How to recognize an attack
It is difficult for a non-specialist to draw a clear line between the onset of an attack of angina pectoris and the initial stage of myocardial infarction - the symptoms of these conditions are similar, but the consequences are very different.
Knowledge of the clinical picture of angina pectoris (an outdated name for angina pectoris) will help to avoid serious consequences for the body. Symptoms of angina:
- pain in the chest area, lasting for a long time (pressing, squeezing, in the form of a burning sensation), often radiating to other areas - neck, arms, back, jaw, abdominal cavity;
- attacks are possible both during physical work (angina pectoris) and during rest (angina pectoris at rest);
- during an attack, a person may feel short of breath, shortness of breath occurs, accompanied by numbness of the limbs;
- panic attack is a frequent guest during an attack of angina pectoris;
- As a result of taking Nitroglycerin, the pain goes away.
Rapid fatigue during physical or emotional stress is the first sign that your cardiovascular system is not coping with its task - providing tissues with blood in a volume sufficient for their functioning in an active mode.
To understand what sudden pain in the heart area can mean, you need to have minimal knowledge about the causes of its occurrence. As you know, the heart is a pump that pumps blood through a branched system of blood vessels to all tissues of the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
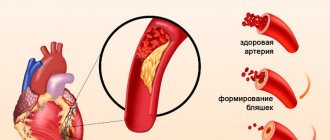
The appearance of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of the coronary arteries narrows their lumen, complicating the outgoing blood flow - and this is the main reason for the development of angina pectoris. At rest, the body has enough blood flow that is available, but during physical activity, the cells’ needs for blood supply increase sharply. Intensifying the work of the heart in the presence of atherosclerosis no longer helps, and the body begins to experience oxygen starvation. Unfortunately, the first to suffer is the myocardium, that is, the heart itself. When experiencing an attack of ischemia, the heart muscle sends an alarm signal to the brain in the form of pain, indicating the onset of an angina attack.
If atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries is significant and covers most of the lumen, angina pectoris can also occur at rest, often during sleep. When an attack does not go away after 20 minutes, this condition can lead to the onset of myocardial cell death, which marks the development of a heart attack. Therefore, it is so important that emergency assistance during an attack of angina pectoris is provided as quickly as possible.
However, atherosclerosis is not the only cause of angina. The following pathological conditions can lead to its development:
- anemia;
- previous myocardial infarction;
- presence of heart defects;
- spasm of the coronary arteries;
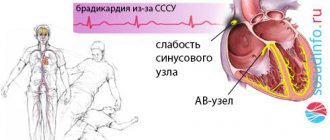
- arrhythmias (bradycardia, tachycardia);
- chronic hypertension;
- aortic pathology;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- menopausal pathological neurosis;
- ENT diseases;
- exceeding 40 years of age;
- genetic characteristics of the organism;
- being male;
- increased psycho-emotional and physical stress.
Lifestyle also plays an important role in the development of angina: bad habits contribute to the deterioration of the condition of blood vessels and a decrease in their elasticity.
Indulging in fatty and sweet foods leads to an increase in lipid levels in the blood, which is considered the main cause of the development of atherosclerosis. Physical inactivity leads to the same results, so eliminating all these factors is the key to preventing heart problems.
Angina attack
An attack of angina occurs when there is insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. Angina should not be considered as an independent disease; rather, it is part of a symptom complex indicating cardiac pathology.
Signs
An integral part of the clinical picture is pain in the chest area. However, if only this symptom is present, it is impossible to talk about a diagnosis. It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis from pathologies with similar manifestations.
An attack of angina will be indicated by:
- Cardialgia. The pain is pressing and squeezing in nature. Characteristic irradiation to the left half of the body: arm, shoulder, shoulder blade.
- The duration of a painful attack during angina pectoris ranges from a few seconds to 15 minutes.
- It can be triggered by high-intensity stress: both physical and emotional. In case of stable angina, to eliminate pain it is necessary to stop the exercise and take nitroglycerin.
Symptoms of an angina attack differ depending on its type:
- In a stable form, an attack of angina lasts 10-15 minutes. Nitroglycerin and cessation of exposure to provoking factors relieve pain.
- With a progressive form, the duration of the attack is 5-15 minutes. For its development, exposure to a provoking factor is not necessary. Pain can occur at rest, during sleep. Moreover, their intensity increases in the lying position. Nitroglycerin doesn't help.
- The spastic type of angina manifests itself as a short attack - no more than 5 minutes. It can occur in any situation that is accompanied by an increased need for oxygen in the myocardium. Emergency treatment for an angina attack is to take nitroglycerin.
Another sign of angina is difficulty breathing. Its appearance is explained by an increase in the need of myocytes for oxygen, the development of hypoxia, and ischemia. In this case, shortness of breath appears, pain occurs during inhalation, a burning sensation and squeezing in the front of the chest.
Most patients, due to respiratory dysfunction, experience panic attacks due to fear of death.
From the cardiovascular system, the following signs of an angina attack occur:
- numbness of the limbs;
- pale skin;
- high blood pressure;
- change in heart rate;
- increased heart rate;
- headache;
- pre-fainting state.
For patients who tend to have elevated blood pressure, there is a real risk of hypertensive crisis.
8
24/7
Causes
An attack of angina can be a consequence of a number of disorders in the body:
- Myocardial ischemia most often results from atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels - narrowing of the lumen due to the deposition of cholesterol on the walls.
- The myocardial need for oxygen also arises as a result of tachycardia - rapid heartbeat; vessels cannot always cope with the increased load.
- Another reason is arterial hypertension. When blood vessels narrow due to high blood pressure, normal blood flow is disrupted.
Factors that increase the risk of developing an attack include:
- Overweight. The greater the body weight, the higher the likelihood of developing an attack.
- Nicotine addiction.
- High cholesterol levels.
- Diabetes mellitus (increases the risk of developing angina by 2 times).
- Severe stress.
- Hypodynamic lifestyle.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Hypothermia/overheating.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Spicy food and overeating.
- Increased blood clotting, which increases the risk of blood clots.
In addition to atherosclerotic lesions, the causes of an angina attack may include:
- thromboembolism - blockage of a vessel with a blood clot;
- spasm - a sharp narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels.
Diagnostics
Laboratory tests are required: the patient undergoes a general blood test (CBC) and biochemistry. CBC allows you to determine the level of hemoglobin and platelets. Biochemistry is needed to determine the level of glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, etc.
Among the instrumental research methods prescribed:
- ECG. Using a cardiogram, they learn about the presence of changes in the heart, myocardial hypertrophy. Prolongation of the cardiac cycle and arrhythmias may indicate a heart attack.
- Holter monitoring. An effective diagnostic method that allows you to take ECG readings over a long period of time (from a day or more). Thanks to the results obtained, it is possible not only to record an attack of angina, but also its duration, and also to identify the causes.
- Load tests. The essence of the procedure is to artificially provoke an attack. The test is accompanied by continuous ECG recording and pressure measurement.
- Scintigraphy. It consists of introducing thallium isotopes into the vessels. Areas affected by ischemia accumulate the substance worse, so there is less radiation from them.
- Echo-KG. During the procedure, the condition of the myocardium is assessed: size, degree of filling of blood vessels, congestion, and impaired blood flow. Angina pectoris is usually accompanied by a deterioration in the mobility of the heart walls in the ischemic area.
- Coronary angiography. Designed to identify vessels affected by atherosclerosis. In addition, you can find out the size of the plaques and the degree of vasoconstriction.
Not all diagnostic methods can be used. The minimum diagnostic set of procedures includes: ECG, EchoCG, stress tests.
The most effective method for studying the severity of angina pectoris and the extent of vascular damage is coronary angiography. It shows the affected areas of the myocardium, their area, and the number of narrowed arteries. Thanks to coronary angiography, thrombosis, tearing of the arterial wall, and spasm are detected. The advantage of the method is the absence of contraindications.
The list of mandatory procedures includes coronary angiography in the following cases:
- angina pectoris of 3-4 functional class, unresponsive/poorly responsive to therapy;
- the presence of symptoms of severe ischemia obtained during ECG, Holter monitoring, stress tests;
- a history of ventricular arrhythmias;
- increase in symptoms despite treatment;
- the need to confirm/refute data obtained as a result of ECG, EchoCG.
8
24/7
How to help someone who is having a seizure
How to relieve an angina attack:
- Control your emotions. You should not panic, as this can lead to increased spasm.
- The patient must be seated in such a way that his legs are down; he is not allowed to stand up. It is important to provide access to fresh air; if a person is indoors, open a window.
- To stop an attack of angina, you need to put a nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue. The concentration of the active substance in the blood after taking the medicine becomes maximum after 4-5 minutes, its decrease is noted after 15 minutes.
- The tablet should be placed under the tongue. Absorption occurs in the oral cavity and the substance quickly reaches the coronary vessels, rather than into the general bloodstream. Vasodilation occurs, blood flow to the myocardium improves, and pain stops.
- Usually the attack goes away within 5-10 minutes after taking the pill. If this does not happen, analgesics should be used, since a prolonged attack may indicate the development of acute myocardial infarction.
- You cannot take nitroglycerin more than 3 times - this can lead to a sharp drop in blood pressure and the development of serious consequences. If the listed emergency aid methods for an angina attack do not help, the patient’s condition does not improve, you need to call a medical team.
It is mandatory to call an ambulance during an angina attack in the following cases:
- the duration of pain is more than 5 minutes, there is no positive dynamics, the pain does not subside;
- first attack of angina;
- intensity increases, accompanied by breathing problems, vomiting;
- in the absence of improvement after taking nitroglycerin.
An attack of angina indicates that the body needs a gentle regime. Therefore, over the next few days, a diet and avoidance of activities with high physical activity are recommended.
Treatment
Treatment of angina pectoris is complex and is aimed at solving the following problems:
- prevention of myocardial infarction and death;
- prevention of disease progression;
- reduction in the number, duration and intensity of attacks.
In addition to taking medications, it is necessary to make adjustments to your lifestyle:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- play sports, providing exercise, the intensity of which has been agreed with the doctor;
- follow a diet and bring your body weight back to normal.
Standard drug treatment includes taking anti-ischemic drugs that reduce myocardial oxygen demand and other medications:
- nitrates;
- beta blockers;
- calcium channel blockers;
- antisclerotic agents;
- antioxidants;
- antiplatelet agents.
8
24/7
If treatment is ineffective, surgical methods are used:
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- vascular stenting.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely insure yourself against an attack of angina, but it is necessary to take measures to prevent attacks of angina in order to reduce the risks.
First of all, it is necessary to control body weight, since excess weight is an unobvious impetus for the development of many diseases. All bad habits must be eradicated as early as possible: both smoking and alcohol lead to vasoconstriction, which can result in artery blockage anywhere and at any time.
You cannot neglect existing diseases - the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the body increases the risk of its spread to the heart.
After an attack of angina, the following recommendations are used as secondary prevention: limit anxiety and the intensity of physical activity, take nitroglycerin before playing sports or emotional situations, and treat existing diseases in a timely manner.
If a person has already experienced an attack, it is necessary to find a specialist who can manage it and monitor it regularly. It is important to prevent the dynamics from deteriorating and not to start the processes of circulatory disorders.
Emergency care for angina pectoris: algorithm of actions
If the attack was caused by overexertion, then with PMP the patient needs rest. Stop the movement and take a comfortable position. Standing up and walking is prohibited, as this can provoke fear and increased pain.
Rest is necessary, take a comfortable position.
You need to immediately count your pulse and track your breathing. The victim needs fresh air. He is freed from restrictive clothing and the temperature is stabilized. For those who have frequent attacks, the first first aid for angina pectoris will be a first aid kit with special medications - nitroglycerin, acetylsalicylic acid and Corvalol.
- Symptoms of an angina attack, how to relieve it at home, what needs to be examined and how to treat it
To help, give a capsule or tablet of nitroglycerin.
How does cupping happen? A capsule or tablet of nitroglycerin is dissolved under the tongue, which dilates blood vessels and stabilizes the heartbeat. It is permissible to use Nitromint aerosol in one dose. To quickly thin the blood, chew an aspirin tablet in a dose of at least 60 mg.
Psychological stress can be relieved with tincture of motherwort, valerian or corvalol. If there is a sharp rise in blood pressure, a special antihypertensive drug, which was prescribed by the attending physician, comes to the rescue. After eliminating the attack, the patient is advised to rest in bed and distribute physical and emotional stress in such a way as to avoid relapse.
Prolonged attack
First aid for a persistent attack of angina is carried out in a hospital setting. An ECG is performed to determine the functioning of the heart. Oxygen therapy will help make breathing easier.
- For variant attacks, along with nitroglycerin, Corinfar is placed under the tongue in a dose of 10 mg. Corinfar is also used under the tongue.
- Intense symptoms, tachycardia and high blood pressure require the administration of adrenergic blockers. Be sure to take into account the patient’s condition and possible contraindications.
- If the symptom lasts for more than 10 minutes or there is no effect from nitroglycerin, chew aspirin at least 250 mg. The tablet should not have a shell. Talamonal is administered if pain persists even after taking nitroglycerin. The drug is replaced with Morphine or Promedol. If there is no effect from nitroglycerin, chew aspirin.
- In the absence of narcotic analgesics, slow intravenous administration of other drugs - Tramadol, Droperidol - is permissible.
- First aid for angina pectoris includes the administration of heparin by the jet method if the cardiogram shows ischemic disorders.
Angina pectoris (angina pectoris) - symptoms and treatment
After collecting complaints, anamnesis of life and illness, and examination, additional laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed.
Laboratory tests are mainly aimed at diagnosing dyslipidemia, which contributes to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. For this purpose, a blood lipid spectrum analysis is prescribed, which includes total cholesterol and its fractions.
Instrumental methods primarily include electrocardiogram (ECG) . Many patients go to the cardiologist with the question “is everything normal with my heart” with only one ECG film. But, unfortunately, these indicators are of informative value only during an attack. In most cases, it is impossible to determine angina pectoris from one ECG film taken at rest, since it can only show rhythm disturbances, hypertrophy (enlargement) of various parts of the heart, conduction disturbances, or the presence of a previous myocardial infarction.
There is also an ultrasound examination of the heart , which shows its structure and can reveal possible abnormalities. Echocardiography is intended to determine the size of the heart and its chambers, the presence of valve defects (stenosis and insufficiency), neoplasms and previous infarction. But this study, like an ECG, is not informative enough if it was carried out outside an attack of angina, at rest.
Holter ECG monitoring (outpatient monitoring) is much more informative than the above studies. It is advisable to perform it in order to identify signs of myocardial ischemia during daily activities. To do this, the patient walks, eats and sleeps with the device attached to it for about a day, i.e., performs normal daily physical activity. When an attack occurs, the person being examined records the incident in a diary and then informs the doctor about when and under what conditions the symptoms arose. The sensitivity of this method in diagnosing coronary heart disease is 44-81%.
Since angina attacks practically do not occur at rest, there are examination methods using physical activity. By analogy with an electrocardiogram, a bicycle ergometry and treadmill test : an ECG is taken while the patient performs physical activity on a bicycle or treadmill. The sensitivity of this method is approximately 68%.
A more sensitive method is stress echocardiography - this is the same ultrasound examination of the heart, only performed after physical activity. As your heart rate increases during running, your myocardium consumes more oxygen and nutrients. When a vessel narrows, a sufficient amount does not enter the muscle, resulting in an attack of chest pain and disturbances in contraction. As a result, hypokinesia develops, which can be seen with ultrasound. This study has greater sensitivity (80-85%) and specificity (84-86%)
If it is impossible to perform an ECG and EchoCG during exercise, you can use transesophageal electrical pacing (TEES) or pharmacological tests . These methods are based on increasing the myocardial oxygen demand by increasing heart rate without significantly changing blood pressure.
There are also two less common research methods: stress myocardial perfusion scintigraphy and multislice cardiac computed tomography.
The main method for assessing the condition of the arteries, in which vessel narrowing can be visually recognized, is coronary angiography (CAG) - a radiopaque examination method that reliably determines the location and degree of narrowing of the arteries, as well as the type of blood supply, signs of thrombosis, ulceration, calcification and spasm of the coronary artery.
According to the timing of completion, this examination is divided into emergency (within 6 hours), urgent (within 6-12 hours) and planned.
Emergency coronary angiography is performed in case of unstable angina or myocardial infarction, when every minute is important.
Indications for planned coronary angiography include:
- objective signs of myocardial ischemia;
- transient ischemic changes detected during an ECG at rest or during 24-hour ECG monitoring;
- positive exercise test with bicycle ergometry, treadmill test, TES, stress echocardiography or myocardial scintigraphy;
- the occurrence of attacks of angina pectoris II-IV FC or angina pectoris at rest;
- condition of early post-infarction angina;
- life history of dangerous ventricular arrhythmias with a high risk of clinical death;
- planning surgery on the heart valve apparatus in people over 40 years of age;
- carrying out differential diagnosis with non-coronary myocardial diseases (including atypical pain syndrome);
- social indications in the presence of minimal and unclear signs of myocardial ischemia, provided that the patient’s profession is associated with a risk to the lives of other people (pilots, drivers), combat duty, etc.;
- undergone heart transplantation (the study is carried out every year, sometimes in combination with intravascular ultrasound).
There are currently no absolute contraindications for prescribing CAG.
An intermediate place is occupied by emergency coronary angiography. It is carried out in the event of a deterioration in the condition of a patient who is being treated in a hospital due to the progression of angina pectoris, when attacks of rest angina pectoris occur, there is no effect from maximum therapy, as well as in case of deterioration in condition after endovascular surgery or coronary artery bypass grafting.[1][10]
In what cases is Nitroglycerin contraindicated during an attack of angina?
The patient or his relatives should be aware that if signs of low blood pressure are detected (with collaptoid angina), taking drugs from the group of organic nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Isoket, etc.) is contraindicated. The following signs may indicate hypotension:
- the patient experiences severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- pallor;
- cold sweat.
In such cases, the sequence of actions should be as follows:
- Lay the patient down.
- Call an ambulance.
- Give him a crushed Aspirin tablet.
- To reduce pain, you can use tablet analgesics (Baralgin, Sedalgin, etc.).
How to recognize an attack?
Assistance for angina pectoris should be provided immediately in the presence of threatening symptoms.
Cardialgia. This term refers to a painful sensation that appears in the left region of the sternum. In most cases, discomfort spreads to other parts of the body - shoulder blades, limbs, neck and forearm. Cardiac arrhythmia is often observed with cardialgia. The most unpleasant and intense pain is felt in the middle of the sternum on the inside, where the spongy tissue is located. It connects the rib cage with the ribs and the spinal column.
Pain in the left sternum.
- Hypertensive crisis - symptoms. Emergency first aid for hypertensive crisis - algorithm of actions
Types of pain by nature:
- burning;
- pressing;
- bursting.
By duration:
- stable (10-15 minutes);
- progressive (5-45 minutes);
- spontaneous (less than 5 minutes).
Problems arise when inhaling and exhaling.
Difficulty breathing. The victim may have trouble breathing in and out. This reaction is caused by myocytes - cells of cardiac tissue that are in dire need of oxygen.
Shortness of breath occurs during hypoxia, and inhalation is accompanied by pain. Help can be provided through medications.
Disturbance in cardiovascular work. There is a feeling of numbness in the limbs, the skin color becomes marbled or pale. Cyanosis or blue discoloration occurs if acute oxygen deficiency develops inside. Blood pressure increases, which increases the risk of stroke or heart attack. The feet and palms may be clammy and cold sweat is common. There are often cases when the victim complains of lightheadedness and headache.
There is a feeling of numbness in the limbs, the skin color becomes marbled or pale.
Atypical signs of pathology:
- panic attack, anxiety, fear of death;
- pain in teeth and throat;
- severe weakness without pain;
- nausea, burning in the stomach, belching.
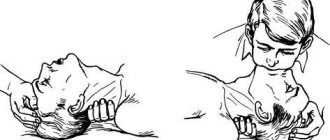
First aid for angina pectoris, which is accompanied by a hypertensive crisis, must be provided before the arrival of medical workers. This condition is dangerous for the patient. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is sometimes required.