If a woman continues to have low or high blood pressure after childbirth, under no circumstances should she ignore this condition or try to cope with the problem herself. The reasons for this situation can be very diverse, so it is the doctor who must determine which factor influenced the change in indicators and eliminate it. Let's consider what factors influence blood pressure readings after childbirth, what symptoms bother a woman during this period, what treatment will help get rid of the pathology without harm to health.
Acceptable pressure levels during breastfeeding
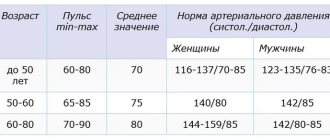
Even children know the correct blood pressure indicator - it is 120/80 mm Hg. But not all people correspond to this value, because everyone has always been a little higher, a little lower, a little lower. This is what you should follow. Normal blood pressure is considered a person who feels well.
The period of breastfeeding is a very important time in the life of every young mother, because it is responsible not only for your health, but also for the well-being and development of your baby. That's why a nursing mother should be careful and think that everything is fine. You cannot underestimate your condition, because only when the mother feels comfortable, the child is calm and joyful.
If the pressure increases to 135/85 mm Hg, there may not be any negative consequences.
When it increases above - 140/90 and much more, and the well-being of the deterioration of the deterioration of the deterioration of privacy, this is already treatment in the clinic.
How does a woman’s blood pressure change during lactation?
During pregnancy, under the influence of strong hormonal levels, a growing uterus and the accumulation of fluid in the body, women often experience high blood pressure, especially in the third trimester. After childbirth, the condition of most mothers returns to normal, but different options are possible:
- normal blood pressure - determined in a physically healthy woman (most often after 2 or 3 births);
- high blood pressure (indices above 140/90 mm Hg) - sometimes occurs in women in labor with hypertension, or in women who have chosen mixed or artificial feeding of the child;
- low pressure (indicators less than 110/70 mmHg). Such values are most often found in primiparous women with impaired vascular tone (vegetative-vascular dystonia) and dehydration. In addition, a significant decrease is associated with breastfeeding.
Jumps in indicators with pronounced symptoms during the day are a sign of serious hormonal or cardiovascular disorders that require medical attention.
Why does blood pressure often drop during breastfeeding?
Lactation is the postpartum period, which is characterized by gradual stabilization of hormonal levels, and can last from 3 months to 2 years, depending on the individual characteristics of the woman. Women in labor who exclusively breastfeed their children often complain of a noticeable decrease in blood pressure to 80/60 or 70/50 mmHg.
The main reasons for the decline in indicators during the GW period:
dehydration (de-loss, hydro-water) – the release of milk is accompanied by a loss of fluid from the mother’s body. Blood plasma volume is one of the components of blood pressure; with a decrease in the amount of water, this indicator drops;- high levels of oxytocin (a hormone produced by nerve cells in the hypothalamus in the diencephalon). This substance not only has a stimulating effect on the tone of the uterus, but also relaxes the smooth muscle cells of the vascular wall. Stimulation of hormone synthesis occurs under the influence of mechanical irritation of the nipple and areola during breastfeeding;
- insufficient fluid intake into the body. The daily volume of water for a nursing mother is at least 13 cups (1.5-2 l).
Low blood pressure during breastfeeding can also develop as a result of the mother’s irrational diet with insufficient vitamins and microelements in the diet.
High blood pressure during breastfeeding
High blood pressure during breastfeeding is not uncommon today. This phenomenon is associated with the stress on the myocardium during pregnancy, when the muscles of this organ are very taxed to ensure the proper functioning of the body of the woman and her child. Also, changes in the hormonal levels of a pregnant woman contribute to heart disease.
Therefore, at every visit to the appetite clinic, the doctor who notices it measures the blood pressure. Its cost shows to what extent the stern woman's circulatory clamshell is able to function properly.
To alleviate the condition of the elderly, a mother can have an experienced doctor who can prescribe such drugs so as not to harm the child.
The course of treatment for hypertension during breastfeeding will be significantly differentiated, in this case including only approved medications and respectful diets.
Why does breastfeeding mothers have high blood pressure?
High blood pressure in the paragraph is caused by the following factors:
- Excessive dependence on coffee, tea, licorice root tincture;
- overwork, stress, lack of sleep;
- smoke;
- hereditary predispositions that reveal themselves after pregnancy;
- take medications that increase smooth muscle tension - oxytocin, methylerometry;
- various cardiovascular disorders;
- diabetes;
- Difficult childbirth or complications after it;
- Problems with the endocrine system.
If excess pressure begins to develop, blood pressure readings gradually increase. Regardless of the reasons that led to hypertension, medical care is necessary to prevent the development of the disease. If nothing is done in this direction, after a while you may notice that it is taking effect and finally leading to pathological changes in the body.
Normal pressure
Both during the period of bearing a child and after his birth, if a young mother practices breastfeeding, the pressure should be within normal limits, this means that the body can fully cope with the loads, and no pathological changes occur in it. In healthy people, blood pressure should not be lower than or exceed the normal range of 90/60-140/60. Blood pressure can fluctuate within acceptable values; such changes depend on the characteristics of the body, age, weight and many other factors.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
120
on
80
Signs of high blood pressure
When the pressure increases, the feeding mother feels the following symptoms:
- Headache;
- nausea;
- Black spots before her eyes;
- chills;
- Fast impulse;
- Breathing and breathing;
- Problems with vision.
Even some of the above-mentioned symptoms indicate improper functioning of the cardiovascular system. It often precedes pregnancy, but even after pregnancy, symptoms of hypertension can persist during breastfeeding.
Causes of low and high blood pressure after childbirth
After the birth of a child, it is possible that residual effects after pregnancy and childbirth will be observed for six months to a year, since the mother’s body takes a long time to return to normal, and this takes time. But if more time has passed after pregnancy, and blood pressure is still fluctuating, this indicates that not everything is in order with the body, and medical intervention is required. After the birth of a child, blood pressure can remain either high or low, let’s look at the main reasons.
Increased
Weight gain during pregnancy leads to blood pressure problems after childbirth.
High blood pressure after the birth of a child is most often caused by the following factors:
- A woman’s weight gain, especially if she does not follow the rules of a healthy diet and lifestyle. In this case, the load on the heart and blood vessels increases, as blood volumes become larger. Therefore, gynecologists so carefully monitor how a pregnant woman gains weight, so that later, after the birth of the child, she does not have problems with the health and functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- If in the last trimester a woman’s blood pressure began to increase abnormally and gestosis developed, then after childbirth the condition may not stabilize for some time. In this case, you should be under constant supervision by a doctor, and if you follow all the recommendations, your blood pressure will gradually return to normal.
- After the birth of a baby, some women do not immediately return to normal psycho-emotional health, as a result of which, due to stress and constant nervous strain, the load on the heart and blood vessels increases, and arterial hypertension develops.
- Some women notice that their blood pressure has increased during breastfeeding, which is affected by lack of sleep at night, fatigue, and disruption of sleep and wakefulness.
- Hereditary predisposition, when in the female line there were cases of increased blood pressure after childbirth.
- Chronic pathologies that worsened and became aggravated during pregnancy and after (chronic kidney failure, hypertension).
- If a woman takes heavy medications after giving birth, this also provokes a rise in blood pressure as a side effect.
Decreased
Low blood pressure after childbirth is less dangerous than high blood pressure, but still, you should not ignore the symptom and try to cope with the problem yourself. The pathology most often worries women of fragile build, prone to depression, and scrupulously monitoring their weight. If you severely limit yourself to normal food, anemia develops, as a result of which your blood pressure drops below normal levels. The cause may be a difficult, complicated birth, during which the woman has lost enough blood. Since the body needs time to recover, hypotension after childbirth will continue to bother you for some time.
If a woman suffered from vegetative-vascular dystonia before pregnancy, this condition may recur after the birth of a child, causing characteristic symptoms. Pathology can also arise as a consequence of a malfunction of the thyroid gland. In this case, only an endocrinologist can help cope with the situation; you can only make the situation worse on your own.
Diagnostic methods
Since this disease is very serious and can cause both heart attacks and strokes, the dieter must necessarily undergo research to determine the causes in which hypertension occurred so that doctors can prescribe effective treatment.
Complex diagnostics includes the following methods:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry. They use it to test for anemia from iron deficiency.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, heart and abdominal cavity.
- Echocardiography.
- Computed tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Urography and aortography.
Carrying out the necessary tests will not only reveal the fact of hypertension in a nursing mother, but also determine its causes and begin effective treatment.
Lactostasis due to high blood pressure
Lactostasis is a blockage of the milk duct. Most often it occurs in first-time mothers in the first days after starting breastfeeding.
This condition can be caused by high blood pressure, but the problem is complex. Inability to express milk and non-compliance with the frequency of feeding the newborn, as well as tight underwear. The thoracic ducts can become worse due to stress and exposure to cold. All these factors also lead to breast swelling.
Therefore, you should take care of yourself and make sure that inattention and high blood pressure do not cause galactorrhea in the mammary glands.
First aid
In case of a sharp increase in blood pressure, you should immediately try to normalize it and seek medical help. If this is not the first time a nursing woman finds herself in a dangerous condition, you need to get a tonometer and have it at hand.
If the ambulance has not arrived yet, in this situation you should:
- Lie down comfortably so as not to put your health at greater risk;
- ask others to open the windows and let cool, fresh air into the room;
- lower your blood pressure with medications (if this is not the first time and the doctor has previously prescribed them for hypertension)
- Place a hot water bottle on your feet to warm them up if you feel shaky;
- stay calm or drink valerian extract to find emotional balance.
After doing all these steps, wait until the doctor tells him about the medications you took.
How to measure?
Correct measurement of pressure will allow you to make a reliable diagnosis.
Before measuring blood pressure, you should sit down and relax. Place a cuff on the arm, above the bend of the elbow, fixing the stethoscope on the inside where the large vein passes. Next, we pump up the air with the bulb so that the cuff fits snugly to the arm. Then the air slowly descends, and the tone is listened to through a stethoscope. The first beat shows the systolic pressure, and the last beat shows the dystolic pressure. For ease of use and obtaining accurate data, it is recommended to use an electronic tonometer. This will help avoid data inaccuracies, and the procedure will not bring any difficulties to a person who does not know how to measure blood pressure.
Permitted and prohibited drugs
In this situation, the question arises, what can be taken for blood pressure while breastfeeding, since most of the drugs pass into milk?
There are such drugs. Here they are:
- Nifediline.
- Methyldol.
- Verapomil.
- Dolegit.
Although these drugs are not absorbed into breast milk, they may cause decreased milk supply. To normalize blood pressure, the tablet is placed under the tongue. The doctor prescribes the drug, determines the duration of its use and dosage.
There are also drugs that are completely prohibited for use by nursing mothers:
- Beta-blockers (Atenolol, Nadolol).
- ACE inhibitors.
- Atgiotensin receptor blockers (reserpine).
- Diuretics (furosemide).
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Dibasol, Papaverine).
A nursing woman bears full responsibility for her health and the health of her child, so she should not take medications without the participation of a specialist.
How to prevent gestosis (preeclampsia)
PRE-ECLAMPSIA (HEREINAFTER PE) is a multisystem pathological condition that occurs in the second half of pregnancy (after 20 weeks), characterized by an increase in blood pressure and protein content in the daily urine, which can lead to complications both in the body of the pregnant woman and fetus
All attempts to explain the causes and mechanisms of preeclampsia to date have not yielded any clear results. However, it is now generally accepted that the placenta plays a key role in the development of this pathology. In the very process of its formation, an error occurs in which the modeling of the blood vessels of the placenta is disrupted, after which the transport of substances through the placenta occurs with an error, and in response to this it begins to produce special compounds to show that it is working hard. These substances enter the mother’s body and trigger a cascade of pathological changes.
This pathology is insidious, often begins without complaints or symptoms, so it is quite difficult to predict it. As a rule, PE begins after 20 weeks, most cases occur in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy and the postpartum period.
RISK FACTORS FOR PE DEVELOPMENT:
- first pregnancy
- multiparous (history of PE, break after last birth of 5 or more years)
- multiple pregnancy
- pregnant woman's age > 35 years
- overweight/obesity (body mass index > 25 kg/m2)
- family history (PE in the mother/sister of a pregnant woman)
- extragenital diseases of the pregnant woman (pre-pregnancy arterial hypertension, kidney disease,
- diabetes mellitus, vascular diseases, APS, collagenosis, SLE).
!!! According to recent studies, this special formation of the placenta, which was mentioned above, occurs on the basis of the interaction of the genes of the mother and the fetus. This suggests that there is a hereditary predisposition to PE on both the maternal and paternal lines. It has been established that in 30-35% of cases the genes of the pregnant woman play a role, in 20% the genes of the fetus and in 13% a combination of the genes of both parents. This means that for men born from women with preeclampsia, their wife may be more likely to experience it during pregnancy... so sometimes it’s even useful to communicate with your mother-in-law)))
CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSIS:
- occurs after 20 weeks of pregnancy
- increased blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. (at the same time, the criterion is also an isolated increase in systolic pressure >140 mmHg, or diastolic pressure >90 mmHg)
- proteinuria (the amount of protein in daily urine > 300 mg)
In the future, symptoms of damage to other systems may occur: impaired renal function (creatinine > 97.2 µmol/l, oliguria), liver (increased levels of ALAT, AST, LDH by at least 2 times), hematological complications, acute lung damage, edema, HELLP /ELLP syndrome, central nervous system damage (eclampsia, etc.). All this is already a criterion for severe PE and entails fetal suffering (oligohydramnios, negative non-stress test, FGR syndrome, antenatal fetal death).
!!! Edema in itself is not a criterion for PE. An important role is played by assessing the rate of growth and area of spread of edema. This helps to assess the severity of PE, but does not make this diagnosis.
DIAGNOSTICS:
- blood pressure measurement (pressure increase with double measurements with an interval of at least 4 hours)
- determination of protein in daily urine (> 300 mg)!!!
- In severe forms of PE, markers of damage to other systems, which every gynecologist knows about, can be added. The patient herself can help by measuring her blood pressure at home herself, taking the urine test that the doctor prescribes (even if it’s tedious/strange/difficult) and coming to the appointment with the frequency the doctor asks for.
!!! YOU SHOULD TELL YOUR DOCTOR ABOUT THE FOLLOWING SYMPTOMS:
- nausea and/or vomiting
- pain in the epigastrium and/or right hypochondrium
- rapid weight gain > 500 g/week)
- appearance/worsening of edema
- Strong headache
- visual impairment
- confusion
- dyspnea
- change in the nature of fetal movements
ONLY WITH COMPETENT COLLABORATION WILL IT BE ABLE TO CORRECT THIS CONDITION IN TIME.
TACTICS OF MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH PE
The main idea is that the cause of PE is pregnancy, therefore, the sooner the pregnancy ends, the sooner recovery will occur.
With moderate PE, at the initial stage there is always hospitalization and a search for a suitable medicine to correct blood pressure, monitoring the condition of the fetus. Everything in this situation is aimed at prolonging pregnancy and preventing complications.
In case of severe PE - hospitalization, decision on delivery after stabilization of the pregnant woman, if possible after prevention of fetal RDS, and transfer of the woman to a higher level of medical care.
Caesarean section is not the mandatory choice for delivery of PE. The method of delivery is selected based on the gestational age, readiness of the birth canal, and the condition of the pregnant woman and fetus.
PREVENTION
- healthy eating, normal body weight and moderate weight gain during pregnancy, physical activity
- taking aspirin 75 mg/day from 12-36 weeks of pregnancy (for women at risk for PE, prescribed by the attending physician)
- calcium intake 1.5-2 g/day from the 12th week of pregnancy (prescribed by the attending physician, the dosage is determined based on the patient’s diet)!!!
There is no evidence base and is not recommended for the prevention of PE: multivitamin complexes, separately vitamins C and E, fish oil, salt and fluid restriction, diuretics, progesterone, heparin, magnesium sulfate, garlic, leeches, bed rest.
Modern scientists are now actively working on the problem of PE; a number of substances have already been isolated by which the placenta signals that there is a problem. All efforts are focused on finding methods for early diagnosis of these compounds and ways to neutralize them. Therefore, we will believe in the power of science, and also work on each pregnancy as a friendly team of patients and doctors, where everyone hears and respects each other (and yes, this applies to both sides).
Herbal treatment
One way to reduce high blood pressure is by consuming medicinal plants.
The calming properties of herbs give a good effect. They are observed when consuming a decoction from the entire list of herbs.
To prepare it, take:
- Juniper cones (2 tablespoons);
- lemon balm (2 tablespoons);
- fennel seeds (1 tbsp.);
- allspice (3 tablespoons);
- Peppermint (3 tablespoons).
Mix all ingredients in the quantities indicated above and pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture into a thermos. Pour boiled water (1 liter) over these herbs. Set aside for 3 hours, then strain. Drink 0.5 glasses twice a day - morning and evening half an hour before meals.
Feeding the child during this treatment cannot be stopped.
Therapeutic baths
Therapeutic baths are effective as one of the additional measures that help a nursing mother relax and reduce blood pressure.
They are available in 2 versions:
- With the addition of a solution of valerian or sea salt. Give a bottle of sedative or 1 tablespoon of salt in water. Treatment can be continued for up to 15 minutes.
- Clay baths. Add 3-4 handfuls of white clay to the water. Grind until completely dissolved and lumps disappear. Add chopped garlic (1 head). The session should last up to 30 minutes. After bathing, dry with a hard towel.
Methods to combat low blood pressure during breastfeeding
Most often, a decrease in pressure (hypotension) does not require correction, since with normal rest and nutrition, indicators are restored independently due to compensatory mechanisms.
Main symptoms of hypotension:
- weakness;
- sleep phase disturbances (nighttime insomnia and pathological daytime sleepiness);
- apathy - lack of desire to do anything, lack of interest in anything;
- diffuse headache;
- visual impairment (double vision, blurred contours);
- dizziness.
Reduced blood pressure disrupts the blood supply to organs and tissues, including the mammary gland, so long-term persistence of these symptoms is accompanied by the risk of a decrease in milk supply.
How can you raise a woman’s blood pressure during lactation?
The period of breastfeeding is characterized by the presence of many restrictions in the mother's lifestyle, therefore traditional methods of blood pressure correction are prohibited.
The safest methods to raise the blood pressure of a nursing mother are presented in the table below.
| Way | Mechanism of action |
| Increased drinking regimen (up to 2.5 liters per day). Allowed: compote, juice (natural), uzvar, fruit juice, clean water | Increasing the volume of circulating fluid in the vessels |
| Balanced nutrition (daily caloric intake of at least 2500 kcal) | Adequate intake of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and mineral salts with foods ensures the normal functioning of the vascular wall and endocrine glands responsible for blood pressure levels |
| Physical activity (morning exercises, special fitness for women in labor) | Increased blood flow in working muscles increases vascular tone throughout the body |
A common cause of low blood pressure in women after childbirth is dysfunction of the thyroid gland. In this case, you can raise the values by systematically using iodized salt or iodine preparations (after preliminary consultation and laboratory tests with a doctor).
How to relieve discomfort during hepatitis B due to low blood pressure at home?
Sudden signs of hypotension, which significantly worsen a woman’s condition and complicate child care, require immediate correction.
A nursing mother can raise her blood pressure at home using several methods:
- drink a cup of coffee. One mug of weak coffee a day will not affect the quality of milk (large quantities make it bitter), but will improve the mother’s condition;
- drink a cup of strong black or green tea with sugar;
- use tincture of ginseng or lemongrass (1 tablespoon, dissolved in a glass of water). The products can only be used after consulting a doctor;
- shake your abs (for women during the first month after a caesarean section or complicated childbirth - it is strictly contraindicated).
Drug treatment using pharmacological drugs is carried out only against the background of concomitant pathology and pronounced changes. Often, women must stop breastfeeding during therapy.
Diet
Nutrition during pregnancy should also be adjusted. A nursing woman should avoid excess salt, fried, fatty and smoked foods. You should also avoid hot and spicy spices and even sweets. Both the child and his mother are harmful.
Instead of junk food, eat more fruits and vegetables, fresh or minimally heated.
Nursing mothers should prohibit smoking and drinking alcohol. Coffee and tea have a negative effect on the health of women with hypertension; it is advisable to limit them. It is extremely important to maintain optimism and peace of mind.
Main reasons
Women usually report low blood pressure after childbirth, and this is due to the fact that bearing a child and childbirth are energy-intensive processes. The body, which spends energy on maintaining the fetus in optimal conditions, simply cannot cope with normalizing the mother’s condition. As a result, low blood pressure occurs. However, in some cases, the pressure, on the contrary, increases, especially in the later stages (after 20 weeks), and jumps.
If there was no history of the disease initially, then the increase in blood pressure may be due to a number of reasons:
- excess body weight;
- hereditary factors;
- stressful situations;
- drinking alcohol, drugs and smoking;
- hormonal imbalance;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- kidney diseases (chronic and acute);
- thyroid diseases;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- taking certain medications.
High blood pressure after childbirth, as can be seen from the list, can occur for a number of reasons. All of them require different types of therapy.
What to do if a nursing mother has low blood pressure
Having learned that high blood pressure is dangerous, it is necessary to deal with low blood pressure. Blood pressure below normal is also common, so the following recommendations will help normalize it:
- A woman should get plenty of rest. Her sleep should be 8 hours a day. You can avoid stress by taking herbal teas that contain sedatives.
- If low blood pressure occurs due to anemia, it is necessary to raise the hemoglobin level to normal using special medications.
- In case of hypotension associated with a lack of iodine in the body, it is obtained from iodized salt. In addition, many of them contain algae and fish.
If your blood pressure is low, a nursing woman should lie down for a while. When he gets better, he will need unsaturated sweet black tea with something nutritious.
Causes of low blood pressure
A condition in which blood pressure is low is called hypotension. In this condition, the upper limit falls below 90. In a woman with HD, many nutrients are transferred to the growth and development of the child. Therefore, iron deficiency anemia is considered one of the causes of hypotension.
Another deficiency of thyroid hormones is hypothyroidism.
There are also factors that contribute to lower blood pressure, such as postpartum depression, stress, and overwork.
conclusions
A decrease in blood pressure in a woman during breastfeeding is a common occurrence, which is accompanied by characteristic complaints. Traditional correction methods using large amounts of coffee, alcohol, and medications are contraindicated during lactation. Doctors recommend that a nursing mother drink strong tea, a lot of compote or juice for blood pressure. The main ways to correct the condition are proper rest, balanced nutrition and adequate physical activity. The methods will help not only raise blood pressure, but also speed up recovery after childbirth.
Symptoms
You can recognize low blood pressure by the following symptoms:
- lack of breast milk;
- general weakness and drowsiness;
- weight loss;
- blue circles under the eyes:
- dizziness;
- apathy.
Low blood pressure can be recognized by these symptoms. This is a fairly dangerous condition and can lead to fainting if not handled correctly.
Low blood pressure during breastfeeding increases with drinking more fluids. During breastfeeding, a woman should consume more as it is necessary for milk production.
Symptoms
| Pressure | Symptoms |
| Increased |
|
| Decreased |
|
Consequences of high and low blood pressure during lactation
If we compare low and high blood pressure, the latter condition is much more dangerous because it can cause swelling of the mammary glands, that is, lactastasis. In this case, the woman’s reproductive health will suffer, in particular, refusal to breastfeed.
In addition, arterial hypertension can cause the following consequences:
- stroke or heart attack;
- atherosclerosis;
- complications of diabetes;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- heart failure.
Therefore, monitoring their well-being is the responsibility of every nursing woman, because we are talking not only about her health, but also about the well-being of the newborn.
Prevention
There are simple and inexpensive preventive measures that can reduce the risk of hypertension in breastfeeding women:
- To do this, if the pressure has already risen many times, you need to monitor its values using a tonometer.
- Move more, breathe fresh air, be physically active.
- Avoid nicotine and alcohol.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Maintain psychological balance.
Although the diagnosis of hypertension in nursing mothers is quite serious, you should not be afraid, because if you follow the recommendations of specialists, the prognosis is favorable. It is enough to monitor your health and, if necessary, undergo therapy.