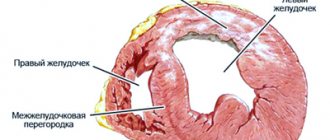
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis (PICS) is an independent form of coronary heart disease (CHD). It is characterized by the formation of connective tissue in the heart muscle, replacing dead cardiomyocytes due to myocardial infarction (MI). This tissue cannot perform the functions of muscle cells of the heart, which is accompanied by dysfunction of the organ.
ABC Clinic provides highly specialized cardiac surgery medical care. Doctors of the highest category work here, who, using innovative high-tech equipment, conduct thorough diagnostics and perform operations of any level of complexity.
Symptoms of post-infarction cardiosclerosis
Symptoms of post-infarction cardiosclerosis include deterioration in pumping function, rhythm disturbances, conduction disturbances, enlargement of the heart chambers, hypertrophy of muscle tissue with the development of heart failure.
Clinically, this is manifested by tachycardia, shortness of breath, fatigue, attacks of suffocation, orthopnea, swelling of the legs, acrocyanosis, hepatomegaly, pericarditis, swelling of the neck veins, and chest pain. The larger the volume of newly formed tissue, the more intense the symptoms.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease depend on the location of scar formation, the width and depth of the affected area of the heart. The less intact myocardium remains, the more likely the occurrence of arrhythmias and heart failure.
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis has the following symptoms, common to all cases:
- Dyspnea. Appears both during physical activity and during rest. While in a horizontal position, the patient feels breathing problems. The attack passes 15-20 minutes after taking a sitting position.
- Increased heart rate. Develops due to acceleration of blood flow and contraction of the myocardium.
Blue discoloration of limbs and lips. Occurs due to lack of oxygen.- Discomfort and pain in the chest. The pain may be pressing or stabbing.
- Heart rhythm disturbance (arrhythmia). Manifests itself in the form of extrasystole and atrial fibrillation. The cause of its appearance is sclerotic deformation of the pathways.
- Swelling. It is provoked by the accumulation of excess fluid in the body cavity and right ventricular failure. Mostly observed in the lower extremities.
Additionally, the following may appear:
- constant fatigue and weakness of the body;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- feeling of lack of air;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased liver size;
- dilatation of the neck veins.
Depending on the severity of the disease, the level of intensity of unpleasant and painful sensations differs. At the beginning of the disease or at the stage of remission, there may be no symptoms at all. After the formation of a lesion, the structure of the entire myocardium may change. In this case, the symptoms appear more clearly.
Types of post-infarction cardiosclerosis
Based on the size and location of the pathological focus, doctors classify this condition into the following types:
- Large-focal post-infarction cardiosclerosis (significant replacement of cardiomyocytes with connective tissue).
- Atherosclerotic (not a type of PICS, its cause is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, as a result of which the heart muscle experiences oxygen deficiency, cells are gradually damaged and replaced by connective tissue).
- Lower (damage to the lower wall of the heart, accompanied by dyspeptic disorders; sometimes involvement of the right ventricle in the pathological process is observed).
Consequences
A patient with the diagnosis in question needs lifelong medical supervision. Knowing what post-infarction cardiosclerosis is, one cannot ignore the situation, as this leads to inevitable complications in the form of the following consequences:
- Why does post-infarction cardiosclerosis (PICS) develop and how does it manifest?
- pericardial tamponade;
- atrial fibrillation;
- thromboembolism;
- blockades;
- pulmonary edema;
- tachycardia;
- decreased automaticity of the sinoatrial node.
These processes negatively affect a person’s quality of life. The patient loses tolerance to physical activity, loses the opportunity to work and lead a normal life. Advanced cardiosclerosis provokes the appearance of an aneurysm, the rupture of which leads to death in 90% of non-operated patients.
Diagnosis of post-infarction cardiosclerosis
Diagnosis of post-infarction cardiosclerosis includes:
- Anamnesis collection.
- ECG.
- Echocardiography.
- RKG.
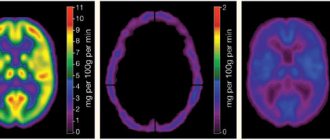
- PET of the heart.
- Coronography, etc.
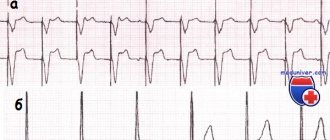
ECG is the most common and simplest method for detecting PICS. He clarifies the presence and location of scars; affected area; associated cardiac changes; rhythm and conduction disturbances; signs of an aneurysm. Post-infarction cardiosclerosis on the ECG has a distinctive feature - a deep Q wave.
But PICS is not always reflected in the conclusion of this survey. Therefore, differential diagnosis of postmyocardial cardiosclerosis is carried out using other methods.
EchoCG is highly informative for PICS. The study can detect cardiac aneurysm (chronic form), increased volume of the left ventricle, and impaired contractility.
Cardiac PET can identify persistent areas of hypoperfusion. Coronography makes it possible to evaluate coronary blood flow. In this case, an X-ray contrast study can show a fairly variable picture: both unchanged coronary arteries and three-vessel lesions.
Treatment and rehabilitation
Treatment of cardiac cardiosclerosis is aimed at reducing the risk of complications, normalizing heart function and blood circulation, and improving the patient’s quality of life.
An integrated approach can be used for this:
- Non-drug post-infarction treatment of the post-infarction condition (regular, but not too intense physical activity, giving up bad habits, proper nutrition with limited animal fat, body weight control).
- Treatment of post-infarction cardiosclerosis with drugs (ACE inhibitors, nitrates, beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents, diuretics, etc.)
- Operation. In case of severe lesions and conduction and rhythm disturbances, an ICD or pacemaker is sometimes necessary. If indicated, CABG, stenting or angioplasty of the coronary arteries is performed. In case of an aneurysm, its removal in combination with CABG is necessary.
- Psychotherapy. Not all patients are ready to change their lives when they learn about the diagnosis. In this regard, it is important that the patient realizes that the duration and course of the disease depend on the lifestyle. This may require psychotherapeutic help.
- Dispensary observation. With PICS, the patient must be observed by a cardiologist for at least a year. It is recommended to do an ECG every month for six months after diagnosis.
Six months later, the patient is sent to MSEC to determine his ability to work. You will first need an ECG, stress test, and echocardiography. Also pass a series of tests: general, biochemistry. Subsequently, electrocardiography must be repeated every year.
Diagnostic procedures
A patient who has suffered a myocardial infarction must be constantly under medical supervision. When the symptoms described above appear, the diagnosis is beyond doubt. The following studies are used to make a diagnosis:
- ECG. Shows disturbances in the functioning of the heart, myocardial defects and contractility disorders.
EchoCG. Deciphering the results of this study is most valuable. Demonstrates the location, the volume of replaced tissue, and also allows you to count the number of ventricular contractions and determine the presence of aneurysmal dilatations.- Radiography. Makes it possible to see the size of the heart and determine whether it is enlarged.
- Scintigraphy. The patient is injected with radioactive isotopes that reach only healthy areas of the myocardium. This allows you to see the microscopically sized affected areas.
- Angiography. Allows you to determine the degree of narrowing of blood vessels and the presence of blood clots in them.
- MRI. Determines the location and size of connective tissue in the myocardium.
The cardiologist needs to carefully examine the patient’s medical history and conduct a detailed interview. An assistant in determining the diagnosis will be the patient’s medical record, which records all the diseases suffered during life. This allows you to predict future complications and prevent them.
Is disability issued to patients after post-infarction cardiosclerosis?
Not everyone gets a disability. Much depends on the general health of the patient and the presence of complications caused by the pathology. To determine the group, the following factors are taken into account: angina pectoris, which is confirmed by electrocardiography data; features of rhythm disturbances (constant, episodic); aneurysm with thrombosis, also confirmed by echocardiography.
The cardiology department of the ABC Clinic deals with the diagnosis and treatment of pathological changes in the heart muscle, vessels of various sizes, and the valve apparatus. Modern equipment makes it possible to detect diseases at an early stage of development, which makes it possible to prevent the development of complications. In their work, doctors are guided by the principles of evidence-based medicine, recommendations of the Russian Ministry of Health, and their own clinical experience.
Causes
The following factors play an etiological role in the development of atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis. Age. Most cases of the disease occur in people over 50 years of age. As the body ages, the activity of elastase, the production and breakdown of cholesterol, and the concentration of acidic mucopolysaccharides increase.
Gender. In men, atherosclerosis develops more often and at an earlier age. In women, under the influence of sex hormones, beta lipoproteins are formed more slowly, and the concentration of alpha proteins, on the contrary, increases, which is why the risks of atherosclerosis are reduced. Smoking. The effect of nicotine on vascular permeability is extremely negative, since with this type of intoxication the production of adrenaline sharply increases, the synthesis of bradykinin is stimulated, and damage to the walls increases.
Hereditary predisposition. Type 3 lipid metabolism disorders mainly occur in families with coronary artery disease and hypertension. But according to Mendel's laws, only type 2 is inherited. Sedentary lifestyle. It has long been recognized by everyone that movement is one of the components of health. The higher a person’s activity, the better the compensation mechanisms and collaterals (bypass paths of blood flow) in his body.
Tendency to overeat. The calorie content of food consumed should not exceed the body's needs, since abundant nutrition will lead to obesity and all related problems. To avoid the development of diseases, you should not be guided by appetite - you need to eat food based on the calories expended.
Eating fatty and high-calorie foods in large quantities leads to increased cholesterol
In addition to predisposing general factors that can lead to the appearance of atherosclerosis, there are several diseases that also provoke and accelerate the pathological process. This list includes:
- arterial hypertension (all types);
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- hypothyroidism;
- gout.
In this case, it is customary to pay attention to the risk factors present for pathology, which imply various changes in the biochemical and clinical parameters of the body, bad habits and the presence of concomitant diseases. They are divided into:
- the main ones are arterial hypertension, hypercholesterolemia (increased cholesterol in the blood) and nicotine intoxication;
- additional – sedentary lifestyle, diabetes, obesity, gout.