Causes of pathology
The reasons for the development of neuralgia can be different: inflammatory processes, injuries, bacteria and viruses, poisoning with drugs and various substances, autoimmune diseases, circulatory disorders in the vessels supplying the nerve.
- infections such as shingles, Lyme disease, or HIV
- pressure on bone nerves, blood vessels or tumors
- kidney disease or diabetes
- age
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia begins with an initial examination. First of all, the doctor pays attention to the position of the patient’s body. As a rule, it is tilted to the opposite side - so as not to provoke a second attack. If several nerve branches are affected, sensitivity in a certain area may be impaired.
To clarify the diagnosis, additional studies and procedures may be required:
- ECG;
- X-rays of light;
- MRI of the spine;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- electroneurography.
Additional research is needed to differentiate intercostal neuralgia from cardiovascular diseases, infections, diseases of the musculoskeletal system and digestive tract. In this regard, you may need additional consultation with a specialized specialist - a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, chiropractor.
Research is also carried out to clarify the nature and location of the disease. Thus, electroneurography helps determine the structure and functionality of nerve fibers and determine the causes of their irritation.
Important! The information is posted on the website for informational purposes. Don't self-diagnose - consult a specialist!
What are the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia?
- Sudden episodes of severe shooting or stabbing pain that follows the path of a damaged or irritated nerve. Symptoms appear on either the right or left side. The pain intensifies with any movement.
- Constant aching or burning pain.
- Tingling or numbness.
- Muscle weakness.
- Loss of muscle mass or atrophy.
- Involuntary muscle twitching or spasms.
In children, characteristic pain occurs during a period of intense growth, when the skeleton is growing rapidly. Severe pain in the affected areas and cramps are the main symptoms of neuralgia by which the disease is recognized in children. Additional signs include profuse sweating, increased excitability, tearfulness, sleep disturbance and stuttering.
The main goal of treatment is to distinguish this disease from others. It is important to distinguish attacks of neuralgia from manifestations of heart attack and angina. With neuralgia, there is no fever, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or blue discoloration of the skin.
Types of neuralgia
Medical professionals divide neuralgia into categories based on the areas of the body that it affects. The following are some common types of neuralgia :
Trigeminal neuralgia
TN can cause shooting pain in the face.
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) involves the trigeminal nerve in the head. It has three branches that send signals from the brain to the face, mouth, teeth and nose.
TN is divided into two divisions: type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 TN causes a painful burning or electric shock sensation in some parts of the face. People with type 1 TN experience irregular episodes that come on suddenly.
The duration of these episodes varies among individuals, but can last up to 2 minutes, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Type 2 TN produces a constant, dull, aching sensation on the face.
The exact cause of TN remains unclear. However, pressure from the enlarged blood vessel can irritate or even damage the trigeminal nerve.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) can lead to TN. MS is a neurological disorder that causes inflammation that damages the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers in the central nervous system.
Postherpetic neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a painful condition that affects the nerves of the skin.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), PHN is the most common complication of shingles, affecting about 10–13% of people who develop it.
Shingles is a viral infection that causes blisters and a painful skin rash. The varicella zoster virus, which causes chickenpox, remains dormant in the nervous system and becomes active later in life, causing shingles.
When the virus is reactivated, it can cause inflammation of nerve fibers. This inflammation can lead to permanent nerve damage, which causes pain even after the infection subsides.
Occipital neuralgia
This form of neuralgia affects the occipital nerves, which originate in the neck and send signals to the back of the head.
Occipital neuralgia causes throbbing or shooting pain that begins at the base of the skull and spreads along the scalp. Pain in occipital neuralgia may flow to the back of the eyes.
Occipital neuralgia has many potential causes, including:
- sudden head movements
- tense neck muscles
- lesions or tumors in the neck
- inflamed blood vessels
- infections
- gout
- diabetes
- neck injuries
Peripheral neuralgia
Peripheral neuralgia, or peripheral neuropathy, refers to pain that occurs due to nerve damage in the peripheral nervous system. This includes all nerve fibers outside the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral neuralgia can affect one nerve or entire nerve groups.
Sustained damage to the peripheral nervous system can affect the nerves that control muscle movement, transmit sensory information, and regulate internal organs.
Peripheral neuralgia can cause pain or numbness in the arms, legs, arms and legs. Other symptoms may include:
- involuntary muscle twitching or spasms
- loss of coordination
- difficulty performing complex motor tasks such as buttoning a shirt or tying shoelaces
- hypersensitivity to touch or temperature
- excessive sweating
- gastrointestinal problems
- difficulty eating or swallowing
- it's hard to talk
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia affects the nerves that sit just below the ribs. Doctors call the muscles in this area the intercostal muscles.
Several potential factors may contribute to intercostal neuralgia, such as:
- injuries or surgical procedures involving the chest
- pressure on the nerves
- shingles or other viral infections
Intercostal neuralgia causes sharp, burning pain that affects the chest wall, upper abdomen, and upper back. Certain physical movements, such as breathing, coughing, or laughing, can make the pain worse.
Additional symptoms may include:
- tightness or pressure that envelops the chest
- tingling or numbness in the upper chest or upper back
- muscle twitching
- loss of appetite
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is the most common complication of diabetes. Because diabetes affects so many people, rates of peripheral neuropathy are now starting to rise.
Symptoms include loss of balance and numbness, tingling and pain. The best way to prevent diabetic neuropathy is to keep your blood sugar levels within an acceptable range.
Diagnostic methods
You need to see a general practitioner. After examination and exclusion of other pathologies, the therapist refers to a neurologist who determines the symptoms and treats intercostal neuralgia. The doctor examines the images, prescribes tests and medical examinations.
Instrumental diagnostic methods of examination:
- Radiography. Allows you to examine the bone structure. Makes it possible to determine the presence of non-traumatic or traumatic disorders. X-rays are taken in direct, oblique and lateral projections.
- CT scan. Examines bone and muscle structure in combination. More often used to detect pathological changes in bone structures.
- Myelography. A contrast agent is injected into the spinal canal. This is the main method for diagnosing soft tissue structures (nerve roots and spinal cord).
- Contrasting discography. During the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the intervertebral disc.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to obtain images of organs and tissues. Detects pathological changes in soft tissue structures: nerve tissue, muscles, ligaments, hernias and degenerative changes in intervertebral hernias.
- Electrospondylography. Using the computer diagnostic method, it is possible to assess the condition of the spinal column, identify the disease at an early stage, determine the extent of damage and monitor the course of the disease.
Expert opinion of a doctor
Intercostal neuralgia on the left side of the heart is often mistaken by patients for a heart attack. It can be distinguished by its characteristic features. If you take a stationary position during intercostal neuralgia, the symptoms will become less pronounced. For cardiovascular diseases - no.
Pain with intercostal neuralgia intensifies due to coughing, laughter, deep breaths, and forced movements. However, it does not change during cardio exercise. With cardiovascular diseases, it's exactly the opposite.
With neuralgia, heart rate and blood pressure do not change, the pain is girdling in nature and intensifies with palpation of the ribs. In cardiovascular diseases, blood pressure and heart rate change, palpation is painless, and the pain syndrome is localized in the projection of the heart or behind the sternum.
Methods for treating intercostal neuralgia
Drug therapy. There is a wide variety of drugs to eliminate pinched nerves: painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, those that increase the body’s defenses, injections, blockades. All drugs have a long list of side effects, so before using them you need to consult a specialist. Any medicine is selected depending on the severity, tendency to allergies, and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
- Anticonvulsants inhibit the conduction of pain impulses.
- Tricyclic antidepressants relieve tension in chronic pain syndromes.
- Venotonics and diuretics relieve swelling.
- Corticosteroid drugs are used in cases of severe inflammation.
- Vitamins B1, B6 and B1 accelerate the restoration of the nerve sheath, reduce inflammation and pain.
Compresses. They can be either hot or cold. They are used to reduce inflammation and also to reduce pain. This is only a temporary measure and has no therapeutic effect.
Other methods: gymnastics, shock wave therapy, massage, physiotherapy - alleviate your condition, ensuring complete recovery. And these procedures do not harm the body.
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy. Intercostal neuralgia is often caused by poor posture. The goal of physical therapy is to relieve the back muscles and open the chest. Therapeutic exercises should be performed 3-4 times a day.
Physiotherapy includes acupuncture, osteopathy, manual therapy, massage with warming creams and ointments, and kinesiotaping. They relax the fascia of the chest and back. Heat helps to temporarily relax muscles, relieve swelling, inflammation and acute pain.
Massotherapy. It should be done while sitting. When performing the procedure, the intercostal spaces are rubbed and stroked with your fingertips. In addition to this, they knead and rub the back muscles with both hands. During acupressure massage, use your fingers to press on active points associated with one or another affected organ. Acupressure can stimulate defenses and relieve pain.
How intercostal neuralgia is treated at the Juno clinic
After the examination and diagnosis, the doctor draws up a treatment plan. Treatment of intercostal neuralgia caused by a disease is carried out in parallel with its elimination. An integrated approach makes it possible to get better results in a shorter period of time.
The following methods can be used for treatment:
- taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of blockades, injections, ointments, tablets;
- general strengthening drug therapy (for example, vitamins);
- fixation of the spine to ensure rest (it is possible to use a bandage or corset);
- physical therapy in the form of electrophoresis, UHF, laser beam exposure, darsonvalization;
- reflexology;
- massage (eliminates muscle spasms, ensures lymph and blood flow in the affected area, improves tissue trophism);
- Exercise therapy, osteopathic correction, etc.
Physical procedures, massage and therapeutic exercises are not prescribed immediately, but after the acute symptoms have been eliminated.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the presence of neuralgia is considered a fairly serious problem. It requires proper attention, which will help avoid complications for the expectant mother and baby.
All treatment that will be given to a pregnant woman for neuralgia must be prescribed by the attending physician. Self-therapy is extremely undesirable, as it can greatly harm the woman and the child in the womb.
Many patients prefer not to take medications. They limit themselves to vitamins and mineral complexes, use ointments and warm compresses, observe bed rest and perform simple physical exercises.
Gymnastics for neuralgic pain in pregnant women is very effective. Physical exercise does not allow blood to stagnate in the joints and parts of the spine.
If the pain becomes unbearable, novocaine blockades are prescribed with caution.
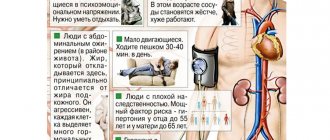
Causes of intercostal neuralgia
The main causes of intercostal neuralgia are as follows:
- a number of diseases of the nervous system: multiple sclerosis, polyradiculoneuritis;
- diseases of the thoracic spine: deforming spondylosis, osteochondrosis, herniated disc, scoliosis;
- hypothermia of the body;
- intoxication of the body with alcohol, medications, salts of heavy metals;
- back and sternum injuries;
- weakening of the immune system;
- lungs' cancer.
Prevention of intercostal neuralgia
The main preventive measure is gymnastics. It is necessary to perform exercises that promote muscle development, strengthening and mobility of the spine. Avoid drafts, uncomfortable positions and excessive physical activity. Everything should be in moderation.
It is important to control your posture, not lift excessive weights, eat a rational and balanced diet, take vitamins, and avoid fasting and mono-diet.
Do not forget to promptly treat diseases that can cause the development of neuralgia.
Read also
Rehabilitation after stroke
It is very important to begin rehabilitation after a stroke as early as possible, since further recovery and the ability to avoid disability depend on this.
For rehabilitation after a stroke in the clinic “First… Read more
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a vascular disease that is caused by a decrease in the elasticity of the vascular wall, the deposition of cholesterol on the inner surface and, as a result, the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis…
More details
Myelitis
Myelitis is a neurological pathology characterized by inflammation of the gray and white matter of the spinal cord, which leads to damage to myelin (the substance that forms the sheath of nerve fibers) and the axon (the process...
More details
Restless legs syndrome
Restless legs syndrome - manifests itself as unpleasant sensations in the lower extremities, mainly in the evening and at night, forcing you to make relief movements with your legs, which leads to…
More details
Vertebral artery syndrome
The main vascular highways carrying blood to the brain pass in the neck - these are two carotid and two vertebral arteries. A decrease in blood flow through the vertebral arteries will lead to the development of acute...
More details