03.10.2020
The human psyche is not always able to cope with the consequences of stress, as a result of which the anxious state becomes pathological and causes the development of neurosis. This condition is accompanied by rapid heartbeat, which is why it is called “cardioneurosis” or “heart neurosis.”
Cardioneurosis
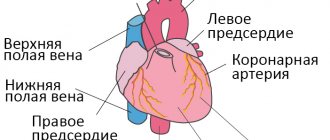
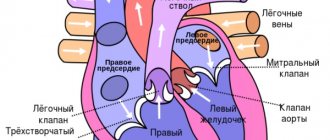
called a malfunction of the cardiovascular system. This pathology is not associated with damage or structural disorder of the heart and is functional in nature. Cardioneurosis occurs more often in women than in men.
Cardioneurosis itself is not dangerous to human health and life, but this pathology requires careful diagnosis to rule out more dangerous diseases.
If a person feels regular pain in the chest, his heart rhythm is disturbed, but no physiological disorders are identified, he is diagnosed with “cardioneurosis.” Cardioneurosis is diagnosed more often in adults than in children. This disease is treated with the help of drug correction in combination with psychotherapeutic influence. Diagnosis and treatment of this disease is carried out by psychotherapists, neurologists and cardiologists.
Gymnastics for heart neurosis
Experts have developed a special complex of physical therapy for this pathology.
- Lunges for 1-1.5 minutes, first with one leg, then the other.
- Deflection of the torso. The leg is pulled back, the upper body also bends back. Then the same is done with the other leg. The exercise is repeated 5-8 times on each leg.
- Squat on one leg, while holding onto a chair. Repeat 2-5 times with each leg.
- Rotational movements of the body, first in one direction, then in the other. Repeat 3-6 times.
- Imitation of boxer punches. You need to breathe in a random order. Make 8-15 blows with each hand.
In some specialized neuropsychiatric clinics, there are special neurosis departments in which patients with different variations of this disease are treated. Often, patients are brought to such departments by the presence of panic attacks, which can often be combined with migraines or other pathologies that debilitate the patient.
What other symptoms can be observed with neurosis?
In addition to the above clinical manifestations, additional symptoms may be observed:
- One of the types of cardioneurosis is autonomic neurosis, which is often present as a symptom complex in pathological menopause, and in addition, in other hormonal disorders. In the presence of a pathological menopause, autonomic neurosis is called autonomic dyshormonal cardiodystrophy. Clinically, this disease can manifest itself as cardialgia of a cutting and pressing nature. Sometimes the pain can radiate to the arm and shoulder blade; among other things, the rhythm may become faster. Such painful sensations do not depend in any way on physical activity, and a state of rest as such does not bring relief. In addition, Nitroglycerin also does not give any effect.
- Symptoms in the form of sweating, hot flashes, shortness of breath, dizziness, parasympathetic crisis, tachycardia or bradycardia, trembling, hyperemia or pallor of the skin indicate some specific autonomic problems.
- With cardiac neuroses, manifestations in the form of high blood pressure, headaches and heart pain can also be observed.
Symptoms of cardiac neurosis
Manifestations of cardiac neurosis that the individual himself can identify:
1. Pain in the heart during neuroses tops the list of “symptoms” in terms of the severity of their perception by the individual. As a rule, pain spreads to nearby areas. This is the so-called cardialgia, which must be distinguished from angina pectoris, which requires serious treatment.
How the heart hurts, symptoms of neurosis.
Heaviness of the heart with neurosis is quite common. Or burning sensations in the heart of varying degrees of manifestation can also help diagnose neurosis. In addition, the pain can be characterized as dull, stabbing, cutting and vary in duration. It all depends on the mental makeup and emotional background of a particular person. Therefore, heart pain due to neuroses does not always require treatment.
2. Chills or hot flashes. Sweating is common.
3. Shortness of breath (rapid shallow breathing), which appears due to lack of air. The symptom may be chronic.
- Cardioneurosis symptoms and treatment
4. Tachycardia (increase in heart rate) or bradycardia (decrease). They can change during the day depending on the psychological state.
5. Involuntary muscle contractions, manifested in the form of nervous tics and tremors (shaking). They may have varying degrees of severity, including involuntary movements of the body.
6. Paleness of the skin, which can be present either constantly or appear at a time of crisis. It all depends on the degree of depression of the nervous system.
7. Decrease in blood pressure or increase, as well as changes in extreme values.
8.Such isolated and seemingly insignificant symptoms as headache or dizziness also occur when considering the question “Heart neurosis symptoms and treatment
So, we answered the question “How is cardiac neurosis expressed?”
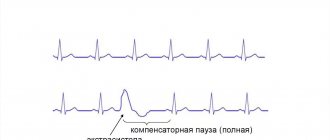
IMPORTANT! All of the listed symptoms do not appear individually if there is a suspicion of cardiac neurosis. For example, emerging negative nervous states provoke all or part of the physiological manifestations of the disease, which in turn entails increased emotional stress. The process is closed. In general, this condition is often characterized as a panic attack, which is an attack of deep, comprehensive fear or anxiety and is accompanied by the listed physiological manifestations. To some extent this is true, but the chain of events can be composed of a rearrangement of symptoms and begin with minor changes in the functioning of the heart. However, Heart Neurosis, symptoms and treatment suggests that the basis for the occurrence of the disease is always a psychological component, which triggers the process in a chain with an absolutely healthy heart or aggravates existing, but minor changes in its work. It is important that the real impact of neurosis on the heart with the listed symptoms is often not observed (for example, on an ECG machine). However, symptoms can develop into actual manifestations that are recorded during the diagnostic process.
In previous sections, we talked about how chronic stress gradually destroys the cardiovascular system and each subsequent stressor makes it even more vulnerable. But one of the most striking and best-known features of heart disease is that heart attacks are common during stressors. A person receives unpleasant news; his wife died; he lost his job; a child who is considered long dead returns home; he wins the lottery. The man cries, screams, rejoices, sighs, holds his breath, amazed by the news. Soon he suddenly clutches his chest and falls dead from sudden cardiac arrest. A strong negative emotion, such as anger, doubles the risk of a heart attack within two hours of its onset. Thus, during the trial of O. J. Simpson, Bill Hodgman, one of the prosecutors, began to experience chest pains when he stood up for the 20th time to argue with Johnnie Cochran, and even fainted (don't worry, he survived) . Because the cardiovascular system is so vulnerable to strong feelings, every Las Vegas casino has a defibrillator. There is even evidence that traveling to New York is a significant risk factor for heart attacks¹.
__________________________________________
¹ This is evidenced by the results of a famous study published in 1999 by Nicholas Christenfeld and colleagues from the University of California at San Diego (did you expect it to be New York University?). The authors did an excellent job of ruling out other factors. They showed that this risk does not occur in other cities in the country. Its reason is the unconscious choice of place of residence (that is, who, except the eternally tense, prone to illness
This phenomenon has been well studied. In one study, a doctor collected newspaper clippings that reported the sudden death of 170 people from cardiac arrest. He identified events that appeared to be associated with these deaths: illness, death, or the threat of loss of a loved one; acute grief; loss of status or humiliation of self-esteem; mourning, anniversary of the death of loved ones; physical danger; threat of injury or rehabilitation period after injury; an important victory or intense joy. Other studies have confirmed these findings. During the 1991 Gulf War, a decrease in fatalities in Israel was attributed to missile malfunctions rather than a decrease in the incidence of sudden cardiac death among frightened pensioners. The 1994 Los Angeles earthquake also saw a spike in heart attacks¹.
The actual causes are obviously difficult to determine (since it is impossible to predict what might happen, and it is impossible to interview dead people to find out how they felt), but in general cardiologists agree that sudden cardiac arrest is simply an extreme case of acute cardiac arrest. stress causing ventricular arrhythmia or, even worse, ventricular fibrillation and ischemia². As one might assume,
_________________________________
hearts of crazy people, wants to live in New York?). It is not a function of socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, or immigrant status. It's not that people happened to be in New York at a time of day when heart attacks are generally more common (like commuters during work hours, for example). And not New York doctors, who often confuse other illnesses with heart attacks. The most common causes were anxiety, fear, and greater disruption of sleep-wake cycles than elsewhere. And this was before the September 11 attacks. Naturally, like all other native New Yorkers, this study gives me a kind of perverse pleasure, and I cannot argue with its conclusions.
¹ I once received a letter from the Chief Medical Examiner of Vermont describing his investigation of what he believed to be a case of stress-induced cardiac arrest: an 88-year-old man with heart disease died of a heart attack next to his favorite tractor, barely able to get out from home. His 87-year-old wife was found dead in the barn, also having died of a heart attack, but later than he did (she had no previous history of heart disease, and the autopsy found no abnormalities). Next to her lay a bell, with which she called him into the house to have dinner.
² Don't be afraid of this jargon. In ventricular fibrillation, half of the heart, called the ventricle, begins to contract rapidly and chaotically, but does not pump blood as well as it should.
it is related to the sympathetic nervous system and occurs more often in damaged heart tissue than in healthy tissue. A person can die from sudden cardiac arrest even if he has never suffered from heart disease, despite increased blood flow in the coronary vessels; however, autopsy often shows that such people had significant atherosclerosis. Sometimes completely mysterious cases occur when seemingly healthy 30-year-old people who do not suffer from atherosclerosis become victims of sudden cardiac arrest.
Fibrillation appears to be the most important event in sudden cardiac arrest, based on animal studies (for example, ten hours of stress makes a rat's heart more vulnerable to fibrillation over the next few days). As one of the reasons, the muscle of a diseased heart becomes more electrically excitable and therefore prone to fibrillation. Additionally, the activation of heart-stimulating factors becomes erratic during times of extreme stress. The sympathetic nervous system sends two symmetrical neural pathway projections to the heart; theoretically, during strong emotional arousal, these two projections are so activated that they lose coordination with each other - severe fibrillation compresses the chest, and the person falls.
Deadly pleasures
Among the various causes of sudden cardiac arrest, one is especially interesting: an important victory or intense joy. Consider the scenario where a person dies after learning that he won the lottery, or when death occurs during sex - but here the person at least dies happy. (Several decades ago, such a case occurred with the former vice president of the United States; the medical details of the incident became the object of especially careful study because the patient was found not in the company of his legal wife.)
The possibility of dying from pleasure seems absurd. Aren't stress-related diseases caused by stress? Can a joyful event destroy us in the same way as a sudden grief? The fact is that the manifestations of both are very similar from a physiological point of view. Intense anger and intense joy have different effects on the physiology of the reproductive system, on growth function, and most likely on the immune system; but regarding the cardiovascular system, their effects are very similar. Once again, we are dealing with the basic concept of stress physiology, which explains similar reactions to different situations: it doesn’t matter if we are too hot or too cold, we are prey or predator, some organs of our body, including the heart, do not care which way we are knocked out of allostatic equilibrium, they are only interested in the degree of imbalance. Whether we weep and bang our heads against the wall in grief or jump and scream in ecstasy of joy, both make serious demands on a sick heart. In other words, our sympathetic nervous system probably has roughly the same effect on our coronary arteries whether we're experiencing a blind rage or a mind-blowing orgasm. Diametrically opposed emotions can have remarkably similar physiological expressions (this reminds me of the famous quote by Elie Wiesel, the writer and Nobel laureate and Holocaust survivor: “The opposite of love is not hatred. The opposite of love is indifference”). When it comes to the cardiovascular system, anger and ecstasy, grief and joy, become equal challenges to allostatic balance.
Women and heart disease
Although men are more likely to have heart attacks than women, heart disease is the leading cause of death among women in the United States, accounting for 500,000 deaths per year (compared to 40,000 deaths per year from breast cancer). And the incidence of heart disease among women has been rising, while mortality from cardiovascular disease among men has been declining for decades. In addition, while the severity of heart attacks in women is equal, they are twice as likely to cause disability as in men.
What does this data say? The increased likelihood of disability after heart attacks may be an epidemiological incident. Women are still less likely to have heart attacks than men and, on average, begin having heart attacks ten years later. Therefore, if a man and a woman have the same serious heart attack, the woman will statistically be ten years older than the man. And therefore it will be more difficult for her to recover.
But what about the rising incidence of heart disease among women? It is associated with various factors. In the United States, obesity is a serious problem primarily among women, and it increases the risk of heart disease (as we will see in the next chapter). Additionally, although smoking rates in the United States continue to decline, they are falling more slowly among women than among men.
Naturally, stress also plays an important role. Kaplan and Carol Shively studied the subordination hierarchy of female monkeys and noted that chronically subordinate animals developed atherosclerosis twice as often as dominant females, even on a low-fat diet. Evidence related to social hierarchy has also been obtained from human studies. The increase in the number of cardiovascular diseases in women began during the period when they began to actively work outside the home. Maybe this causes stress? Some studies have shown that working outside the home does not increase the risk of heart disease in women. Provided that they are not busy with clerical work. And provided that they have a good relationship with the boss. So try to figure it out. And just to dispel the myth that as more women work outside the home, the more men take on household duties, another factor that increases the risk of heart disease in women who work outside the home is having children.
Why does stress increase the risk of cardiovascular disease in female primates and women? Due to the actions of our "prime suspects" - too much stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system, too much production of glucocorticoids. But there is an additional factor that causes very controversial assessments - estrogen.
When the previous edition of this book was published, no one was interested in estrogens. It has been known for decades that estrogen protects against cardiovascular disease (as well as stroke, osteoporosis, and possibly Alzheimer's disease), mainly because estrogen acts as an antioxidant, ridding the body of harmful oxygen free radicals. This explains why serious heart disease in women often occurs after menopause, when estrogen levels drop. This was widely known and was one of the rationales for estrogen hormone therapy after menopause.
The important role of estrogens in protection against cardiovascular diseases is indicated not only by morbidity statistics among the population, but also by serious experimental studies. As we will see in Chapter 7, stress causes estrogen levels to decrease, and Kaplan's subordinate female monkeys had estrogen levels as low as ovariectomized monkeys. And if a female who had had a low status for many years was given synthetic estrogen, raising its level to the level characteristic of dominant females, then her risk of atherosclerosis decreased. Remove the ovaries of a high-status female and she risks developing atherosclerosis. The conclusions of such studies seemed clear.
Then, in 2002, a landmark report was published based on the Women's Health Initiative's study of thousands of women. Its purpose was to evaluate the effect of eight years of hormone therapy after menopause, when women took estrogens and progestins. This was expected to demonstrate exemplary protective effects of such therapy against cardiovascular disease, stroke and osteoporosis. After five years of research, scientists mixed up who took the hormone and who took the placebo. The ethics committee of this gigantic project called for it to be stopped. Why do you think? Maybe the benefits of estrogen and progestin were so obvious that the committee decided it was unethical to give half the women just a placebo? No. It turned out that estrogens and progestin increase the risk of heart disease and stroke so much (while still protecting against osteoporosis) that continuing the study is not only unethical, but simply dangerous to the lives of the subjects.
It was a real bomb. The main news of the year. Similar trials have been stopped in Europe. Pharmaceutical companies began to stop production. A huge number of women who have entered menopause have begun to doubt that they need estrogen replacement therapy.
How could this happen? Conflicting results from years of clinical statistics and careful laboratory testing on the one hand, and extensive, excellent research on the other? One of the most important factors was that, for example, Kaplan's experiments studied only the effect of estrogen, while the most extensive clinical study studied both estrogen and progestin. Perhaps that makes all the difference. In addition (here is an example of the petty quibbles that scientists love and drive everyone else crazy), the dose of hormones mattered, as well as the type of estrogen (estradiol, estrol or estrone, synthetic or natural hormone). Finally, and this is also an important point, laboratory studies were based on the hypothesis that estrogen protects against the onset of atherosclerosis, but cannot get rid of it once it has already occurred. This is quite logical, because, given our Western style of nutrition, atherosclerotic plaques begin to form in us after 30 years, and not after menopause, that is, at 50 or 60 years.
The debate is still ongoing. It may be that taking estrogen after menopause does not protect against cardiovascular disease, but it is likely that estrogen produced in a woman's body at a younger age does. And stress, by reducing estrogen levels, can thereby contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Death by Witchcraft
It's time to explore a topic that is very rarely discussed in the scientific community. Proven examples of death from witchcraft are known in all traditional non-Western cultures. The person ate forbidden food, insulted a leader, slept with someone he shouldn't have slept with, or committed an unacceptable act of cruelty or blasphemy. Outraged villagers call a shaman, he performs some ritual manipulations in relation to the offender, sculpts a voodoo doll or “curses” the person in some other way. And the intruder falls dead.
Ethnobotanist Wade Davis and cardiologist Regis Desilva of Harvard researched this topic¹. Davis and Desilva object to the term "death by witchcraft" as it strongly smacks of Western condescension towards "native" loincloths, nose bones, etc. They prefer the term "psychophysiological death" and note that in many cases even this the term is not entirely accurate. Sometimes the shaman knows which one
________________________________________________
¹ Wade Davis is horror fans' favorite nerd. As detailed in the references section, his previous research focused on the possible pharmacological basis for the existence of zombies (humans in a trance without their own will) on the island of Haiti. Davis's Harvard doctoral dissertation on zombification was first published under the title "The Serpent and the Rainbow" (The Serpent And. The R in bow), and then it was made into a creepy horror film with the same name - the dream of any graduate student, the topic of the dissertation which raises doubts among reviewers.
villagers is seriously ill, and claims to have “cursed” him to confirm his reputation. Or a shaman can simply poison a person in order to thereby confirm his “magical” abilities. It also happens that a shaman curses a person in front of everyone, and the whole village says: “The curse works; this man is doomed, so don’t waste food and water on him.” A person who is not allowed to eat and drink simply dies of hunger; However, another curse has come true, and the shaman increases the fee for his services.
Nevertheless, cases of psychophysiological death do occur. They aroused the interest of some of the great physiologists of the last century. Walter Cannon (the man who invented the concept of “fight or flight”) and Kurt Richter (a great authority in the field of psychosomatic medicine) interpreted the mechanisms of psychophysiological death differently. Cannon believed that its cause was an overactivity of the sympathetic nervous system: a person is so excited by the fact that he was cursed that his sympathetic system “winds up”, narrows the blood vessels, they burst and this leads to a fatal drop in blood pressure. And Richter thought that the reason for such death was the overactive work of the parasympathetic system: a person, realizing the seriousness of the curse, simply gives up. At the same time, vagus nerve activity increases and the heart rate slows, until the heart stops, due to what he called a “vagal storm.” Both Cannon and Richter were never able to test their theories, since they were never able to find anyone who died from psychophysiological death, witchcraft or anything like that. It later turned out that Cannon was probably right. The heart almost never stops directly from a “vagal storm.” Davis and Desilva suggest that such cases are simply obvious examples of death from sudden cardiac arrest, when sympathetic activity leads to ischemia and fibrillation.
This is very interesting and explains why psychophysiological death can occur in a person who already has heart disease. But psychophysiological death in traditional societies has a strange feature: it can happen to a young person who is unlikely to have any cardiac pathology. This mystery remains unsolved, perhaps indicating a hidden risk of heart disease that we are not even aware of, or perhaps it demonstrates the power of cultural beliefs. As Davis and Desilva write, if faith can heal, it can also destroy.
Personality and Heart Disease: A Brief Overview
Two people find themselves in the same stressful social situation. But only one of them develops hypertension. Two people have been going through ups and downs for ten years. But only one of them develops cardiovascular disease.
Such individual differences may be due to the fact that one person already has a pathology of the cardiovascular system, for example, poor patency of the coronary arteries. Perhaps it is also due to genetic factors influencing the mechanics of the system - the elasticity of blood vessels, the number of norepinephrine receptors, etc. Perhaps the difference is the presence of risk factors - which of them smokes or eats more foods rich in saturated fats? (Interestingly, individual differences associated with such risk factors explain less than half the variance in heart disease.)
When two people face the same stressors, big or small, their risk of cardiovascular disease may also be related to their personality traits. In Chapters 14 and 15, we'll look at some of these factors—how hostility, Type A personality, and clinical depression increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Unfortunately, such personal risk factors have a rather strong influence. But fortunately, there is often something you can do about it.
This discussion is the first example of the style of analysis that we will use in subsequent chapters. In a short-term physical emergency, the cardiovascular response is vital. But in a situation of chronic stress, the same reaction becomes dangerous. Its negative effects are especially harmful when interacting with the adverse effects of an overactive metabolic stress response, which we will discuss in the next chapter.
Previous – Chapter 3: Stroke, Heart Attacks and Death by Witchcraft | Next – Chapter 4. Stress, Metabolism and Asset Liquidation
Does your heart really hurt, or does it just seem like it?
Heart pain in the presence of neuroses can be considered a natural phenomenon. Considering that patients suffering from neurosis are characterized by pronounced emotionality, cardialgia in such patients can often be provoked by anxiety, conflict or simple expectation. Thus, everything is built on emotions, not only on negative impressions, but also on positive ones. For example, upon learning good news, a person clutches his heart.
How do pain in the heart manifest itself during neurosis?
- Pharyngeal neurosis: can your throat hurt from nerves?
The main manifestations of cardiac panic
The difference between this process within the framework of cardiac neurosis is pronounced palpitations, tachycardia, painful discomfort under the ribs, heaviness in the chest, a feeling of embossing, a feeling as if there is not enough air and a panicky fear of death. Symptoms often include weakness, excessive sweating, fatigue, tremors in the limbs, and a feeling as if about to faint. Also, in some cases, the leading symptom is excitement and an urgent desire to run somewhere - to the street, to the hospital, to where there are people.