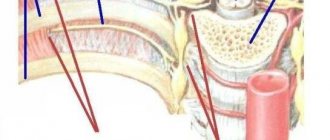
Thoracic osteochondrosis
is a degenerative-dystrophic disease in the middle parts of the spine. It occurs much less frequently than lumbar and even cervical osteochondrosis and accounts for about 10% of all cases of the disease. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are associated with several features of the spine in the thoracic region: rigid fixation of the vertebrae due to the ribs and skeletal muscles and less mobility, a semicircular bend of the ridge in this region and the corresponding distribution of the load.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a disease of the middle parts of the spine.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis begin with a violation of tissue trophism and dehydration of the intervertebral discs. Lack of nutrients and fluid leads to the fact that cartilage loses its elasticity, begins to crack and “sag”
.
This state of affairs is fraught with compression of the nerve roots, deterioration of sensitivity and functioning of internal organs, as well as severe pain. Often, the destruction of the vertebrae in the thoracic region is accompanied by the appearance of osteophytes
- bone outgrowths that injure the paravertebral tissues and lead to chronic inflammation.
Contrary to popular belief, thoracic osteochondrosis is not a natural age-related process and requires special treatment. The onset of the disease can occur at the age of 25 years
;
approximately 70% of the total number of patients are women aged 35 to 55 years. Since the disease begins long before retirement age, it can lead to limitations and even loss of ability to work
.
Unlike other types of osteochondrosis, thoracic osteochondrosis may not manifest itself for a long time - or disguise itself as other pathologies, which is why it is called a chameleon disease. It is also the most difficult to treat. Therefore, it is very important to promptly monitor the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis.
- and today we will tell you which ones.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases most often cause characteristic chest pain on the left. These may be conditions that threaten a person’s life or indicate the development of serious diseases.
Heart attack and ischemia
Chest pain on the left, radiating to the arm, is a typical sign of a heart attack, when the heart muscle becomes inflamed and atrophies. The precursor to this disease is coronary heart disease, which occurs as a result of impaired blood flow due to atherosclerosis.
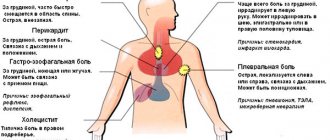
Pericarditis
If the chest pain on the left side is sharply stabbing, this may be a sign of pericarditis. Pericarditis is an inflammation of the heart sac that is caused by infections and autoimmune processes. Pericarditis can easily be mistaken for a heart attack, but the pain associated with pericarditis is reduced when the person is standing.
Angina pectoris
Angina is an attack of pain in the chest on the left, as during a myocardial infarction. But it arises as a result of strong experiences, emotional upheavals and lasts no more than 5 minutes. Angina occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart. If chest pain on the left side lasts more than 5-7 minutes, it may be a sign of myocardial infarction.
Aortic aneurysm
Acute tearing pain in the chest on the left is one of the signs of an aortic aneurysm. An aortic aneurysm is a pathological enlargement of an artery that threatens human life. It is accompanied by difficulty breathing, numbness of the limbs, and difficulty speaking. Death is possible as a result of aortic rupture, so this pathological condition is especially dangerous.
Types of pain under the shoulder blade on the left
Before proceeding with diagnosis and treatment, it is important to understand the nature, localization, intensity of pain, their connection with movement, breathing, and eating. If it hurts below the left shoulder blade after eating, then heart pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be ruled out. The cause of pain is diseases of the gallbladder, pancreas, and stomach.
The nature of the pain syndrome can be girdling, acute, burning, increasing, aching, dull, sharp.
Aching pain in the left shoulder blade
It can be constant or periodic, indicating both pathologies of internal organs and diseases of the spine. Without treatment, it can turn into a stabbing, burning sensation. Attacks more often occur when raising an arm, physical activity, or staying in one position for a long time.
Appears with scoliosis, chronic cholecystitis, scapular-costal syndrome, intervertebral disc herniation, initial stages of cervical osteochondrosis, bruises and other mild injuries, intercostal neuralgia.
Acute pain under the left shoulder blade
This is a severe pain syndrome in the back below the shoulder blade, which limits movement and makes breathing difficult. Characteristic for myocardial infarction, bursitis of the shoulder joint, exacerbation of osteochondrosis, spondylosis, hernia, subphrenic abscess, pleurisy, acute cholecystitis, intercostal neuralgia.
In case of myocardial infarction, pain under the scapula from behind is not relieved by analgesics, it decreases after taking nitroglycerin
Sharp pain in the area of the left shoulder blade
It may occur suddenly or be the result of prolonged aching pain. Shooting, sharp pain is a sign of osteochondrosis, hernia, trauma, intercostal neuralgia, tuberculosis of the scapula, aortic aneurysm, perforated gastric ulcer, radiculitis.
Stitching pain behind the left shoulder blade
It manifests itself as lumbago, which is typical for pinched nerve endings in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. If it is accompanied by compression of the chest and lack of air, then myocardial infarction or lung abscess cannot be ruled out.
With a perforated stomach ulcer, pain occurs, as if stabbed with a knife.
Nagging pain in the left side of the back under the shoulder blade
Inherent in most pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, as well as bronchopulmonary diseases.
Constant pain on the left side under the shoulder blade
Such pain does not leave the patient even in a lying position. It interferes with sleeping, breathing, and walking. More often, pain intensifies with physical activity, coughing, and sneezing.
Constant nagging or aching pain occurs with injuries to the spine or scapula, scapular-costal syndrome, bronchopulmonary diseases, pyelonephritis, and oncology. Girdle pain with disorders of the digestive system is characteristic of patients with acute pancreatitis.
Burning pain on the left side of the shoulder blade
It is simply unbearable and occurs with intercostal neuralgia, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, muscle strain.
Important! If a burning sensation that spreads to the sternum is accompanied by shortness of breath, you should immediately call an ambulance. This is a sign of a heart attack.
Respiratory diseases
The human chest contains not only the heart, but also the bronchi and lungs. Therefore, chest pain on the left may be a sign of diseases of the respiratory system, among which there are also serious pathological conditions.
Pleurisy
Acute pain in the chest on the left, intensifying with inspiration, is characteristic of pleurisy. The lining of the lungs - the pleura - becomes inflamed during infectious diseases and secretes a special secretion that irritates the nerve endings and causes pain. Pleurisy accompanies pneumonia and other infectious lung diseases.
Spontaneous pneumothorax
If the integrity of the pleura is compromised (usually due to injury), air enters the lining of the lungs during inhalation, which causes pain. Pain in the chest area on the left side is accompanied by difficulty breathing, weakness and dizziness. The cause of spontaneous pneumothorax may be damage to the pleura as a result of chronic diseases.
Emphysema
With emphysema, the lungs lose their ability to get rid of excess air, which occurs due to loss of elasticity in the walls of the bronchi. Chest pain on the left or above the chest can occur due to this serious disease, which causes complications such as pneumothorax and respiratory failure. This dangerous condition requires immediate treatment.
Pulmonary embolism
The lungs are supplied with oxygen through the blood vessels, and a blood clot entering the pulmonary artery is called an embolism. This disease manifests itself as aching pain in the chest on the left and problems with breathing. Pulmonary embolism is characterized by increased pain with deep inspiration. It is not associated with cardiovascular diseases, but poses a potential threat to human life.
Pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium
Gastritis
Ulcer
32120 May 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
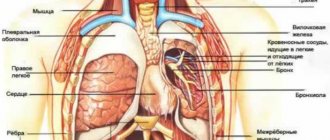
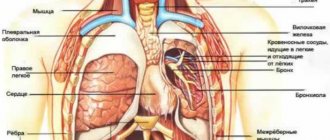
The left hypochondrium is the area of the anterior abdominal wall located below the left costal arch. To understand the reasons for the development of pain in the left hypochondrium, it is necessary to know which organs are projected onto the area of the anterior abdominal wall.
The stomach is a section of the gastrointestinal tract, which is a muscular sac. Gastric juice is produced here, the main components of which are hydrochloric acid, pepsin (an enzyme that breaks down proteins) and mucin (mucus that protects the walls of the stomach from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid). Once in the stomach, protein food undergoes denaturation (a process of structure change, which can be represented as a change in egg white during heat treatment - thickening, as a result of which proteins become insoluble in water) due to the presence of hydrochloric acid, and the denatured protein, in turn, is digested under the action of pepsin. From the stomach, food enters the duodenum, where digestion continues.
The spleen is an organ of the immune system. The content of lymphocytes in the spleen reaches 85% of the total number of cells, which is almost 25% of all lymphocytes in the body. About 50% of spleen lymphocytes are represented by B-cells - humoral immunity depends on them. Thus, it is the spleen, along with the lymph nodes, that is the organ that provides humoral immunity. In addition, the destruction of old and abnormal red blood cells and platelets occurs in the spleen, which helps to renew the cellular composition of the blood.
In newborns, in addition to the stomach and spleen, the left lobe of the liver can be projected into the area of the left hypochondrium.
This is due to the fact that the liver occupies almost the entire epigastrium in infants. Types of pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium
Pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium can be acute or chronic. The pains are drawing, dull, bursting, spastic, “dagger”, shooting.
Depending on the presence of a provoking factor, pain can be spontaneous, or it can develop during meals or as a result of hunger, physical activity, or emotional stress.
According to the mechanism of development, pain is classified into spastic, distensional, peritoneal and vascular.
Possible causes of pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium
The cause of pain is irritation of pain receptors located in the abdominal organs, in the peritoneum (the serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity from the inside and passes to the abdominal organs), in the wall of the abdominal cavity. Spasmodic pain occurs due to uncontrolled persistent tension in the smooth muscles of the wall of a hollow organ, such as the stomach.
Muscle spasm can be triggered by the influence of the aggressive environment of gastric contents on the wall of the organ, activation of the structures of the autonomic nervous system.
The cause of the development of distension pain is excessive stretching of a hollow organ from the inside by its contents, which can happen when consuming an excess amount of food or impaired evacuation of contents from the stomach due to impaired motility or some mechanical obstruction in the outlet section of the stomach.
Peritoneal pain occurs due to irritation of the peritoneum. The peritoneum is a thin film that covers the inside of the abdominal wall and the organs located in it (some completely, others on several sides). As a result of the inflammatory process in the wall of the organ, local peritonitis develops - inflammation of the peritoneum, which is accompanied by pain.
Finally, the cause of vascular pain is cell death due to insufficient blood flow in any organ. Impaired blood flow is most often caused by blockage of a vessel (artery or vein) with a blood clot (thrombus).
Diseases leading to pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium
One of the most common causes of pain in the left hypochondrium is stomach pathology. Gastritis
is an inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the stomach from the inside.
Gastritis can be associated with the entry of any aggressive chemicals into the stomach, with autoimmune inflammation, but most often the disease is associated with an infection caused by Helicobacter pylori
.
Helicobacter pylori bacterium
, being present in the body for a long time, can lead to more serious diseases - peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, and in some cases - to tumor damage to the stomach.
Heaviness and pain in the left hypochondrium, often combined with pain behind the sternum, may indicate the presence of gastroesophageal reflux
(reflux of gastric contents back into the overlying esophagus).
Impaired evacuation of food from the stomach is more common in children in the first year of life due to pyloric spasm
and
pyloric stenosis
(transient or permanent organic disturbance of the patency of the pyloric - outlet - section of the stomach). In adults, this condition can be caused by neoplasms that become a mechanical obstacle to food in both the stomach and intestines.
Among the pathological conditions of the spleen that can lead to pain in the left hypochondrium, it is worth highlighting its enlargement (splenomegaly) and impaired blood supply (splenic infarction).
Splenomegaly
develops in various infectious diseases, diseases of the blood system, incl.
leukemia, as well as cirrhosis of the liver. The cause of splenic infarction
is thrombosis of its vessels, which occurs against the background of conditions characterized by increased blood clotting.
Separately, it is worth mentioning traumatic ruptures of the spleen
, which also lead to the development of pain, but the doctor will primarily be concerned about massive life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding from the damaged organ.
It is important to remember that due to the proximity of the heart to this area, pain in the left hypochondrium can develop due to damage to the heart muscle - myocardial infarction
.
Which doctors should you contact if you have pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium?
If you experience pain and a feeling of heaviness in the left hypochondrium, you should contact or. After a survey, clinical examination and the appointment of a number of laboratory and instrumental studies, the patient can be referred to specialized specialists - a hematologist, a nutritionist.
It should be remembered that acute intense pain in the left hypochondrium, especially in the presence of a previous injury or peptic ulcer, can be a symptom of acute surgical pathology.
In this case, an emergency consultation or calling an ambulance is indicated.
Diagnostics and examinations for pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium
Identification of the cause of pain and heaviness in the left hypochondrium is based on data from an objective medical examination and auxiliary data from laboratory and instrumental studies. These include:
- clinical blood test with determination of the leukocyte formula, necessary to exclude anemia, blood diseases, as well as inflammatory processes in the body;
Spinal problems
The spine is connected to many organs, so spinal pain often radiates to the sternum. Often, a pressing dull pain on the left side of the chest may indicate problems in the thoracic spine.
Osteochondrosis
Pain in the chest and back on the left with osteochondrosis usually appears at a serious stage of the disease, when complications arise in the form of a vertebral hernia. In the thoracic region, osteochondrosis is most complex, since it is often accompanied by difficulty breathing and limited freedom of movement.
Injuries
With injuries to the sternum, aching or sharp pain in the left chest may appear, sometimes this is a sign of a rib fracture on the left side of the chest. The nature of the pain depends on the severity of the injury. In some cases, with spinal injuries, pain radiates to the left side of the chest.
How to relieve pain under the left shoulder blade
Pain sensations below the shoulder blade on the left, especially if they are quite intense, interfere with movement and breathing freely, require qualified help, since they pose a threat to human health and life. You cannot ignore them and self-medicate. Taking analgesics, antispasmodics and other painkillers can relieve pain, but will not eliminate the cause, which must be discovered by a doctor.
Important! Emergency care will be required in case of severe pain with increasing intensity and rapid deterioration in well-being.
Diagnostics
Such a complex symptom as aching or acute pain in the left chest requires careful diagnosis. The therapist decides where exactly to look for its cause.
by collecting detailed information about the circumstances under which the pain occurs and the patient's health status.
If necessary, the patient can be sent to a specialist neurologist
.
Diagnosis often begins with the exclusion of diseases of the cardiovascular system - an ECG
and a visit to
a cardiologist
; if necessary, the patient is prescribed
an echocardiogram
. In other cases, to diagnose diseases that cause chest pain on the left, blood tests, endoscopic, ultrasound and x-ray examinations can be prescribed.
Which doctor should I contact for chest pain?
If you have chest pain, you should first consult a general practitioner - family doctor or therapist. It is he (and not the patient himself) who should draw up the examination plan. Your GP can refer you to:
- to a cardiologist - if there is reason to believe that the pain is caused by heart disease (localized behind the sternum and to the left of it, relieved with nitroglycerin, accompanied by shortness of breath, etc.);
- see a pulmonologist if you suspect pneumonia or pleurisy (if pain is accompanied by cough and fever);
- to a gastroenterologist - if you suspect diseases of the esophagus and stomach (if the pain is accompanied by belching, heartburn, or occurs after eating);
- see a neurologist in case of “shooting” pain.
What are the dangers of heart pain?
Pain in the heart area is a dangerous symptom that may indicate the development of a fatal disease. According to statistics, heart disease causes death in 30% of adults in all countries of the world.
If cardialgia is a manifestation of a heart attack, ignoring it can lead to irreversible consequences:
- necrosis - “death” of part of the heart muscle (infarction),
- development of arrhythmia - irregular heart rhythm,
- heart failure - inability of the heart to perform its function,
- sudden death.
In the event of a myocardial infarction, when a vessel leading to the heart is blocked, minutes count: blood flow must be restored within 1.5 hours. If you seek medical help late, changes in the affected area of the heart will be irreversible: the organ will no longer be able to work effectively (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. What is myocardial infarction Source: prostress.by
Treatment of pain on the left side of the shoulder blade
All therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the root cause and relieving pain. The doctor selects medications based on why the pain in the shoulder blade area occurs.
If the cause is a disease of the musculoskeletal system or its complications, then drug therapy looks like this:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs;
- muscle relaxants;
- analgesics;
- local anesthetic agents.
Drug therapy must be supplemented with physiotherapeutic treatment, massage, and therapeutic exercises. A neurologist from the SmartMed clinic draws up a comprehensive therapy program, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
If conservative therapy does not provide the desired therapeutic effect, the patient is indicated for surgery