In neurological practice, dizziness (vertigo) is one of the most common complaints of patients. For older people, the feeling of disorientation in space can become a serious problem: the risk of falls and injuries increases, the condition is often accompanied by phobias, depression, and deterioration of auditory and visual functions.
You can get rid of this unpleasant syndrome at any age. To do this, it is important to establish the causes of dizziness, especially since sometimes they turn out to be dangerous diseases that can be fatal. Complex diagnosis and timely treatment can help avoid severe complications.
How does dizziness manifest?
We recommend
“How to care for a bedridden elderly person” More details
During dizziness, it seems to a person that not only his head is spinning, but that he himself is spinning, or that the objects around him are spinning. When dizziness occurs in older people, nausea may occur, a feeling similar to intoxication and other unpleasant symptoms may occur, including loss of consciousness and falling.
Old people begin to blur before their eyes not only from external influences, but also due to the occurrence of diseases. Perhaps any person over the age of sixty has at least once felt suddenly dizzy. If this happens regularly, it becomes a serious problem that interferes with a normal life. In order to properly deal with the disease, it is important to determine the causes of its occurrence.
What is dizziness?
True dizziness or vertigo is a condition during which patients have a feeling of rotation of surrounding objects around them or a false sensation of their own movement or rotation.
An example of true dizziness, but not in any way related to the disease, is the dizziness that appears in people after riding a carousel, when, after an abrupt stop, they continue to see the movement of surrounding objects relative to themselves, as if the carousel were still in motion.
In most cases, the occurrence of true dizziness is a symptom of diseases of the system of control of balance and body position in space. This system includes the eyes, the vestibular apparatus of the inner ear, and sensory receptors in the human muscles, joints, and bones. Very often, dizziness, which is caused by a disruption in the balance system, is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Causes of dizziness in older people
Why might an elderly person feel dizzy? Most often, this is an age-related manifestation, caused by problems with the vestibular apparatus, neurological abnormalities, vascular diseases, and damage to nerve cells. Here are some of the most common causes of dizziness in older people:
- Consequences of injury.
- Sudden changes in pressure.
- Chondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Brain tumor.
- Diabetes.
- Arrhythmia.
- Ischemic disease.
- Damage to the eardrum.
- Meniere's disease (fluid accumulation in the inner ear).
- Benign tumor of the auditory nerve (neurinoma).
- Depression, fatigue, lack of sleep.
But the main thing that causes dizziness in older people is:
1. For 30–35% of cases - BPPV (benign positional paroxysmal vertigo). In older people, this is usually a consequence of degenerative changes in the area of the inner ear. The receptors of the vestibular apparatus are irritated by microscopic deposits (otoliths), resulting in dizziness. More often, older people feel such symptoms when they wake up in the morning.
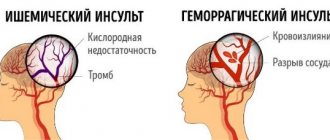
2. Diseases of the cerebral vessels, so-called cerebrovascular diseases, and atherosclerosis. A characteristic manifestation of these ailments is insufficient blood supply to the brain due to partial damage to blood vessels. This is a very dangerous condition, and dizziness with it is the most harmless symptom.
3. Poor blood circulation in the brain (stroke). According to statistics, stroke occurs in 450 thousand people in the world every day, and over 80% of them are old people. One of the manifestations of a stroke is dizziness, which can recur in a person even after undergoing a course of treatment.
4. Drug abuse (polypharmacy). Taking a large number of drugs at the same time increases the risk of adverse symptoms. It is impossible to list at once all the pills that cause dizziness in older people. Typically these are heart medications, blood pressure medications, painkillers (analgesics), antibiotics, beta blockers, diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tranquilizers and antidepressants, sleeping pills, anti-seizure medications.
We recommend
“Lonely elderly people: how to help them” More details
5. Dizziness in elderly people with normal blood pressure is rare; rather, the cause of mild weakness and faintness is too high or too low blood pressure.
6. Weakened (due to old age) vestibular apparatus. This can cause not only a feeling of unsteadiness, but also dizziness in older people.
7. There are a number of concomitant diseases for which you have to take a large number of medications (diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease). Then the cause of dizziness in the elderly can be both medications and the disease itself.
8. Many older people have a very difficult time psychologically and emotionally experiencing the changes in the body that come with age. They are afraid of losing consciousness or falling if they suddenly feel dizzy. Attacks of anxiety and even panic can cause so-called psychogenic dizziness, and with them comes chills, arrhythmia, general weakness, lack of air and faintness.
A serious problem that requires treatment is severe dizziness in older people with a weak vestibular system. Objects seem to be moving in a circle; a person cannot clearly perceive their outlines. This is a common occurrence in older people with hypertension. There are also other symptoms:
- spots before the eyes;
- feeling of blindness;
- feeling that the head has become heavy;
- feeling as before loss of consciousness;
- weak legs and arms, apathetic state.
Sometimes isolated manifestations of such symptoms occur, then this most likely means that the person is simply overtired. After rest, the unpleasant feeling will pass.
However, such signs should not be ignored if they occur after a stroke or, for example, during menopause. This has serious health consequences. An elderly person may become frightened during an attack, faint, or injure himself - all this is very unsafe.
Even one of the listed symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. The reasons for poor health must be found out. Let a therapist, endocrinologist, or neurologist examine you. The process can be complex and lengthy; you will have to examine the central nervous system and other organs and take the necessary tests.
Recommended articles on this topic:
- Boarding home for the elderly: features and rules of choice
- Low blood pressure in older people: causes, symptoms and treatment
- Health of the elderly: old age is not a problem
Symptoms other than dizziness
As can be seen from the above, the term “dizziness” has a rather narrow medical interpretation (a false sensation of rotation of surrounding objects or one’s own rotation). But, despite this, people also use this term to refer to other symptoms that are not actually dizziness. So, most often “dizziness” is called such phenomena as:
- darkening in the eyes after abruptly rising to your feet from a sitting or lying position;
- a veil before the eyes;
- feeling of imminent loss of consciousness (fainting);
- weakness, nausea, feeling of confusion and unsteadiness in the legs;
- feeling of unsteady gait and impaired balance.
When a person suffering from dizziness comes to see a doctor, he should describe his condition, how he is feeling and the symptoms he is experiencing as accurately as possible, and not simply say that he suffers from “vertigo.” The further examination and treatment plan will depend on the accuracy of the description of the existing symptoms.
In contrast to true dizziness, which appears due to a disruption in the functioning of a person’s balance system, false dizziness, which patients describe as a feeling of weakness, instability, darkening in the eyes, blurred vision, etc., can most often be a sign of anemia, chronic fatigue , hypovitaminosis, hypotension and vegetative-vascular dystonia. In addition, fainting, episodes of lipothymia (a sharp decrease in muscle tone with great physical stress) and short-term attacks of epilepsy can also be confused with dizziness.
We pay special attention to attacks of sudden dizziness and weakness in people who have diabetes. In this category of patients, dizziness and weakness may indicate a dangerous decrease in blood glucose levels.
First aid for severe dizziness in an elderly person
Here's what to do if there are complaints of weakness and dizziness in older people:
- put the person horizontally as soon as possible;
- ensure air flow into the room;
- eliminate possible sources of noise: loud music, radio, TV;
- remove too bright light (but there should be enough lighting).
If the person is dizzy but not vomiting, give the person water or tea with sugar. You can wipe your face with a damp cloth (not too cold). Atropine (0.1% solution, 8–10 drops) helps well. If the patient's condition does not improve within an hour, call an ambulance.
Often, older people immediately experience dizziness and nausea, and black spots appear before the eyes. At the same time, the person turns pale, body temperature drops. Such symptoms can be heralds of a hypertensive crisis, and if you do not quickly call an ambulance, it will lead to myocardial infarction.
It is also worth paying attention if a person experiences speech impairment, numbness in half of the face, headaches, or fainting. All these are signs of a cerebral stroke, and if doctors are not called urgently, the life of the pensioner will be threatened.
We recommend
“Interests of older people: how to improve the life of a pensioner” Read more
Symptoms of otitis media in adults
With external otitis, the most common complaints are:
- pulsation in the ear, sharp pain radiating to the neck, eye or teeth;
- increased pain when chewing food, talking, closing the jaw;
- redness of the ear canal and auricle;
- hearing loss if there is discharge of pus into the ear canal area.
Acute otitis media begins with a rise in temperature along with shooting pain inside the ear.
It increases as mucus and pus accumulate in the cavity; after 2–3 days, the membrane ruptures, pus flows out of the ear and the condition improves. The temperature drops and the pain subsides. Then the rupture of the membrane heals without a trace. In the chronic form, mesotympanitis may occur - inflammation is localized in the area of the Eustachian tube and the lower, middle part of the tympanic cavity. A hole is formed in the membrane, but the membrane itself is stretched.
Key complaints:
- hearing loss;
- periodic appearance of pus from the ear;
- noise in the ear;
- dizziness;
- during exacerbation - pain and fever.
With the development of epitympanitis, a sharp decrease in hearing occurs, the release of foul-smelling pus, pressure in the ear, pain in the temples, and dizziness. Periods of exacerbation are followed by remissions, but hearing does not improve completely.
Diagnosis of dizziness in older people
The success of treating dizziness in older people depends on correct diagnosis. Often the cause of dizziness is changes in the functioning of the brain. In this case, it is necessary to conduct appropriate research. Surveys of this kind are carried out according to the following scheme:
- Determine what type of dizziness is.
- Find the reasons for its appearance.
- The presence of neurological or ENT symptoms is determined.
- Additional methods are used to study the patient’s condition, depending on what pathologies were identified during the examination and interview.
1. History taking and external examination.
First you need to make sure that you really have dizziness. Old people often mistake one condition for another and may mistake nausea or blurred vision for dizziness.
An examination is very important; you need to take a closer look at how the person’s coordination of movements is, and whether the reflexes work normally. You should understand why weakness and dizziness occur in older people, what factors influence the development of the disease, and how it progresses.
If the head begins to feel dizzy gradually, this is classified as dizziness of central origin, and if suddenly and quickly, this is classified as peripheral. The latter are characterized by tinnitus and poor hearing (these symptoms are called local disorders). Central vertigo is accompanied by damage to the cortex and brain stem. A general serious condition with frequently recurring vomiting are signs of vestibular disorders.
To identify the diagnosis, the patient is asked to change the position of the head, for example, tilt it to the left or to the right. If the head becomes more dizzy when bending over, then we are talking (most often) about benign dizziness in older people, the cause of which is a weak vestibular apparatus.
Through a survey, they will find out what autoimmune or inflammatory diseases, intoxications (medicines or alcohol), and head injuries have been suffered. Check to see if the person being examined has nystagmus. Nystagmus is an oscillatory movement of the eyes independent of the patient. They study the spontaneous form of nystagmus (caused by gaze), when a person first looks straight ahead and then moves his eyes to the side.
Another diagnostic method is the Hallpike test. The patient is placed on the couch in a sitting position, he looks to the right, turning his head about 45 degrees. Holding the person by the shoulders, he is asked to quickly lie on his back so that his head hangs off the couch. The same is repeated by turning the head to the left.
An otolaryngologist examines the outer, middle, inner ear, eardrum, removes wax plugs, checks for infections (acute or chronic), and finds the consequences of injuries.
2. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
CT and MRI are prescribed to ensure the absence of neoplasms and demyelinating processes. Structural pathologies (congenital or acquired) are identified. It may be necessary to take an X-ray of the skull (if there is an assumption that the person has new or old fractures).
We recommend
“Adaptation of older people: in modern society and boarding homes” Read more
The cause of weakness and dizziness in older people may be vascular dysfunction. In case of such suspicions, Doppler ultrasound of the cervical and cephalic great vessels is performed.
A complete blood test will help rule out the possibility of infection. If a pathogen is found, antibodies are determined for it.
If there is concomitant hearing impairment, the patient undergoes pure-tone audiometry. A person drinks Glycerol, after which one can notice better speech perception and recognition of low-frequency sounds. If such signs are found, then we are talking about Meniere's disease, which, as a rule, is accompanied by dizziness.
Dizziness against a background of apathy, hypochondria, accompanied by a decrease in mental activity and causeless painful health, indicate that the patient has a diagnosis of a psychiatric or neurological nature.
Cases when you should consult a doctor immediately
You should consult a doctor as soon as possible in cases where dizziness is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- persistent vomiting;
- severe headache, weakness of arm or leg muscles;
- severe dizziness lasts more than an hour;
- during an attack of dizziness the person lost consciousness;
- when dizzy, the patient fell and was seriously injured;
- A patient with diabetes mellitus and hypertension developed severe dizziness.
Anti-dizziness medicine for older people
What drug treatment is used for dizziness in older people? Since the diagnosis is so common, there are a number of drugs that make attacks less frequent and have a beneficial effect on the brain. These are so-called nootropics, that is, drugs that accelerate neural processes in the brain. They are excellent for helping with memory loss, complications of mental activity, sclerosis and dementia. In addition, they can be prescribed to improve blood circulation, to combat prolonged fatigue, insomnia and depression.
Nootropics have a wide spectrum of action and are completely safe for the body. They can be given to children and prescribed to absolutely healthy people for whom maximum concentration at work is important. But you should not try to choose a drug for yourself; let a doctor prescribe it. The main nootropics are Glycine, Phenotropil, Piracetam, Cinnarizine, Bilobil.
We recommend
“Boarding home for the elderly: how to place an elderly relative there” More details
Any of these medications improves blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, fights hypoxia, and establishes neural connections in the central nervous system. Some drugs have a sedative effect. Medicines in this group improve cellular metabolism and activate energy processes inside cells. This increases the ability to perceive and remember information and learn. Nootropics are used to treat dizziness in older people because they improve mood and sleep, and make a person more active.
Here is a more detailed description of some nootropics:
- Piracetam is on the first step in popularity. Many people experience sleep disturbances when taking the drug, so it is not prescribed for use in the evening, only before lunch.
- Cinnarizine. It is prescribed not only as a nootropic, but also as an anti-allergy remedy. It should be borne in mind that the drug causes drowsiness, dry mouth, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Glycine is good because it does not cause adverse reactions. A very popular drug among students, especially during study periods. The main component is gamma-aminobutyric acid, which accelerates brain function and is important for metabolic processes.
- Phenibut. Its main component is the same gamma-aminobutyric acid. This medicine may cause you to feel sleepy, especially when you first start taking it.
How else to treat dizziness in older people? Nootropics based on herbal components are also used:
- Vinpocetine. The basic component is the small periwinkle. It has a beneficial effect on brain function, improves blood circulation in areas of blood vessels susceptible to ischemia (relaxes their walls). Helps lower blood pressure.
- Bilobil. The main herbal component is ginkgo biloba. Supplies the brain with oxygen and glucose, making blood vessels more resilient in case of oxygen deficiency. Improves attentiveness, memory and learning abilities. Has a weakening effect on numbness of the limbs.
All of the above remedies and others like them should be taken for at least three months. Only after a month will the first changes be noticeable. The frequency of administration is usually one to three times a day. The treatment regimen must be prescribed by a doctor.
Anatomy and mechanism of development of pathology
With dizziness, there is a growing lack of coordination of movements and balance. To find out its cause, one must understand how the transmission of nerve impulses that play a role in proprioception occurs. This term refers to a person’s ability to identify and sense the position of parts of his own body relative to each other and objects in the environment. Information is perceived by proprioceptor organs, including muscle tissue, and then moves along peripheral nerves to the spinal cord, from where it enters the brain. The necessary picture is formed in the parietal lobe of the brain after nerve impulses pass through the thalamus.
The inner ear is an organ that is responsible for a person's ability to maintain balance. It has a complex structure and consists of several sections: the vestibule, 3 semicircular canals and the cochlea. The inner ear is protected by bone tissue that forms the temporal lobe of the skull. It is filled with aqueous fluid - it moves when a person tilts and turns his head, and this information is perceived by sensitive cells to identify the position of the body in space.
The nervous system collects information that comes from the visual apparatus, tactile receptors and other sensory organs, as well as from the inner ear, and then analyzes it. The center of balance is located in the cerebral cortex, namely in its temporal region. Along the nerves, impulses reach the vestibular nuclei - clusters of nerve cells capable of perceiving, analyzing and coordinating information received from different areas.
Dizziness is a disturbance in the sense of balance. Anatomically, it can occur at several levels:
- peripheral - in case of disturbance of impulse conduction at the level of the vestibular nerve or inner ear (organ of balance);
- intermediate - the pathological process is localized at the stage of transmitting information from the inner ear to the central nervous system;
- central - associated with diseases of the brain, in which it is unable to analyze the information received.
Clinical signs of dizziness of different origins do not differ. The patient experiences a feeling of disorientation in space and abnormal movement of environmental objects. However, short-term loss of balance cannot be a consequence of serious diseases of the cerebral cortex. Such dizziness is accompanied by a number of additional symptoms and occurs after injury or certain diseases. To diagnose the cause and mechanism of development of this symptom, doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain carry out a comprehensive examination to determine accompanying symptoms.
Treatment of dizziness in older people with folk remedies
Along with drug treatment, it is permissible to use traditional medicine recipes. It is better to consult a doctor first so that the effect does not turn out to be the opposite. Some simple remedies:
- Sage. Brew 4 tbsp in 0.5 liters of boiling water. l. sage flowers. Leave for half an hour, you can mix with honey. Drink before meals. The decoction is a good tonic.
- Common parsley. Grind the seeds of the plant in a coffee grinder, brew 1 tsp in a glass of boiling water. crushed mass, leave overnight. In the morning, strain and take four times a day in equal parts, before meals. It stops dizziness well in older people.
- A collection of peppermint leaves, lemon balm, linden flowers and mistletoe. The herbs need to be brewed with boiling water and allowed to brew. It helps well with a weakened vestibular apparatus.
- Red clover. Brew 1 tsp in half a glass of boiling water. dried flowers, let it brew. Take 50 ml twice a day 40 minutes before meals. Helps cleanse the walls of blood vessels, activates life processes, and reduces dizziness.
- Elecampane root. Brew a pinch of crushed root in a glass of boiling water, let it brew for half an hour and strain. Take 4 times a day in equal parts. Tones, destroys infections and parasites, has a beneficial effect on the vestibular system and stops dizziness.
- Simple kelp (sea kale). Eat 1 tsp once a day. dried plant with water. Strengthens the immune system, helps cleanse toxins, normalizes the central nervous system, and stops dizziness.
We recommend
“Centers for pensioners: what they are and how to get there” Read more
- Veronica grass. Brew 1 tbsp in 250 ml boiling water. l. dried plant, infuse. Take the infusion warm, 80-100 ml before meals. Acts as a sedative and relieves dizziness.
- Onion. Scroll it through a meat grinder. The dizziness goes away if you breathe over the resulting mush. Mix chopped onion and honey in a glass jar in equal parts and leave in a cool place for 5 days. The remedy stops severe dizziness in older people and gives strength.
Basically, soothing herbal decoctions are used as herbal remedies:
- Chamomile tea with mint. Brew a tablespoon of dried herbs in a glass of boiling water and strain after 15 minutes. If you are not allergic to honey, you can add one teaspoon to your tea.
- Calming drink. Brew chamomile, mint and valerian (one teaspoon each) in 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 12 hours. The best option is to prepare the decoction overnight, strain it in the morning, add honey and apple cider vinegar (one teaspoon each). Drink before meals.
- Dried ginger root is an excellent folk remedy for treating dizziness in the elderly. The root is taken in powder form three times daily before meals. Dry, powdered garlic is also a good tonic. You can take both remedies at once.
- Hawthorn relieves spasms and has a strengthening effect on the walls of blood vessels. A self-prepared infusion is much more effective than a pharmaceutical alcohol preparation. To prepare, brew one tablespoon of dry herb in 200 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour.
- Dizziness stops after two weeks of taking plantain infusion.
You can also prepare tinctures:
- From garlic. Pour half a liter of alcohol into 300 g of garlic in a glass container and leave in a cool place for 15 days. Method of administration: add 20 drops of tincture to half a glass of milk. The product cleanses the body of toxins, fights infections, improves the functioning of the heart muscle, and relieves dizziness.
- From chestnut. Crushed chestnut buds are poured with half a liter of Cahors (preheated to 70 degrees) and kept for 15 minutes in a water bath. When it cools down, add two tablespoons of honey and a little vanilla powder. Take 50 ml before meals. Improves general condition and activates the activity of brain vessels.
Juice treatment:
- Carrot. Drink 0.5–1 glass three times a day before meals. Strengthens the immune system, relieves dizziness. An excellent remedy is a mixture of carrot, pomegranate and red beet juices (in a ratio of 3:2:2). Take the same way, 0.5–1 cup three times a day before meals. Improves the overall well-being of older people.
- Pineapple. Pineapple is a very strong antioxidant, rich in minerals and vitamins. Its juice rejuvenates the body and has a strengthening effect on the walls of blood vessels. Relieves dizziness in older people and is good for anemia.
- Juice from salad. Drink 25 ml 4 times a day if dizziness occurs due to heart failure or disorders of the central nervous system.
- Juice of young zucchini (possibly with the addition of carrot). It is taken in cases where dizziness occurs due to cardiac problems or high blood pressure.
Causes of pneumonia
Pneumonia develops when bacteria and viruses, as well as foreign agents, enter the lungs and affect part or all of the lung tissue. Pathological agents enter the human body through the respiratory route, and rarely through the blood.
Why does the disease develop quickly in the body of a person with reduced immunity? Bacteria are constantly present in our body, but protective mechanisms do not allow them to multiply, causing pathology. But if the immune system is weakened, harmful microflora increases in population, which leads to the appearance of an inflammatory process.
Viral pneumonia also often develops against the background of the spread of colds of the upper respiratory tract (bronchitis, tracheitis). Pneumonia can also be caused by hypothermia, stress, overwork, or smoking abuse. The risk of developing the disease increases in people with chronic diseases and obesity.
Other treatments for dizziness in older people
Dizziness in older people is best treated by a combination of medications, folk remedies and the following methods:
- Physiotherapy. Properly selected exercises strengthen the spine and stimulate the functioning of blood vessels. Regular exercise can sometimes give more significant results than taking medications.
We recommend
“Gymnastics for the elderly: the best exercises for various diseases” Read more
- Physiotherapy. Modern technologies in this area are multifaceted; water, sound, light, magnetic, and laser treatments are available. Regular implementation of these procedures has a very beneficial effect on the nervous system.
- Reflexology, in particular acupuncture. It normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system, relaxes muscles and activates blood circulation.
- Psychotherapy. The likelihood of dizziness in older people is significantly reduced if measures are taken to relieve nervous tension and anxiety.
Entering into old age will be much easier if you take care of your health in advance. The physical capabilities of the body directly depend on compliance with the daily routine, proper nutrition, intensity of exercise, and abuse of bad habits. Think about what is easier - to prevent the disease or to treat it later? Provide your body with normal functioning, do not neglect examinations if you are already about sixty. Be active, walk more, look at the world positively. Then you definitely won’t have to deal with bouts of dizziness.
Vestibular neuronitis
Why does it happen? The cause of the disease is considered to be an inflammatory process (probably of viral origin), selectively affecting the vestibular nerve.
Article on the topic
Movement therapy. How to regain coordination and balance
How it manifests itself. A single attack of dizziness, the intensity of which increases with changes in posture and may decrease when the patient tries to remain motionless and fixate his gaze on one point.
How to treat it. In the acute period, with the help of symptomatic therapy aimed at relieving dizziness, in the recovery period with the help of vestibular exercises.
Diagnostic methods
The Clinical Brain Institute has all the conditions for a full diagnosis of dizziness. The process is carried out by analyzing the work of the vestibular apparatus and the brain, after which the localization of the pathological process and its stage can be detected. During the initial examination, it is important to conduct a detailed interview with the patient and obtain a detailed description of the complaints. At this stage, it is possible to differentiate true dizziness from other conditions that are also often called by this term. Next, specialists will select an individual diagnostic scheme, which may include the following steps:
- examination of the spinal column (analysis of X-rays, CT or MRI) to identify osteochondrosis, vertebral displacements and other pathologies that cause impaired blood supply to parts of the brain;
- examination by a neurologist, which includes determination of nystagmus, various tests and assessment of the ability to coordinate movements;
- examination of the state of the brain using MRI or CT - carried out to exclude tumors and other diseases leading to demyelination of nerve fibers;
- electroencephalography is a way of assessing brain activity by capturing the signals it produces;
- study of the functioning of the vestibular apparatus - may include rotational tests, vestibulometry and other tests.
Instrumental techniques are prescribed after a general examination. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can determine what examinations need to be performed in order to conduct a differential diagnosis and exclude possible causes of dizziness. Thus, if Meniere's disease is suspected, patients are offered a test to detect low-frequency sound signals.
Treatment in Moscow
The best treatment for vestibular disorders is considered to be exercises for dizziness or vestibular rehabilitation. Vestibular rehabilitation is carried out in many special centers, including the rehabilitation center of the Yusupov Hospital. Therapeutic gymnastics is carried out by an instructor, classes are developed individually for each patient. A preliminary examination by a neurologist will help determine the cause of dizziness, and the doctor will prescribe effective drug treatment. A neurologist will tell you what examination to undergo and how to cure vestibular vertigo during your consultation.