Doppler ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound is a research method using ultrasound using the Doppler effect.
In 1842, the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler discovered the famous physical effect, which was later named after him. The effect is universal for any waves (sound, light, radio waves) and allows, by recording changes in the frequency characteristics of the wave, to determine the direction of movement and measure the speed of a moving object.
The Doppler effect is used everywhere today, in astronomy when observing the movement of stars and planets, in radar, by traffic police officers, and it has found a place in medicine.
The Doppler effect in medicine is used to determine the speed and direction of blood movement in the blood vessels and cavities of the heart, as well as the direction and speed of movement of the walls of the heart during its contractions. The effect is used when conducting ultrasound examinations using ultrasonic waves in the diagnostic frequency range.
The use of the Doppler effect in medical ultrasound devices is called ULTRASONIC DOPPLEGRAPHY or USDG.
There are several technologies for applying the effect, these are methods such as color mapping, when the lumen of the vessel is painted in different colors, depending on the properties of the flow, and spectral analysis, when blood flow rates are calculated in different phases of the cardiac cycle, with the calculation of a number of diagnostic coefficients (indices) ).
In modern devices, these technologies are combined, and you can often hear the terms “duplex” or “triplex” Dopplerography of blood vessels, “duplex” or “triplex” scanning.
General characteristics of the examination
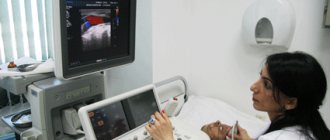
To explain what kind of examination this is – Doppler ultrasound – and how it is done, you need to start by deciphering the abbreviation: Doppler ultrasound (you can also hear the name “duplex scanning”). In more detail, Doppler ultrasound is a combined study that combines standard ultrasound and the Doppler effect. Ultrasound allows you to visualize a patient’s specific organ on the screen, determine its size, structure, assess its integrity, and so on. Doppler allows you to assess the condition of the vessels of the examined organs, as well as the quality of blood flow in them.
An ultrasound examination, as practice shows, is informative for both assessing venous and arterial circulation. This procedure is safe, painless, non-invasive.
USDG BCA
Hello. The neurologist prescribed an ultrasound examination of the BCA. What is this procedure, how is it carried out and is special preparation required? Olga M.
Answered by Nadezhda Ivanovna, ultrasound diagnostics doctor at the MedMix Plus clinic.
Doppler ultrasound of the BCA is an ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic vessels, that is, in other words, ultrasound of the vessels of the neck. This examination is very important in assessing the condition, anatomy and patency of arteries and veins. Using this ultrasound technology, it is possible to judge the state of the blood supply to the brain, determine the degree of stenosis, thereby enabling the attending physician to determine treatment tactics.
In medical practice, there are several methods for studying the vessels of the neck:
1.USDG (ultrasound Dopplerography ) is a method aimed at assessing the patency of blood vessels and their condition. This method gives a general idea of the vessels. Allows you to identify the internal cause of obstruction, for example, a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque.
2. Duplex/triplex scanning , which is used by ultrasound diagnostic doctors at our MedMix Plus clinic. On the monitor screen, a specialist sees a vessel in color against a gray background and evaluates its blood flow. This method allows you to assess the cause of the disturbance in the blood supply to the vessels, whether it is external or internal.
Using BCA ultrasound, you can diagnose diseases such as:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels;
- delamination of the vessel wall;
- arterial aneurysms;
- vasculitis, etc.
Before the symptoms of the disease appear, BCA should be performed when:
- hypertension;
- suffered a stroke;
- lupus;
- diabetes mellitus;
- smoking.
Research is also necessary in the presence of conditions such as:
- dizziness;
- decreased visual function;
- memory impairment;
- headache;
- fainting, etc.
Preparing for the study.
Before performing an ultrasound examination, you need to stop taking foods that can affect vascular tone: tea, coffee, energy drinks, alcohol. You should not visit stuffy or smoky rooms, and you should also stop taking medications that improve memory and attention. It is better to discuss the discontinuation of vascular and cardiac medications with your doctor.
Conducting research.
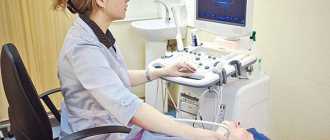
Doppler ultrasound of the BCA is a standard ultrasound examination procedure. The patient lies on the couch, a cushion is placed under the head. A gel is applied to the neck area, and a specialist conducts a study with a special sensor. The procedure lasts on average 30–35 minutes.
Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels is a painless and accurate ultrasound examination method, which in less than an hour will give an answer about the condition of the neck vessels and the causes of discomfort. Performed routinely, ultrasound of the neck vessels will prevent stroke by 80%. Be healthy!
Why is Doppler ultrasound prescribed?
There are many indications for Doppler ultrasound. This can be any disease (or just a suspicion of it) associated with impaired blood flow in the vessels. Among the main pathologies in the diagnosis of which ultrasound plays an important role:
- cerebrovascular accident in acute or chronic form;
- heart failure;
- venous insufficiency and impaired blood flow in the extremities;
- renal failure;
- endocrine diseases.
Examination of the vessels of the head and neck
Doppler ultrasound is most often used to examine the vessels of the head and neck. The doctor prescribes an appropriate prescription if the patient complains of periodic headaches, flickering spots in the eyes, dizziness, or even loss of consciousness. Signals that it is necessary to undergo an examination may also include fluctuations in blood pressure or general weakness in the body for no apparent reason.
If ultrasound examination is prescribed for relatively young patients to diagnose pathologies with severe symptoms, then people aged (after 50-55 years) are recommended to undergo this procedure to prevent stroke.
Doppler of the veins of the lower extremities
Doppler is widely used to assess the condition of the deep and superficial venous systems of the lower extremities. With a probability of 90-100%, such an examination will reveal pathologies of valves, vein walls, and detect varicose transformations of blood vessels.
The most common indications for ultrasound examination of the lower extremities
:
- feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- swelling of the legs;
- leg pain;
- cramps of the calf muscles;
- enlargement, bulging of veins (most often observed in the popliteal fossa).
Doppler ultrasound is used both to diagnose diseases of the veins of the lower extremities and to determine the scope of upcoming surgical intervention. In the second case, during the examination, which is carried out in a standing position, specialists mark with a marker those places on the legs where it will be necessary to ligate and remove the vein.
Examination of heart vessels
Duplex scanning allows specialists to study the structure and evaluate the functional development of the cardiovascular system. Indications for this procedure are as follows:
- pain or discomfort in the chest area;
- high blood pressure;
- congenital heart defects;
- myocardial infarction;
- suspicion of the presence of tumors in the cardiovascular system.
Ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed as an additional study if, for example, a cardiogram or simple echocardiography revealed heart murmurs, angina pectoris, metabolic syndrome and other pathologies.
The use of color Dopplerography allows specialists to study quantitative and qualitative indicators of blood flow in real time, to analyze the state of blood flow not only in the vessels of the heart, but also inside the organ itself.
Doppler testing of the fetus and diagnosis of placental vessels
Today, with the help of Dopplerometry, it is possible to identify pregnancy complications associated with impaired blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system in the early stages. Perhaps a pregnant woman does not yet feel any problems with her health, while the fetus in her womb is already beginning to experience a lack of nutrients and oxygen. An ultrasound with Doppler will definitely show this, and the attending physician will be able to prescribe effective therapy in a timely manner.
In addition to scheduled diagnostics with Doppler, a pregnant woman may also be prescribed unscheduled diagnostics if the following indications exist:
- on the mother’s side – gestosis, kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, Rh conflict;
- on the part of the fetus - developmental delay, oligohydramnios, congenital malformations of organs, asynchronous development of fetuses in multiple pregnancies.
Examination of the vessels of the peritoneal cavity
Ultrasound scanning of the abdominal cavity is prescribed when there is a need to determine the condition of the vessels supplying the kidneys, adrenal glands, and pancreas. Doppler ultrasound allows you to examine the abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava and its branches, paired and semi-gyzygos veins, thoracic lymphatic duct and lymph nodes.
Indications for Doppler ultrasound may include: poor urinalysis, kidney tumors or cysts (can be detected on a simple ultrasound), injuries to the abdominal organs. For preventive purposes, ultrasound examination should be performed if there is a history of chronic or acute inflammatory processes in the pyelocaliceal system (for example, chronic pyelonephritis), in the postoperative period, or with hypertension.
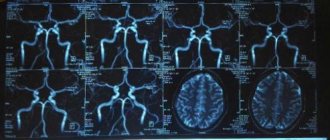
Indications for Dopplerography of head vessels:
- chronic and acute cerebral circulatory disorders or suspicion of them;
- the patient belongs to groups at increased risk of atherosclerosis and other pathological vascular conditions;
- absence of pulse and blood pressure in the arteries of the arms against the background of intense deterioration of visual acuity;
- abnormal changes in the cervical spine due to diseases or congenital anomalies, which can lead to compression of the vertebral artery;
- suffered traumatic brain injuries, as a result of which the vessels were damaged;
- vascular damage due to toxic effects or surgery.
Methodology
The technique for performing an ultrasound scan depends on which part of the patient’s body will be examined: head and neck, brain, abdominal cavity, lower or upper limbs, and so on.
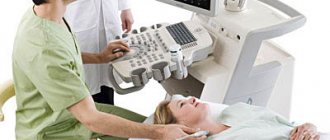
The patient lies down on the couch and frees a certain part of the body from clothing and jewelry. The doctor applies a special thick gel to the skin, which will facilitate the movement of the ultrasound sensor. During the procedure, the sensor is smoothly moved by the doctor, the image displayed on the screen is evaluated, and conclusions are immediately drawn about the state of blood flow in the veins and arteries.
Why is ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck prescribed?
The main task of Doppler ultrasound is to determine the patency of the vascular bed and blood flow parameters. Depending on which vessels are being examined, there are two types of diagnostics:
| Type of ultrasound | Distinctive features |
| Doppler ultrasound of intracranial vessels | A complex branched network is subject to diagnosis, which is represented by:
|
| Doppler ultrasound of extracranial vessels | Vessels that are located outside the skull are examined. Their task is to deliver blood from the heart, and they themselves are represented by:
|
Both examination methods are usually used simultaneously, covering not only the head, but also the neck in order to provide an accurate and objective assessment. The goals of diagnostics are as follows:
- making a diagnosis and determining treatment;
- the need to prescribe additional diagnostic studies;
- control of the treatment and the need for its correction.
How is research done?
The procedure does not involve surgical intervention, that is, it is non-invasive. There is also no radiation exposure, so the study can be carried out both for certain indications and for preventive purposes.
After the patient comes to see the doctor, he is asked to remove clothes that interfere with the examination and lie down on a special couch. After this, a special gel is applied to the sternum, which will help the sensor glide over the skin. Using a sensor, the doctor examines the organ and takes pictures, and also notes the condition and size of all structures. The data obtained will be compared with the norm of Doppler ultrasound of the heart, after which the doctor will draw up a conclusion and give it to the patient.
Pulsation index
PI in the third trimester should be 0.4 -.64. Ultrasound examination results make it possible to understand:
- whether the fetus suffers from intrauterine hypoxia, and if there is a lack of oxygen, then how dangerous the condition is;
- are there any problems due to a conflict regarding the Rh factor;
- the degree of damage to the vessels of the uterus, placenta and fetus due to diabetes mellitus, cardiac pathology or hypertension of the woman;
- Are there any developmental problems during multiple pregnancies, how are the blood vessels connected and developed in twins.
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound examination of the neck and head
In the process of studying the results obtained, the doctor compares them with normal indicators in a number of categories:
- lumen diameter and vessel wall thickness;
- the nature of blood flow and its quality;
- indications of blood flow in the arteries of the same name, synchronicity of the process;
- Vd, Vs and TAMX indicators (diastolic, peak systolic and maximum blood flow velocity, respectively);
- RI and PI (resistance index, pulsatility index, respectively).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the average indicators of blood flow in certain arteries of the head, presented in our table below:
| Artery name | General sleepiness | Vertebrate | External carotid | Internal sleepy |
| D lumen | from 4.2 to 6.9 mm | from 2 to 4.4 mm | from 3 to 6 mm | from 3 to 6.3 mm |
| Vs | from 50 to 104 cm/s | from 20 to 61 cm/s | from 37 to 105 cm/s | from 32 to 100 cm/s |
| Vd | from 9 to 36 cm/s | from 6 to 27 cm/s | from 6 to 27 cm/s | from 9 to 35 cm/s |
| TAMX | from 15 to 51 cm/s | from 6 to 21 cm/s | from 5 to 26 cm/s | from 9 to 35 cm/s |
| R.I. | from 0.6 to 0.8 | from 0.6 to 0.8 | from 0.6 to 0.9 | from 0.6 to 0.8 |
| P.I. | from 1.1 to 3.5 | from 0.6 to 3 | from 1.1 to 3.9 | from 0.8 to 2.8 |
Correct decoding allows us to identify a number of pathological conditions of the patient’s vascular system.
Application area
Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels has a wide range of applications. Almost any area of the body where large vessels pass can be examined.
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the upper and lower extremities. The study of the venous network of the lower extremities as potential sources of thromboembolism in the first place has become widespread. The doctor looks at the vessels from the groin area to the foot. Venous valves of leg vessels are assessed in the diagnosis of varicose veins. In case of obliterating endarteritis, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis of the arteries of the leg and foot, the blood flow is examined, the speed and volume of blood that the vessel is able to pass through is assessed. Based on the results, the choice of treatment tactics is decided. Sometimes the question may be acute: to use surgical treatment or continue conservative treatment. The examination of the brachiocephalic arteries plays an important role in making this decision. Common carotid artery stenosis can impair the patient's quality of life for many years. The parameters studied during ultrasound doppler help the surgeon make an important decision about surgical intervention.
- Much less commonly used is the diagnosis of vessels located inside the skull - transcranial Doppler sonography or duplex scanning. In some cases, Doppler ultrasound is also used to determine the location of cerebral vascular lesions, anatomical abnormalities and aneurysms.
- The largest artery in the human body is the aorta, a vessel extending from the left ventricle of the heart to the iliac arteries of the lower extremities. Congenital or acquired disorders fortunately do not occur often, but in most cases they are life-threatening - aortic aneurysm, dissection.
Indications and contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications for ultrasound diagnostics. The research is one of the safest in the medical field. Myths about the dangers of ultrasonic signals have long been dispelled by scientists.
Indications for ultrasound examination are determined by the doctor. There is a large list of diseases for which ultrasound is clinically advisable. Varicose veins, atherosclerosis, aneurysms, thrombosis are conditions that cannot be diagnosed and monitored without ultrasound.
In addition, ultrasound helps doctors in conditions where other, more informative research methods are not possible. Ultrasound is a quick examination that requires minimal equipment and can be performed in any department if there is a machine and a specialist.
Norm of SDO in the umbilical cord artery
| Duration, week | The norm of the systole-diastolic ratio in blood vessels |
| 16-19 | 4, 45 — 4,67 |
| 20-22 | 3,75 -3,95 |
| 23-25 | 3,41-3,6 |
| 26-28 | 3,1-3,27 |
| 29-31 | 2,82-2,94 |
| 32-35 | 2,48-2,52 |
| 35-37 | 2,4-2,45 |
| from 38 | 2,19-2,22 |
The norm of SDO in the arteries of the uterus in the third trimester: 1.3-3.7