavities; compression of the lungs with pneumothorax, hydrothorax.
- Neurological complications in multiple sclerosis, myasthenia, functional and neurotic breathing disorders in hysteria, neurasthenia, etc.
- Blockage of the airway lumen with viscous secretion (with bronchitis, bronchial asthma), tumor, foreign body (button, food, vomit).
- Swelling and thickening of the bronchial wall, spasm of the bronchial muscles of an allergic or inflammatory nature in bronchial asthma, pneumonia, etc.
- Heart failure, in which there is stagnation of blood in the vessels of the pulmonary circulation, effusion of fluid into the alveoli of the lungs, a decrease in the vital capacity of the lungs, and a decrease in peripheral blood flow.
- Coronary heart disease, when the main symptom of insufficient blood supply to the myocardium is shortness of breath.
- For anemia as a result of decreased hemoglobin levels and a decrease in the number of red blood cells due to blood loss; in case of poisoning with certain chemicals that bind hemoglobin.
- Obesity and physical detraining can also cause shortness of breath with minimal physical activity.
Intense exercise, extreme temperatures, obesity, and high altitude can all cause shortness of breath in a healthy person. Outside of these examples, dyspnea is a sign of a medical problem. If you experience unexplained breathing problems, especially if they occur suddenly, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Literature:
- COVID-19, coronavirus infection caused by SARS-CoV-2 / 2020 / ORGZDRAV: News. Opinions. Education. VSHOUZ Bulletin.
- COVID-19: respiratory infection caused by a new coronavirus: new data on epidemiology, clinical course, patient management.
- Medical rehabilitation for new coronavirus infection (Covid-19) / Ivanova G. E., Balandina I. N., Bakhtina I. S., Belkin A. A., Belyaev A. F., et al. / 2021 / Physical and rehabilitation medicine, medical rehabilitation
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Symptoms of shortness of breath
Dyspnea can be characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations due to the large number of possible causes. However, the most common symptoms are coughing and changes in breathing patterns. Signs may appear when a person is at rest and during intense exercise.
Symptoms that accompany shortness of breath:
- fatigue, weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- sudden lack of air;
- difficulty breathing in and out;
- signs of dizziness;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- fast, irregular heartbeat;
- decreased physical activity;
- cough or wheezing when breathing;
- hemoptysis (coughing up blood);
- blueness of nails and lips due to poor circulation;
- pain, tightness in the chest (if shortness of breath occurs as a result of a heart attack).
The patient feels as if after intense physical activity or hard physical work. Respiratory dysfunction prevents a person from speaking normally and pronouncing long words and phrases. Speech becomes short and abrupt.
All breathing problems, whether sudden or long-term, regardless of symptoms, should be taken seriously. Although many of the possible causes are harmless and easily treatable, you should still see a doctor for a thorough medical examination.
How to assess lung function after COVID-19
There is a no-false breath test that anyone can do on their own. According to its terms, it is necessary:
- Take a deep breath through your nose.
- Hold your breath for ten seconds.
- Exhale slowly.
If during testing no discomfort arises, a cough does not start, or a strong sore throat does not appear, then everything is fine with the lungs. If your health worsens when you try to hold in air, a medical examination is indicated.
Difficulties in self-diagnosis
Shortness of breath, which occurs due to narrowing of the nasal passages and swelling of the mucous membranes during a runny nose, and which manifests itself due to deterioration of the lungs - these are two completely different problems. A person is not able to independently understand what causes his illness.
Therefore, if you have difficulty breathing, you should still seek help from a therapist or pulmonologist. Self-medication for such symptoms is unacceptable.
What to do if you have severe shortness of breath?
Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) provides relief for increased breathing needs. This procedure is less useful for patients with defects in oxygen diffusion in the alveolar arteries. The most effective component of pulmonary rehabilitation is special breathing exercises.
Recommendations to follow in case of severe shortness of breath:
- If you have serious breathing problems, it is better to sleep with the head of the bed raised. This will help the lungs expand and promote drainage of secretions.
- While sitting, lean forward on your elbows. This will also help your lungs expand and make breathing easier.
- To reduce anxiety, you can use relaxation techniques (take slow, even, deep breaths and try to focus on pleasant things).
- Take medications strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
- If you experience side effects from your medications, especially if they are severe, tell your doctor or emergency team members.
- Use pursed-lip breathing when you feel short of breath. Inhale through your nose and exhale very slowly through your mouth, pursing your lips slightly. The exhalation should last twice as long as the inhalation.
- If you experience sudden breathing problems, you should open a window, move to another room where there are fewer people, or go outside.
- Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can make shortness of breath worse. Electronic cigarettes also contain nicotine.
- Cold air and using fans to blow air onto the face can significantly improve shortness of breath. Supplemental oxygen has only been shown to be beneficial in hypoxic patients.
Simple but effective recommendations help improve your shortness of breath. Additional measures are aimed at reducing anxiety and providing an increased sense of control.
There are a huge number of reasons for shortness of breath. It is impossible to determine on your own whether it is a symptom of a serious illness. Only a highly qualified specialist can determine which organ disease caused the pathology and prescribe the appropriate examination. Make an appointment with your doctor to determine the cause of your discomfort.
sign up for a consultation
Diagnostic stages
Consultation with a therapist. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination of the patient and ask him about accompanying symptoms. If necessary, he will refer the patient to other specialists at our hospital - a cardiologist, hematologist, and psychotherapist.
Laboratory diagnostics
:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry.
Instrumental diagnostics
:
- spirography
- ECG;
- ECHO-KG
- Chest CT scan or radiography.
Additional examination
, the volume of which is determined individually depending on the direction of the diagnostic search.
Treatment of shortness of breath
Treatment of shortness of breath is carried out in accordance with the cause and individually for each patient.
For bronchitis with difficulty in sputum discharge, the therapist may prescribe sputum thinners and expectorants; for bronchial obstruction, bronchodilators.
Treatment of shortness of breath in heart failure is complex and prescribed by a cardiologist.
For hematogenous dyspnea, treatment is aimed at combating anemia.
The psychogenically caused feeling of lack of air, characteristic of panic attacks and other forms of neurotic disorders, is treated in a course of psychotherapy.
In case of massive pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity and compression of the lung), puncture of the pleural cavity (removal of fluid) may be necessary, performed by a surgeon.
In acute conditions with severe life-threatening respiratory disorders, urgent hospitalization of the patient in the intensive care unit for mechanical ventilation is required.
If you are concerned about shortness of breath, you should consult a doctor. The multidisciplinary team of doctors at the Yauza Clinical Hospital will help you correctly prescribe and conduct an examination, establish the cause, and prescribe effective treatment.
Complications after difficulty breathing
People suffering from shortness of breath are limited in daily and social activities. This affects independence and reduces social significance. As it progresses, anxiety and worry arise. Sleep disturbance occurs and depression develops. Chronic heart failure is especially dangerous.
Metabolism and gas exchange disorders in the body can lead to dangerous complications:
- decrease in blood pressure;
- pulmonary edema;
- persistent breathing problems;
- attacks of suffocation against the background of cardiac cardiac asthma.
As the disease progresses, the following disorders are observed:
- blueness of the limbs and lips (cyanosis);
- suffocating cough at night;
- gurgling sensation in the heart area;
- the appearance of profuse cold sweat;
- development of pulmonary emphysema;
- discharge of sputum with traces of blood;
- decreased elasticity of lung tissue and blood vessels.
Pulmonary edema and heart failure are very serious and dangerous pathologies for human health. If shortness of breath occurs at rest, you should immediately seek medical help.
Prognosis and prevention
Dyspnea does not fall into the category of systemic diseases. This is a sign of the development of cardiac or pulmonary pathology. The problem can only be dealt with by treating the underlying disease. With dystrophic changes as a result of the development of cardiac pathologies, survival rate decreases to 60%. Only early diagnosis and timely treatment can guarantee a favorable outcome.
To relieve the symptoms of shortness of breath or for prevention purposes, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Perform simple exercises to train the respiratory system and increase muscle tone, unless there are contraindications.
- Avoid contact with allergens that may worsen the condition.
- Prevent seasonal infections.
- Stop smoking.
- Control body weight.
The main condition for preventive measures is strict compliance with all recommendations of the attending physician.
Shortness of breath may make it difficult to eat. Here are some practical tips for saving energy and getting the most out of your food:
- eat in small portions;
- try to breathe calmly and evenly while eating;
- Frozen convenience foods, ready-made meals, or take-out and delivery can make life easier;
- it is recommended to limit the amount of products that cause gas formation;
- You can keep a food diary to determine which foods worsen your overall condition.
In some cases, acupressure and/or acupuncture can help. Before deciding to prescribe procedures, you should definitely consult your doctor. Both practices focus on stimulating hot spots to optimize energy flow and release blockages.
Dyspnea at rest is a rare phenomenon that accompanies severe and advanced diseases. This phenomenon usually appears during physical activity. Pay attention to whether you have difficulty breathing when climbing stairs or walking quickly. If you notice a lack of oxygen, be sure to make an appointment with your doctor for consultation.
Ways to improve lung function on your own
What can a person suffering from shortness of breath after coronavirus do? There are simple ways to normalize pulmonary activity:
- Eating foods that increase lung capacity. Preference should be given to fruits and vegetables. Tomatoes, blueberries, nuts, onions, and citrus fruits are especially useful. Spices and fatty foods should be avoided.
- No smoking. Tobacco smoke and the toxins it contains make the lungs extremely vulnerable. In order for the tissue to recover and the inflammatory process to stop progressing, it is important to stop smoking.
- Do cardio workouts. You need to start them only if you are in good physical health. Cardio increases lung capacity, normalizes blood circulation, and increases heart rate. It is good if the exercises are performed in the fresh air. But the load should be increased gradually.
- Respiratory protection from environmental pollution. A person who has recently had Covid-19 should not be in polluted conditions. If his professional activity involves being in harmful conditions, it is better to take a long vacation.
Patients who strictly follow the doctor's instructions, take medications, perform breathing exercises and eat properly quickly stop suffering from shortness of breath. Take care of your health and don't let the coronavirus deprive you of your ability to breathe deeply.