Medicine is a very multifaceted science, filled with many interesting terms. Many of them have one or more synonyms, which may sound completely different, but mean the same concept. One of them is ROE. The decoding of this abbreviation sounds like the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction. That's what doctors called her before. Out of habit, older generation doctors still use this term today. This introduces certain misunderstandings among patients who do not know the basics of medical terminology, and even more so, the correct assessment of such an indicator.
What is ROE and its significance for the body
What is RO ESR (ESR)—erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The analysis is one of the main basic blood tests. A referral for examination is issued upon initial consultation with a doctor, before medical procedures or surgical interventions.
Laboratory essence of the method: healthy red blood cells precipitate slowly. Aggregated (glued) red blood cells have a greater mass and settle at a faster rate. Factors that indicate the activation of the immune response to pathology in the body lead to the sticking of red blood cells.
The erythrocyte sedimentation reaction is a nonspecific laboratory indicator that indirectly indicates pathological disorders in the body. Based on ROE, a final diagnosis cannot be made, but the direction of further research can be determined.
What do leukocytes and ESR mean?
Leukocytes, also known as white blood cells, are the general name for blood cells that are quite different in appearance and function, but nevertheless work together on the most important problem - protecting the body from foreign agents (mainly microbes, but not only). In general terms, white blood cells capture foreign particles and then die along with them, releasing biologically active substances, which, in turn, cause the symptoms of inflammation familiar to us all: swelling, redness, pain and fever. If the local inflammatory reaction is very active and leukocytes die in large numbers, pus appears - this is nothing more than the “corpses” of leukocytes that died on the battlefield with infection.
Within the team of leukocytes, there is its own division of labor: neutrophils and monocytes are mainly “responsible” for bacterial and fungal infections, lymphocytes and monocytes for viral infections and the production of antibodies, eosinophils for allergies.
On the analysis form you will see that neutrophils are also divided into band and segmented . This division reflects the “age” of the neutrophils. Rod cells are young cells, and segmented cells are mature, adult cells. The more young (band) neutrophils on the battlefield, the more active the inflammatory process. It is the bone marrow that sends young soldiers who are not yet fully trained and have not been fired to war.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a measure of the ability of red blood cells to stick to each other and fall to the bottom of a test tube. This rate increases when the content of inflammatory proteins, primarily fibrinogen, increases. As a rule, an increase in ESR is also considered as an indicator of inflammation, although there are other reasons for its increase, for example, when the number of red blood cells in the blood decreases (with anemia).
The table is normal
The analysis is deciphered taking into account norms that are different for each age. The high variability of norms in women is associated with changes in hormonal levels during different periods of life.
Standards for children:
| Child's age | Floor | ESR norm mm/hour |
| 0-1 month | m/f | 2-3 |
| 1-12 months | m/f | 2-8 |
| 1-5 years | m/f | 4-12 |
| 5-10 years | m/f | 4-12 |
| teenagers | M F | 1-10 2-15 |
For men, the ROE indicator is in the range of 2-15 mm/hour.
In women, ESR has its own characteristics:
- indicators are on average higher than those of men;
- in the morning the indicator increases;
- large variation in the indicator at different periods of life;
- severe pathology is indicated only by long-term and significant deviations of ESR from the norm.
The ROE norm in the blood of women by age is studied in flasks like these. Table below
ROE (the norm for women by age), a table with the value of which shows their change, can range from 2 to 45 mm/hour.
| Age | ESR norm mm/hour |
| Children under 13 years old | 4-12 |
| Teenagers 14-17 years old | 3-18 |
| Young women 18-30 years old | 2-15 |
| Middle-aged women 31-40 years old | 2-20 |
| Middle-aged and perimenopausal women 41-50 years old | 2-30 |
| Women 51-60 years old, menopause, menopause, postmenopause | 2-30 |
| Women over 60 years old | 2-40 |
| pregnant women | 2-45 |
As can be seen from the table, the ROE norm can differ significantly at different age and physiological periods of a woman. The ESR indicator indicates physiological and pathological abnormalities in the body.
Age-related changes in the female body after 60
| CHUZ "RZD-Medicine" Vikhorevka" |
The health of a woman after 60 years largely depends on herself. In order to stay healthy and vigorous for as long as possible, it is necessary to monitor the main indicators of the body’s activity and constantly engage in health improvement. This includes a healthy diet, an active lifestyle, weight control and, if necessary, rehabilitation courses.
Age-related changes in the female body after 60
At 60, a woman is postmenopausal. Her hot flashes and changes in blood pressure (BP) stopped, her mood stabilized, and her overall health improved. But against this background, new problems arise related to age-related changes. All problems are surmountable, you just need to be aware of them and adhere to the generally accepted recommendations of specialists for their correction.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis in women begins late; the most dangerous age in this regard begins after 55-60. The first signs of angina pectoris appear in the form of attacks of acute short-term pain in the heart. The condition is dangerous because blocking the access of arterial blood to the heart muscle (myocardium) can lead to necrosis of its area (myocardial infarction). And the same process in the vessels feeding brain tissue leads to the development of ischemic stroke.
Arterial hypertension
Changes in blood pressure due to hormonal changes at this age are almost no concern. Stably high blood pressure may appear - a threat of developing arterial hypertension and associated hemorrhagic strokes (bleeds in the brain).
Mineral metabolism disorders
Osteoporosis develops: bone tissue, with estrogen deficiency, intensively loses calcium. Bones become brittle and prone to fractures. A fracture of the femoral neck is especially dangerous at this age: the bones hardly heal, and many older people become disabled after this.
A lack of potassium and magnesium negatively affects the condition of the heart muscle: angina attacks intensify and heart rhythm disturbances appear.
Decreased immunity
Immunity (general and local - skin and mucous membranes) is reduced due to metabolic disorders. After 60 people are more likely to suffer from colds, and the risk of acute infections turning into chronic infectious and inflammatory processes increases. Decreased immunity also contributes to the development of tumor processes.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine and joints
Metabolic disorders lead to the destruction of cartilage tissue first, and then the bones of the spine (osteochondrosis) and joints (osteoarthrosis) are injured and destroyed. All this is accompanied by pain, first when moving, and then by other disorders. Cervical osteochondrosis, complicated by compression of the vertebral arteries carrying blood to the brain, is especially dangerous. Cervical migraine and fainting appear.
Diabetes
The disorder begins due to the fact that tissues cannot absorb glucose. Type 2 diabetes mellitus develops. If it is not compensated for, severe dehydration develops. Due to glucose deficiency, all types of metabolism and the functioning of internal organs are disrupted. The formation of new cells (including immune cells) is disrupted, and atherosclerosis progresses.
Excess body weight
Age-related changes in fat metabolism and a general slowdown in metabolic processes in women contribute to the development of obesity, which negatively affects the entire body. Maintaining a normal weight is one of the main tasks after 60.
Genitourinary organs
The problems are associated with the increasing dryness of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs, which causes thinning of the mucous membranes and suppression of their barrier functions: they are easily injured and do not prevent the penetration of infection. Sometimes this is accompanied by weakness of the sphincter muscles - a circular muscle that prevents involuntary urination. As a result, a woman suffers from urinary incontinence, cystitis, infectious and inflammatory processes of the external genital organs, which, with insufficient general immunity, can spread to the internal genital organs.
Thyroid dysfunction
The thyroid gland in women after 60 gradually reduces the secretion of its hormones, and a tendency to develop hypothyroidism appears. It manifests itself in increased dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, an increase in body weight and a gradual decrease in mental abilities.
How to stay healthy at 60
Health at 60 years old must be constantly maintained at the required level. In order for a woman to stop noticing her age, she needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, adhere to proper nutrition and monitor her weight and basic indicators of the functioning of the body for the timely detection of serious diseases.
The psychological attitude is also very important: you need to remember about age-related changes in your body, but you should not forget about the joys of life. An optimistic attitude helps improve the quality of life.
Regular medical examination is mandatory
Every woman over 60 years of age must undergo an annual medical examination. Medical examination includes examinations by a therapist and specialists, examination of key indicators, changes in which indicate serious disorders in the body. If you carry out medical examinations regularly, you can promptly notice small changes and correct them with the help of diet, therapeutic exercises or drug therapy. This will allow you to stay healthy for a long time.
What tests need to be taken and the norms of indicators
Some vital signs of the body are of great importance during the aging period. They give an idea of how physiologically this process occurs. Small periodic fluctuations in indicators do not play a big role. Sustainable change is important.
Blood sugar
Normally it is 3.3 - 5.5 mmol/l. This indicator needs to be monitored. If there is a suspicion of diabetes mellitus (constant thirst and frequent excessive urination), then blood sugar testing should be done outside of medical examination.
Blood cholesterol
Cholesterol levels can tell a lot about the threat of developing or progressing atherosclerosis. This disease does not threaten everyone; it is mainly associated with family history. But you need to control your cholesterol levels. Three types of cholesterol are studied: total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and NSAID cholesterol. LDL and HDL are lipoprotein (protein-fat) complexes that transport cholesterol from the liver to tissues that need it vitally for metabolism.
Cholesterol is the same everywhere, but the complexes are different: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) is a “leaky” carrier; it loses cholesterol during transportation, which is deposited on the walls of blood vessels in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. It is LDL that is most abundant in the blood. HDL (high density lipoprotein) carries cholesterol without loss, this cholesterol enters into metabolic processes and prevents the development of atherosclerosis. But it is not enough, which is why it is so important to consume foods that maintain high levels of HDL in the blood (vegetable oils).
Cholesterol standards:
- general - 4.45 - 7.7 mmol/l;
- as part of LDL - 2.59 - 5.80 mmol/l;
- as part of HDL - 0.98 - 2.38 mmol/l.
Pressure
Blood pressure is one of the most important health indicators. After 60, changes in blood pressure are rare; pressure stabilizes at 130/80 mm Hg. But these are average numbers, they are individual for each woman: the norm may be 140/85 and 110/80. You should focus on your well-being. A rise in lower (diastolic) pressure and a decrease in pulse pressure (the difference between upper and lower) are dangerous. If your lower blood pressure is consistently above 90 and you are experiencing headaches, you should consult a doctor to maintain your health.
Normal ESR in the blood
ESR or erythrocyte sedimentation rate is an indicator, an increase in which reflects the presence of an inflammatory process or a malignant tumor in the body. The generally accepted standard for ESR is 2 – 15 mm Hg. But there are also age standards. After 60 years, you can have a much higher upper level of ESR, as physiological changes in the body and chronic diseases accumulate. Each individual case of high ESR should be dealt with individually.
Blood creatinine
Creatinine is a residual product of protein metabolism formed in the liver, pancreas and muscle tissue. Its daily content in blood and urine is constant and corresponds to the volume of skeletal muscles. An increase in creatinine in urine indicates kidney disease, injuries or diseases of the muscular system, and dehydration. A temporary increase in this indicator can occur when taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, or eating large amounts of animal proteins (meat, fish, dairy products).
Standards for women over 60:
- blood creatinine: 38-70 (µmol/l)
- daily excretion of creatinine in urine: 7.1-15.9 mmol/day. (0.8-1.8 g);
- residual nitrogen: 14.3 - 28.6 mmol/l.
Hemoglobin is normal after 60
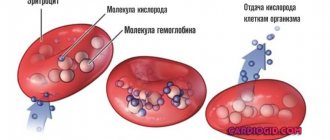
Another important indicator is hemoglobin. This iron-containing protein carries oxygen to tissues, so a decrease in its content in the blood will affect the condition of all organs and tissues. The age norm of hemoglobin is 117 – 160 g/l, which is slightly higher than after 50 years. The increase in the norm is associated with the absence of menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding after 60 years.
TSH and its norm in elderly women
The pituitary gland is the main endocrine gland that regulates the work of other glands by secreting its hormones. The pituitary gland itself is under the same control of the hypothalamus.
At the age of 60 years and older, the thyroid gland significantly reduces the secretion of its thyroid hormones (TG) - thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Therefore, the pituitary gland works hard, producing the maximum amount of thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH), which stimulate the production of thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
The condition of hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) is very harmful to the body, especially to the brain, as it leads to the development of dementia. Therefore, it is important to monitor the levels of TG and TSH in the blood. The first indicator will be reduced, and the second will be overestimated compared to other age categories.
TSH norm: 1 – 10 mU/l. Exceeding the norm even in the absence of symptoms of the disease indicates the presence of subclinical (asymptomatic) hypothyroidism.
Intraocular pressure and its norm
Aging is often accompanied by an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) and impaired outflow of intraocular fluid. If you do not pay attention to unpleasant symptoms for a long time, optic nerve dystrophy occurs with the development of blindness. Symptoms of increased IOP are: headache, pain in the eyeballs, blurred vision, flashing “floaters” before the eyes, deterioration of lateral vision.
But low IOP is also bad; it can lead to a significant decrease in vision. Symptoms: rare blinking, sunken eyeballs, decreased vision.
The normal IOP ranges from 10 to 23 mm Hg. Art.
How to maintain health and beauty after 60?
After 60, a woman feels better than at fifty-five, when she was still bothered by hot flashes and changes in blood pressure. The changes taking place are more dangerous, although they do not cause such unpleasant sensations. But all these changes in the body can be corrected, trying to keep aging within physiological limits and suppressing the development of pathological processes.
Hormonal background
After 60 years, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can stimulate the growth of malignant tumors, the risk of which is quite high at this age. The hot flashes have already passed, and there is no urgent need to fix any problems. Therefore, gynecologists-endocrinologists prescribe HRT with caution, trying to replace it with hormone-like substances contained in plants and animals.
Phytohormones are found in soybeans, hop cones, red clover, and licorice roots. Recently, many medications and dietary supplements with these substances have been produced: Estrovel, Feminal, Klimadinon, Klimadinon Uno, Qi-Klim. You can also use homeopathic remedies - Remens, Klimaxan, etc.
Cytamines, biologically active substances obtained from animal organs and tissues, act similarly to phytohormones. An example of a dietary supplement with cytamines is Ovariamine.
You can activate your general metabolism, which will lead to an improvement in hormonal levels, by taking special vitamin and mineral complexes for older women.
Osteoporosis
Advice from a specialist on the prevention of osteoporosis:
- eating foods high in calcium, such as: dairy products, eggs, sardines, shrimp, sesame seeds, cabbage, almonds, chocolate;
- strengthening skeletal muscles that support the musculoskeletal system; muscles protect bones from fractures;
- taking medications and vitamin-mineral complexes that contain calcium - Calcium D3 Nycomed, Kalcemin, etc.
Genitourinary system
Problems with the genitourinary system can increase due to dry mucous membranes. Expert advice: a way out may be to use topical medications with hormones (vaginal suppositories and Ovestin cream). To strengthen the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, special gymnastics complexes are prescribed.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a serious problem in older people. Therefore, you should limit or not consume sweets at all; baked goods are a source of simple carbohydrates. Fatty animal products should also be limited - they can also produce glucose. By following such a diet, diabetes in the initial stages is compensated. If blood sugar does not decrease, hypoglycemic drugs such as metformin (Siofor, Glucophage) are prescribed.
Physical exercise
High physical activity at 60 is contraindicated, but physical activity and feasible sports or gymnastics are vital. It is important to alternate physical activity with rest. Evening walks are very useful: they not only strengthen muscles, but also help you fall asleep quickly.
Cosmetology
It is worth taking care of your face and body, as they determine a woman’s appearance, her age and state of health. To achieve the desired result, you need to adhere to the following expert advice:
- cleanse your face daily, removing decorative cosmetics with special milk;
- clean with a scrub once a week;
- use age-appropriate nourishing creams; Apply day cream with photoprotective properties in the morning, and night cream in the evening; Do not apply the cream in a thick layer; if you do this before bed, swelling may appear on your face in the morning;
- Apply nourishing masks to the skin of the face and neck twice a week; ready-made nourishing masks for your age can be bought in the store; you can also use folk remedies;
- use age-appropriate cosmetic serums in courses;
- Visit a beauty salon 1 – 2 times a year to conduct courses of cosmetic procedures.
Sexual life of women over 60 years of age
Sex life at sixty should continue. Studies have shown that in most cases, married couples at this age retain sexual desire and sexual activity. This strengthens the muscles of the pelvis and perineum (prevention of prolapse of the internal genital organs) and makes life brighter.
The health of a woman in old age requires constant support. But this does not mean that you need to do only examination and treatment. And in your declining years, life should be bright, happy and full of pleasures.
Address: Vikhorevka, st. Komsomolskaya, 1a Contact numbers.
Symptoms of an increased rate
Symptoms indicating increased ROE:
- inflammatory processes accompanied by pain;
- dental pain;
- acute pain in the abdomen;
- heartache;
- pain in the joints and spine.
With a low ESR, the following conditions are observed:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
A reduced ROE in the body can also be a signal of dangerous pathologies.
Reasons for the increase
The ESR indicator can be increased as a result of physiological processes and pathological changes in the body.
ROE (normal blood levels in women by age), a table with the value of which shows their changes, can reach 45 mm/hour. Thus, during puberty in adolescents, ROE can normally reach up to 19 mm/hour, during pregnancy up to 45 mm/hour, during menopause and menopause up to 30 mm/hour, in women with impaired ovarian function up to 40 mm/hour.
Physiological reasons for an increase in ROE are also allergic reactions, various diets, and fasting.
A pathological increase in ROE occurs in many diseases:
- Inflammatory diseases of various etiologies. Joint pathologies—arthritis, arthrosis, rheumatism, inflammatory-degenerative diseases of the spine.
- Viremia of various origins. Flu, ARVI, herpes diseases.
- Bacterial infections and their complications. Tuberculosis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia.
- Endocrine and autoimmune diseases. Diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, thyrotoxicosis.
- Ulcers, abscesses, sepsis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the female genital area. Endometriosis, ovarian cysts, inflammation of the appendages and fallopian tubes.
- Hematopoietic disorders.
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases—pancreatitis, cholecystitis, stomach ulcers.
- Long periods of high ROE may be a sign of the onset of an oncological process.
Causes of pathological increase in indicator
ROE is an indicator whose increase does not occur immediately after the development of pathology in the body. Such a reaction can be registered only after a few days. An increased ROE can be recorded for a long time after recovery from the disease, which is quite logical, since pathological red blood cells must be gradually replaced with normal ones.
High ROE in the following diseases:
- Inflammatory process: Acute and chronic sinusitis, otitis, tonsillitis;
- Menignoencephalitis;
- Pleuropneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis;
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle);
- Carious-destructive changes in teeth;
- Inflammatory processes of the digestive system (hepatitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis, enterocolitis);
- Inflammatory processes of the organs of the excretory system (paranephritis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, cystitis);
- Pathology of the genital organs of an inflammatory nature (orchitis, endometritis, adnexitis);
- Inflammation of bones and joints (reactive and specific arthritis, osteomyelitis).
- Any viral infections (herpes, measles, rubella, hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, infectious mononucleosis);
A slowdown in ROE can be recorded very rarely and indicates blood thickening due to intoxication or dehydration.
Important to remember! When assessing increased ROE, first of all, all possible causes of physiological acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are excluded. A slight deviation from the norm can be considered physiological. Pronounced fluctuations always speak in favor of immune-inflammatory changes in the body or malignant neoplasms!
Indications for research
A referral for ESR analysis is most often prescribed by a general practitioner. The analysis is carried out after acute viral and bacterial diseases to exclude the presence of complications.
Subspecialists can prescribe a referral for analysis:
- rheumatologist for joint pain; temperature, increased fatigue;
- surgeon for abscesses, suppuration, abdominal pain;
- nephrologist for problems with the urinary system;
- gynecologist for pain, pathological discharge;
- gastroenterologist for pain in the abdominal cavity, heaviness in the right hypochondrium, yellowing of the skin;
- endocrinologist for specific symptoms indicating metabolic disorders in the body;
- hematologist for a comprehensive examination of the hematopoietic process.
A referral for ESR testing is issued during planned hospitalization and surgical interventions. ESR is part of express tests during emergency operations.
How is the indicator determined?
The ROE indicator is determined using two methods.
Method according to Panchenkov. Blood from the ring finger is examined. The material is transferred to glass and an anticoagulant is added. The resulting laboratory solution is placed in a Panchenkov capillary with 100 divisions.
The erythrocyte sediment deposited within 60 minutes is assessed. The scale readings will be an indicator of the ROE value in mm/hour.
Westergen method . It is used more often; at high ROE levels it is more sensitive. Venous blood is collected for analysis.
The anticoagulant is mixed with the test material in a ratio of 1:4 and placed in a Westergen tube with a graduated scale of 200 mm. The number of red blood cells deposited as sediment is measured in mm/hour.
In the absence of disease, red blood cells precipitate singly, having a negatively charged potential that pushes them away from each other.
Inflammatory and other pathological processes lead to an increase in acute phase proteins in the blood plasma: immunoglobulin, fibrinogen, C-reactive protein. The presence of proteins leads to platelet sticking (aggregation), which causes acceleration of their precipitation.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is influenced by the presence of antibodies and lipids in the blood plasma. Plasma can have different oxidation states and ionic charges. The ROE values are affected by the number and shape of red blood cells and blood viscosity.
What is this indicator
The erythrocyte sedimentation reaction (ERS) is one of the indicators of a general clinical blood test. Its modern name is ESR, which refers to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is based on determining the ability of erythrocyte cells to settle under the influence of gravity when they are placed in a narrow glass capillary simulating a vascular lumen. The value of the ROE indicator depends on how quickly this happens. It is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h), which indicates how many millimeters the red blood cells have settled while remaining in an upright position for an hour.
Preparing for analysis
The ESR indicator is part of the general clinical blood test, but sometimes it is determined separately. Blood is taken from a vein or from a finger, depending on the method used by the laboratory to evaluate the value of the indicator.
To ensure that the test does not show a false positive or false negative result, you need to prepare for the test for several days.
For an accurate measurement:
- take the test before 10 am, strictly on an empty stomach; as an exception, it is permissible to drink a small amount of liquid;
- 2-3 days before the examination, avoid spicy, salty, smoked foods;
- follow a diet, eat boiled or steamed foods;
- Do not drink alcohol or smoke for several hours before the test;
- before the examination, reduce the intensity of physical activity and training;
- Discuss taking medications and performing medical procedures with your doctor.
The results of the analysis may be affected by:
- cyclical changes, hormonal fluctuations in the female body (pregnancy, menopause, menstruation, ovulation);
- stress, psycho-emotional stress;
- other studies and physical procedures performed previously.
When testing blood from a finger, a scarifier, sterile needle or lancet is used. Modern machines for drawing blood from a finger contain a lancet enclosed in a plastic case with a puncture depth regulator. The upper phalanx of the ring finger is wiped with a cotton swab moistened with an antiseptic. After this, blood is drawn.
Only a person qualified as a nurse, paramedic or doctor can take venous blood for analysis. Most often, the median ulnar vein or external superficial vein is used. In some people it is difficult to find a vein. In such cases, blood is drawn from the back of the hand.
A tourniquet is applied to the forearm, and the bend of the elbow is treated with an antiseptic. The needle is inserted at an angle of 45°. After blood is drawn, the arm is bent at the elbow to prevent bruising. The period for performing analysis by any method does not exceed one day.
Conducting research
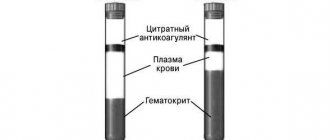
To determine ROE, no special techniques or equipment are needed. The indicator is studied as part of a general blood test, for which capillary blood is taken from a finger according to a method familiar to everyone. Determining ROE is one of the easiest stages of clinical analysis, since it does not require any manipulation of the blood after collection. It is simply left in a glass capillary for one hour. After this time, they look at what level the boundary of blood separation into light and dark layers is located. The height of the light layer in millimeters is used to determine the resulting erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Decoding the analysis results
If the test result shows an increased level of ROE, there is no need to immediately panic.
It must be remembered that many factors can influence the increase in the indicator:
- physical and emotional stress;
- taking certain medications—salicylates, hormonal contraceptives;
- recent vaccination;
- helminthic infestations;
- high blood cholesterol, obesity;
- taking vitamins;
- violation of the temperature regime in the room where the analysis was taken.
ROE (normal blood levels in women by age), a table with the value of which shows their changes, may increase for physiological reasons.
Experts say that errors in measurement and physiology can cause a slight increase in ROE to 30-33 mm/hour. The same indicators are observed in anemia and hypoproteinemia, conditions after acute infectious diseases.
An increase in ESR above 60 mm/hour indicates the presence of a serious pathology in the body. High rates occur in sepsis, acute appendicitis, and peritonitis. Joint diseases, especially rheumatoid arthritis, can cause high ESR.
An acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction may be the first symptom of malignant tumors, leukemia, and autoimmune diseases. Acute pathologies of the urinary system lead to sharp jumps in ROE.
Causes of pathologically low ESR:
- anemia, thrombocytopenia and other hematopoietic disorders;
- epilepsy;
- pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
Low ROE may have physiological causes: dehydration, vitamin deficiency. Deviations from normal values require re-testing to exclude false results.
Reasons for high ROE
An increased ROE does not always mean the presence of any pathologies in the body. If the indicators are elevated, it is necessary to exclude physiological causes of this phenomenon.
These include:
- Elderly age.
- Postpartum period.
- Menstruation.
- Puberty period.
- Pregnancy.
- State of stress.
- Taking estrogens and glucocorticoids.
About 5% of the world's inhabitants have abnormal ROE indicators from birth. Moreover, they do not have any chronic diseases or other pathologies that could contribute to this process. Why the analysis shows high numbers has not yet been established.
In other cases, it is important to contact your doctor, who will prescribe a number of additional tests for an accurate diagnosis.
An increased ROE is observed when:
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Infections.
- Serious lead or arsenic poisoning.
- After operations and other surgical interventions.
- With elevated cholesterol levels.
- Liver diseases.
- Anemia.
- Worm infestation.
- Significant blood loss.
- Hemolysis.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Massive injuries and wounds.
- Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- Kidney diseases.
Erythrocyte sedimentation
In most cases, ROE is increased in inflammatory and infectious pathologies. After competent antibacterial therapy, the indicator quickly returns to normal.
In such serious diseases as diabetes mellitus, anemia and hemolysis, ROE is increased over a long period, and is accompanied by a number of other unpleasant symptoms such as:
- Weaknesses.
- Loss of strength.
- Losing or, conversely, gaining weight.
High ROE is observed in diseases such as:
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Rheumatism.
- Arthritis.
- Dermatomyositis.
Pathologies associated with connective tissue and vasculitis are accompanied by long-term inflammatory processes. The analysis can be of high value over a long period of time. In this case, timely and competent treatment of the underlying disease is required.
Increased rates are observed in pathologies that cause tissue death. These include:
- Tuberculosis.
- Heart attack.
- Diseases with the formation of pus.
- Intestinal pathologies.
If the indicator is sharply increased to values from 60 to 80, then the presence of tumors can be suspected. At the initial stage of tuberculosis in an adult, the indicators may be slightly increased, but in the absence of treatment they rise to 90. With various infections, the ROE does not increase immediately, but after a few days.
A similar situation occurs with inflammation of the appendix. In a child, ROE is most often increased in inflammatory and infectious diseases.
ROE is always higher than normal in rheumatism and arthritis. During the last trimester of pregnancy, the ROE may exceed 40-50 mm/hour, which is normal. It may take several months for the number to return to normal.
A woman’s weight plays an important role in this: with low body weight, the indicator may not exceed 30, and with excess weight during pregnancy, it can reach 70.
When ESR decreases, several components of correct erythrocyte sedimentation are not in order
At what level should you consult a doctor?
Repeated high ROE readings (above 30 mm/hour) require contacting a therapist. The doctor will weigh the possible reasons for the increase and prescribe additional examinations. If a specific pathology is suspected, a referral is issued to a specialist who conducts a detailed examination of the diseased organ.
The main goal of the examination is to find the cause of the anomaly and not to miss the early stage of a dangerous disease. In some situations, it is not possible to find out the reason for the increase in ROE. In this case, they take a wait-and-see position and watch the indicator over time.
Decreased white blood cells
A few words about low leukocyte levels. This is a situation that always requires certain diagnostic maneuvers, since suppression of hematopoiesis is a rather serious symptom. Therefore, the advice here is very simple: if your white blood cells are below normal, go to the doctor. The diagnostic path may not be very simple, but it must be followed.
By the way, one of the reasons for the decrease in leukocytes may be, oddly enough, headache pills. Yes, yes, banal analgesics, when taken frequently and regularly, can inhibit bone marrow function. Don't forget about this, those who swallow painkillers by the handful.
A young woman arrives. There is nothing to worry about, only the leukocytes in the blood test are low. In several repeated tests the indicator was <2 thousand/µl. There are no other obvious complaints. I invite a hematologist to a consultation and ask in more detail. Sometimes headaches bother me.
— Painkillers? Well, yes, I take it sometimes: analgin and other various analgesics that are sold in pharmacies. Often, yes, almost every day.
A full hematological examination was carried out, including a bone marrow puncture, and, fortunately, nothing wrong was found. I was forbidden to take painkillers, and after a couple of months my blood counts recovered.
Over-the-counter analgesics are not a toy. Drugs based on metamizole (analgin, baralgin, etc.), although rare, can cause very severe bone marrow damage.
But chronic headaches must be treated completely differently.
Advertising
How to get it back to normal
Reducing ESR without finding out the reasons for the increase in the indicator does not make sense. ROE is not a disease, but a diagnostic parameter indicating problems in the body. Self-medication is especially dangerous.
Medications
Some medications have the effect of reducing ROE in the body:
- Aspirin and other medicines containing salicylic acid;
- Calcium chloride;
- mercury-containing preparations;
- antihistamines.
The attending physician makes a diagnosis, as a result of which the ROE level was increased. Treatment of the underlying disease will help normalize the indicator. For infectious pathologies and their complications, antibiotics are usually prescribed: Metronidazole, Tetracycline, Levomycetin, Erythromycin.
For inflammatory lesions of the joints and spine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are most effective. The most popular are Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin. New generation drugs that have a gentle effect on the gastrointestinal tract—Meloxicam, Arcoxia.
Indicators of anemia are corrected with the help of medications containing hemoglobin and folic acid: Hemodin, Irovit, Maltofer.
For tuberculosis, drugs active against Koch's bacillus are used: Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Parazinamide. Treatment of autoimmune and endocrine diseases requires specific therapy. Suspicion of a malignant tumor is the basis for immediately sending the patient for consultation to an oncology clinic.
ROE (normal blood levels in women by age), the table with the value of which shows their changes, in some cases can increase significantly. Temporary surges in ESR do not require treatment; after some time the indicator will return to normal on its own.
Traditional methods
To reduce the ESR, you can use folk remedies that will not cause harm to the body and will help strengthen the immune system. Consultation with your attending physician is advisable.
Lemon juice with chopped garlic—the mixture has an antimicrobial effect, improves immunity, and helps lower cholesterol. Mix 100 g of peeled garlic with juice squeezed from four lemons. The mixture should be stored in a cool place. 1 tsp Take the medication once a day before bed.
Honey is a unique natural product that promotes overall health of the body. Accepted according to Art. spoon in the morning or diluted in a glass of warm water.
Beets are rich in B vitamins, potassium, and beneficial microelements. Three well-washed root vegetables are boiled for 2-3 hours. Beetroot decoction is used as a medicine, which is drunk before meals, 2 tbsp. l., course of treatment 2 weeks.
A herbal collection of sea buckthorn berries, chamomile and calendula flowers has antispasmodic, bactericidal, and anti-inflammatory properties. 2 tbsp. l. berries and flowers are brought to a boil and left in a water bath for 20 minutes. Take 100 g before meals 2 times a day.
It is useful to drink herbal teas using coltsfoot grass, linden blossom, and raspberry leaf. Use honey instead of sugar.
Other methods
With minor fluctuations in ROE, a decrease can be achieved by changing your lifestyle in favor of healthy habits. Walking in the fresh air, moderate physical activity, proper nutrition and quitting smoking and alcohol improve laboratory blood counts.
A special diet has been developed to help reduce inflammation in the body and normalize metabolism. Add to the diet: beef, liver, legumes, nuts, beets, dried fruits, green vegetables.
Eating all types of citrus fruits and chocolate helps reduce ESR. Good results are achieved by a course of treatment with B vitamins. An effective drug is Milgamma.
All of the above methods work only with a slight increase in the ROE norm in a blood test in women according to the table. If the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction is more than 30 mm/hour, the attending physician must adjust the indicator.
Reasons for low ROE
It is necessary to show concern not only with high, but also with too low indicators.
Most often this occurs when:
- Muscle dystrophy.
- Presence of nervous disorders.
- Jaundice.
- Hepatitis.
- Cholecystitis.
- Circulatory failure.
- Leukemia.
- Fasting.
- Heart failure.
- Vegetarianism.
- Taking steroid hormones.
- Treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
ROE below 2 mm/h may indicate the presence of serious diseases. If it is slightly reduced, then it is necessary to change the diet and add iron and protein to it. Very often, this situation occurs in women who have lost weight dramatically and adhered to strict diets.
A decrease in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is extremely rare.
Increased swelling does not always mean that a person is sick and an inflammatory process is occurring in his body. In order to accurately decipher the analysis and understand why the ROE indicator is increased, you need to visit a specialist. Only with the help of additional tests and studies can an accurate diagnosis be made and the correct treatment prescribed.
Possible complications
If an ESR indicator is detected that is significantly higher than normal, it is necessary:
- identify the cause;
- carry out therapy for the underlying pathology;
- observe ESR values over time until readings appear that correspond to the norm.
Some life-threatening conditions may occur in an atypical form, with no characteristic symptoms. High ROE helps diagnose acute appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, ruptured ovarian cyst, myocardial infarction, and sepsis. These diseases, if not treated promptly, can be fatal.
For a long time, the ESR rate is above 75 mm/hour, with negative dynamics, requiring a persistent search for an oncological process in the body.
Every woman who cares about her health should know the ROE norm in a blood test according to her age. The table indicates which deviations can be caused by physiological reasons, which indications indicate pathological changes in the body.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Increased white blood cells and antibiotics
By the way, from what I just wrote, paradoxically, one very important thesis follows.
In case of uncomplicated acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI), there is no need to take a general blood test “just in case.”
You will definitely see lymphocytosis there and will worry where it came from! You will rush to search the Internet for the causes of leukocytosis, you will definitely find horror stories about leukemia there, you will not sleep for two nights, you will make an appointment with a hematologist... And leukocytosis in this case was simply a “witness” of a viral infection. Moreover, it can remain in the blood for up to a month after a cold.
And the second very important idea: leukocytosis is not a disease, but only a symptom of a wide variety of conditions. Hence the conclusion, which is useful to remind not only patients, but also many doctors.
You cannot simply prescribe antibiotic treatment based on the detection of leukocytosis without making a diagnosis and identifying the source of infection.
The fact is that there is no universal “broad-spectrum” antibiotic; For different infectious diseases, completely different drugs and their dosages are used. As a rule, trying to prescribe treatment in a situation where the disease has not been found, but the doctor says: “You have an infection somewhere in your body...” only leads to further diagnostic confusion.
The fact is that pathogens of infectious diseases do not just float in circles in the blood; they always strive to “settle” somewhere, causing a picture of a specific disease. Not to mention the fact that not every fever and not every leukocytosis are signs of a bacterial infection, which, in fact, should be affected by antibiotics.
So, I repeat, with rare exceptions, there is no need to take antibiotics until there is an answer to the question of the name of the disease that we are treating.