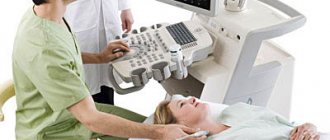
Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the safest and most effective ways to detect various diseases of internal organs. This technique is used in various fields of medicine, including assessment of the condition and possible pathologies of blood vessels. In this case, Doppler ultrasound or ultrasound is performed, which is used to examine the neck and head. Early diagnosis allows you to choose gentle and effective treatment methods and prevent the development of complications. First you need to understand what an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck shows, why this method is effective in diagnosing many diseases.
The Doppler ultrasound effect is based on the ability of ultrasound waves to be reflected from blood cells. As a result, electronic impulses appear that appear on the device screen in the form of images of veins and arteries with blood flow.
This ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of the large arteries that supply the brain, carotid and vertebral arteries, determine the intensity of blood flow, and also identify traces of obstruction.
How is Dopplerography performed?
This examination is carried out in the presence of certain symptoms. Preliminary preparation is necessary so that the results of the ultrasound examination give an accurate picture of the patient’s condition.
There are two types of procedure:
- Transcranial. The sensor is installed on the skull bones in those places where they are thinnest. The procedure gives an accurate picture of the vessels located directly in the brain.
- Extracranial. The technique is used to examine large vessels passing through the neck (carotid arteries, jugular veins, etc.). The sensor is located at each site separately.
What the results look like
After performing an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images of the vascular pattern with the ability to construct a three-dimensional model. The patient can pick up the images on electronic media or in printed form. The photographs are accompanied by a report from a radiologist.
Normally, the internal carotid arteries are located symmetrically, have clear contours, are not displaced, and are not compressed. The cerebral arteries arise in a typical place, the diameter is not changed, and there is no pathological tortuosity of the vessels. The cerebral veins and sinuses should be of normal diameter, without areas of blood flow disturbance, filling defects or deformations.
On MRI images of the vessels and arteries of the neck you can see signs inherent in certain diseases:
- an aneurysm is a round formation with a high signal intensity; when a thrombus attaches, a layered structure appears;
- vascular malformations appear as linear or tortuous structures with dilated vessels;
- dissection of the arterial wall is characterized by the appearance of a crescent-shaped hematoma located along the vessel, while the lumen of the artery is narrowed evenly or in the form of a rosary;
- atherosclerosis of the vascular system looks like an area of increased intensity on the vessel wall, the lumen is narrowed;
- hemangioma is a high-intensity formation with clear edges and a lobular structure.
Despite a detailed description of all identified pathological formations, the conclusion of a radiologist is not a diagnosis. The MRI result of the area of the cerebral vascular system should be shown to the doctor who ordered the study. Clinics offer the opportunity to consult with the radiologist who performed the procedure. If necessary, he will recommend contacting specialized specialists - a neurologist, oncologist or surgeon.
Indications for the procedure
Doppler sonography is indicated in the following cases:
- Problems with coordination and other symptoms indicating a malnutrition of the brain (the patient is dizzy, has tinnitus, etc.).
- Unstable heart rhythm.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Transient ischemic attacks.
- IOP.
- Previous stroke or heart attack.
- There are suspicions of atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes.
- Fatigue quickly for no apparent reason.
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
This procedure is also indicated if heart surgery is to be performed, if there are pulsating formations in the neck, or if thrombosis is suspected. In children, it is performed in case of serious postural problems and delayed development of the child.
Preparing for the study
First of all, you should make sure that there are no contraindications, and if there are any, collect all the technical documentation describing the devices and endoprostheses implanted into the body. The examination becomes possible after analyzing the composition of metal implants.
It is advisable to have with you a doctor’s referral, extracts from medical documents, expert advice, as well as the results of previous studies, if any. A patient who is scheduled to receive a contrast agent should undergo a kidney function test in advance. Women should be sure that they are not pregnant.
There is no need for special preparation for MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head. If an examination with contrast is prescribed, you must arrive on an empty stomach.
Are there any contraindications?
Ultrasound waves are absolutely safe for humans, so there are no special contraindications to this type of ultrasound. The only exception is a violation of the integrity of the skin. The procedure involves contact of sensors with the head or neck, so the examination is postponed until the wound heals.
However, there are a number of special cases that make duplex examination of blood vessels difficult:
- cardiac arrhythmia, which changes the speed of blood circulation through healthy arteries and veins;
- the area under study is hidden under bone tissue;
- slow blood flow in the patient.
These are not contraindications, but in this case changes in the location of the sensors are required. It will be necessary to navigate non-standard conditions, which requires professionalism on the part of the doctor.
What is the difference between duplex and triplex scanning?
These diagnostic methods are very similar to each other and have practically no differences, with the only difference being that with triplex scanning the vessels can be viewed in three-dimensional space. Duplex mode presents information in only two planes. In fact, triplex scanning is positioned as an additional procedure when conducting a duplex study.
And if we take into account the fact that the crystal transmitting and receiving the signal is the same, then the resolution of the triplex method is considered slightly worse than the duplex one. The quality of the work will depend entirely on the quality of the apparatus and the qualifications of the doctor conducting the research, and not on the diagnostic method.
Features of ultrasound examination
As a rule, Doppler sonography is planned in advance, but it can be performed urgently. The procedure itself is painless, so patients tolerate it calmly.
The examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The patient lies on his back. The head should be relaxed (a flat pillow is placed under it).
- You need to remain calm, breathe evenly and, if possible, not move.
- A special gel is applied to the area under study to prevent the penetration of air between the skin and the sensor.
- The movement of the sensors is controlled by a specialist. As a result, an image of the vessels appears on the monitor screen.
The study lasts no more than 1 hour. During the study, the doctor may ask the patient to do some action: turn his head, squeeze a vein in a certain place, breathe less often, etc.
Dopplerography of extracranial vessels begins with examination of the right lower segment of the carotid artery. The sensor is then moved up the neck. Next, the color mode is activated, which makes it possible to identify a number of pathologies: deformations of the walls of blood vessels, impaired blood flow in certain areas, etc.
General characteristics of the examination
To explain what kind of examination this is – Doppler ultrasound – and how it is done, you need to start by deciphering the abbreviation: Doppler ultrasound (you can also hear the name “duplex scanning”). In more detail, Doppler ultrasound is a combined study that combines standard ultrasound and the Doppler effect. Ultrasound allows you to visualize a patient’s specific organ on the screen, determine its size, structure, assess its integrity, and so on. Doppler allows you to assess the condition of the vessels of the examined organs, as well as the quality of blood flow in them.
An ultrasound examination, as practice shows, is informative for both assessing venous and arterial circulation. This procedure is safe, painless, non-invasive.
What can she show?
Duplex scanning allows you to determine areas of narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, the direction of blood flow, its speed, as well as the condition of the vascular walls. This study can show the location of cholesterol plaques and the presence of blood clots, which is very important when diagnosing atherosclerosis.
A decrease in the elasticity of the walls of the arteries, as well as their thickening, indicate that the patient has hypertension (high blood pressure). If a change in blood flow is diagnosed, this indicates the presence of obstacles. For example, an aneurysm is a sac-like protrusion of a vessel.
What is a diagnostic method
This method of vascular diagnostics provides complete information about the state of the human vascular system. Using ultrasound, you can evaluate and analyze the speed and nature of blood flow, as well as determine the presence of blood clots or other vascular pathologies.
The study usually proceeds in two stages: two-dimensional mode and duplex study.
Content:
- What is a diagnostic method
- Why is the procedure necessary?
- What is the difference between duplex and triplex scanning?
- Who needs the procedure
- Preparation for the procedure and contraindications
- How the procedure works
- Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
In two-dimensional mode, you can see the vessels and adjacent tissues, limited only by this information. It does not provide any information about blood supply.
With a duplex study, the doctor sees a complete picture of what is happening in the vessels, with a detailed description and a color two-dimensional picture.
What pathologies can be diagnosed?
Doppler ultrasound has certain limitations in diagnosing diseases. For example, she will not be able to study small veins - for this she needs to perform angiography. But there are a number of pathologies that can be identified:
- Atherosclerosis. By examining the head and neck using ultrasound, it is most often possible to diagnose atherosclerotic disorders. This condition is indicated by echogenicity, the presence of plaques, and thickening of the vascular walls. Moreover, if the lumen of the artery narrows by more than 20%, then the patient is diagnosed with “stenosis.”
- Thrombosis. Thrombosis is characterized by blocking of the arterial lumen by a blood clot. On Doppler ultrasound, inflammation of the vessel wall with a homogeneous formation inside is clearly visible.
- Compression of blood vessels. The examination allows you to see areas where blood flow is impaired due to the impact of swollen tissue on the channels. This allows you to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis and identify problems with blood circulation after injuries.
In addition, these ultrasound examinations can detect a number of other diseases, including vasculitis, post-traumatic dissections of the arterial walls and other pathologies.
Doppler ultrasound is a safe diagnostic method that can be performed in any case if there is a medical need for it. Timely implementation of the procedure allows you to identify the disease at an early stage of its development.
If you are worried about dizziness, tinnitus, ringing in the head, headaches, heaviness, weather dependence, etc. - this may be a sign of impaired, insufficient blood circulation to the brain.
In such a situation, it is necessary to study the blood flow in the vessels of the brain. The most accessible and informative method for assessing the state of cerebral circulation is ultrasound examination of blood vessels, which is aimed at identifying obstacles to blood flow to the brain as the cause of vascular diseases of the brain.
Previously, ultrasound equipment made it possible to study vessels only “blindly” - without visualizing the vessel itself, only by the nature of the blood flow in it (using the Doppler effect, the speed and direction of blood flow was determined. This method is called “USDG” - “Ultrasound Dopplerography of Vessels”) .
Currently, the Doppler ultrasound method is not used independently; it is part of a more modern ultrasound examination of blood vessels, which is called “Vascular Duplex Scanning” (vascular DS). Some doctors continue to call this method in the old way: “USDG”. Therefore, there is confusion in the name of this method of ultrasound examination of blood vessels.
The term “ Duplex scanning of vessels ” means “double scanning of vessels” and allows not only to determine the nature of blood movement through the vessels using the Doppler effect (this is ultrasound scanning), but also to examine the vessels in detail: determine their size, the structure of the vascular wall (which becomes denser and thickens with atherosclerosis, thickens with inflammation of the vessel, etc.); determine the course of blood vessels (which can be smooth or tortuous, up to “loop-shaped”), identify intravascular formations - atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots that create an obstacle to blood flow.
Modern ultrasound machines add to these two components of the study the ability to color vessels depending on the direction of blood flow . Therefore, the term “ Triplex vascular scanning ” (that is, triple scanning) appeared.
The terms “Duplex scanning of vessels”, “DS of vessels”, “Triplex scanning of vessels”, “USDG of vessels” mean one thing - ultrasound examination of blood vessels, which is carried out in triplex mode on modern ultrasound machines.
When performing an ultrasound examination of the vessels carrying blood from the heart to the brain, it is customary to distinguish two levels: the vessels of the neck and the vessels of the brain.
For more reliable information about the state of cerebral circulation, it is necessary to examine both levels of blood flow to the brain, since the “neck and head” are one whole: blood flow in the arteries of the neck is an intermediate stage in the movement of blood from the heart to the brain, and blood flow in the cerebral vessels - this is the final result. Blood flow disturbances can occur at any of these levels.
The first stage of ultrasound diagnostics is the examination of the arteries and veins of the neck :
- common carotid arteries and their branches (internal carotid arteries - carry blood to the brain, external carotid arteries - supply blood to the face)
- vertebral arteries, which at the level of the neck pass through the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae and carry blood to the posterior parts of the brain.
Obstacles to the flow of blood to the brain at the level of the neck can be tortuosity of blood vessels - congenital (up to the formation of a “loop” by the vessel), or acquired (for example, an uneven tortuous course of the vertebral arteries, formed against the background of spinal osteochondrosis); or there may be narrowing of the arteries - congenital (narrow diameter of the artery), or acquired (narrowing of the lumen of the arteries due to inflammation of the vascular wall, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, etc., up to complete blockage of the lumen of the artery). The veins of the neck - jugular and vertebral - are also examined to identify disturbances in the outflow of venous blood from the brain to the heart.
The second stage of ultrasound diagnostics is a study of the arteries and veins of the brain , which is performed through the bones of the skull (transcranial). The arteries of the brain are a continuation of the arteries of the neck on the surface of the brain inside the skull, and form two pools of blood circulation in the brain: “Carotid pool” - from the terminal branches of the internal carotid artery (ultrasound examination is carried out through the temporal bone); and the “Vertebro-basilar basin” - consisting of the terminal segments of the vertebral arteries, which, after entering the cranial cavity, merge with each other into the main (or basilar) artery of the brain (ultrasound examination is carried out through the foramen magnum).
Ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels reveals the resulting indicators of cerebral blood flow: either the blood supply to the brain is not impaired, or there are disturbances in arterial blood flow in one or another circulatory system of the brain (arterial spasm, insufficient blood flow to the brain, etc.) or there are signs of obstructed outflow venous blood from the brain (which leads to increased intracranial pressure). This study is called “Transcranial ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels”, its synonyms: “TCDG” “Transcranial Dopplerography”.
Therefore, it is impossible to study, for example, only transcranial blood flow through the vessels of the brain, without knowing the characteristics of blood movement through the arteries of the neck, where there may be various obstacles to the blood flow to the brain.
And vice versa - the study of only the vessels of the neck will be incomplete in its information content without taking into account the resulting indicators of blood flow in the cerebral vessels.
Carrying out an ultrasound examination of the neck arteries separately is only possible to track the growth dynamics of atherosclerotic plaques identified earlier in them (for timely referral of the patient to vascular surgeons).
There are cases when doctors prescribe a blood flow study in only one of the levels of blood flow to the brain: either in the vessels of the neck or in the vessels of the brain. It is not right.
This may be due to terminological confusion in the name of the method of ultrasound examination of blood vessels (out of habit, they continue to call it “USDG of the neck”).
Or it may be due to mistrust in the results of transcranial examination of cerebral blood flow, which developed in the era of “blind” Doppler examination of cerebral vessels. But those days are already gone. Modern ultrasound equipment allows you to clearly locate cerebral vessels and the movement of blood through them.
The method of ultrasound examination of blood vessels is fast, simple, informative and safe for the patient’s health.
To clarify the state of cerebral blood flow, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck and brain for such complaints as:
- headache
- dizziness
- tinnitus, ringing in the head
- decreased vision and hearing
- memory loss
- sleep disorders
- emotional disorders, psycho-emotional overload, etc.
To prevent the development of stroke, thanks to the identification of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck and brain is indicated for all patients:
- over 40 years of age
- with obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
- for coronary heart disease, heart rhythm disturbances
- for arterial hypertension
- diabetes mellitus
- kidney diseases
- patients who have had a stroke or myocardial infarction.
No other studies other than Duplex Vascular Scanning provide information about the functional state of the vessels of the head and neck and the movement of blood through them. Including this study is not replaced by MRI or CT scan of the brain (since they characterize the structure and condition of the brain tissue itself, and do not characterize cerebral blood flow). Ultrasound examinations of cerebral vessels, MRI or CT scans of the brain complement each other in their information content.
In our department, ultrasound diagnostics of blood vessels is carried out by very experienced and responsible specialists using modern ultrasound equipment. In addition to studies of the vessels of the neck and brain, studies are carried out of the arteries and veins of the upper and lower extremities, arteries of the kidneys, and vessels of the abdominal cavity.
| Name of service | Price |
| Functional diagnostics | |
| Code: A04.12.001.002 (5.067) Duplex scanning of the arteries and veins of the kidneys, | 1050.00 |
| Code: A04.12.003 (5.069) Duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta | 1050.00 |
| Code: A04.12.003.002 (5.070) Duplex scanning of arteries and veins of the iliac segment | 1600.00 |
| Code: A04.12.005.002 (5.042) Duplex scanning of the arteries of the upper extremities | 1500.00 |
| Code: A04.12.005.003 (5.003) DS of brachiocephalic arteries and veins | 1700.00 |
| Code: A04.12.005.004 (5.040) Duplex scanning of the veins of the upper extremities | 1500.00 |
| Code: A04.12.006.001 (5.043) Duplex scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities | 1500.00 |
| Code: A04.12.006.002 (5.041) Duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities | 1500.00 |
| Code: A04.12.018 (5.038) DS transcranial arteries and veins | 1100.00 |
Extracranial Dopplerography
Ultrasound using grayscale imaging, spectral Doppler analysis, and color Doppler imaging (CDI) is a validated method for assessing the extracranial cerebrovascular system. Although it is not possible to detect every anomaly, adherence to practical parameters will maximize the likelihood of detecting the majority of extracranial cerebrovascular anomalies. Sometimes additional and/or specialized examination may be required.
Transcranial Dopplerography
(TCD) provides rapid, non-invasive, real-time measurement of cerebrovascular function. TCD can be used to measure blood flow velocity in the basal arteries of the brain to assess relative changes in blood flow, diagnose focal vascular stenosis, or detect embolic signals in these arteries. TCD can also be used to assess the physiological state of a specific vascular territory by measuring the response of blood flow to changes in blood pressure, changes in final CO2 concentration (cerebral vasoreactivity), or cognitive and motor activation. TCD is widely used in the clinical diagnosis of a number of cerebrovascular disorders such as acute ischemic stroke, vasospasm, subarachnoid hemorrhage, sickle cell disease, as well as other conditions such as brain death. Clinical indications and research applications for this imaging modality continue to expand.
Where can I get Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels?
The study is carried out in municipal clinics and public hospitals, specialized clinics, and general medical centers. Depending on the location of the ultrasound, the cost of each type of Doppler ultrasound will be in the range of 500-6000 rubles. The procedure has many advantages, including painlessness and the absence of side effects. Within 20 minutes, a sonologist will be able to determine the presence of anomalies in venous or arterial inflow and assess the degree of development of danger to blood vessels.
However, the procedure will not help determine the cause of compression of the thin arteries, since the capabilities of the device do not allow them to be seen from the outside.