How the heart works
To make the description of atrial fibrillation as clear as possible, it is worth understanding how our heart works and works.
The heart is a hollow muscular organ consisting of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The principle of operation is probably known to everyone: like a pump, it moves blood throughout the body, saturating the organs with oxygen.
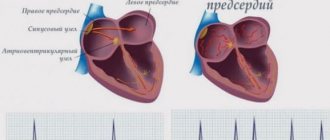
The sinus node, an electrical system located in the wall of the atrium, is responsible for the beating of the heart. It generates an impulse that is evenly distributed over the area of the heart, causing rhythmic contraction and relaxation - the pulse.
What is atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a heart disorder in which the electrical impulse is distributed unevenly throughout the heart. Because of this, the heart chambers work uncoordinatedly: instead of contractions, twitching or “flickering” occurs in the atrium, and the ventricles also contract in the wrong rhythm.
The picture on the left shows a normal heart rhythm, sinus. The electrical signal is generated in the sinus node and spreads evenly through the conduction system of the heart. The right shows how electrical impulses are generated randomly in different places and cause atrial fibrillation.
There are 3 forms of atrial fibrillation:
Paroxysmal or paroxysmal - manifests itself in short attacks that go away on their own within a few minutes or hours. Some people may have only one attack in their entire life, while others may have them several times a day. In this case, you need to consult a doctor to rule out pathology and other forms of the disease.
Persistent or temporarily stable - attacks can last several days, weeks or months. Characterized by the inability to restore heart rhythm without drug treatment and therapy.
Chronic or permanent - occurs, as a rule, with prolonged atrial fibrillation. In this case, the heart rhythm is not restored with the help of treatment, but learning to maintain normal well-being of the body is a feasible and important task.
If an attack lasts longer than 48 hours, blood begins to stagnate in the upper parts of the heart: clots form and the risk of complications increases - blood clots and, subsequently, stroke. Therefore, seeking cardiac care for any manifestation of arrhythmia is a vital necessity.
How to relieve an attack yourself?
If signs of a sharp deterioration in the condition appear, it is important to act quickly. The algorithm for providing first aid is as follows :
- Call an emergency medical immediately
- Avoid any physical activity. Take a lying position .
- Try to calm down . During an attack of atrial fibrillation, you should not be nervous or think about bad consequences. It is important to try to normalize the breathing process - you need to breathe evenly, inhale through your nose, exit through your mouth.
- Provide fresh air flow (open a window). You need to remove all uncomfortable clothing - outerwear, tight T-shirt or sweater, scarf. It is necessary that nothing is squeezing your neck; to do this, you should unbutton the collar of your shirt. Remove all belts from the belt and unfasten the top button on trousers, jeans, skirt, etc.
- Wipe your face with a damp, cool towel. This will help the person calm down and normalize the functioning of the sweat glands.
- Drink a glass of cool water . Often the cause of atrial fibrillation is dehydration. Fluid intake ensures normalization of heart rate.
- Taking sedatives (infusion of motherwort or valerian, Corvalol) will help stop the attack.
Important! If emergency methods do not bring relief, then you must wait for an ambulance to arrive. Before the arrival of specialists, the patient is not recommended to remain alone; it is important that a loved one be with him.
Causes and symptoms
Most often, heart rhythm disturbances are diagnosed in patients with risk factors such as:
- coronary heart disease - myocardial infarction, hypertension, angina pectoris;
- congenital pathology, trauma, heart surgery;
- diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction, obesity;
- old age - over 65 years old.
Causes of heart problems, regardless of age, also include: smoking, taking drugs and certain medications, frequent consumption of alcohol and caffeinated drinks - coffee, strong tea, energy drinks.
How you feel with atrial fibrillation largely depends on the heart rate per minute:
- pulse exceeds 90 beats - anxiety, increased sweating, tremors of the limbs appear;
- pulse is less than 60 beats - the brain does not have enough oxygen, so pre-syncope and fainting, cloudiness of consciousness, and increased fatigue occur.
- The pulse is normal - disorders can be asymptomatic, detected by chance or during a routine examination. The danger lies in the absence of warning factors - a person cannot control the consequences, such as blood clots or stroke, because he does not know about the disease.
Common signs of the disease include dizziness, shortness of breath, pain in the chest or shoulder blades, and a feeling of heartbeat. But it cannot be said that these symptoms only signal arrhythmia or heart disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, diagnostics is needed.
Causes of arrhythmia
Unstable heartbeat in most cases is characteristic of people with cardiovascular diseases. Arrhythmia can be provoked by a previous heart attack or other cardiac pathology.
The most common causes of cardiac arrhythmia:
- inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis);
- myocardial ischemia, angina pectoris and atherosclerosis;
- defective functioning of the heart valves;
- prolonged stress, increased anxiety;
- autoimmune diseases, etc.
There are a number of other factors that increase the risk of developing chronic arrhythmia. Timely prevention and diagnosis can eliminate pathology at an early stage and avoid surgery.
Diagnostic methods
To determine atrial fibrillation, a comprehensive examination of the heart and related organs is performed, and the patient’s physical condition is also analyzed.
The examination includes:
- electro- and echocardiography,
- daily or multi-day ECG monitoring,
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and hormone analysis,
- clinical and biochemical blood test,
- determination of potassium and magnesium levels,
- lipid profile,
- physical stress testing.
It is convenient to undergo complex diagnostics in a specialized cardiac center: you don’t have to waste energy, time and additional money on visiting doctors in different clinics in your city. The result of the diagnosis should be a detailed plan for further treatment.
Ready-made recipes
Dill seeds help with symptoms of atrial fibrillation. To do this, pour boiling water over the seeds and let them stand for 30 minutes. You will need boiling water - 1 cup, seeds - a third of a cup. The resulting finished decoction can be drunk three times a day, 1/3 cup. It is recommended to do this before eating.
Lovage and its roots are used as medicine. You need to grind them, wash them, and leave them in a liter of warm water for about 12 hours. You can take the tincture throughout the day.
Another recipe includes mint, St. John's wort and rosemary, as well as valerian roots. You need to pour boiling water into this mixture and then simmer over steam for about half an hour. The broth cannot be brought to a boil. The resulting tincture must be filtered and allowed to cool. It is taken up to four times a day (1/3 cup).
You can take rose hips - 20 g, hawthorn fruits - 20 g. Add 3 tablespoons of motherwort to them. The whole thing is poured with boiling water and infused for 12 hours in a dark place. The decoction is taken 100 ml in the morning and evening.
A good remedy is obtained if you take yarrow, valerian roots, hops (cones), and lemon balm. Herbs are taken in two parts, and lemon balm needs three parts. Mix the collection thoroughly. Then pour 1 tablespoon of herbs with boiling water (a glass) and leave for about 40 minutes. Drink up to 5 times a day.
Another collection consists of mint and calendula. You need to take 50g of the mixture and pour boiling water (0.5l). Let cool, strain, add a couple of tablespoons of honey. You need to drink up to 4 glasses a day.
Treatment options
There are two treatment tactics: monitoring the rhythm or frequency of the heart. The cardiologist determines how to treat arrhythmia and what to take individually, depending on the case.
Control of the rhythm of contractions - restoration of sinus, that is, normal, heart rhythm. It is achieved by taking antiarrhythmic drugs or electrical stimulation of the heart - cardioversion. Antiarrhythmic drugs have a positive effect on the electrical conductivity of the heart, thereby reducing the likelihood of repeated failures.
They may also prescribe ablation - the impact of radiofrequency pulses on the arrhythmic area of the heart.
Ablation treatment can be successful in 70% of cases or more: it depends on the severity and nature of the lesion, the duration of the arrhythmia, and the size of the heart cavities. Risks associated with the procedure are rare.
Monitoring your ventricular rate helps eliminate heart palpitations and the risk of heart failure. This method is used in cases where it has not been possible to restore a normal heart rhythm, or the patient does not show symptoms.
Frequency control is carried out in several ways:
- reduce the spread of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles with the help of drugs,
- ablation is performed to eliminate the delay in pulse propagation,
- a pacemaker is installed to simulate an electrical impulse.
Atrial fibrillation became permanent
In a certain proportion of patients suffering from attacks of atrial fibrillation, sooner or later there comes a time when it is no longer possible to restore sinus rhythm. Atrial fibrillation becomes permanent. As a rule, this happens in patients with significantly increased sizes of the left atrium (4.5 cm or more). Such an enlarged atrium is simply unable to maintain sinus rhythm. With a permanent form, the patient also needs medical supervision.
The goals of treatment are to maintain the heart rate within 60-70 beats per minute at rest, prevent the formation of blood clots in the cavities of the heart and reduce the risk of thromboembolic complications.
Heart rate control is carried out with beta blockers, digoxin or calcium antagonists (verapamil group), selecting an individual dose of the drug according to the principle “the higher the dose, the lower the heart rate.” The titration is completed at the optimal dose, and the patient receives it daily. The effectiveness of heart rate control can be assessed using 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring. If a reduction in heart rate cannot be achieved with pills, doctors resort to surgical methods. An arrhythmologist surgeon isolates the atria from the ventricles and implants a pacemaker, which is programmed for a certain number of heartbeats at rest and adapts to stress.
To prevent blood clots, medications that thin the blood are used, that is, they slow down the blood clotting process. For this purpose, aspirin and anticoagulants (most often warfarin) are used. To date, the approach to the tactics of anticoagulant therapy has been determined on the basis of an assessment of the risk of thromboembolic complications and the risk of bleeding while taking these drugs, and is approved in the National Russian VNOK recommendations (see table).
Many patients are afraid to start taking medications, since the instructions indicate complications such as bleeding. You should know that before prescribing anticoagulants, the doctor always weighs the benefits and risks of drug treatment, and prescribes only when he is completely sure that the benefits significantly outweigh the risks. Strict adherence to recommendations and regular monitoring of blood tests (international normalized ratio (INR) for patients receiving warfarin) plus your awareness of the basic mechanisms of action of the drug and the tactics of your actions at the first signs of bleeding make such treatment completely predictable and as safe as possible.
Table 1
Ways of control in everyday life
Irregular heart rhythm is not a death sentence. An active and harmonious life is possible both during the treatment period and after it. It’s enough to learn to live by new rules that embody a healthy lifestyle:
- follow a balanced diet - do not indulge in fatty, fried and too salty foods;
- reduce bad habits to a minimum - reduce alcohol consumption and stop smoking;
- engage in physical activity - walk regularly or add an hour of cardio training per day;
- maintain normal weight and blood pressure;
- monitor your blood sugar levels.
At the Chernaya Rechka Heart Medicine Center, we not only treat arrhythmia and other heart diseases, but also help them adapt to life after them: we teach them a healthy lifestyle and make it a habit.