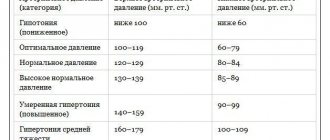
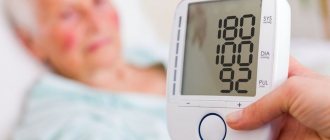
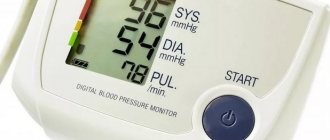
Blood pressure indicators are an important diagnostic criterion by which the quality of functioning of the vascular, cardiac system, and kidney function is assessed. In a healthy person, normal blood pressure (BP) levels are considered to be 120 per 70 mm Hg. Art., however, values may fluctuate depending on age, gender, food intake and a number of other factors. If indicators increase, it is necessary to take into account the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure. So, when a pressure of 140 to 60 is recorded, the patient should consult a specialist, since an increase in the upper reading may indicate the development of arterial hypertension. What does this mean for the patient’s health, and what conditions provoke dissonance between indicators?
Reasons for the growth of indicators
The difference between the values of systolic and diastolic pressure is called pulse pressure, which is an indicator of the functional state of the cardiovascular system. A pressure of 140 over 60 indicates a pathological increase in the upper reading and a moderate decrease in the lower reading, which is characteristic of isolated systolic hypertension. The pulse difference may be due to age-related vascular changes, when the upper pressure increases in different age categories, and the lower pressure increases mainly in people over 45 years of age. In this condition, an increase in pulse pressure occurs without exception, but the average blood pressure level can remain unchanged.
A pressure of 140 over 60 can be either short-term or permanent, which is a sign of the development of a pathological condition in the body. The reasons for the increase in the upper blood pressure indicator are the following processes:
- increased strength of heart contractions;
- rapid pulse;
- excessive vascular tone;
- sclerotic process in arterial walls;
- blocking the lumen of a vessel with atherosclerotic formation.
A decrease in diastolic indicator is associated with a decrease in the elasticity of the arterial walls, resulting in hemodynamic disorder. In hypertensive patients, diastolic pressure may decrease as a result of improper use of long-acting antihypertensive drugs. This disorder is short-term in nature, since the lower indicator is restored over time. Short-term changes in blood pressure levels can also be triggered by stressful situations or physical fatigue.
First aid at home
At home, first aid before the arrival of doctors may be required only against the background of a sharp deterioration in health, which is associated with heart rhythm disturbances. By itself, blood pressure 140/70 (140/60) does not require any intervention. For tachycardia, in addition to rest, loosening tight clothing and allowing fresh air into the room, you can give sedative drops: Corvalol. If substernal discomfort occurs, use Nitroglycerin under the tongue.
In case of bradycardia, absolute rest is recommended; the patient should be placed in bed with a support for the back (a bolster, a blanket), a heating pad for the legs or a mustard plaster for the calves. No medications are given unless previously prescribed by a doctor.
What diseases contribute to pulse differences?
A significant pulse difference may indicate the development of pathological conditions in the body that require emergency medical care. High pulse pressure can be caused by various reasons. Thus, a PP of more than 60 mmHg is considered a deviation from the norm. Art. To determine PP, a special formula is used, for example, with indicators of 140/60, its value will be equal to 80 mm Hg. Art. (140-60=80). In the presence of pathologies, blood pressure will remain at a constant level, reflecting degenerative changes in organs and systems.
As a rule, high systolic pressure in combination with low diastolic pressure is observed in elderly people. The imbalance is caused by the progression of the atherosclerotic process, which, affecting the vascular system, reduces the flexibility of the arteries.
The main diseases characterized by a high pulse difference:
- Atherosclerosis.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Chronic heart failure.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Endocarditis.
- Total vascular spasm.
Important! A sharp increase in systolic pressure with a decrease in heart pressure increases the risk of stroke and myocardial infarction. In addition, insufficient blood supply to the adrenal cortex and degenerative changes in the cardiac chambers are diagnosed.
How to treat high blood pressure
An increase in blood pressure cannot always be noticed without using a tonometer. Often the symptoms are similar to general fatigue and overwork. In the absence of help, the disease gradually gains unpleasant momentum.
As an emergency treatment, drugs that have an immediate effect are used.
The drugs are available in different dosages, so a doctor’s advice is required so as not to harm the body, but to prevent the development of a stroke. To obtain a hypotensive effect, the tablet is placed under the patient’s tongue and gradually dissolves.
If you have hypertension, you will have to constantly take medications to keep your blood pressure normal. Their effect is usually limited to a day. To obtain a cumulative effect, hypertensive patients are advised to take prescribed medications at one time of day.
To control the disease, complex therapy is sometimes prescribed. Antihypertensive, diuretic, and cardiac medications are used. If there is no desired effect, the medications must be changed after 2 weeks.
No drug is used without a doctor's prescription. The treatment regimen is selected individually.
Only a doctor determines the need to use diuretics, beta and alpha blockers.
Provoking factors
An unhealthy lifestyle negatively affects the functional state of the cardiovascular system. Various factors influence changes in pulse pressure and aggravate the course of pathologies.
Provoking factors causing differences in blood pressure levels:
What does it mean when systolic pressure is high and diastolic pressure is low?
- excess body weight;
- deficiency of microelements and vitamins;
- mental and physical stress;
- alcohol abuse;
- hypovolemia;
- metabolic disease;
- cardiosclerosis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pathology of the adrenal cortex.
Systolic hypertension at a young age is caused by poor nutrition, bad habits and exposure to frequent stressful situations. Systematic violation of the rest and work regime causes changes in biological rhythms, which lead to disruption of the nervous system, which is reflected in the growth of the upper indicator.
Therapeutic measures
When the pressure increases to 140 to 60 atmospheres, which is called isolated, first of all, you need to carefully monitor it. Blood pressure measurements are taken twice a day – in the morning and in the evening.
Drug effects
In case of strong surges, the doctor will prescribe a specific therapy suitable for the individual case of each patient. As a rule, these are the following drugs:
To prevent vasoconstriction, that is, blocking angiotensin-II: Lisinopril, Captopril.- To remove excess fluid from the body and reduce the risk of edema (Indap, Veroshpiron, Mannitol, Furosemide, Spironolactone).
- Calcium channel blockers, also aimed at vasodilation (Diltiazem, Verapamil, Nifedipine).
In this case, you should not self-medicate; without knowing the full picture of the disease, you can provoke a stroke or heart attack. Maximum - you can take Folic acid, diuretics, multivitamin complexes
General rules
If a high difference in indicators does not cause much discomfort, you can try to change its parameters for the better by completely correcting your usual lifestyle. To do this, it is important to follow a few simple rules, by following which you can improve not only blood pressure, but also overall well-being and quality of life:
- give up bad habits;
- stop drinking coffee and black tea;
- drink more clean water;
avoid meat products;- minimize the consumption of salt, sugar and products containing them;
- drink ginger tea;
- keep calm;
- normalize your weight;
- walk in the fresh air, move more;
- rotate your head in different directions;
- raise your legs above your head for at least 15 minutes a day;
- eat foods rich in folic acid (cabbage, legumes, brown bread, cucumbers, lettuce, parsley);
- massage or self-massage the collar area (neck);
- ventilate the room you are in;
- take a contrast shower;
- regulate your sleep (at least 8 hours in comfortable conditions).
These and other simple recommendations will help you feel the ease of life again and gain a surge of vigor and strength. Sometimes they are enough to cope with the disorder, but with a long course and progression of the pathology, medication is needed. An experienced doctor, examining the symptoms and course of the disease, will select the necessary medications.
Signs of the condition
The symptoms of the pathological condition are similar to the clinical picture of arterial hypertension, when fluctuations in blood pressure levels affect the functional state of the main organs and systems.
The first signs of systolic hypertension are:
- recurrent headaches;
- causeless fatigue;
- visual impairment;
- squeezing pain in the chest area;
- decreased tolerance to physical activity.
An increase in systolic pressure is accompanied by headache, which is localized in the temporal and parietal zones
When the level of upper pressure increases and the lower pressure remains normal, pain occurs in the myocardium. Patients experience pressing pain that increases with physical activity and decreases with rest.
When systolic hypertension is combined with a slow pulse, the circulatory process is disrupted, which leads to damage to the brain and myocardium. When the pulse becomes critically low (less than 55), sharply reduced hemodynamics provokes the occurrence of a heart attack, stroke, as a result of impaired hemodynamics of myocardial and brain cells. With minor changes in the contractile activity of the heart muscle, compensatory mechanisms are activated to prevent the development of acute conditions. However, the combination of bradycardia with high pulse pressure is a reason to consult a specialist.
Decrease in diastolic indicator
One of the most common pathologies is a decrease in diastolic reading with high systolic pressure. Thus, a pressure of 140 to 50 increases the risk of a heart attack as a result of excessive stress on myocardial cells.
Prolonged maintenance of this level of blood pressure negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system, since increased load depletes cardiomyocytes, which can lead to the formation of coronary heart disease. The pathological condition poses a threat to the body of both elderly and young patients. If indicators are detected, you should immediately contact a cardiologist for a thorough diagnosis of the cause of the condition.