Since the last quarter of the twentieth century, cardiovascular diseases have steadily occupied a leading position among the most common diseases of mankind. They overtook all possible infectious diseases and even cancer. Cardiovascular diseases are such a widespread phenomenon that scientists, when talking about them, often use the term epidemic, emphasizing their prevalence.
But about a century ago, at the beginning of the twentieth century, they were extremely rare. But by the 50s of the last century, heart disease was already in 10th place in overall statistics. Today, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), they are in sad first place.
Causes of cardiovascular diseases
What is the reason for the incredible prevalence of cardiovascular diseases? First of all, with a change in the way of life of mankind:
- people began to move less : many “office professions” have appeared, where employees spend 8 or more hours in a “sedentary” position. Cars brought not only convenience and speed to travel, but also eliminated the need for walking. The leisure time of a modern person is more often spent watching TV, a computer, a tablet, or with a phone in hand.
- the diet has changed : fruits and vegetables have been replaced by fast carbohydrates (sweets, flour products), fat consumption has increased (fatty meat, lard, sausages, etc.).
- the quality of products has deteriorated : instead of expensive high-quality ingredients, cheap analogues are used, preservatives, dyes, flavors, stabilizers, etc. are added to products.
- smoking has become widespread
Over time, these factors lead to negative consequences: metabolic disorders, obesity, diabetes, accumulation of “bad” cholesterol in blood vessels and, ultimately, atherosclerosis.
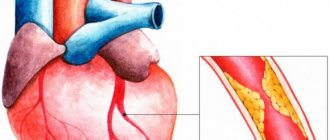
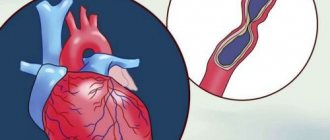
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which cholesterol and its compounds are deposited on the walls of arteries and atherosclerotic plaques form. By sticking, the fatty substance narrows the lumen of the arteries and interferes with the normal flow of blood through them.
Typically, atherosclerosis does not make itself felt until atherosclerotic plaques reach impressive sizes and cover more than 70%
lumen of arteries.
At this time, a person may first experience symptoms of coronary heart disease : shortness of breath, dizziness, chest pain during physical or emotional stress, etc.
It is important to understand that coronary heart disease (CHD) is not one disease, but a general name for a whole group of diseases, including angina pectoris and myocardial infarction .
All types of coronary heart disease are characterized by insufficient oxygen saturation of the heart due to narrowing (in some cases spasm) of arterial vessels.
Treatment and medications
There are many options for treating angina, including lifestyle changes, medications, angioplasty, and stenting or coronary artery bypass surgery. The goals of treatment are to reduce the frequency and severity of your symptoms and reduce your risk of heart attack and death.
Lifestyle changes
If your angina is mild, lifestyle changes may be all you need to do. Even if your angina is severe, lifestyle changes are worthwhile and will definitely be beneficial. These changes include the following:
- If you smoke, quit smoking.
- If you are overweight, talk to your doctor about weight loss options.
- If you have diabetes, monitor your sugar levels regularly.
- Since angina pectoris is often triggered by exercise, do not exhaust yourself and take rest breaks more often.
- Don't overeat.
- Avoid stressful situations. Of course, this is easier said than done, but try to find ways to relax.
- Eat healthy foods with plenty of whole grains, plenty of fruits and vegetables, and limit saturated fat.
- Talk to your doctor about exercise that is safe for you.
Medicines
If lifestyle changes do not help, you may need to take medication. These may include:
- Nitrates. Nitrates are often used to treat angina. Nitrates relax and dilate blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to the heart muscle.
- Aspirin. Aspirin reduces the blood's ability to clot, making it easier for it to pass through narrowed vessels. Taking aspirin may also reduce the risk of a heart attack. But don't start taking daily aspirin without talking to your doctor.
- Antiplatelet agents. Antiplatelet agents are drugs that inhibit platelet aggregation, preventing the development of blood clots.
- Beta blockers. Beta blockers block the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. As a result, the heart beats slower and with less force, thereby lowering blood pressure. Beta blockers also help blood vessels relax and open, which improves blood flow and thereby reduces or prevents angina.
- Statins. Statins are medications used to lower blood cholesterol levels. They also trigger the use of cholesterol that has already been deposited in plaque on artery walls, helping to prevent further blockage of blood vessels.
- Calcium channel blockers. Calcium channel blockers, also called calcium antagonists, relax and dilate blood vessels by affecting the muscle cells in the walls of the arteries. This increases blood flow to your heart and reduces or prevents angina.
Medical procedures and operations
Lifestyle changes and medications are often used to treat stable angina. But there are also procedures such as angioplasty, stenting and coronary artery bypass grafting that are also used to treat angina.
- Angioplasty and stenting. During angioplasty—also called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)—a tiny ball is inserted into the narrowed artery. A balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and then a small wire mesh (stent) is inserted into the damaged artery to hold the artery in place. This procedure improves blood flow to the heart and reduces or eliminates angina. Angioplasty and stenting are good treatment options if you have unstable angina or if lifestyle changes and medications are not effective.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery. During coronary artery bypass surgery, veins or arteries from elsewhere in your body are used to bypass blocked or narrowed arteries in the heart. Bypass surgery increases blood flow to the heart and reduces or eliminates angina attacks. This treatment option is suitable for both unstable and stable angina that has not responded to other treatments.
What is angina?
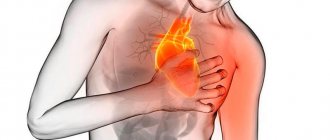
Angina pectoris is manifested by pain, a feeling of tightness in the chest . Sometimes the pain is transmitted to neighboring areas of the left side of the body: to the left arm, left shoulder, left side of the neck, left half of the lower jaw, to the area of the left shoulder blade.
In the old days, the disease was called “angina pectoris” because of the way patients described the painful sensation: “as if a huge heavy toad had sat on the chest and was preventing you from breathing freely.”
.
Such symptoms appear mainly during increased work of the heart muscle:
- during physical activity
- emotional outburst
- when the body is cold (the heart goes into overdrive to prevent hypothermia of vital organs)
- when smoking (nicotine contributes to the narrowing of arteries already narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques)
- with increased blood pressure
When working hard, it is important for the heart to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen. However, if the lumen of the arteries through which oxygen is delivered to the heart is narrowed, then the heart begins to experience oxygen starvation and gives an alarm about this in the form of chest pain .
Angina pectoris (1, 2, 3, 4 FC)
Angina pectoris is an attack of chest pain that occurs due to emotional or physical stress. They increase the metabolic needs of the myocardium. Typically, such pain disappears with rest or after taking drugs from the nitrate group. Depending on how a person tolerates physical activity, angina pectoris can be of several functional classes (FC).
Functional classes
- In the first class (angina pectoris FC I), exercise diseases are tolerated well, pain is caused only by certain excessive overloads, which last a long time and are intense.
- In the second class (angina pectoris FC II), walking on level ground for a distance of half a kilometer or climbing more stairs than going up to the second floor may be enough for an attack.
- The third class (angina pectoris FC III) severely limits normal physical activity; for an attack, going to the first floor is enough.
- The fourth class (angina pectoris FC IV) is the most severe, with it it develops even at rest.
What to do if you have an angina attack?
- First of all, you need to try to pull yourself together and calm down
. Sometimes attacks of angina pectoris cause feelings of fear and panic in patients, which leads to an additional release of adrenaline into the blood, an even greater increase in heart rate, and as a result the attack intensifies. It turns out to be a vicious circle. - It is important to take a comfortable sitting or reclining position
. You cannot walk, stand or continue physical activity because... this may make the attack worse. You need complete rest until the pain symptoms go away. - Take the nitrate preparation under the tongue
.
Nitrate drugs dilate blood vessels and thereby stop an attack of angina. This could be, for example, nitroglycerin in tablets or spray form. - If, after taking a nitrate drug, the chest pain does not subside, it is recommended to take a second dose of the drug
(in total, up to 3 doses of the drug are allowed to be taken at intervals of 5 minutes).
If the medicine does not work, the pain does not subside for more than 10 minutes and even intensifies, you must urgently call an ambulance
!
How does the pulse behave in such patients and what can be done about it?
Not only pressure, but also pulse is important during angina.
An increase in heart rate (HR) above 70 beats per minute indicates that the heart is working hard. This means that the muscle's need for oxygen increases. In addition, since the coronary arteries receive blood during relaxation (diastole), when the heart rate increases, the duration of their filling is reduced. Under such conditions, chronic ischemia occurs, which leads to degeneration of the muscle fibers of the heart. If the heartbeat increases sharply during physical and emotional stress, for example, when you are simply catching up with a minibus, the need for oxygen rapidly increases. If against this background an attack of angina occurs with spasm of the coronary vessels, ischemia can have serious consequences.
Beta blockers are the drugs of choice in patients with high heart rates. They are included in treatment regimens for arterial hypertension.
Why is angina pectoris dangerous? Transition to myocardial infarction.
An angina attack usually goes away within 2 to 10 minutes.
after the first dose of a nitrate drug.
If an attack lasts more than 20–30 minutes
, it runs the risk of developing into
a myocardial infarction .
necrosis (death) of cells in one or more areas of the heart muscle occurs
Why does necrosis occur in the heart muscle?
Myocardial infarction is the result of severe oxygen starvation of the heart, when blood flow to the heart is reduced to a very low, dangerous level.
In such cases, the body uses compensatory mechanisms: additional small arteries send blood to the heart. But compensatory mechanisms cannot always cope with their task. For example, during a prolonged attack of angina.
In such a situation, first irreversible damage occurs, and then the death of those areas of the heart muscle that do not receive sufficient oxygen.
How to treat angina pectoris at home?
ETHNOSCIENCE
To treat angina pectoris at home, mainly decoctions and mixtures are used. They should include agents with an anticoagulant effect, that is, preventing rapid blood clotting,
as well as cardiotonic drugs - they improve blood circulation.
The list of such drugs includes: hawthorn, rose hips, motherwort, fruits and herbs of dill, roots and herbs of chicory, rhizomes and shoots of asparagus.
Recipes
- Take seven tablespoons of a mixture of hawthorn berries and rose hips, pour two liters of boiling water, wrap in a warm cloth and leave for a day. Strain, squeeze out the swollen berries and put the infusion in the refrigerator. Drink a glass a day with meals for 2-3 weeks.
- Place seven tablespoons of hawthorn berries (whole or chopped) and seven glasses of boiling water in a jar. Then close the jar and wrap it, put it in a warm place for a day. After infusion, strain the medicine, place it in the refrigerator and take three glasses a day with meals. You can add 1-2 tablespoons of rose hips to the preparation for sweetness and increasing the vitamin C content. At the beginning of treatment, you can mix hawthorn berries with motherwort herb in equal proportions, and then you can use only hawthorn berries.
- Hawthorn fruits, sweet clover herb, wild strawberry - two parts each, calendula flowers, meadowsweet herb, lemon balm herb, rue herb, yarrow herb, dill fruits, immortelle flowers - one part at a time (8 g of collection) pour 300 ml of boiling water, heat over water bath without boiling for 15 minutes, leave in a warm place for two hours, strain. Take everything 4-5 times warm an hour before meals and the last time an hour before bedtime. For night attacks, take half a glass hot.
- Take two parts of caraway fruits, periwinkle leaves, three parts of rhizomes with valerian roots, lemon balm leaves, four parts of hawthorn flowers, six parts of mistletoe leaves. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for two hours and strain. Take two glasses a day for angina pectoris.
- Mix two parts of wild strawberries and one part each of lingonberry leaf, yarrow herb and dog violet herb. Pour a tablespoon of this mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour and strain. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- Take two parts of canine violet herb and one part of the rhizome with valerian roots. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour, strain. Take half a glass of the folk remedy three times a day.
TREATMENT OF ANGINA WITH GARLIC
Like hawthorn, garlic occupies a special place in the treatment of angina. It is ineffective in combating angina pectoris, but it seriously helps prevent coronary heart disease, as it fights atherosclerosis and cholesterol plaques.
Recipes
- Grind 200-300 grams of peeled garlic cloves into a paste and mix with the same amount of honey. The mixture is sealed in a jar and infused for at least a week. Take a tablespoon three times daily before meals (30-40 minutes). The course can last up to 3 months.
- For angina pectoris, ascorbic acid is indispensable. You can add freshly squeezed lemon juice to the honey-garlic mixture, and this will only increase its medicinal qualities. You will need 10 lemons, a kilogram of honey and 10 large heads of garlic. This mixture is infused for the same amount of time, a week, and taken 3-4 teaspoons once daily. It is important to take your time and take at least a minute break after each spoon.
- You can boil thick chicken broth and pour two glasses of it into a dozen large cloves of garlic. Then the broth is boiled for 15 minutes, and about 50 g of parsley is added three minutes before removing from the heat. Boiled garlic and parsley are ground through a fine sieve and mixed again with the broth. This is a ready-to-use product that is useful to drink 75 ml half an hour before meals.
Risk factors for developing angina
Factors contributing to the development of angina:
- Physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle)
- High calorie diet, high in fat and cholesterol
- Obesity
- Increased levels of total cholesterol and in particular “bad” cholesterol in the blood plasma
- Diabetes
- Arterial hypertension
- Smoking
- Heredity
According to statistics, angina pectoris more often affects men under the age of 60–65 years , but after 70 years the ratio of male and female patients levels out. This situation is associated with the peculiarities of the endocrine system .
Oddly enough, cholesterol, considered the basis of all ills, is actually produced by the human body itself
and is involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones, including
sex hormones (testosterone in men, estradiol in women)
.
With age, the level of production of sex hormones decreases. In men, a noticeable decrease occurs at the age of 40–45 years, in women – after menopause (50–55 years).
Consequently, the body's need for cholesterol for the synthesis of sex hormones decreases, but cholesterol production remains at the same level. Thus, unused, “extra” cholesterol
. It is he who is involved in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, the development of coronary disease and, in particular, angina pectoris.
As can be seen from the figures, a noticeable decrease in the synthesis of sex hormones in men is observed 10 years earlier than in women, which leads to an earlier onset of cardiovascular problems in men.
Prevention of angina
The best method of preventing disease is prevention. If you have at least one of the listed risk factors, except for heredity, which, unfortunately, cannot be influenced, it is advisable to exclude them.
- If you have physical inactivity
(sedentary lifestyle), include in your daily schedule
physical activity
that is suitable for you (for example, fitness, running, Nordic walking or regular walking for at least 30-60 minutes a day). It is not the severity of the physical activity that is important, but the involvement of a large number of muscle groups in the body. - Replace a high-calorie diet
based on eating fatty foods that contain a lot of cholesterol
with a balanced diet
that includes plenty of vegetables and fruits. Limit your salt and sugar intake. Instead of fried foods, choose steamed, boiled or baked foods. - The presence of excess weight
, as a rule, is a consequence of physical inactivity and a diet containing not only a lot of fat, but also a lot of fast carbohydrates.
To cope with extra pounds, daily physical activity
(you don’t have to go to the gym right away, you can start with walking) and
switching to a balanced diet
. It is important to limit the consumption of fatty foods, flour and sweets, and instead choose vegetables, fruits, honey, nuts, and dried fruits in small quantities! - If there is an increased level of cholesterol
in the blood plasma,
diabetes mellitus
or
arterial hypertension
it is important
to consult a doctor
so that a specialist can help you choose the appropriate treatment and give individual dietary recommendations. - It is advisable to quit smoking
, because it can provoke not only angina, but also other, no less dangerous diseases.