What is cardioneurosis and is it dangerous for humans? Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD) and cardioneurosis – similar concepts or not? What psychological factors can provoke the development of these psychosomatic disorders? The most typical symptoms of cardiac neurosis and methods of its treatment. Which specialists should you contact and when should you start treatment in order to prevent panic attacks and a significant deterioration in your quality of life? We asked these and other questions on the topic of functional disorders of the cardiovascular system to the Chief Medical Psychiatrist, Psychiatrist-Narcologist and Psychotherapist Vladislav Sipovich.
Tell us in more detail about vegetative failures, what causes them and how they manifest themselves?
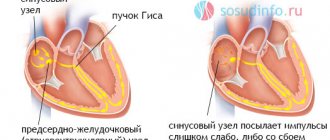
To begin with, we should remember that the main function of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is to regulate the activity of all internal human organs. Its two departments are responsible for this, acting in different directions: • Sympathetic, when activated, there is an increase in heart rate (tachycardia), increased blood pressure and body temperature, tremor, etc. • Parasympathetic, responsible for slowing the heart rate (bradycardia), lowering blood pressure and temperature , decreased activity, etc.
With balanced and synchronized work of both departments, the body functions like a well-oiled clockwork mechanism. Adequately responds to environmental changes, is resistant to stressful situations, has a strong immune system, all its reactions are aimed at protecting the body from negative influences and survival.
When the coordinated work of the ANS departments is unbalanced, the body loses many of its advantages in this duel with the outside world, and with pronounced autonomic dysfunction, various diencephalic crises can develop: • With predominant and excessive activity of the sympathetic ANS, a sympathoadrenal crisis occurs in the form of an attack of headache and heart pain, tachycardia , increased blood pressure and temperature, chills, flushing or pallor of the face. All these phenomena are often accompanied by fear of death and anxiety for one’s life. And this is quite understandable. After all, normally a person does not feel his heart, except under severe anxiety and stress. You can imagine how he feels the whole range of symptoms that have befallen him, especially if he is experiencing a crisis for the first time. Fear can be so strong that it forever settles in a person’s memory and plunges him into constant anxious anticipation of a repetition of the attack. It turns out to be a vicious circle: attack → fear → anxiety → new attack. It is almost impossible to interrupt this cycle without the help of specialists and appropriate treatment. • With hyperactivity of the parasympathetic division of the ANS, we are dealing with the so-called vagoinsular crisis. Its main manifestations are sudden severe weakness up to fainting, darkening of the eyes, sweating, dizziness, nausea, decreased blood pressure and body temperature, bradycardia (slow heart rate).
With particularly severe vegetative failures, accompanied by severe fear and panic, we are already dealing with panic attacks, which are easier to prevent than to stop. But this is a topic for another discussion.
Autonomic instability most often develops after infectious diseases, head injury, severe stress, during hormonal changes and taking hormonal medications.
What is characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia
It is important for a VSD patient to understand that his arrhythmia is of a functional nature. And no matter where exactly and in what quantity it occurs, one thing is clear: the heart is healthy, and the reason lies in something completely different.
Extrasystole in such patients manifests itself when a large amount of adrenaline enters the blood. But as soon as it decreases to normal, all sensations subside. That is, the problem is temporary and reversible. But patients tolerate it very hard. For them, this is like death: heart failures catch them suddenly, they can be repeated for several months and even years, until the cause is eliminated.
At this moment, a person is seized by a feeling of fear. He begins to choke, his legs give way, and he may lose consciousness. The patient becomes pale, begins to rush about, and scream. The sensation in the chest resembles a blow to the rib cage.
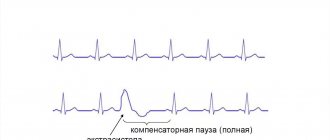
An even greater fear is the compensatory break after an extraordinary compression. The patient fears that his heart will stop. It seems to him that he will die, and this cannot be avoided.
If the excitement intensifies, then the symptoms worsen. Atrial fibrillation occurs. It seems that the heart works outside the regime, chaotically, as it pleases. Fortunately, this condition rarely occurs.
Cardioneurosis, what symptoms suggest its presence in the patient?
It should be noted that the symptoms of this disorder are quite diverse and do not always fit into its typical picture. According to the main clinical manifestations, the symptoms of cardioneurosis are differentiated into the following types: • Cardialgic, accompanied by pain and discomfort in the heart area, rapid heartbeat, sensation of blood pulsation throughout the body, arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances), etc. • Respiratory, associated with the respiratory system and manifested increased breathing, sensations of lack of air, a lump in the throat, difficulties when trying to take a full breath, as well as unexpectedly occurring deep breaths, as if compensating for the lack of air. • Dystonic, expressed by sharp fluctuations in blood pressure of the hypotonic or hypertonic type. • Associated with impaired thermoregulation, leading to temperature fluctuations of the subfebrile type (up to 37-38 degrees) or hypothermic type with a decrease to 35 degrees. • Dyspeptic, manifested by disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dyskinesia, belching, flatulence, etc. • Asthenic – irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbances, lethargy, general weakness, development of frailty, headaches, dizziness, persistent bad mood, decreased activity, etc. With VSD, a person has difficulty riding in transport, is characterized by severe weather dependence, and is prone to fainting and so on.
The most common symptoms of impaired autonomic regulation in cardioneurosis are the following: • Excessive sweating. • Hot flashes alternating with feelings of chilliness. • A condition described by patients as “internal trembling”, “tremor throughout the whole body”. • Numbness of the hands and feet, changes in sensitivity and pain in different parts of the body. • Irritable bladder syndrome, manifested by a frequent urge to urinate.
The mental sphere also suffers from cardioneurosis. Against this background, depression, hypochondriacal moods, and various phobias can develop, including fear of crowds (demophobia) and open spaces (agoraphobia), especially without the presence of accompanying persons.
How does pain in the heart during ischemia differ from cardioneurosis?
Experienced cardiologists can name a number of differences in the pain syndrome that manifests itself in coronary heart disease (CHD) and cardiac neurosis. Here are the main ones:
- With cardioneurosis, the pain has a clear localization, and with ischemic heart disease, pain can cover the entire chest and even radiate to the back area.
- A painful attack with cardioneurosis, as a rule, lasts less than an hour, and with ischemia it lasts much longer (from several hours to several days).
- With cardiac neurosis, pain arising from psycho-emotional stress can easily be relieved after relaxation, which does not happen in the case of cardiac ischemia.
- Nitroglycerin is effective in relieving pain from ischemia, but does not help with cardioneurosis, in which sedatives and hypnotics help.
- During studies (ECG, ultrasound), specialists in functional diagnostics of medical centers confidently diagnose the presence of pathological changes from coronary artery disease, and if pain in the heart is neurotic in nature, then violations are not detected during such studies.
What examinations are necessary to make a reliable diagnosis of cardioneurosis?
In order to exclude organic heart pathology and other serious diseases hidden behind a variety of symptoms, the patient must be observed for at least 2 months. At the same time, the connection of attacks with stressful situations and circumstances that have a stimulating effect on the patient’s psyche is of decisive importance in favor of cardioneurosis. Only after excluding structural changes and making sure of the functional nature of the symptoms can a diagnosis of cardioneurosis be made.
Specifically, the examination plan should include the following activities: • Detailed and thorough history taking. • Physical (physical) examination of the patient with determination of signs of asthenia, excessive sweating, skin color, etc. • Electrocardiographic examination (one-time and in the form of daily monitoring), ultrasound of the heart, ultrasound of the cervical vessels, etc. • Breathing tests to study the function of external respiration . • Clinical and biochemical blood test with determination of AST, LDH, lipid profile, C-reactive protein, creatine kinase, thyroid hormones and potassium. To exclude the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction, cardiac troponins and myoglobin are determined. • FGDS for severe dyspeptic syndromes. • Electroencephalogram for studying the brain and identifying its pathologies (epilepsy, neoplasms, inflammatory processes and vascular disorders).
Consultations with specialized specialists are required - cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist, gastroenterologist, etc.
Types of pathology and its symptoms
In medical sources you can find various names for cardioneurosis, such as: cardiac neurosis or cardiac neurosis, neurocirculatory, vegetative-vascular dystonia, functional cardiopathy or psychovegetative syndrome. These are all different names for the same disease.
The main forms of manifestation of cardioneurosis are:
1. Cardiological, which is expressed by attacks of pain in the heart.
- Panic. This form is characterized by manifestations of a panic attack.
Prevalence
Symptoms of cardioneurosis affect from 21 to 56% of the population. Among hospital patients, cardialgia of a neurotic nature is detected in 80%. At an appointment at the clinic - up to 35%.
In specialized cardiology departments, after a detailed examination, the final diagnosis of “Cardioneurosis” is made in 15 to 30% of discharged patients. Over the past 10 years, there has been an increase in the frequency of detection of pathology.
Among people with various chronic diseases, the frequency of cardioneurotic disorders is 4.7%, often “competing” in terms of complaints with the underlying disease.
HEALING MIXTURE
Myocardial infarction
I would like to offer a recipe for strengthening the heart muscle and nervous system.
Take 2 tbsp. spoons of nettle leaves, valerian root, coltsfoot leaves, lily of the valley flowers and leaves, mint leaves, walnut leaves, 1.5 tbsp. spoons of yarrow flowers, flowers and leaves of marshmallow, linden blossom, oregano, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of chamomile and 4 tbsp. spoons. crushed rose hips. Mix the herbs thoroughly. 3 tbsp. spoons of the mixture pour 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 4 hours, strain, squeeze out. Add the juice of one lemon and 1-2 teaspoons of honey.
Divide the resulting product into 3 parts and take warm 20 minutes before meals.
The infusion can be drunk by people who have suffered a myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, or hypertension. The medicine is useful for patients with increased nervous stress and neuroses.
Treatment of neurosis
During an attack of cardioneurosis, it is very important to provide the patient with proper first aid. Having noticed signs of neurosis, loved ones need, first of all, to calm down themselves, not to fuss, not to make sudden movements, to speak calmly and measuredly. Sometimes a simple conversation can relieve pain, which will distract the patient from his worries. It is also important to do the following:
- Place the person in a well-ventilated area and allow access to air.
- Remove or unfasten restrictive clothing.
- Measure your pulse and, if possible, your blood pressure.
- Give a sedative (tincture of valerian, motherwort, Persen, Novopassit and others).
If a person does not feel better within 15 minutes or his condition worsens, you need to call an ambulance. But even if the attack passed quickly enough, the person should definitely visit a cardiologist. Firstly, there is a possibility that the pain was caused by diseases of the cardiovascular system. Secondly, heart neurosis also requires treatment, since it significantly affects well-being and over time can provoke serious illnesses.
For confirmed cardioneurosis, therapy is prescribed individually, after a complete examination and identification of the cause. Self-medication is prohibited and can only worsen the condition - the patient will stop attacks of neurosis, but will not be able to reduce their number, moreover, each time they will be experienced more emotionally.
When should you see a doctor?
- If a decrease in mood has been observed for more than two weeks, and attempts at self-treatment have been ineffective.
- If you have thoughts about not wanting to live or suicidal thoughts.
- If a depressive state significantly disrupts the usual course of life: you cannot work, fully communicate with your family, or enjoy what previously brought joy.
You can contact a psychiatrist confidentially. Information about the fact of treatment, not to mention the diagnosis and treatment, is a medical secret: it is not reported to work, it is not disclosed. It is better to diagnose depression on time and begin treatment than to bring it to advanced stages.
Literature
- BAUER M., PFENNIG A., SEVERUS E., WYBROW P.S., ANGST J., MÜLLER H.-YU CLINICAL RECOMMENDATIONS OF THE WORLD FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES OF BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY FOR BIOLOGICAL THERAPY OF UNIPOLAR DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS PART 1: ACUTE AND CONTINUED TREATMENT OF UNIPOLAR DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS AS OF 2013//MODERN THERAPY OF MENTAL DISORDERS Number: 4 Year: 2015 Pages: 33-40
- Antidepressant therapy and other treatments for depressive disorders. Report of the CINP Working Group based on a review of the evidence. M., 2008; 215 p.
- Baklanov V.V., Anikeeva A.G., Karataeva Zh.E. METHODOLOGICAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION IN HEALTH INSTITUTIONS PROVIDING PRIMARY HEALTH CARE TO THE POPULATION Syktyvkar, 2011
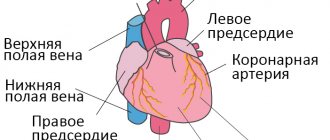
Ultrasound of the heart
With organic, cardiac dyspnea, ultrasound reveals disturbances in either the diastolic (relaxation function) or systolic (contractile) function of the heart.
In respiratory neurosis, both functions of the heart are preserved.
▶️️ Cardiac shortness of breath is treated together with the underlying disease. Diuretics in adequate doses, ACE inhibitors, and beta-blockers are prescribed.
▶️ The success of treating respiratory neurosis is 90% a way of life.
The patient is convinced that the symptom is harmless, and distraction therapy is recommended.
Physical activity, good sleep, and a change of environment have an effect.
Medicines include sedative herbs and light daytime tranquilizers.
If the course persists, the patient is recommended to consult a psychotherapist.
Please note that medications must be prescribed by a DOCTOR
Why can't you take antidepressants without a prescription?
- Only a doctor can assess the risk of side effects for a particular patient.
- Different antidepressants have different nuances of therapeutic action. If the medicine is chosen incorrectly, at best it will not help, at worst it will harm.
- Dose selection is carried out individually. If you increase the dose too quickly on your own, you can experience a lot of unpleasant consequences.
- Cancellation should also be carried out gradually and under the supervision of a doctor. Otherwise, you risk withdrawal symptoms.