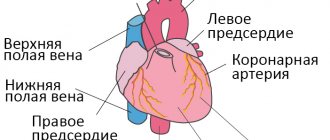
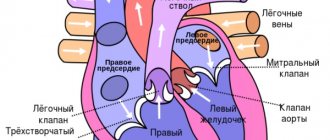
Respiratory arrhythmia is an increase in heart rate during deep inhalation and a slowdown during exhalation. The dependence of the pulse rate on the phases of breathing is more common in childhood and adolescence. This condition does not carry organic or functional disorders of hemodynamics (the movement of blood through the vessels) and refers to the physiological type of change in heart rhythm. Less commonly, arrhythmia associated with breathing occurs in adult patients, which indicates severe illness of the body.
Causes of pathology
- Alcohol abuse, smoking, drug use
- Including plenty of caffeine-containing foods and drinks in your diet
- Side effects of certain medications
- Psycho-emotional stress and hard physical labor
- Somatic diseases (coronary heart disease, consequences of myocardial infarction, arterial hypertension, diseases of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland)
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Menopause
Methods of influence
Treatment of respiratory arrhythmia is prescribed depending on the results of the examinations. Medication is necessary only if another disease is detected in the background.
Under no circumstances should you prescribe medications on your own; doctors say that this is fraught with serious consequences. Nowadays, a method such as breathing exercises is gaining popularity. There is such a program as “Strelnikova’s gymnastics,” which is aimed at optimizing blood circulation, as well as saturating the blood vessels of the upper and lower extremities with oxygen. This method is more related to prevention, and it is not for nothing that doctors say that a disease is much easier to prevent than to treat.
A kind of training of the cardiovascular system, as well as the respiratory system, given the modern lifestyle, is very necessary. If earlier this happened in the process of physical labor, now most professions involve sitting in one position for a long time, which is also stressful. Breathing exercises are definitely very important, but certain conditions and additional time must be provided for it.
Clinical symptoms
Clinically, various rhythm disturbances may not manifest themselves in any way, that is, the patient himself does not complain, or predictors of arrhythmia are identified during a preventive or any other examination (during ECG registration, examination by a therapist). With a clinically pronounced course, a number of symptoms can be identified:
- tachycardia (increased heart rate)
- bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- feeling of heart failure
- sensation of a foreign body, heaviness in the chest
- change in the frequency and depth of breathing movements
- general weakness
- loss of consciousness (in extremely severe clinical cases)
Types of arrhythmias
Bradycardia
With sinus bradycardia, heart rate is recorded up to 60 beats/min or less. Subjectively, it is felt as a feeling of tightness in the chest , in particular in the cardiac region, general weakness up to loss of consciousness.
It must be remembered that a decrease in heart rate is possible in a completely healthy person during sleep or at rest and is not a pathological condition!
Bradycardia can be triggered by low blood pressure, hemodynamic disorders associated with reduced blood flow in the peripheral arteries, and hypothyroidism.
Sinus tachycardia
An increase in heart rate of more than 90 beats/min is registered and is subjectively felt by the person as a feeling of heartbeat in the chest.
This type of arrhythmia can be symptomatic and associated with temporary psycho-emotional and heavy physical stress, and be a symptom of fever during viral and bacterial infections.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
According to the ECG, the rhythm in this pathology is correct, sinus, but frequent (up to 120-240 beats/min), which is subjectively defined by a person as a feeling of pronounced heartbeat, and may be accompanied by dizziness and weakness, sweating.
Atrial fibrillation
This is a type of rhythm disorder in which the atria contract chaotically at a frequency of 350-700 beats/min (there are many pacemakers - non-sinus rhythm), which creates conditions for discoordinated contraction of the muscle fibers of the heart and manifests itself in the form of an irregular weak pulse.
With paroxysms of atrial fibrillation, the clinical manifestations can be mild, but with a long course of the disease and the absence of proper treatment, the disease goes into a more severe stage, manifested clinically by signs of heart failure (shortness of breath, discomfort in the chest, congestion in the pulmonary or systemic circulation), dizziness, general weakness, sometimes loss of consciousness.
The cause of this pathology is congenital and acquired heart defects, intoxication with harmful substances, alcohol, and medications.
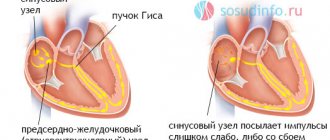
Respiratory arrhythmia
This is a type of rhythm disorder in which the heart rate increases as you inhale (tachyarrhythmia), and decreases as you exhale (bradyarrhythmia). This condition can be a temporary phenomenon (during heavy physical exertion, deep and rapid breathing) and is not a pathology. It most often occurs in children and adolescents, but adults are no exception. Respiratory arrhythmia does not require special treatment and may not manifest itself clinically.
Extrasystoles
Extrasystoles are characterized by extraordinary contractions of the heart muscle. They are felt as a temporary feeling of tightness in the chest, interruptions in the functioning of the heart, or this condition does not manifest itself clinically. Can be recorded in healthy people.
Heart blocks
A type of arrhythmia characterized by a slowdown in the passage of an electrical impulse through the myocardial conduction system. The causes of this pathology may be congenital and acquired heart defects, various types of intoxication, as well as diseases that contribute to the degeneration of muscle tissue into connective tissue (cardiosclerosis, myocardial infarction, myocarditis). The main symptoms of blockades are: general weakness, dizziness, sensations of interruptions in the heart area, and in severe clinical cases even fainting and convulsions.
Blockades can be of 3 degrees depending on the severity of the condition, as well as complete and incomplete.
Treatment
The manifestation of arrhythmia associated with breathing in children and young people is physiological in nature and is considered an age-related feature of the work of the heart in an ever-growing body. This condition does not require special treatment, but preventive measures can normalize the functioning of the body during a period of intensive physical development.
Preventive measures include:
- compliance with the optimal mode of activity and rest (night sleep of at least 9 hours, daytime rest);
- balanced diet with foods rich in calcium, vitamins, magnesium, potassium (seafood, dairy dishes, fresh fruits and vegetables, herbs);
- walks in the fresh air, sports without intense physical activity (swimming, skiing, cycling);
- normalization of the state of the nervous system (hobbies, interests, mental peace);
- strengthening the immune system to prevent infectious diseases.
If concomitant heart pathology is detected, comprehensive treatment must be carried out. Depending on the cause, cardiac glycosides, belladonna preparations, and sedatives are prescribed. Regardless of the nature of the process, an adult or child should be under the supervision of a specialist - a cardiologist.
Arrhythmia associated with the breathing process usually does not require treatment and goes away on its own without causing hemodynamic disturbances. In childhood, this condition is considered physiological, but in adults it occurs against the background of other pathologies of organs and systems.
Diagnosis of arrhythmias
Quite often, many types of arrhythmias do not manifest themselves clinically, so they can be detected accidentally during a routine examination (examination by a therapist, ECG registration), or during accidental hospitalization in a hospital (during an examination).
Diagnostic methods:
- Electrocardiography
- Holter blood pressure monitoring
- Echocardiography
- Ultrasound examination of the heart
The gold standard in diagnosing arrhythmias is the ECG, but the disadvantage of this method is that only a certain fragment is recorded on the film, but it is impossible to monitor the work of the heart muscle over the course of a day, as with Holter monitoring. For a more thorough and detailed study of the structures of the heart and blood vessels, research methods such as echocardiography and ultrasound of the heart are used.
Diagnostics
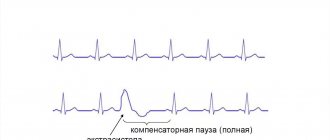
It was said above that respiratory arrhythmia does not have pronounced symptoms, but it is quite easy to detect with the help of an electrocardiogram, because it is immediately visible there. Arrhythmia manifests itself in that the intervals that separate heartbeats have different lengths, sometimes shorter, sometimes longer, while the PQ interval remains normal.
Looking at the results of the electrocardiogram, the doctor draws appropriate conclusions, because the difference in the duration of the intervals is characteristic only of arrhythmia in the sinus node. In addition to the ECG, deviations can be detected by auscultation and pulse determination.
Principles of arrhythmia treatment
- Regular events
- Diet therapy
- Drug therapy
Must remember! Before starting treatment measures, it is necessary to know exactly the cause of this pathological condition and whether it is pathological at all. Once the cause is established, it will be easy for the doctor to select the correct treatment and avoid complications of the disease.
If arrhythmia is not an independent nosology, but a complication of any other pathological condition, then it is necessary to eliminate not the effect, but the cause that caused it.
Regular events
It is necessary to do light physical exercise (squats, light walking and swimming in the morning) to strengthen the heart muscle and improve its function. It is necessary, together with the instructor, to develop the correct set of exercises to obtain the desired effect and try to avoid excessive physical activity (lifting weights, speed running, jumping, strength training for all muscle groups)
Diet therapy
It is necessary to exclude pickled, salty, fatty and fried foods from the diet. It is worth eating as many fresh vegetables (cabbage, potatoes, beets, parsley) and fruits (apples, bananas, dried apricots, raisins) as possible, rich in vitamins and microelements that are necessary for the implementation of various metabolic processes in the body. Important! An important role in diet therapy is played by the vitamin load and consumption of foods rich in certain microelements, especially potassium (bananas, dried apricots, greens) and magnesium (legumes, seeds, nuts, avocados).
Drug therapy
The drugs of choice are antiarrhythmic drugs that can affect the electrical activity of myocardial cells, the process of conducting an electrical impulse from one bundle to another.
There are 4 main groups of these drugs
Fast Na channel antagonists:
- 1A – increase repolarization time (“Quinidine”, “Procainamide”)
- 1B – shorten the repolarization time (“Lidocaine”, “Mexiletine”)
- 1C – do not affect the repolarization time (“Propafenone”, “Etatsizin”, “Aprindin”)
Beta blockers - block adrenergic receptors of the myocardium:
- "Concor"
- "Acebutolol"
- "Nadolol"
K channel antagonists:
- "Amiodarone"
- "Nibentan"
- "Sematilide"
Ca channel antagonists - prevent the passage of calcium ions through the channels of the same name to the muscle fibers, which reduces the contractile activity of the myocardium. There are 2 groups of these drugs:
- Non-dihydropyridine blockers: Nifedipine, Amlodipine
- Dihydropyridine blockers: Verapamil, Gallopamil
Must remember! The dosage of drugs and the method of their administration depend on the morphofunctional characteristics of the patient and the severity of his condition.
Way of life with respiratory arrhythmia of the heart
As stated above, this disease does not require any treatment, however, experts recommend that people who are prone to this condition lead a healthy lifestyle and, if possible, engage in sports.
Equally important is a healthy diet, which includes proper and healthy foods that help normalize heart function. The diet should be varied, well-balanced, preferably a predominance of seafood, raw vegetables and fruits, dairy products, herbs, etc.
Ideal conditions for normal heart function are the absence of stress and quiet activities, for example, hobbies, forest walks, yoga. Remember, if a patient with respiratory arrhythmia leads a healthy lifestyle and does not have bad habits, he will not feel any discomfort.
Prevention of rhythm disturbances
- Treatment of somatic diseases and regular medical examination for these conditions (coronary heart disease, hypertension)
- Proper balanced nutrition (products rich in vitamins and microelements);
- Light physical activity (morning exercises, walking in the fresh air, swimming), exercise therapy according to a specially designed scheme
- Correct work and rest schedule
- Categorical refusal to smoke, drink alcohol, coffee, strong tea
- Weight control (obesity prevention)
- Psycho-emotional peace
Symptoms of respiratory arrhythmia
The main sign of respiratory arrhythmia is the following: during deep breathing, when exhaling, the heartbeat slows down, and when inhaling, it increases. Sinus rhythm increases during emotional stress and physical activity.
Some patients with respiratory arrhythmia experience:
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- nausea.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.