The force with which blood flows through the vessels is one of the most important indicators that determines the state of health. Diastolic pressure is used by doctors to diagnose various diseases. What indicators are considered normal, what diseases are indicated by their increase or decrease?
Diastolic pressure - what is it?
When measuring pressure, the tonometer shows 2 values, their correct interpretation is not familiar to every person:
- The upper numbers, cardiac pressure, mean the force with which the left ventricle of the heart pumps blood into the arterial bed. Blood passes through all vessels, the walls expand, resisting the incoming fluid.
- The lower number characterizes the intensity of blood movement at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle - the stronger the walls of blood vessels contract, the higher these data are. This is diastolic pressure.
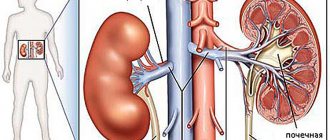
The kidneys, which produce a special hormone - renin, are responsible for the resistance of blood vessels in the body. Therefore, diastolic indicators are also called renal pressure.
If vascular permeability is normal, then the tonometer will show optimal values. As the resistance increases, the lower values also increase, and as the resistance decreases, the diastolic numbers drop below acceptable values.
To determine the state of health, pulse pressure is also important, which is the difference between cardiac and renal parameters. Normally it should be within 40 units.
If diastolic readings deviate from the norm, the first thing you should do is check your kidney function.
Lower blood pressure
It shows the force with which blood presses on the vascular walls at the time of diastole (relaxation of the heart muscle). This pressure is called diastolic and is the minimum. It depends on the tone of the arteries, their elasticity, heart rate and total blood volume. Normal lower pressure is 70-80 mmHg.
Causes of elevated diastolic blood pressure
Isolated cases of its increase are not a pathology, just like a temporary increase during physical activity, emotional stress, changes in weather conditions, etc. We can talk about hypertension only when it increases steadily. You can read more about the causes of increased lower pressure and its treatment here.
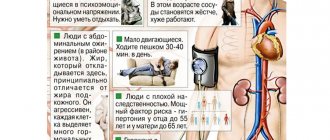
The following may lead to an increase:
- kidney disease;
- high kidney pressure;
- disruption of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland (increased hormone production);
- diseases of the spine.
Symptoms of elevated lower blood pressure
When diastolic pressure increases, the following complaints may appear:
- dizziness;
- chest pain;
- labored breathing.
With a prolonged increase, visual impairment, cerebral circulation, and the risk of stroke and heart attack may occur.
Increased diastolic blood pressure increases the risk of strokes and heart attacks
Causes of low diastolic blood pressure
This symptom is typical for the following pathologies:
- dehydration;
- tuberculosis;
- disorders of the aorta;
- allergic reactions and others.
Diastolic blood pressure may drop in women during pregnancy. This can cause hypoxia (oxygen starvation), which can be dangerous for the unborn child. More information about the reasons for lowering lower pressure and ways to increase it can be found here.
Symptoms of low diastolic blood pressure
If your blood pressure is low, you may experience symptoms such as:
- drowsiness;
- lethargy;
- headache;
- dizziness.
Normal diastolic pressure
Normal lower pressure values for a healthy middle-aged person are 70–90 mmHg. Art., ideally the tonometer should show a value of 80 units. Diastolic data is influenced by gender, age, and level of physical activity. In women, the indicators are slightly lower than in men, but with age against the background of hormonal changes, the trend changes in the opposite direction.
Norms of diastolic pressure by age
| Age (years) | Indicators for males (mm Hg) | Indicators for females (mm Hg) |
| Up to a year | 66 | 65 |
| 2–10 | 69 | 70 |
| 10–20 | 76 | 72 |
| 20–30 | 79 | 75 |
| 30–40 | 81 | 80 |
| 40–50 | 83 | 84 |
| 50–60 | 85 | 85 |
| 60–70 | 82 | 85 |
In elderly people, diastolic values within 90 mmHg are allowed. Art. with a deviation in any direction of 5–10 units.
If cardiac parameters are normal, but diastolic pressure increases or decreases, isolated hypertension or hypotension is diagnosed.
What should be the difference between upper and lower pressure
We know what pressure is optimal. This is 120/80 mmHg. This means that the normal difference between lower and upper blood pressure is 40 units. It is called pulse pressure. If this difference increases to 65 or more, the likelihood of developing cardiovascular complications increases significantly.
Most often, a large difference between upper and lower pressure is diagnosed in older people
A large gap is most often observed in the elderly, since their age is characterized by an isolated increase in upper blood pressure. With age, the likelihood of developing isolated systolic hypertension only increases, and especially sharply after 60 years.
The level of pulse pressure is affected by the distensibility of the aorta and nearby large arteries. The aorta has high distensibility, which decreases with age due to natural wear and tear of the tissue. Elastic fibers are replaced by collagen fibers, which are stiffer and less elastic. In addition, as many people age, cholesterol, lipids and calcium salts are deposited on the walls of their arteries. Thus, the more calcium salts and collagen, the worse the aorta stretches. The worse the artery walls stretch, the greater the difference between the lower and upper pressure.
High pulse pressure is a major risk factor for strokes and other cardiovascular complications in older people.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing lower indicators
Minor deviations from the norm in diastolic indicators in an adult or child are observed under stress, nervous and physical fatigue; the values change under the influence of weather and climate. Lower pressure increases during training, physical work, after eating salty, sweet, spicy foods, tonics and alcoholic drinks.
Unstable blood pressure in pregnant women
During pregnancy, isolated hypotension can occur in the early stages due to toxicosis, dehydration, and hormonal imbalance. An increase in diastolic blood pressure occurs after week 20, the main reasons being weight gain and fluid retention in the body. Hypertension is almost always diagnosed in multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, diabetics, and women who are about to become mothers for the first time.
Important! The most dangerous causes of isolated hypertension in pregnant women are preeclampsia and eclampsia. With these pathologies, gestosis develops, the likelihood of placental abruption and premature birth increases, and severe swelling appears. This condition is extremely dangerous for a child - the baby may be born with congenital defects.
Causes of high lower pressure
Diastolic readings often increase in people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle - smoke, abuse alcohol, and indulge in junk food. Sometimes it is enough to adjust your diet, get rid of addictions, and move more for high blood pressure to normalize.
Why does lower blood pressure increase:
- prolonged stress;
- chronic diseases of the adrenal glands;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, heart, blood vessels;
- obesity;
- injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
What does hypertension mean from a psychosomatic point of view? Psychologists say that the reason for high blood pressure is selfishness, the desire to set difficult goals for oneself. This allows a person to achieve success in his career, but has a negative impact on the condition of blood vessels.
Causes of low diastolic pressure
The primary cause of decreased diastolic indices is vegetative-vascular dystonia. For a more accurate diagnosis, you should visit a cardiologist, neurologist, or endocrinologist. From a psychosomatic point of view, hypotension can be a consequence of low self-esteem, hidden fears, grievances, and depression.
Low diastolic pressure - what does it mean:
- kidney disease, dysfunction of the excretory system, hypofunction of the adrenal cortex;
- cardiovascular diseases, myocardial dysfunction;
- endocrine system disease;
- severe allergies;
- ulcers;
- varicose veins;
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- large blood loss, anemia;
- diseases of inflammatory, infectious origin.
A sharp decrease in blood counts can be caused by overheating, prolonged stay in a stuffy room, or dehydration. Hypotension is a consequence of shock, severe stress, chronic lack of sleep, and low-calorie diets.
Physiological hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure in healthy people against the background of genetic predisposition and asthenic body type. At the same time, the person does not suffer from unpleasant symptoms of the disease and copes well with physical and mental stress.
Causes
Renal hypertension is classified as secondary (symptomatic) hypertension. This kidney pathology occurs in 7-10% of cases of increased blood pressure. The cause of the condition can be any kidney disease:
- fibromuscular dysplasia of the renal artery;
- polycystic kidney disease;
- atherosclerosis, thrombosis, compression of the renal artery;
- nephropathy;
- kidney malformations;
- glomerulonephritis;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- kidney amyloidosis;
- chronic pyelonephritis and other pathologies that can cause changes in the structures of the kidneys.
Very often, renal hypertension occurs in combination with diabetes mellitus and other diseases of the endocrine system. Quite often, the development of renal hypertension occurs while taking certain medications.
Treatment of diastolic pressure
To normalize diastolic parameters, medications and traditional medicine are used. To avoid the development of hypertension and hypotension, you need to eat properly, irregularly, move more, and get rid of bad habits.
If the condition quickly returns to normal and does not cause deterioration in well-being, then there is no particular cause for concern, but for prevention, you should undergo a full examination once a year.
How to lower diastolic pressure?
Various medications are used to treat isolated hypertension, but they should be taken under constant medical supervision - almost all drugs provoke a decrease in systolic parameters, which can lead to the development of concomitant pathologies.
Main groups of medicines:
- Beta blockers - Metoprolol, Nebivolol. Effectively reduces the frequency and strength of heart contractions, which leads to normalization of diastolic values. It should not be taken by people with asthma or lung diseases.
- Calcium channel antagonists – Phenigidine, Corinfar. They influence the functioning of the smooth muscles of the myocardium, improve vascular tone - the pressure is equalized.
- Myotropic antispasmodics – Papaverine, Papazol. The safest antihypertensive drugs.
- Nitrates – Erinite, Cardiket. Promote the expansion of the duct in the veins and arteries, the pressure quickly decreases.
- Diuretics – Lasix, Furosemide. Remove excess fluid and eliminate swelling.
All drugs are initially prescribed in a minimum dosage, and the doctor can gradually increase it if necessary. If the condition does not improve within 3–4 weeks, therapy should be completely reconsidered and re-examined.
Cold will help to quickly reduce blood pressure - you need to lie face down and place ice or a bottle of cold water on your neck. The duration of the procedure is a quarter of an hour, then you should massage your neck to restore blood circulation. Additionally, you can rub your ears red and take a few deep breaths.
Alternative therapy methods
Many folk remedies help to effectively reduce diastolic readings and prevent the development of hypertension. Even natural medicines can only be taken with the permission of the attending physician.
- A tincture of spruce or pine cones helps well with hypertension - you need to fill a 1-liter glass jar with the raw material, compact it a little, and fill it to the top with high-quality vodka. Close the container, place in a dark room for 3 weeks, filter, take 5 ml before each meal. Treatment should be continued until the tincture runs out.
- If the pressure is very high, viburnum will help - squeeze the juice from 500 g of fresh berries, mix with 500 ml of fresh honey, add 180 ml of cognac. Place the mixture in a closed container in a dark place for 4 weeks, stir the medicine once a day. Take 15 ml tincture three times a day with meals.
Proper nutrition will help improve the condition of the circulatory system and blood vessels; the diet should contain more foods that contain sodium and potassium - baked potatoes in their skins, all types of cabbage, corn and bananas. There is a lot of magnesium in raw nuts, seafood, and legumes.
Increase in lower pressure readings
If there is a sharp decrease in diastolic readings, you need to lie down and put your feet on a small hill to normalize blood circulation. Strong, sweet green or black tea will help improve your well-being, or you can eat something salty. 1-2 tablets of Citramon will help improve your performance.
Folk remedies for the treatment of hypotension
Tinctures and decoctions of medicinal plants, juices, and herbal teas will help normalize diastolic indicators.
Effective ways to increase blood pressure:
- Every morning for a month, drink 200 ml of natural grape juice with the addition of 25 drops of lemongrass or ginseng tincture.
- Mix 10 g each of tansy, immortelle, key steelweed and immortelle. Brew 5 g of the collection with 220 ml of boiling water, leave in a closed container for 20 minutes. Drink the drink every morning before breakfast.
- Cinnamon will help to quickly and permanently increase diastolic pressure - ¼ tsp. Brew 200 ml of boiling water, cool, add 15 ml of honey. Take the medicine in the morning before breakfast, 2 hours before bedtime.
If you have low blood pressure, you need to sleep for at least 9 hours in a cool room and take a contrast shower in the morning. The diet should contain moderately salty and sweet foods.
What to eat if you have hypotension
Proper nutrition is a safe way to increase diastolic values without worsening systolic values.
What foods help increase blood pressure:
- berries – black currant, sea buckthorn, lingonberry;
- citrus fruits;
- natural pomegranate juice;
- potatoes, carrots, celery;
- spicy vegetables - onions, garlic, horseradish;
- medium fat dairy products – cottage cheese, hard cheese;
- red lean meat, fish;
- bitter dark chocolate;
- raw nuts, dried fruits.
You need to drink more - pure water without carbon, regular and herbal teas, and a decoction of rose hips.
Only a doctor can determine the reason for the increase or decrease in diastolic readings. Isolated hypotension and hypertension require careful diagnosis, which will reveal the true cause of the decrease in pressure.