07/20/2017 Olga Migunova 4 comments
Hemoglobin is a pigment that colors blood red, which consists of a protein part and iron.
The main function of this blood component is the transport of oxygen from the lung tissue to all cells of the body.
The level of hemoglobin in the blood is one of the most important indicators of the health of the human body, which is determined using a general blood test.
The level of hemoglobin in the blood of women directly depends on age. The female body is more prone to changes in this indicator, which is associated with its physiological characteristics (pregnancy, menstrual cycle, menopause, etc.).
In addition, a decrease or increase in the amount of hemoglobin can be a symptom of various diseases (anemia, polycythemia, and others).
Taking into account the above, we would like to tell you what the hemoglobin norms may be for women of different age groups, as well as what causes their change.
Hemoglobin: norm for women by age, table
| Woman's age, years | Amount of hemoglobin, g/l |
| 17-19 | 112-148 |
| 20-29 | 110-152 |
| 30-39 | 112-150 |
| 40-49 | 112-152 |
| 50-59 | 112-154 |
| 60 and older | 114-160 |
The female body is characterized by hormonal changes that occur throughout life: puberty, the onset of menstruation, expecting a child, menopause.
Hormones affect the level of hemoglobin in the blood. In addition, this indicator may change during the month due to the period of the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, the hemoglobin level decreases slightly, but at the end of the critical days it returns to normal.
As you can see, the hemoglobin level in women after 40 years is slightly reduced, which is explained by the onset of menopause and changes in hormonal levels. Menopause occurs mainly between 45 and 55 years of age, so this must be taken into account when analyzing your blood test.
This is also associated with a change in the hemoglobin norm in women after 50 years. In addition, the upper limit moves slightly upward due to the fact that with age there is a tendency for blood to thicken.
Since women over 60 years old do not have a menstrual cycle, this indicator should be stable.
Don't make mistakes!
For pills to work well, it is important to take them correctly. It is best in the second half of the day, it is at this time that iron is absorbed more actively. And no later than an hour before meals - once in the intestines, it should be absorbed without contacting food.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the anemia. While taking iron supplements, the stool may be dark in color - this is normal. But sometimes constipation or loose stools occur, and nausea occurs. If such symptoms persist for a long time, it is necessary to change the drug or reduce the dose. If you have an acute respiratory viral infection or the flu due to anemia, then you should not take iron supplements during illness.
After a month of treatment, a control blood test is done. If during this time the hemoglobin level has not increased or continues to decrease, the doctor suspends treatment and refers the patient for a new examination, since the diagnosis needs to be clarified - perhaps anemia is caused not by iron deficiency, but by other reasons.
What is the normal hemoglobin level for women during pregnancy?
Pregnant women often experience changes in hemoglobin levels. Moreover, this indicator directly depends on the duration of pregnancy and the characteristics of its course.
In the first months, pregnant women have the same amount of hemoglobin in their blood as non-pregnant women - ranging from 110 to 150 g/l.
In the second trimester, the minimum hemoglobin rate in pregnant women can decrease to 100 g/l. This trend is associated with an increase in blood volume in the body. But hemoglobin itself does not disappear anywhere, it is simply diluted in more blood. This does not affect the well-being of the pregnant woman and baby.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the female body has already become accustomed to the increased needs of the belly fat, so the hemoglobin norm should be in the range from 110 to 140 g/l.
The 3rd trimester of pregnancy is characterized by active growth and weight gain of the child. Therefore, all pregnant women must undergo monthly monitoring (general blood test) in order to timely determine a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and exclude oxygen starvation or delayed fetal development.
Iron is different from iron
It is believed that the best way to increase hemoglobin levels is to eat more foods containing iron. Old folk recipes advise: cook liver dishes, eat carrots, beets, walnuts, apples, drink pomegranate juice, and you will quickly increase hemoglobin.
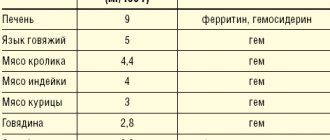
Actually this is not true. Because iron is different. Indeed, many fruits and vegetables and legumes contain a lot of iron, but it is poorly absorbed. As well as from the liver, where iron compounds are presented in the form of complex proteins that are not easy for the body to “take away”. The so-called heme iron, found only in meat and poultry, is best absorbed.
But in order for it to be absorbed, it is also important what the meat is eaten with. For example, if you serve pasta or porridge as a side dish, much less iron will be absorbed: cereals contain phytates that bind it. An excellent partner for meat dishes are vegetable side dishes made from zucchini, broccoli, onions, and herbs (they contain substances that stimulate hematopoiesis). It makes it difficult to absorb iron and calcium, so dairy and meat products are not compatible.
Fats inhibit hematopoiesis, so fatty meats and fish, and especially lard, are excluded. But butter and any vegetable oil - sunflower, olive, corn, pumpkin, etc. - should definitely be on your table. Do not drink tea immediately after meals - tannin binds iron, preventing it from being absorbed. And don’t get too carried away with coffee - this drink “washes” iron from the body.
Vitamins, especially C, help the absorption of iron. It is useful to drink orange and tomato juices every day. And eat more fruits and vegetables: the best suppliers of ascorbic acid are black currants, citrus fruits, kiwi, and bell peppers. In winter, when the vitamin C content in fresh fruits and vegetables drops sharply, sauerkraut and rosehip infusion perfectly replenish it.
Norm of glycosylated hemoglobin, table
| Amount of glycosylated hemoglobin in blood, % | Interpretation of the result |
| 5.6 or less | Norm of glycated hemoglobin |
| from 5.7 to 6.0 | Increased likelihood of developing diabetes |
| from 6.1 to 6.4 | Very high risk of developing diabetes |
| 6.5 or more | Diabetes |
An analysis for glycated hemoglobin can be taken at any time of the day, on an empty stomach or after a meal, after stress or after physical strain, since the listed factors will not affect the objectivity of the result.
In letter and in spirit
If, during repeated blood tests, hemoglobin remains at the same level or continues to decrease, it is necessary to switch to iron supplements. For children, they are available in the form of dragees, capsules, syrups (there are also solutions for injections). For adults – in tablets and injections. There are monocomponent preparations - that is, those that contain only iron (they are usually prescribed to those who suffer from allergies) and combined ones, where iron is combined with various vitamins that promote its better absorption.
The doctor may prescribe injections in cases where the absorption of iron in the intestines is severely impaired (with inflammatory bowel diseases, severe diarrhea).
But in our country, as a rule, preference is given to tablets. Because, on the one hand, iron “in the injection” is absorbed worse, on the other (paradox!) – you can overdo it with its dosage. Which is also not good. Because iron, once it enters the body, is not removed from it itself, but lies in the so-called “depots”. Excess iron storage can trigger the development of diabetes, severe liver disease, heart disease, and even breast cancer.
Increased hemoglobin: causes and symptoms
Hemoglobin in women may be elevated for the following reasons:
- congenital heart defects;
- increased number of red blood cells in the blood;
- extensive thermal injuries to the skin;
- intestinal obstruction;
- pulmonary failure;
- heart failure;
- diabetes;
- dehydration;
- smoking;
- living in high mountain regions;
Symptoms of increased hemoglobin in women:
- local hyperemia of the skin;
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- thirst;
- dry skin;
- causeless surges in blood pressure;
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- mood swings;
- emotional lability;
- algodismenorrhea (painful menstruation);
- heavy menstrual bleeding and others.
If a girl or woman notices the above symptoms, she needs to see a general practitioner, who will give a referral for a general blood test and determine their cause. Untimely normalization of hemoglobin levels in the blood can lead to serious complications, such as vascular thrombosis, ischemic stroke and pulmonary embolism.
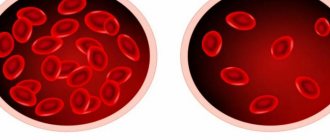
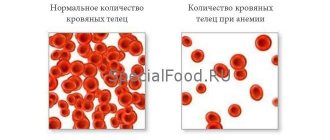
Low hemoglobin - why it is dangerous
Hemoglobin is a complex chemical component of blood, which consists of protein and iron molecules. This constituent component is part of red blood cells and circulates through the bloodstream of the human body. The main task of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen molecules from the lungs to tissues, cells and internal organs.
With low hemoglobin, oxygen saturation of the body's cells decreases, which causes a decrease in immunity, a person loses vitality, organs do not receive proper nutrition, as a result of which their functionality is significantly reduced. Tissue cells suffer from oxygen depletion.
The most important complication of low hemoglobin is iron deficiency anemia. Its severe forms can cause loss of consciousness due to a high degree of brain hypoxia.
Decreased hemoglobin: causes and symptoms
Hemoglobin may decrease for the following reasons:
- unbalanced diet, which consists of a deficiency in the daily diet of foods containing iron;
- mono-diets;
- starvation;
- vitamin deficiencies C and B12, which are caused by helminthiasis and unbalanced nutrition;
- bleeding and large blood loss during menstruation;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- diseases of the digestive system, which lead to inability to absorb iron and vitamins;
- diseases of an infectious nature that accelerate the destruction of red blood cells (hepatitis, tuberculosis and others);
- autoimmune diseases that also contribute to the death of red blood cells (rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus and others) and others.
A decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is called anemia or anemia in medicine.
Symptoms of anemia:
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- dry skin;
- brittleness of hair and nails;
- angular stomatitis (cracks in the corners of the lips);
- headache;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased ability to work;
- tachycardia;
- insomnia;
- dyspnea;
- caries;
- yellowing of tooth enamel;
- coating on the tongue;
- smoothing of papillae on the tongue and others.
Now we can summarize the above. Hemoglobin is the most important blood marker not only in women, but also in men. By its level in the blood one can judge the presence of both physiological conditions and various diseases. To monitor this indicator, a healthy person is recommended to undergo a general blood test twice a year.
Both adults and children
With iron deficiency anemia, the balance is disturbed: the loss of iron in the body exceeds its absorption. This happens in children during periods of rapid growth (in the second year of life and adolescence) or due to infection with worms. Anemia is a frequent companion of pregnant and lactating women, whose iron needs increase sharply - after all, they have to “share” it with the child.
But the most common cause of iron deficiency in adults is frequently recurring small bleeding (from 5-10 ml per day). They can be caused by a variety of diseases: from bleeding ulcers and hemorrhoids to stomach cancer. In women, the main cause of iron deficiency is uterine bleeding (caused by endometriosis or other gynecological diseases) and heavy menstruation; in men, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
Often we rob ourselves: fasting days, independent diets are a very short path to iron deficiency.
When is it necessary to take a hemoglobin test?
In modern medical practice, a blood test for hemoglobin is considered basic. The study is prescribed when registering pregnant women, to clarify the diagnosis if anemia or the development of other pathologies is suspected. Living in a deteriorating environment and constant mental and physical stress require careful attention to your health. Chronic fatigue, frequent depression, loss of interest in life are serious reasons to visit a doctor and get a referral for a blood test.
Indications for prescribing a hemoglobin test are:
- frequent headaches;
- the appearance of dry mouth;
- lethargy, drowsiness or painful insomnia;
- paleness of the skin, long-lasting bruises;
- severe thirst and increased urge to urinate;
- deterioration of vision and memory;
- poor healing of cuts and wounds;
- instability of psycho-emotional state.
Clarifying the level of hemoprotein in the blood is especially important for pregnant women carrying a child, parents planning to replenish the family, and patients with persistent hyperglycemia.
A blood test for hemoglobin itself does not eliminate the problem, but it can prompt dramatic lifestyle changes. Giving up bad habits, a balanced diet and proper rest can protect against irreversible changes in the endocrine system. To improve your quality of life and calmly greet each new day, it is enough to periodically set aside a few minutes to submit biomaterial for research.
Transcription of analyzes online.
cost of service: 500,300 rubles
Order
General practitioner Khanova Irina Ivanovna will interpret your tests during an online call in the Zoom or WhatsApp application.
- detailed explanation from the general practitioner.
- an alternative opinion from a competent specialist in interpreting the analyses.
- the opportunity to ask questions to the doctor regarding test results.
Diagnostics
If the symptoms described above appear, especially if this is accompanied by the presence of factors predisposing to a decrease in hemoglobin, you should take a general blood test and consult a physician with its results. To confirm anemia, a repeat clinical blood test is usually prescribed. This eliminates the possibility of mistakes being made in the laboratory.
If a decrease in hemoglobin levels is confirmed, treatment for anemia is immediately prescribed. And in parallel with this, a comprehensive examination of the body is carried out in order to identify the causes of its development. This is especially important in cases where there are no obvious prerequisites for this, for example, having undergone surgery in the recent past, injuries with large blood loss, etc. For this, the following may be prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- stool test for occult blood;
- colonoscopy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys.
How to take a blood test for hemoglobin
To donate blood, no special preparation is needed, but there are rules that should be followed. Obtaining the most reliable result depends on them:
- hemoglobin test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach;
- the last meal is taken 10-12 hours before blood sampling;
- on the eve of going to the laboratory, it is recommended to avoid heavy physical labor, strenuous training, and stressful situations;
- Fatty foods and alcohol, which distort the data, must be eliminated from the diet within 24 hours.
To carry out the procedure, venous or capillary blood (from a finger) is taken. For prevention purposes, it is enough to undergo a test for hemoprotein levels once every 2-3 years.